Abstract
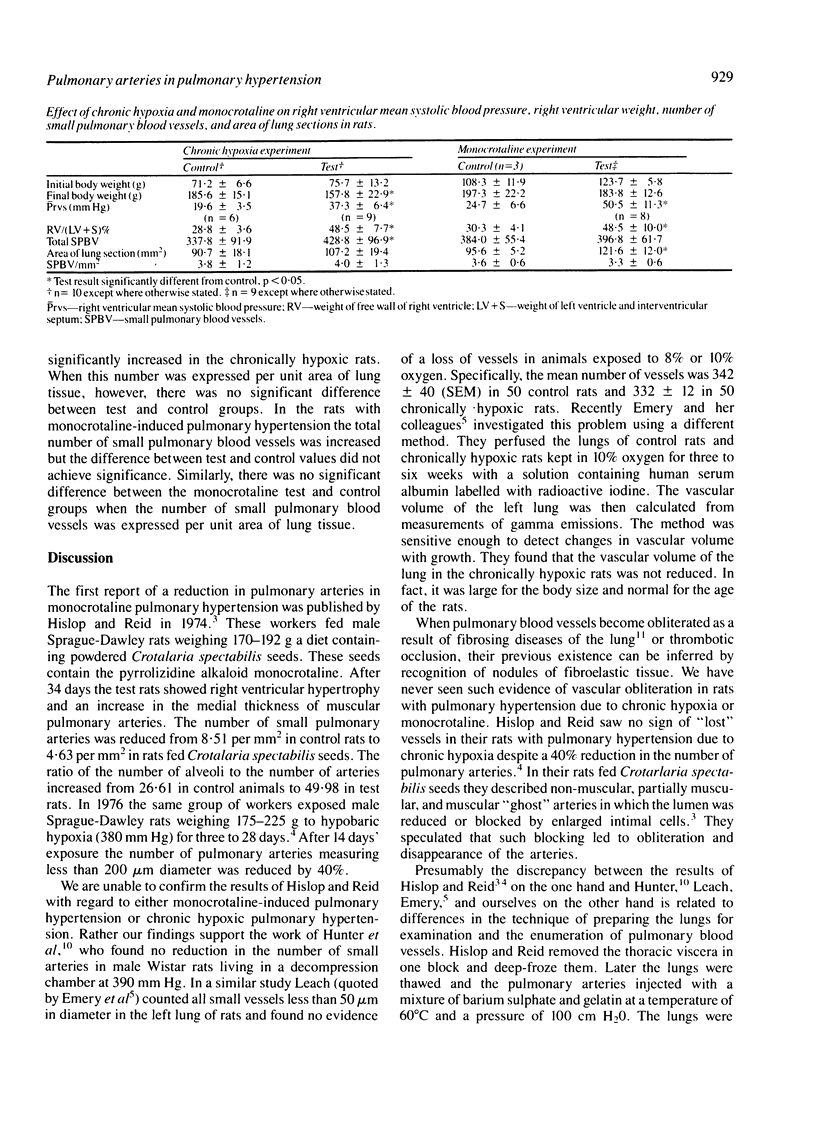
We induced chronic pulmonary hypertension in one group of rats by exposing them to chronic hypobaric hypoxia (380 mm Hg for three weeks) and in another group by administering a single subcutaneous dose of monocrotaline (60 mg/kg body weight). Both groups of rats showed increase of the right ventricular mean systolic blood pressure and right ventricular hypertrophy. We measured the surface area of histological sections of the left or right lungs and counted all small blood vessels with an external diameter of less than 50 microns and with a definite elastic coat lying distal to respiratory bronchioles. In the 10 rats with chronic hypoxic pulmonary hypertension the mean total number of small pulmonary blood vessels was 428.8 +/- 96.9 (SD) compared with 337.8 +/- 91.9 in 10 untreated control rats. The number of small pulmonary blood vessels per mm2 of lung tissue was 4.0 +/- 1.3 in the chronically hypoxic rats compared with 3.8 +/- 1.2 in the controls. The mean total number of small pulmonary blood vessels in nine rats with monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension was 396.8 +/- 61.7 compared with 384 +/- 55.4 in three control rats. The number of small pulmonary blood vessels per mm2 lung tissue was 3.3 +/- 0.6 in the rats treated with monocrotaline compared with 3.6 +/- 0.6 in the control group. We conclude that the number of small pulmonary blood vessels is not reduced in rats with pulmonary hypertension induced by chronic hypoxia or monocrotaline.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham A. S., Kay J. M., Cole R. B., Pincock A. C. Haemodynamic and pathological study of the effect of chronic hypoxia and subsequent recovery of the heart and pulmonary vasculature of the rat. Cardiovasc Res. 1971 Jan;5(1):95–102. doi: 10.1093/cvr/5.1.95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heath D., Gillund T. D., Kay J. M., Hawkins C. F. Pulmonary vascular disease in honeycomb lung. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1968 Apr;95(2):423–430. doi: 10.1002/path.1700950212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hislop A., Reid L. Arterial changes in Crotalaria spectabilis-induced pulmonary hypertension in rats. Br J Exp Pathol. 1974 Apr;55(2):153–163. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hislop A., Reid L. New findings in pulmonary arteries of rats with hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension. Br J Exp Pathol. 1976 Oct;57(5):542–554. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter C., Barer G. R., Shaw J. W., Clegg E. J. Growth of the heart and lungs in hypoxic rodents: a model of human hypoxic disease. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1974 Mar;46(3):375–391. doi: 10.1042/cs0460375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay J. M. Effect of intermittent normoxia on chronic hypoxic pulmonary hypertension, right ventricular hypertrophy, and polycythemia in rats. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980 Jun;121(6):993–1001. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.121.6.993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay J. M., Keane P. M., Suyama K. L., Gauthier D. Angiotensin converting enzyme activity and evolution of pulmonary vascular disease in rats with monocrotaline pulmonary hypertension. Thorax. 1982 Feb;37(2):88–96. doi: 10.1136/thx.37.2.88. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay J. M., Suyama K. L., Keane P. M. Effect of intermittent normoxia on muscularization of pulmonary arterioles induced by chronic hypoxia in rats. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1981 Apr;123(4 Pt 1):454–458. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1981.123.4.454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyrick B., Gamble W., Reid L. Development of Crotalaria pulmonary hypertension: hemodynamic and structural study. Am J Physiol. 1980 Nov;239(5):H692–H702. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1980.239.5.H692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyrick B., Reid L. Development of pulmonary arterial changes in rats fed Crotalaria spectabilis. Am J Pathol. 1979 Jan;94(1):37–50. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller P. J. An elastin stain. Med Lab Technol. 1971 Apr;28(2):148–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinovitch M., Gamble W., Nadas A. S., Miettinen O. S., Reid L. Rat pulmonary circulation after chronic hypoxia: hemodynamic and structural features. Am J Physiol. 1979 Jun;236(6):H818–H827. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1979.236.6.H818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinovitch M., Haworth S. G., Vance Z., Vawter G., Castaneda A. R., Nadas A. S., Reid L. M. Early pulmonary vascular changes in congenital heart disease studied in biopsy tissue. Hum Pathol. 1980 Sep;11(5 Suppl):499–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


