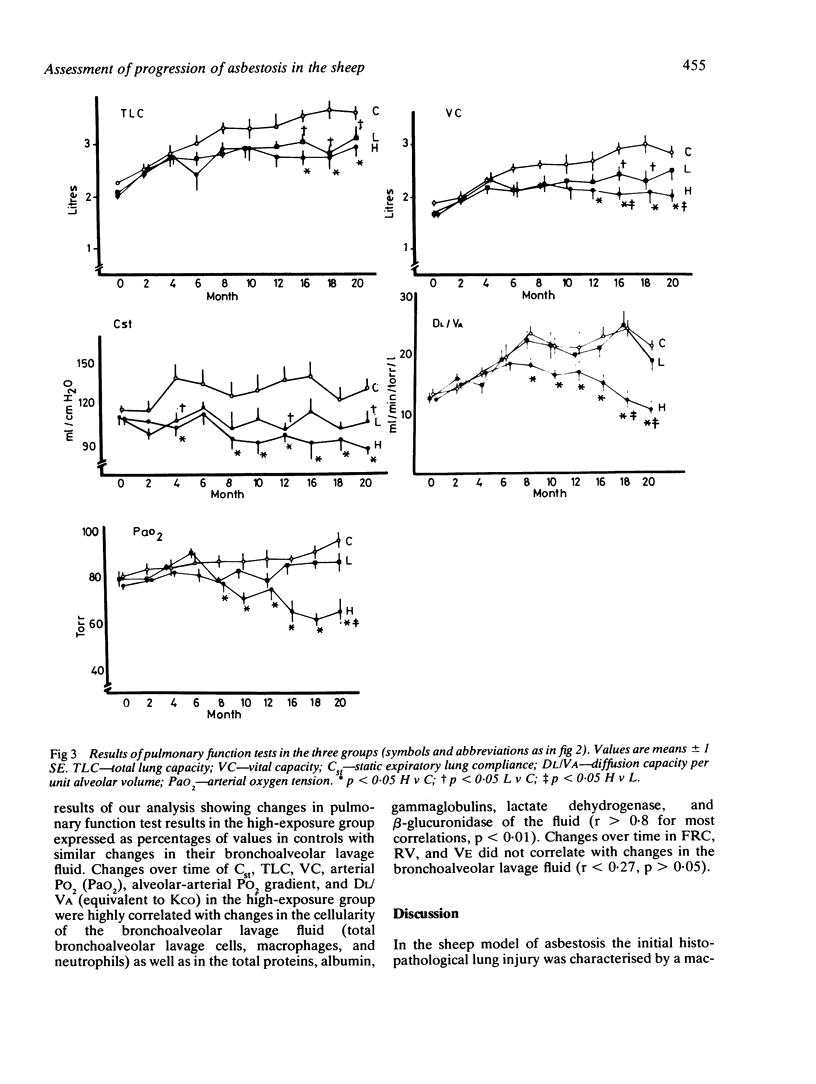
Abstract
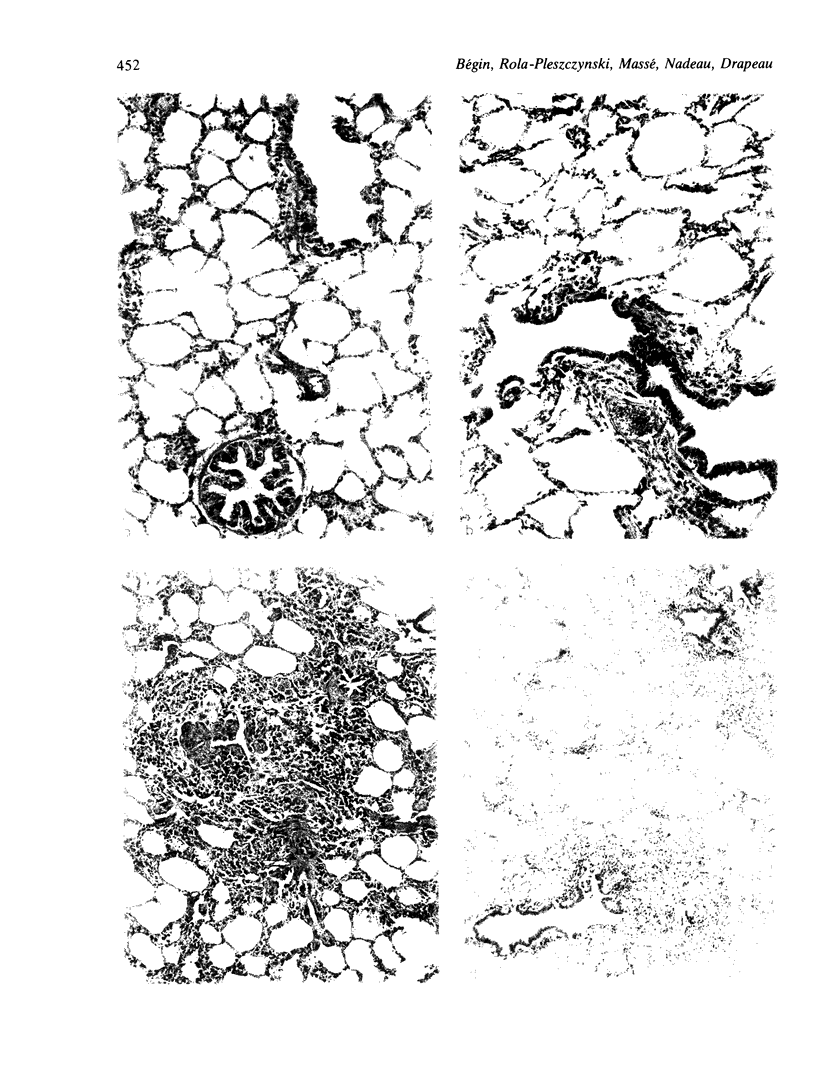
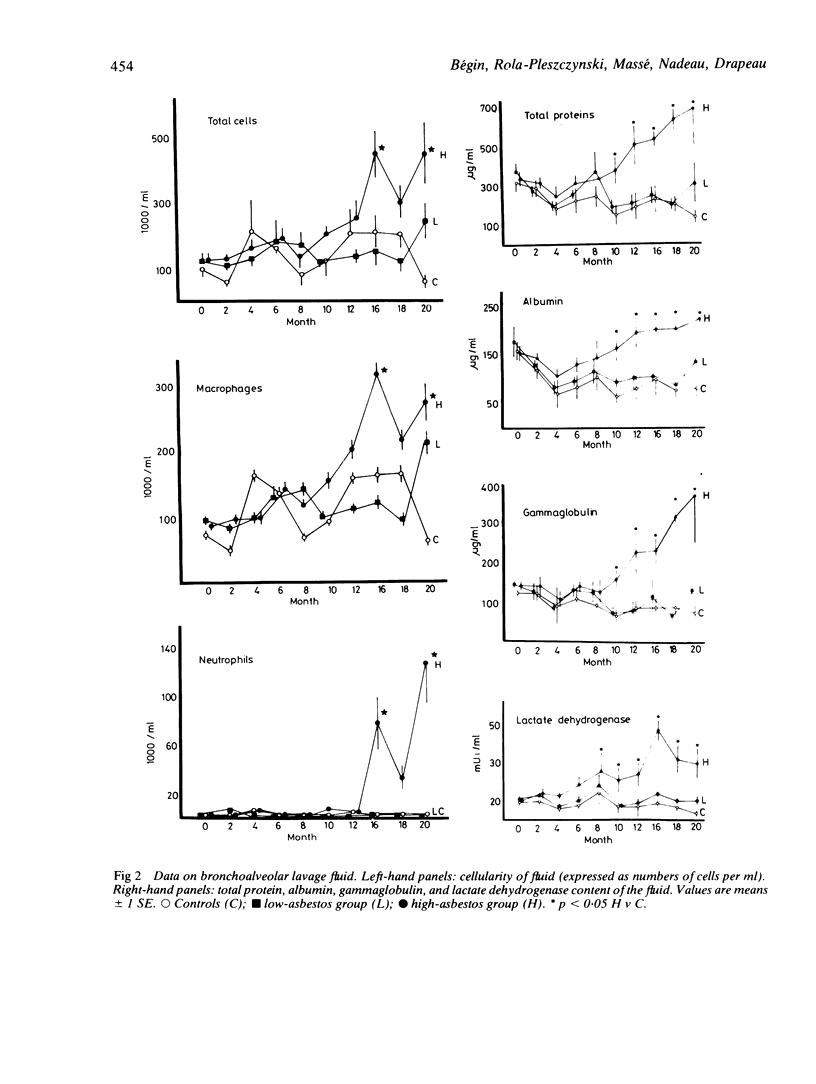
To study the relationship between the results of bronchoalveolar lavage and pulmonary function tests during induction and progression of asbestosis, three groups of six sheep were exposed repeatedly by intratracheal injection to either saline (controls), low doses of Canadian chrysotile UICC asbestos (cumulative exposure 328 mg) (low-dose group), or high doses of the same fibres (cumulative dose 2282 mg) (high-dose group) until there was clear evidence of alveolitis from the lung biopsy specimens of all sheep of the high-dose group. During the course of this induction and for the following eight months lung biopsies, bronchoalveolar lavage and pulmonary function tests were performed at two-month intervals. At the time of initial alveolitis in the high-dose group there was no significant change in the cellularity of the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid, but static lung compliance (Cst), vital capacity (VC), arterial oxygen tension (Pao2), and diffusion capacity (DL/VA) were significantly lower than in the other groups. In the following months, as the alveolitis evolved into a fibrosing process, macrophages and neutrophils from the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid increased significantly and pulmonary function deteriorated. Proteins and enzymes in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid also increased significantly in the high-dose group. These data show that in the sheep model of asbestosis simple tests of pulmonary function correlate well with histological changes and changes in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid in the course of the disease and can be used to assess progression of asbestosis.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bader M. E., Bader R. A., Tierstein A. S., Selikoff I. J. Pulmonary function in asbestosis: serial tests in a long-term prospective study. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Dec 31;132(1):391–405. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb41121.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becklake M. R. Asbestos-related diseases of the lung and other organs: their epidemiology and implications for clinical practice. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1976 Jul;114(1):187–227. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1976.114.1.187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becklake M. R., Fournier-Massey G., McDonald J. C., Siemiatycki J., Rossiter C. E. Lung function in relation to chest radiographic changes in Quebec asbestos workers. I. Methods, results and conclusions. Bull Physiopathol Respir (Nancy) 1970 Jul-Sep;6(3):637–659. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boushy S. F., North L. B. Pulmonary function in infiltrative lung disease. Chest. 1973 Oct;64(4):448–453. doi: 10.1378/chest.64.4.448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britton M. G., Hughes D. T., Wever A. M. Serial pulmonary function tests in patients with asbestosis. Thorax. 1977 Feb;32(1):45–52. doi: 10.1136/thx.32.1.45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bégin R., Rola-Pleszczynski M., Sirois P., Masse S., Nadeau D., Bureau M. A. Sequential analysis of the bronchoalveolar milieu in conscious sheep. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1981 Mar;50(3):665–671. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1981.50.3.665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen D., Crowther T. S., Gibbs G. W., Becklake M. R. Magnetic lung measurements of relation to occupational exposure in asbestos miners and millers of Quebec. Environ Res. 1981 Dec;26(2):535–550. doi: 10.1016/0013-9351(81)90229-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crystal R. G., Fulmer J. D., Roberts W. C., Moss M. L., Line B. R., Reynolds H. Y. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Clinical, histologic, radiographic, physiologic, scintigraphic, cytologic, and biochemical aspects. Ann Intern Med. 1976 Dec;85(6):769–788. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-85-6-769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crystal R. G., Gadek J. E., Ferrans V. J., Fulmer J. D., Line B. R., Hunninghake G. W. Interstitial lung disease: current concepts of pathogenesis, staging and therapy. Am J Med. 1981 Mar;70(3):542–568. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(81)90577-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulmer J. D., Roberts W. C., von Gal E. R., Crystal R. G. Morphologic-physiologic correlates of the severity of fibrosis and degree of cellularity in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 1979 Apr;63(4):665–676. doi: 10.1172/JCI109349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaensler E. A., Carrington C. B., Coutu R. E., Tomasian A., Hoffman L., Smith A. A. Pathologica, physiological, and radiological correlations in the pneumoconioses. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1972 Dec 29;200:574–607. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1972.tb40218.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gee J. B., Fick R. B., Jr Bronchoalveolar lavage. Thorax. 1980 Jan;35(1):1–8. doi: 10.1136/thx.35.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslam P. L., Turton C. W., Heard B., Lukoszek A., Collins J. V., Salsbury A. J., Turner-Warwick M. Bronchoalveolar lavage in pulmonary fibrosis: comparison of cells obtained with lung biopsy and clinical features. Thorax. 1980 Jan;35(1):9–18. doi: 10.1136/thx.35.1.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslam P. L., Turton C. W., Lukoszek A., Salsbury A. J., Dewar A., Collins J. V., Turner-Warwick M. Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid cell counts in cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis and their relation to therapy. Thorax. 1980 May;35(5):328–339. doi: 10.1136/thx.35.5.328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunninghake G. W., Kawanami O., Ferrans V. J., Young R. C., Jr, Roberts W. C., Crystal R. G. Characterization of the inflammatory and immune effector cells in the lung parenchyma of patients with interstitial lung disease. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1981 Apr;123(4 Pt 1):407–412. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1981.123.4.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keogh B. A., Crystal R. G. Clinical significance of pulmonary function tests. Pulmonary function testing in interstitial pulmonary disease. What does it tell us? Chest. 1980 Dec;78(6):856–865. doi: 10.1378/chest.78.6.856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOURENCO R. V., TURINO G. M., DAVIDSON L. A., FISHMAN A. P. THE REGULATION OF VENTILATION IN DIFFUSE PULMONARY FIBROSIS. Am J Med. 1965 Feb;38:199–216. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(65)90174-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LYONS H. A. Pulmonary compliance in granulomatous disease of the lung. Am J Med. 1958 Jul;25(1):23–30. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(58)90194-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Line B. R., Hunninghake G. W., Keogh B. A., Jones A. E., Johnston G. S., Crystal R. G. Gallium-67 scanning to stage the alveolitis of sarcoidosis: correlation with clinical studies, pulmonary function studies, and bronchoalveolar lavage. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1981 Apr;123(4 Pt 1):440–446. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1981.123.4.440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall R. A rebreathing method for measuring carbon monoxide diffusing capacity. A supplement to the single-breath method. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1977 Mar;115(3):537–539. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1977.115.3.537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy R. L., Jr, Ferris B. G., Jr, Burgess W. A., Worcester J., Gaensler E. A. Effects of low concentrations of asbestos. Clinical, environmental, radiologic and epidemiologic observations in shipyard pipe coverers and controls. N Engl J Med. 1971 Dec 2;285(23):1271–1278. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197112022852301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy R. L., Jr, Gaensler E. A., Ferris B. G., Fitzgerald M., Solliday N., Morrisey W. Diagnosis of "asbestosis". Observations from a longitudinal survey of shipyard pipe coverers. Am J Med. 1978 Sep;65(3):488–498. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(78)90775-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy R. L., Jr, Gaensler E. A., Redding R. A., Belleau R., Keelan P. J., Smith A. A., Goff A. M., Ferris B. G., Jr Low exposure to asbestos. Gas exchange in ship pipe coverers and controls. Arch Environ Health. 1972 Oct;25(4):253–264. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1972.10666171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pesce M. A., Strande C. S. A new micromethod for determination of protein in cerebrospinal fluid and urine. Clin Chem. 1973 Nov;19(11):1265–1267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds H. Y., Newball H. H. Analysis of proteins and respiratory cells obtained from human lungs by bronchial lavage. J Lab Clin Med. 1974 Oct;84(4):559–573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rola-Pleszczynski M., Massé S., Sirois P., Lemaire I., Bégin R. Early effects of low-doses exposure to asbestos on local cellular immune responses in the lung. J Immunol. 1981 Dec;127(6):2535–2538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rola-Pleszczynski M., Sirois P., Bégin R. Cellular and humoral components of bronchoalveolar lavage in the sheep. Lung. 1981;159(2):91–99. doi: 10.1007/BF02713902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudd R. M., Haslam P. L., Turner-Warwick M. Cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis. Relationships of pulmonary physiology and bronchoalveolar lavage to response to treatment and prognosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1981 Jul;124(1):1–8. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1981.124.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SILVERTON R. E. GROSS FIXATION METHODS USED IN THE STUDY OF PULMONARY EMPHYSEMA. Thorax. 1965 Jul;20:289–297. doi: 10.1136/thx.20.4.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timbrell V., Gibson J. C., Webster I. UICC standard reference samples of asbestos. Int J Cancer. 1968 May 15;3(3):406–408. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910030312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zitting A., Huuskonen M. S., Alanko K., Mattsson T. Radiographic and physiological findings in patients with asbestosis. Scand J Work Environ Health. 1978 Dec;4(4):275–283. doi: 10.5271/sjweh.2698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]