Abstract
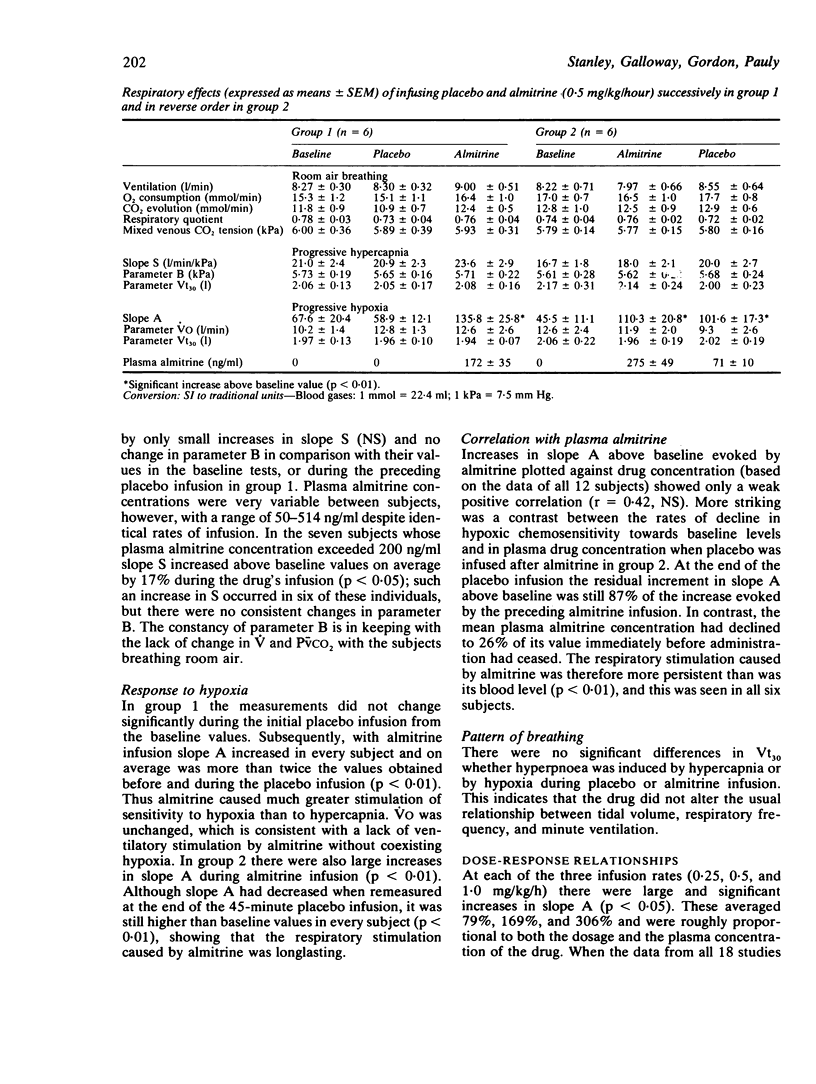
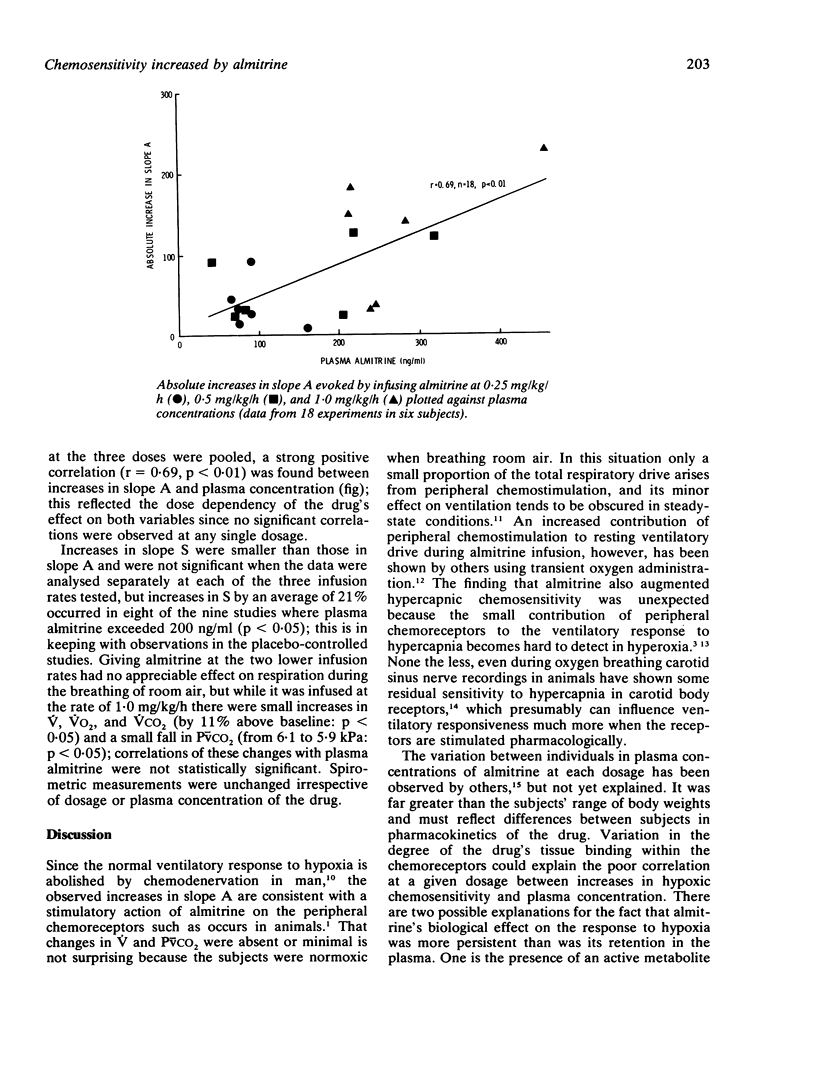
The respiratory effects of intravenously infused almitrine were evaluated in healthy volunteers. In the dose range 0.25-1.0 mg/kg/hour it caused large and dose-dependent increases in hypoxic chemosensitivity, which were longlasting and more persistent than the drug's retention in the plasma. Increases in sensitivity to hypercapnia were much less and were detected only when the plasma almitrine exceeded 200 ng/ml. Small increases in resting ventilation and metabolic rate with a decrease in mixed venous carbon dioxide tension occurred only at the highest infusion rate. The findings accord with an action of almitrine in the peripheral chemoreceptors, which may be of therapeutic value in managing some cases of respiratory failure.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baune A., Bromet N., Courte S., Voisin C. Trace determination of almitrine in plasma by gas-liquid chromatography using a nitrogen-phosphorus detector. J Chromatogr. 1981 Apr 10;223(1):219–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bickerman H. A., Chusid E. L. The case against the use of respiratory stimulants. Chest. 1970 Jul;58(1):53–56. doi: 10.1378/chest.58.1.53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bromet N., Aubert Y., Baune A., Courte S., Guillaudeux J. Etude de pharmacocinétique de l'almitrine. Rev Fr Mal Respir. 1980;8(6):569–576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAMPBELL E. J., HOWELL J. B. Rebreathing method for measurement of mixed venous PCO2. Br Med J. 1962 Sep 8;2(5305):630–633. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5305.630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHERNIACK R. M., YOUNG G. AN EVALUATION OF ETHAMIVAN AS A RESPIRATORY STIMULANT IN BARBITURATE INTOXICATION, AND ALVEOLAR HYPOVENTILATION IN EMPHYSEMA AND OBESITY. Ann Intern Med. 1964 Apr;60:631–640. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-60-4-631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEJOURS P. Control of respiration by arterial chemoreceptors. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1963 Jun 24;109:682–695. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1963.tb13497.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flandrois R., Guérin J. C. Action de l'almitrine sur le contrôle chémoréflexe de la ventilation chez l'homme sain et l'insuffisant respiratoire chronique. Rev Fr Mal Respir. 1980;8(6):561–567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holton P., Wood J. B. The effects of bilateral removal of the carotid bodies and denervation of the carotid sinuses in two human subjects. J Physiol. 1965 Nov;181(2):365–378. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt C. E., Inwood R. J., Shannon D. C. Respiratory and nonrespiratory effects of doxapram in congenital central hypoventilation syndrome. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979 Feb;119(2):263–269. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1979.119.2.263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lahiri S., DeLaney R. G. Stimulus interaction in the responses of carotid body chemoreceptor single afferent fibers. Respir Physiol. 1975 Sep;24(3):249–266. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(75)90017-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laubie M., Schmitt H. Long-lasting hyperventilation induced by almitrine: evidence for a specific effect on carotid and thoracic chemoreceptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1980 Jan 25;61(2):125–136. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(80)90155-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read D. J. A clinical method for assessing the ventilatory response to carbon dioxide. Australas Ann Med. 1967 Feb;16(1):20–32. doi: 10.1111/imj.1967.16.1.20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebuck A. S., Campbell E. J. A clinical method for assessing the ventilatory response to hypoxia. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1974 Mar;109(3):345–350. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1974.109.3.345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade J. G., Larson C. P., Jr, Hickey R. F., Ehrenfeld W. K., Severinghaus J. W. Effect of carotid endarterectomy on carotid chemoreceptor and baroreceptor function in man. N Engl J Med. 1970 Apr 9;282(15):823–829. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197004092821501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil J. V., Byrne-Quinn E., Sodal I. E., Friesen W. O., Underhill B., Filley G. F., Grover R. F. Hypoxic ventilatory drive in normal man. J Clin Invest. 1970 Jun;49(6):1061–1072. doi: 10.1172/JCI106322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winnie A. P. Chemical respirogenesis: a comparative study. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand Suppl. 1973;51:1–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



