Abstract
Background
Although frailty has been linked to higher risk of falls and fracture in the general population, few studies have examined the extent to which frailty is associated with these outcomes among patients with ESRD, who are at particularly high risk for these events.
Methods
1,646 patients beginning maintenance hemodialysis in 297 dialysis units throughout the United States from September 2005 to June 2007 were enrolled in the Comprehensive Dialysis Study (CDS), and 1053 Medicare beneficiaries were included in this study. Self-reported frailty defined by patients endorsing two or more of the following: poor physical functioning, exhaustion, or low physical activity. Falls and fractures requiring medical attention were identified through Medicare claims data. We examined the association between frailty and the time to first fall or fracture using the Fine-Gray modification of Cox proportional hazards regression, adjusted for demographics, Quételet’s (body mass) index (BMI), diabetes mellitus, heart failure, and atherosclerosis.
Results
Seventy-seven percent of patients were frail by self-report. The median length of follow up was 2.5 [1.0, 3.9] years. Crude rates of first medically urgent falls or fractures were 66 and 126 per 1000 person-years in non-frail and self-reported frail participants, respectively. After accounting for demographic factors, comorbidities and the competing risk of death, self-reported frailty was associated with a higher risk of falls or fractures requiring medical attention (hazard ratio 1.60, 95% confidence interval 1.16–2.20).
Conclusion
Participants reporting frailty experienced nearly twice the risk of medically urgent falls or fractures compared to participants who did not report frailty.
Keywords: Fracture, Frailty, Hemodialysis
Introduction
In the general elderly population, falls and associated adverse outcomes, including fractures, are a substantial healthcare problem associated with a significant risk of death [1–3]. In the dialysis population, the one-year risk of death following a fracture is nearly 4-fold higher compared to individuals with no fracture [4]. Even in the absence of fracture, falls carry a substantial risk of death in the ESRD population. Patients who fall have 60% higher one-year risk of death compared to individuals who do not report a fall [5–7].
In the general population, frailty, a syndrome of decreased physiological reserve, has been linked to higher rates of falls and fracture [8, 9]. Frailty has been associated with adverse outcomes including hospitalization, disability, and death among patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) [10–13]. Although it is logical to expect that patients with ESRD who are frail should be prone to falls and subsequent fractures [14], only one study has evaluated self-reported falls among patients on dialysis from a single center [15]. Risk of fracture among patients with ESRD is related to serum PTH concentrations [16], and recent data suggest that treatment of CKD-MBD may affect fracture rates [17, 18]. Thus, it is possible that CKD-MBD is responsible for the higher rates of fracture observed among patients with ESRD and that the impact of frailty may be less important than among community-dwelling elders. On the other hand, if the risk of fall and fracture is higher among frail patients, early identification of frailty and intervention to address it could lead to a reduction in these events.
The purpose of this analysis was to examine rates of falls or fractures requiring a medical visit or hospitalization in a diverse cohort of patients enrolled in the Comprehensive Dialysis Study, a United States Renal Data System Special Study [19]. We hypothesized that patients who were frail by self-report would be at higher risk for falls or fracture, even after accounting for the confounding effects of advanced age and other clinical factors.
Methods
Data Source
We used data from the Comprehensive Dialysis Study (CDS), a prospective cohort study in which information regarding physical activity, health-related quality of life, and data on work and disability were collected among 1,678 incident patients receiving maintenance hemodialysis across 297 dialysis units throughout the United States from September 2005 to June 2007 [19]. Participants provided informed consent. The study was approved by institutional review boards at the US Renal Data System (USRDS) Coordinating Center (University of Minnesota), the USRDS Rehabilitation/Quality of Life Special Studies Center (Emory University), and the USRDS Nutrition Special Studies Center (University of California, San Francisco). For this analysis, the study sample was restricted to participants who were receiving hemodialysis and had Medicare part A and B as the primary payer prior to or within 60 days of the study start date and had Medicare claims data to allow us to identify fall and fracture events. Participants were followed for outcomes of interest until December 31, 2010.
Definition of Self-reported Frailty
We defined self-reported frailty using questionnaire measures of physical function, exhaustion, and physical activity as previously described [10]. This approach is an adaptation of the well-validated Fried frailty phenotype [9]. A similar adaptation has been shown to be predictive of hospitalization, disability, and death among older women [20], and this definition was associated with higher mortality among patients with ESRD. We defined low self-reported function as a Medical Outcomes Study Short Form-12 (SF-12) Physical Function score < 75 (1 point). We categorized “exhaustion” as positive if participants answered either “a little of the time” or “none of the time” when asked how often they felt they had a lot of energy during the past 4 weeks (1 point). Participants met the low physical activity criterion if their score on the Adjusted Activity Score of the Human Activity Profile was in the lowest quintile of age- and sex- stratified normative data (1 point). If two or more of the criteria were met, the participant was considered to exhibit self-reported frailty [10].
Fall or Fracture Identification
We identified falls or fractures severe enough to require hospitalization or medical evaluation via Medicare claims data. We identified falls using International Classification of Disease, Ninth revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-9-CM) codes and fractures using ICD-9-CM diagnosis codes and Current Procedural Terminology Codes (CPT) codes for related procedures (Supplemental Table A) [21]. Non-pathologic fractures of the leg, wrist, hip, vertebra, and pelvis were included in the analysis. Pelvic fractures included fractures of the acetabulum, ilium and ischium. Hip fractures were primarily of the femur. If an individual had multiple admissions for fall or fracture over the time period of the analysis (N=55 had more than one event), only the first event was considered in the analysis. The date of fall or fracture event was the date of the first documented physician, hospital or institutional claim. However, we required a hospital claim for hip and pelvic fracture to avoid capturing historical events.
Statistical Methods
We compared characteristics of CDS participants with and without self-reported frailty using the Mann Whitney test for continuous variables and the Mantel-Haenszel test for categorical variables. We plotted cumulative incidence curves to examine the time to first fall or fracture in patients with and without self-reported frailty. For our primary analysis, we used the Fine-Gray modification of Cox proportional hazards regression, with time to first fall or fracture as the dependent variable, self-reported frailty as the primary explanatory variable, and adjusting for age, BMI, sex, race, ethnicity, diabetes mellitus, heart failure and atherosclerotic disease (includes coronary heart disease, cerebrovascular disease, peripheral vascular disease or amputation) as covariates, accounting for the competing risk of death. We subsequently examined the associations of the individual components of self-reported frailty (poor physical function, exhaustion, and low physical activity) with time to first fall or fracture using Cox proportional hazards models adjusted for the same covariates. We considered a 2-tailed p-value <0.05 as statistically significant. We performed all analyses using SAS version 9.4 (SAS Institute Inc., Cary NC).
Results
Participant Characteristics
Of 1678 individuals in the original CDS cohort, 1086 were Medicare beneficiaries, of whom 1053 had complete data for assessment of self-reported frailty. The median age was 63 [25th, 75th percentile 52, 73] years, and 55% were men. Median dialysis vintage was 127 [111,148] days.
Prevalence of Self-reported Frailty
The overall prevalence of self-reported frailty was 77%. The vast majority of individuals met the inactivity criterion (94%). Seventy-eight percent of individuals met the definition of low self-reported function. The exhaustion component of frailty was endorsed by just over half (51%) the cohort. Table 1 shows the baseline participant characteristics overall and by the presence of or absence of self-reported frailty. On average, frail individuals had higher BMI than those were not frail (30.0 ± 8.3 kg/m2 vs 28.1 ± 7.7 kg/m2 among the non-frail, p<0.01). As expected, patients reporting frailty had a higher burden of comorbidity as compared to patients who did not.
Table 1.
Characteristics of Cohort according to Self-reported Frailty.
| Cohort Characteristics | All N=1053 |
Frail N=808 |
Not Frail N=245 |
P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex, female | 45% (472) | 48.8% (394) | 31.8% (78) | <0.001 |
| Median Age, years | 63 (52,73) | 62.5 (52,73) | 65 (52,72) | 0.80 |
| Race | ||||
| African American | 26.8% (282) | 25.5% (206) | 31% (76) | 0.20 |
| Caucasian | 70.6% (743) | 71.7% (579) | 66.9% (167) | |
| Other | 2.7% (28) | 2.8% (23) | 2.0% (5) | |
| Comorbidities | ||||
| Diabetes mellitus | 58.5% (616) | 63% (509) | 43.7% (107) | < 0.001 |
| Heart Failure | 33.8% (356) | 36.4% (294) | 25.3% (62) | 0.001 |
| Atherosclerotic diseaseŦ | 37.9% (399) | 40.1% (324) | 30.6% (75) | 0.007 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 29.6 (8.2) | 30.1 (8.26) | 28.1 (7.72) | <0 .001 |
| Laboratory Parameters | ||||
| Serum Albumin (g/dL) | 3.14 (0.7) | 3.13 (0.7) | 3.20 (0.70) | 0.30 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 10.1 (1.73) | 10.2 (1.74) | 9.94 (1.71) | 0.12 |
| Dialysis Related Parameters | ||||
| Dialysis Vintage (days) | 127[111,148] | 127 [112,149] | 127 [112,149] | 0.85 |
| Self-Reported Frailty Components | ||||
| Inactivity | 94% (985) | 99.6% (805) | 73.5% (180) | <0.001 |
| Poor Physical Function | 70.8% (746) | 91.5% (739) | 2.9% (7) | |
| Exhaustion | 51.1% (538) | 65.3% (528) | 4.1% (10) | |
Displayed as mean (standard deviation) for normally distributed variables, median [25th, 75th percentile] for non-normally distributed variables, and % (n) for categorical variables.
Atherosclerotic disease includes: coronary heart disease, cerebrovascular disease, peripheral vascular disease or amputation.
Incidence of Fall or Fracture
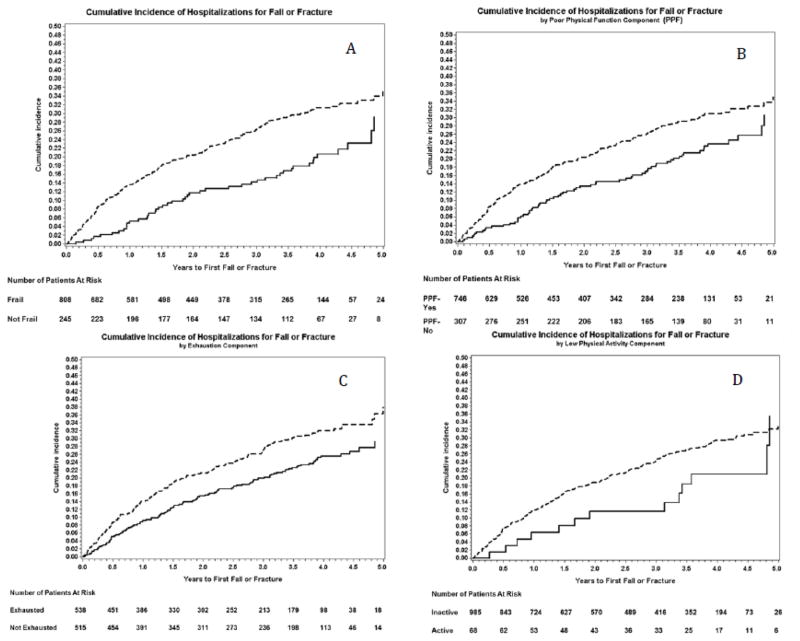
During a median follow up of 2.5 [1.0, 3.9] years, 283 episodes of medical care for first fall or fracture were observed. The first event incidence rate was 66 per 1000 person-years in non-frail participants as compared to 126 per 1000 person years for those who reported frailty (p<0.001) (Figure 1A).
Figure 1.
Cumulative Incidence Plots of Self-reported Frailty and its Components with time to First Fall or Fracture. Panel A: Frailty; Panel B: Poor Physical Function (PPF); Panel C: Exhaustion; Panel D: Low Physical Activity. Dashed line; Individuals who endorsed frailty or component, Solid line those who did not.
Association of Self-reported Frailty with Time to First Fall or Fracture
In unadjusted analyses, self-reported frailty was associated with a higher risk of first fall or fracture (hazard ratio (HR) 1.66 95% confidence interval (95% CI 1.22, 2.26). Adjusting for demographics, BMI, and select comorbidities did not attenuate the association of self-reported frailty with time to first fall or fracture (HR 1.60, 95% CI 1.16 – 2.20) (Table 2). As expected, older age, white race and female sex were associated with a higher risk of first falls or fracture.
Table 2.
Multivariable Cox Proportional Hazards Model Examining the Association of Self-reported Frailty with Time to First Fall or Fracture Requiring Medical Attention.
| Variables | Hazard Ratio (95%CI) | P-value |
|---|---|---|
| Frail | 1.60 (1.16–2.20) | <0.01 |
| Female | 1.70 (1.33–2.17) | <0.0001 |
| Age, per 10 years | 1.20 (1.10–1.33) | <0.0001 |
| White (vs. other race) | 1.36 (1.02–1.82) | <0.01 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 0.97 (0.76–1.25) | 0.83 |
| Atherosclerotic diseaseŦ | 0.96 (0.73–1.24) | 0.74 |
| Heart Failure | 0.88 (0.67–1.14) | 0.32 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 0.99 (0.97–1.00) | 0.18 |
Atherosclerotic disease includes: coronary heart disease, cerebrovascular disease, peripheral vascular disease or amputation.
In fully adjusted analyses of the separate components of frailty, poor self-reported functioning (HR 1.33, 95%CI 1.01 – 1.75) and exhaustion (HR 1.40, 95%CI 1.10 – 1.76) were significantly associated with risk of fall or fracture (Figure 1B and 1C, Figure 2). Although the point estimate for low physical activity was similar, the association did not reach statistical significance (HR 1.36, 95%CI 0.78 – 2.37) (Figure 1D, Figure 2), perhaps because the proportion of patients without low physical activity was small.
Figure 2.
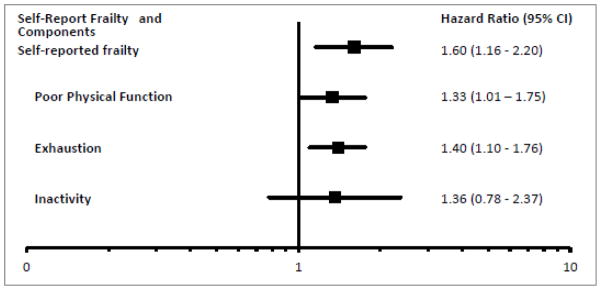
Forrest Plot of the association of self-report frailty and its components with risk of fall or fracture adjusted for female sex, age per 10 years, Caucasian race, diabetes, atherosclerosis, heart failure and body mass index.
Discussion
We found a strong association between self-reported frailty and first fall or fracture severe enough to require medical attention in a cohort of patients new to dialysis. Patients reporting frailty had a higher risk of a fall or fracture compared to their non-frail counterparts. Although only poor self-reported functioning and exhaustion components of our frailty definition were significantly associated with medically urgent first fall or fracture, the association between low physical activity was of a similar magnitude.
The impact of falls and associated complications, including fracture and death, is well documented in the general elderly population [2, 6, 22, 23]. The overall rate of non-fatal falls requiring health-care professional contact was 43 per 1,000 person-years in 2010 [24]. Physiologic derangements associated with CKD and ESRD heighten the risk of falls. In a prior study of 162 elderly patients receiving dialysis, 47% reported a fall during the 2.5-year study period, with a fall incidence of 1.60 falls per person-year based on patient report [25]. In the present study, we used Medicare claims to identify fall events severe enough to require medical evaluation, which may account, at least in part, for the lower observed event rates compared to the aforementioned study. Data from a longitudinal pilot study found that the risk of death and hospitalization was 2-fold higher among patients receiving dialysis who had fallen over a 2-year follow up period compared to those who had not [26]. Patients who reported even one accidental fall had a 78% percent higher risk of death over a 1-year follow-up period compared to “non-fallers” [6].
Hip fracture has been most extensively studied, and patients on dialysis have been observed to have a 2 to 4-fold higher hip fracture rate than that of the general elderly population [17, 27]. For example, among Medicare beneficiaries, the adjusted hip fracture event rate for persons on hemodialysis was 21.9/1000 person-years for patients receiving dialysis versus 10.6/1000 person-years among patients not receiving dialysis [17]. Prior studies have suggested that the incidence of hip fracture may be increasing in the ESRD population. In a study of older dialysis patients, hip fracture rates were significantly higher in 2009 than in 1996 despite multiple advances in management of metabolic bone disease in CKD [28]. Even with the high overall risk of hip fracture among patients with ESRD, risk of death is twice as high among patients who experience a hip fracture as among those who do not [29].
Based on observations showing the association between frailty and fracture in the general population, we hypothesized that rates of fracture would be higher in patients receiving dialysis who were frail by self-report, even given higher baseline rates in the ESRD population. Our study confirmed this expectation, with an event rate of 126 per 1000 person-years in individuals who were frail compared to 66per 1000 person-years in those who were not frail. In addition, a single-center study of 115 prevalent patients receiving dialysis reported a 3-fold higher risk of patient-reported falls among patients who were frail based on the Frailty Index compared to those who were non-frail [15].
Our study had the advantage of capturing falls or fractures using claims data in an incident ESRD population from across the United States. However, we cannot extrapolate event rates in the CDS cohort to all patients on dialysis. Patients enrolled in the CDS were somewhat younger and less disabled than the general incident dialysis population in 2005 [19]. As for the outcome, we captured only falls or fractures severe enough to require hospitalization or emergency room evaluation, whereas other studies have used patients’ report of fall events [5, 6, 15, 26]. Although less severe falls would have been missed with our approach, the use of Medicare claims abrogates a dependence on patient recollection (possibly a serious shortcoming of other studies), as few medical visits go unbilled.
In light of our findings, identification of frail dialysis patients who are at higher risk of fall and fracture could potentially improve outcomes. Frail individuals could be targeted for interventions beyond routine management of CKD-MBD, such as home safety fall risk assessment, referral to physical therapy for gait or strength training, and careful evaluation for potential contribution of polypharmacy. Integrated secondary prevention measures of this type have been shown to significantly lower the risk of repeat falls [30, 31] and to reduce mortality by almost 50% in person over the age of 50 diagnosed with a minimal trauma fracture [32].
Although we demonstrated a higher risk of fall or fracture among frail patients, a number of limitations must be acknowledged. Prevalence of self-reported frailty in this study was higher than in a previous evaluation of the full cohort using the same definition of frailty [10]. This is likely attributable to the need to restrict our analysis to the incident dialysis patients who were Medicare eligible near the start of dialysis, a group that has been shown to have a higher burden of comorbidity than patients who are not Medicare eligible at the start of dialysis [33]. Indeed, the prevalence, although high, was quite similar to the prevalence of self-reported frailty previously reported among patients in this age range in a cohort of incident dialysis patients in the US [11]. Although it would be of interest to the nephrology community to examine falls occurring on patients’ dialysis days, we were unable to determine whether falls occurred on dialysis or non-dialysis days in this study. Because we were investigating events severe enough to require medical attention, there were a relatively small number of events, which restricted our ability to evaluate associations with falls and fractures separately.
Conclusion
Self-reported frailty was associated with higher risk of fall or fracture among patients new to dialysis. Further studies should examine potential interventions to reduce these rates.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
This project is support by contract numbers N01-DK-7-0005 and KD-7-5004 from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK). The interpretation and reporting of the data presented here are the responsibility of the authors and in no way should be seen as an official policy or interpretation of the US government.
Funding sources: Supported by contract N01-DK-7-0005 and KD-7-5004 from the National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes, Digestive and Kidney Disease.
Dr. Delgado’s work is supported by the Department of Veterans Affairs, Clinical Science Research and Development Program under Career Development Award 1IK2CX000527-01A2. Her contribution is the result of work supported with the resources and the use of facilities at the San Francisco VA Medical Center.
Dr. Johansen is supported by 1K24DK085153 and Dr. Dalrymple is supported by K23 DK093584 from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK).
Footnotes
Conflict of Interest Statement: None of the authors has any financial conflict of interest with the information presented in this manuscript. KLJ is the Deputy Editor of CJASN. GMC serves on the Board of Directors of Satellite Healthcare, Inc. and the Scientific Advisory Board of DaVita Clinical Research.
References
- 1.Tinetti ME, Williams CS. Falls, injuries due to falls, and the risk of admission to a nursing home. N Engl J Med. 1997;337(18):1279–84. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199710303371806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Tinetti ME, Speechley M, Ginter SF. Risk factors for falls among elderly persons living in the community. N Engl J Med. 1988;319(26):1701–7. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198812293192604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Braithwaite RS, Col NF, Wong JB. Estimating Hip Fracture Morbidity, Mortality and Costs. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2003;51(3):364–370. doi: 10.1046/j.1532-5415.2003.51110.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Tentori F, McCullough K, Kilpatrick RD, Bradbury BD, Robinson BM, Kerr PG, Pisoni RL. High rates of death and hospitalization follow bone fracture among hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int. 2014;85(1):166–173. doi: 10.1038/ki.2013.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Desmet C, Beguin C, Swine C, Jadoul M. Falls in hemodialysis patients: prospective study of incidence, risk factors, and complications. Am J Kidney Dis. 2005;45(1):148–53. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2004.09.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Li M, Tomlinson G, Naglie G, Cook WL, Jassal SV. Geriatric comorbidities, such as falls, confer an independent mortality risk to elderly dialysis patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2008;23(4):1396–400. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfm778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.System, U. S. R. D. USRDS 2013 Annual Data Report: Atlas of Chronic Kidney Disease and End-Stage Renal Disease in the Unites States. Vol. 2013 National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; Bethesda, MD: 2013. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Delgado C, Frassetto L. Hip fractures in hemodialysis patients. Am J Kidney Dis. 2013;62(4):653–5. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2013.07.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Fried LP, Tangen CM, Walston J, Newman AB, Hirsch C, Gottdiener J, Seeman T, Tracy R, Kop WJ, Burke G, McBurnie MA. Frailty in older adults: evidence for a phenotype. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2001;56(3):M146–56. doi: 10.1093/gerona/56.3.m146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Bao Y, Dalrymple L, Chertow GM, Kaysen GA, Johansen KL. Frailty, dialysis initiation, and mortality in end-stage renal disease. Arch Intern Med. 2012;172(14):1071–7. doi: 10.1001/archinternmed.2012.3020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Johansen KL, Chertow GM, Jin C, Kutner NG. Significance of frailty among dialysis patients. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007;18(11):2960–7. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2007020221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Roshanravan B, Khatri M, Robinson-Cohen C, Levin G, Patel KV, de Boer IH, Seliger S, Ruzinski J, Himmelfarb J, Kestenbaum B. A Prospective Study of Frailty in Nephrology-Referred Patients With CKD. American Journal of Kidney Diseases. 2012;60(6):912–921. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2012.05.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Shlipak MG, Stehman-Breen C, Fried LF, Song X, Siscovick D, Fried LP, Psaty BM, Newman AB. The presence of frailty in elderly persons with chronic renal insufficiency. Am J Kidney Dis. 2004;43(5):861–7. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2003.12.049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Naylor KL, McArthur E, Leslie WD, Fraser L-A, Jamal SA, Cadarette SM, Pouget JG, Lok CE, Hodsman AB, Adachi JD, Garg AX. The three-year incidence of fracture in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2014 doi: 10.1038/ki.2013.547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.McAdams-DeMarco MA, Suresh S, Law A, Salter ML, Gimenez LF, Jaar BG, Walston JD, Segev DL. Frailty and falls among adult patients undergoing chronic hemodialysis: a prospective cohort study. BMC nephrology. 2013;14(1):224. doi: 10.1186/1471-2369-14-224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Block GA, Klassen PS, Lazarus JM, Ofsthun N, Lowrie EG, Chertow GM. Mineral metabolism, mortality, and morbidity in maintenance hemodialysis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004;15(8):2208–18. doi: 10.1097/01.ASN.0000133041.27682.A2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Arneson TJ, Li S, Liu J, Kilpatrick RD, Newsome BB, St Peter WL. Trends in hip fracture rates in US hemodialysis patients, 1993–2010. Am J Kidney Dis. 2013;62(4):747–54. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2013.02.368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Cunningham J, Danese M, Olson K, Klassen P, Chertow GM. Effects of the calcimimetic cinacalcet HCl on cardiovascular disease, fracture, and health-related quality of life in secondary hyperparathyroidism. Kidney Int. 2005;68(4):1793–800. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-1755.2005.00596.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kutner NG, Johansen KL, Kaysen GA, Pederson S, Chen SC, Agodoa LY, Eggers PW, Chertow GM. The comprehensive dialysis study (CDS): a USRDS special study. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009;4(3):645–50. doi: 10.2215/CJN.05721108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Woods NF, LaCroix AZ, Gray SL, Aragaki A, Cochrane BB, Brunner RL, Masaki K, Murray A, Newman AB Women’s Health I. Frailty: emergence and consequences in women aged 65 and older in the Women’s Health Initiative Observational Study. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2005;53(8):1321–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2005.53405.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Danese MD, Kim J, Doan QV, Dylan M, Griffiths R, Chertow GM. PTH and the risks for hip, vertebral, and pelvic fractures among patients on dialysis. Am J Kidney Dis. 2006;47(1):149–56. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2005.09.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Tinetti ME, Williams CS. The effect of falls and fall injuries on functioning in community-dwelling older persons. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 1998;53(2):M112–9. doi: 10.1093/gerona/53a.2.m112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Hu G, Baker SP. An explanation for the recent increase in the fall death rate among older Americans: a subgroup analysis. Public Health Rep. 2012;127(3):275–81. doi: 10.1177/003335491212700307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Centers fo Disease Control and Prevention, N. C. f. I. P. a. C. Web-based Injury Statisitics Query and Reporting System (WISQARS) [accessed 11/24]. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Cook WL, Tomlinson G, Donaldson M, Markowitz SN, Naglie G, Sobolev B, Jassal SV. Falls and fall-related injuries in older dialysis patients. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;1(6):1197–204. doi: 10.2215/CJN.01650506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Abdel-Rahman EM, Yan G, Turgut F, Balogun RA. Long-term morbidity and mortality related to falls in hemodialysis patients: role of age and gender - a pilot study. Nephron Clin Pract. 2011;118(3):c278–84. doi: 10.1159/000322275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Alem AM, Sherrard DJ, Gillen DL, Weiss NS, Beresford SA, Heckbert SR, Wong C, Stehman-Breen C. Increased risk of hip fracture among patients with end-stage renal disease. Kidney Int. 2000;58(1):396–9. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1755.2000.00178.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Nair SS, Mitani AA, Goldstein BA, Chertow GM, Lowenberg DW, Winkelmayer WC. Temporal Trends in the Incidence, Treatment, and Outcomes of Hip Fracture in Older Patients Initiating Dialysis in the United States. Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology. 2013;8(8):1336–1342. doi: 10.2215/CJN.10901012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Mittalhenkle A, Gillen DL, Stehman-Breen CO. Increased risk of mortality associated with hip fracture in the dialysis population. American Journal of Kidney Diseases. 2004;44(4):672–679. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Lih A, Nandapalan H, Kim M, Yap C, Lee P, Ganda K, Seibel MJ. Targeted intervention reduces refracture rates in patients with incident non-vertebral osteoporotic fractures: a 4-year prospective controlled study. Osteoporosis International. 2011;22(3):849–858. doi: 10.1007/s00198-010-1477-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Van der Kallen J, Giles M, Cooper K, Gill K, Parker V, Tembo A, Major G, Ross L, Carter J. A fracture prevention service reduces further fractures two years after incident minimal trauma fracture. International journal of rheumatic diseases. 2014;17(2):195–203. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.12101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Huntjens KM, van Geel TA, van den Bergh JP, van Helden S, Willems P, Winkens B, Eisman JA, Geusens PP, Brink PR. Fracture liaison service: impact on subsequent nonvertebral fracture incidence and mortality. The Journal of bone and joint surgery American volume. 2014;96(4):e29. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.L.00223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Muntner P, Gutiérrez OM, Zhao H, Fox CS, Wright NC, Curtis JR, McClellan W, Wang H, Kilgore M, Warnock DG, Bowling CB. Validation Study of Medicare Claims to Identify Older US Adults With CKD Using the Reasons for Geographic and Racial Differences in Stroke (REGARDS) Study. American Journal of Kidney Diseases. (0) doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2014.07.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.