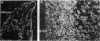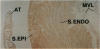Abstract
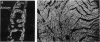
Prior studies using transient transfection assays in cultured avian and murine skeletal myotubes indicate that the proximal 2-kb segment of the 5' flanking region of the human myoglobin gene contains transcriptional control elements sufficient to direct muscle-specific and developmentally regulated expression of reporter genes. To examine the function of the human myoglobin gene promoter during development of skeletal and cardiac myocytes in the intact animal, a 2.0-kb myoglobin gene upstream fragment was fused to an Escherichia coli lacZ reporter gene and injected into fertilized mouse oocytes. beta-Galactosidase (beta-gal) activity was detected selectively in cardiac and skeletal myocytes of fetal and adult transgenic mice. A distinctive spatial pattern of myoglobin promoter activity was observed in fetal hearts: beta-gal staining was more pronounced within the left ventricular subendocardium than within the subepicardium and was essentially undetectable in the ventricular trabeculae or atria. Expression of endogenous myoglobin mRNA and protein, assessed by in situ hybridization and immunohistochemistry, demonstrated a similar spatial pattern. In contrast, hearts from adult transgenic mice demonstrated essentially homogeneous expression of beta-gal and of endogenous myoglobin mRNA and protein throughout the myocardium, including the trabeculae and atria. These data indicate that the 2.0-kb upstream region of the human myoglobin gene includes cis-acting regulatory elements sufficient to direct transgene expression during murine cardiac development that is myocyte-specific and responsive to positional cues in a similar manner to the endogenous myoglobin gene.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Annex B. H., Kraus W. E., Dohm G. L., Williams R. S. Mitochondrial biogenesis in striated muscles: rapid induction of citrate synthase mRNA by nerve stimulation. Am J Physiol. 1991 Feb;260(2 Pt 1):C266–C270. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1991.260.2.C266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassel-Duby R., Hernandez M. D., Gonzalez M. A., Krueger J. K., Williams R. S. A 40-kilodalton protein binds specifically to an upstream sequence element essential for muscle-specific transcription of the human myoglobin promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;12(11):5024–5032. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.11.5024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchetot A., Price M., Jeffreys A. J. The mouse myoglobin gene. Characterisation and sequence comparison with other mammalian myoglobin genes. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Sep 15;159(3):469–474. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09909.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun T., Buschhausen-Denker G., Bober E., Tannich E., Arnold H. H. A novel human muscle factor related to but distinct from MyoD1 induces myogenic conversion in 10T1/2 fibroblasts. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):701–709. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03429.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cserjesi P., Olson E. N. Myogenin induces the myocyte-specific enhancer binding factor MEF-2 independently of other muscle-specific gene products. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):4854–4862. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.4854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. L., Cheng P. F., Lassar A. B., Weintraub H. The MyoD DNA binding domain contains a recognition code for muscle-specific gene activation. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):733–746. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90088-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donoghue M. J., Merlie J. P., Rosenthal N., Sanes J. R. Rostrocaudal gradient of transgene expression in adult skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5847–5851. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmondson D. G., Olson E. N. A gene with homology to the myc similarity region of MyoD1 is expressed during myogenesis and is sufficient to activate the muscle differentiation program. Genes Dev. 1989 May;3(5):628–640. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.5.628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohman M. A., Boyle M., Martin G. R. Isolation of the mouse Hox-2.9 gene; analysis of embryonic expression suggests that positional information along the anterior-posterior axis is specified by mesoderm. Development. 1990 Oct;110(2):589–607. doi: 10.1242/dev.110.2.589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grieshammer U., Sassoon D., Rosenthal N. A transgene target for positional regulators marks early rostrocaudal specification of myogenic lineages. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):79–93. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90120-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henriksson J., Chi M. M., Hintz C. S., Young D. A., Kaiser K. K., Salmons S., Lowry O. H. Chronic stimulation of mammalian muscle: changes in enzymes of six metabolic pathways. Am J Physiol. 1986 Oct;251(4 Pt 1):C614–C632. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.251.4.C614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes S. M., Blau H. M. Migration of myoblasts across basal lamina during skeletal muscle development. Nature. 1990 May 24;345(6273):350–353. doi: 10.1038/345350a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly D. P., Gordon J. I., Alpers R., Strauss A. W. The tissue-specific expression and developmental regulation of two nuclear genes encoding rat mitochondrial proteins. Medium chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase and mitochondrial malate dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 15;264(32):18921–18925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraus W. E., Bernard T. S., Williams R. S. Interactions between sustained contractile activity and beta-adrenergic receptors in regulation of gene expression in skeletal muscles. Am J Physiol. 1989 Mar;256(3 Pt 1):C506–C514. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.256.3.C506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller P. R., Wold B. In vivo footprinting of a muscle specific enhancer by ligation mediated PCR. Science. 1989 Nov 10;246(4931):780–786. doi: 10.1126/science.2814500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEARSON B., WOLF P. L., VAZQUEZ J. A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF A SERIES OF NEW INDOLYL COMPOUNDS TO LOCALIZE BETA-GALACTOSIDASE IN TISSUES. Lab Invest. 1963 Dec;12:1249–1259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parmacek M. S., Bengur A. R., Vora A. J., Leiden J. M. The structure and regulation of expression of the murine fast skeletal troponin C gene. Identification of a developmentally regulated, muscle-specific transcriptional enhancer. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 15;265(26):15970–15976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinney D. F., Pearson-White S. H., Konieczny S. F., Latham K. E., Emerson C. P., Jr Myogenic lineage determination and differentiation: evidence for a regulatory gene pathway. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):781–793. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90095-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Underwood L. E., Williams R. S. Pretranslational regulation of myoglobin gene expression. Am J Physiol. 1987 Apr;252(4 Pt 1):C450–C453. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.252.4.C450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wefald F. C., Devlin B. H., Williams R. S. Functional heterogeneity of mammalian TATA-box sequences revealed by interaction with a cell-specific enhancer. Nature. 1990 Mar 15;344(6263):260–262. doi: 10.1038/344260a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Tapscott S. J., Davis R. L., Thayer M. J., Adam M. A., Lassar A. B., Miller A. D. Activation of muscle-specific genes in pigment, nerve, fat, liver, and fibroblast cell lines by forced expression of MyoD. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5434–5438. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller P. A., Price M., Isenberg H., Edwards Y. H., Jeffreys A. J. Myoglobin expression: early induction and subsequent modulation of myoglobin and myoglobin mRNA during myogenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4539–4547. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller P., Jeffreys A. J., Wilson V., Blanchetot A. Organization of the human myoglobin gene. EMBO J. 1984 Feb;3(2):439–446. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01825.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson D. G., Bailes J. A., Champion J. E., McMahon A. P. A molecular analysis of mouse development from 8 to 10 days post coitum detects changes only in embryonic globin expression. Development. 1987 Apr;99(4):493–500. doi: 10.1242/dev.99.4.493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. S., Garcia-Moll M., Mellor J., Salmons S., Harlan W. Adaptation of skeletal muscle to increased contractile activity. Expression nuclear genes encoding mitochondrial proteins. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 25;262(6):2764–2767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. S. Mitochondrial gene expression in mammalian striated muscle. Evidence that variation in gene dosage is the major regulatory event. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 15;261(26):12390–12394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. S., Salmons S., Newsholme E. A., Kaufman R. E., Mellor J. Regulation of nuclear and mitochondrial gene expression by contractile activity in skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):376–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittenberg B. A., Wittenberg J. B. Transport of oxygen in muscle. Annu Rev Physiol. 1989;51:857–878. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.51.030189.004233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright W. E., Sassoon D. A., Lin V. K. Myogenin, a factor regulating myogenesis, has a domain homologous to MyoD. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):607–617. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90583-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeller R., Bloch K. D., Williams B. S., Arceci R. J., Seidman C. E. Localized expression of the atrial natriuretic factor gene during cardiac embryogenesis. Genes Dev. 1987 Sep;1(7):693–698. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.7.693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]