Abstract
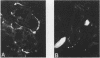
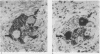
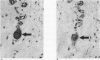
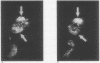
Lung innervation has been studied in the past by methylene blue staining and silver impregnation and more recently by histochemical methods. These techniques give only a partial picture of the total innervation. We have delineated the innervation of the lung in man and three other mammalian species by immunostaining with antibodies to two new markers of nervous tissue. These markers are neurone-specific enolase (NSE), an enzyme present in nerve cells in both the central and the peripheral nervous systems, and S-100, a protein found in glial cells. Throughout the respiratory tract NSE was localised in ganglion cells and nerve fibres in all species examined, while S-100 was found in the supporting glial cells of ganglia and in Schwann cells of peripheral nerves. The distribution of NSE immunoreactivity in serial sections was compared with that of acetylcholinesterase-containing, noradrenergic, and peptide-containing nerves. In all areas NSE was found to be a specific marker for all three types of nerves. Thus these two antibodies provide an effective histological means of examining both the neuronal and the non-neuronal components of the lung innervation and should be of value in investigating this system in lung disease.
Full text
PDF

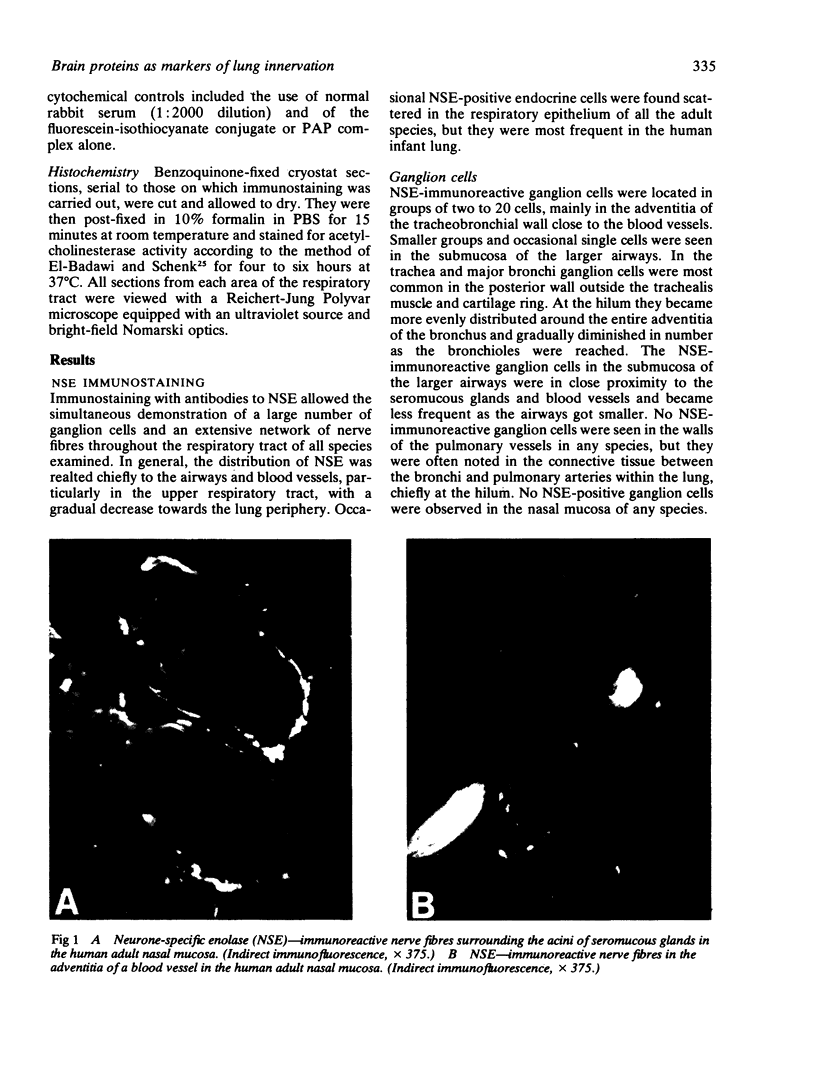
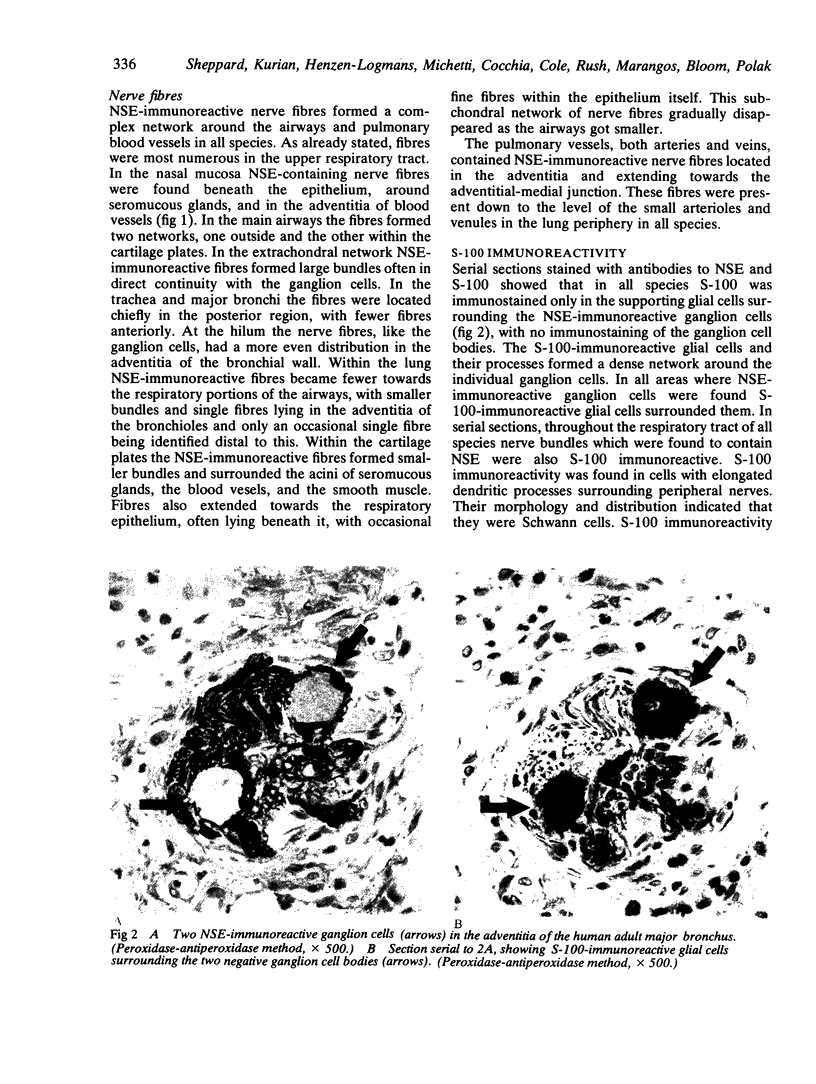

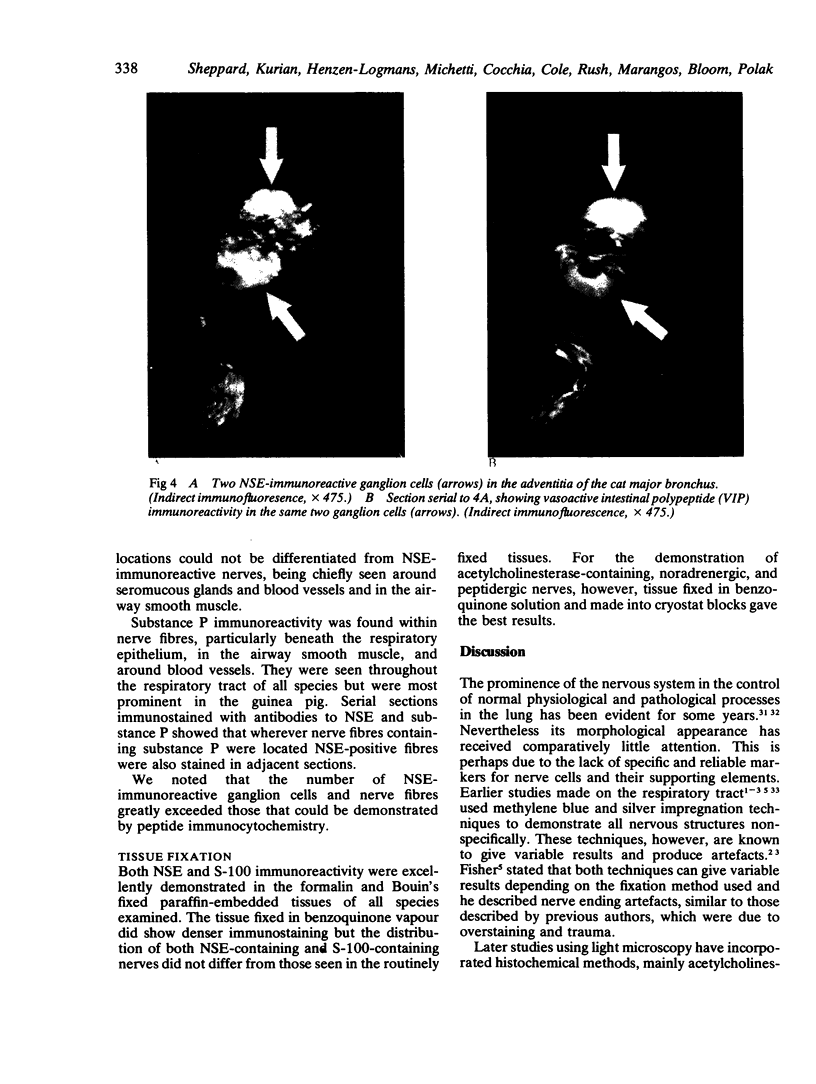


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bishop A. E., Polak J. M., Facer P., Ferri G. L., Marangos P. J., Pearse A. G. Neuron specific enolase: a common marker for the endocrine cells and innervation of the gut and pancreas. Gastroenterology. 1982 Oct;83(4):902–915. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. E., McNary W. F., el-Bermani A. W. The distribution of acetylcholinesterase and catecholamine containg nerves in the rat lung. Anat Rec. 1970 Jun;167(2):205–207. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091670208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COONS A. H., LEDUC E. H., CONNOLLY J. M. Studies on antibody production. I. A method for the histochemical demonstration of specific antibody and its application to a study of the hyperimmune rabbit. J Exp Med. 1955 Jul 1;102(1):49–60. doi: 10.1084/jem.102.1.49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech S., Dolezel S. Monoaminergic innervation of the pulmonary vessels in various laboratory animals (rat, rabbit, cat). Experientia. 1967 Feb 15;23(2):114–115. doi: 10.1007/BF02135949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chubb I. W., Hodgson A. J., White G. H. Acetylcholinesterase hydrolyzes substance P. Neuroscience. 1980;5(12):2065–2072. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(80)90124-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocchia D., Michetti F. S-100 antigen in satellite cells of the adrenal medulla and the superior cervical ganglion of the rat. An immunochemical and immunocytochemical study. Cell Tissue Res. 1981;215(1):103–112. doi: 10.1007/BF00236252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dey R. D., Shannon W. A., Jr, Said S. I. Localization of VIP-immunoreactive nerves in airways and pulmonary vessels of dogs, cat, and human subjects. Cell Tissue Res. 1981;220(2):231–238. doi: 10.1007/BF00210505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downing S. E., Lee J. C. Nervous control of the pulmonary circulation. Annu Rev Physiol. 1980;42:199–210. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.42.030180.001215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Badawi A., Schenk E. A. Histochemical methods for separate, consecutive and simultaneous demonstration of acetylcholinesterase and norepinephrine in cryostat sections. J Histochem Cytochem. 1967 Oct;15(10):580–588. doi: 10.1177/15.10.580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Bermani A. W., Grant M. Acetylcholinesterase-positive nerves of the rhesus monkey bronchial tree. Thorax. 1975 Apr;30(2):162–170. doi: 10.1136/thx.30.2.162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISHER A. W. THE INTRINSIC INNERVATION OF THE TRACHEA. J Anat. 1964 Jan;98:117–124. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher A. W. The intrinsic innervation of the pulmonary vessels. Acta Anat (Basel) 1965;60(4):481–496. doi: 10.1159/000142658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghatei M. A., Sheppard M. N., O'Shaughnessy D. J., Adrian T. E., McGregor G. P., Polak J. M., Bloom S. R. Regulatory peptides in the mammalian respiratory tract. Endocrinology. 1982 Oct;111(4):1248–1254. doi: 10.1210/endo-111-4-1248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klee C. B., Crouch T. H., Richman P. G. Calmodulin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:489–515. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.002421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marangos P. J., Schmechel D., Parma A. M., Clark R. L., Goodwin F. K. Measurement of neuron-specific (NSE) and non-neuronal (NNE) isoenzymes of enolase in rat, monkey and human nervous tissue. J Neurochem. 1979 Jul;33(1):319–329. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb11735.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marangos P. J., Schmechel D. The neurobiology of the brain enolases. Essays Neurochem Neuropharmacol. 1980;4:211–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marangos P. J., Zomzely-Neurath C., York C. Determination and characterization of neuron specific protein (NSP) associated enolase activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Feb 23;68(4):1309–1316. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90339-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore B. W. Chemistry and biology of two proteins, S-100 and 14-3-2, specific to the nervous system. Int Rev Neurobiol. 1972;15:215–225. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7742(08)60332-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell S. R., Saar N., Wood L. J. Tne density of adrenergic nerves at various levels in the guinea-pig lung. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1978 Jul-Aug;5(4):325–332. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.1978.tb00681.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEPLER W. J., PEARSE A. G. The histochemistry of the esterases of rat brain, with special reference to those of the hypothalamic nuclei. J Neurochem. 1957;1(3):193–202. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1957.tb12072.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearse A. G., Polak J. M. Bifunctional reagents as vapour- and liquid-phase fixatives for immunohistochemistry. Histochem J. 1975 Mar;7(2):179–186. doi: 10.1007/BF01004561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickel V. M., Reis D. J., Marangos P. J., Zomzely-Neurath C. Immunocytochemical localization of nervous system specific protein (NSP-R) in rat brain. Brain Res. 1976 Mar 19;105(1):184–187. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90936-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rush R. A., Geffen L. B. Dopamine beta-hydroxylase in health and disease. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 1980;12(3):241–277. doi: 10.3109/10408368009108731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPENCER H., LEOF D. THE INNERVATION OF THE HUMAN LUNG. J Anat. 1964 Oct;98:599–609. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmechel D., Marangos P. J., Brightman M. Neurone-specific enolase is a molecular marker for peripheral and central neuroendocrine cells. Nature. 1978 Dec 21;276(5690):834–836. doi: 10.1038/276834a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefansson K., Wollmann R. L., Moore B. W., Arnason B. G. S-100 protein in human chondrocytes. Nature. 1982 Jan 7;295(5844):63–64. doi: 10.1038/295063a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefansson K., Wollmann R. L., Moore B. W. Distribution of S-100 protein outside the central nervous system. Brain Res. 1982 Feb 25;234(2):309–317. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90871-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor I. M., Smith R. B. Intrinsic innervation of the human foetal lung between the 35 and 140 mm corwn-rump length stages. Biol Neonate. 1971;18(3):193–202. doi: 10.1159/000240362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uddman R., Alumets J., Densert O., Håkanson R., Sundler F. Occurrence and distribution of VIP nerves in the nasal mucosa and tracheobronchial wall. Acta Otolaryngol. 1978 Nov-Dec;86(5-6):443–448. doi: 10.3109/00016487809107524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wharton J., Polak J. M., Bloom S. R., Will J. A., Brown M. R., Pearse A. G. Substance P-like immunoreactive nerves in mammalian lung. Invest Cell Pathol. 1979 Jan-Mar;2(1):3–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wharton J., Polak J. M., Cole G. A., Marangos P. J., Pearse A. G. Neuron-specific enolase as an immunocytochemical marker for the diffuse neuroendocrine system in human fetal lung. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 Dec;29(12):1359–1364. doi: 10.1177/29.12.7033363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widdicombe J. G., Sterling G. M. The autonomic nervous system and breathing. Arch Intern Med. 1970 Aug;126(2):311–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]