Abstract
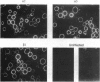
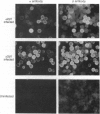
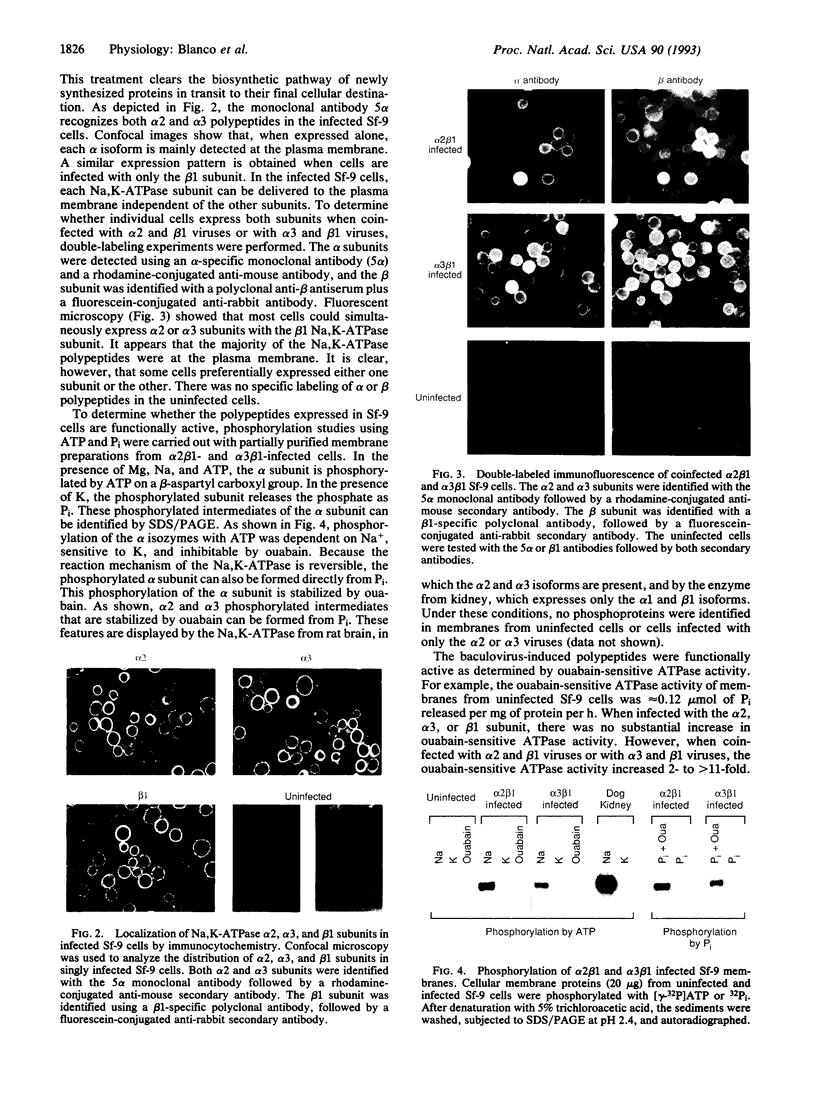
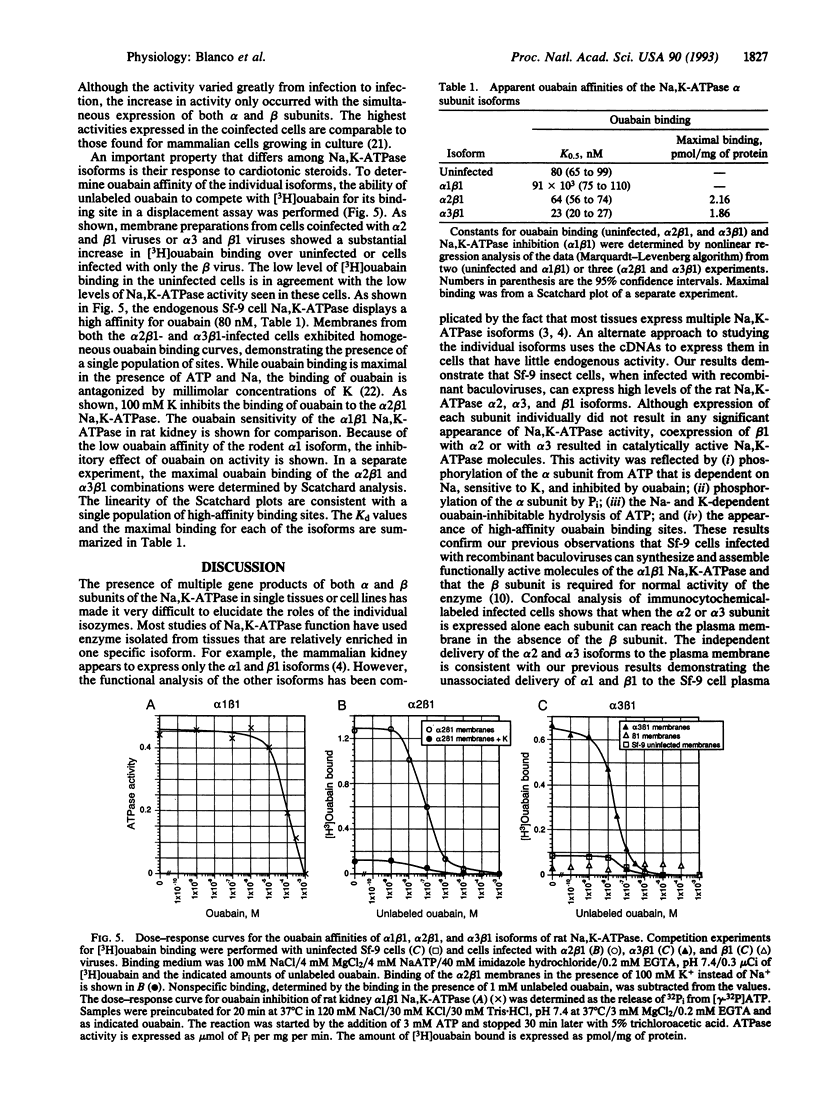
Multiple isoforms of both the alpha and beta subunits of Na,K-ATPase have been identified. Elucidating their roles has been complicated by the fact that most tissues express multiple isoforms and purification techniques specific for each isoform have not been achieved. The baculovirus expression system, which uses the baculovirus Autographica californica to infect insect cells, is an ideal system for studying the Na,K-ATPase isoforms since high amounts of foreign proteins can be produced and some insect cell lines have low levels of endogenous Na,K-ATPase. Recombinant baculoviruses containing the cDNAs for the alpha 2, alpha 3, and beta 1 isoforms of the rat Na,K-ATPase were prepared and used to infect Sf-9 cells, an insect cell line derived from the ovary of the fall armyworm Spodoptera frugiperda. By using this system, Na,K-ATPase alpha 2 and alpha 3 subunits that were antigenically and electrophoretically indistinguishable from the native subunits were produced. When each subunit is expressed independently in the Sf-9 cells, it is primarily delivered to the plasma membrane. Although the isolated expression of each Na,K-ATPase subunit did not render active Na,K-ATPase molecules, the coexpression of alpha 2 or alpha 3 with beta 1 resulted in catalytically active molecules. This activity could be measured as a ouabain-sensitive ATPase activity or directly demonstrated using either [gamma-32P]ATP or 32Pi to identify the phosphorylated intermediates of the alpha 2 and alpha 3 isoforms. [3H]Ouabain binding studies showed that both isoforms are capable of binding the cardiotonic steroid with high affinity, alpha 3 being more sensitive to ouabain. These results demonstrate that the baculovirus system is suitable for the expression of the Na,K-ATPase isoforms and should provide a useful method for the characterization of the enzymatic properties of each isoform.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackermann U., Geering K. Mutual dependence of Na,K-ATPase alpha- and beta-subunits for correct posttranslational processing and intracellular transport. FEBS Lett. 1990 Aug 20;269(1):105–108. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81130-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Askari A., Huang W. H., McCormick P. W. (Na+ + K+)-dependent adenosine triphosphatase. Regulation of inorganic phosphate, magnesium ion, and calcium ion interactions with the enzyme by ouabain. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):3453–3460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Askari A., Huang W., Antieau J. M. Na+,K+-ATPase: ligand-induced conformational transitions and alterations in subunit interactions evidenced by cross-linking studies. Biochemistry. 1980 Mar 18;19(6):1132–1140. doi: 10.1021/bi00547a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaugé L., Campos M. A. Calcium inhibition of the ATPase and phosphatase activities of (Na+ + K+)-ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Mar 23;729(1):137–149. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90464-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berrebi-Bertrand I., Maixent J. M., Christe G., Lelièvre L. G. Two active Na+/K+-ATPases of high affinity for ouabain in adult rat brain membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Jan 29;1021(2):148–156. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(90)90027-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanco G., Berberian G., Beaugé L. Detection of a highly ouabain sensitive isoform of rat brainstem Na,K-ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Aug 10;1027(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(90)90039-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charlemagne D., Maixent J. M., Preteseille M., Lelievre L. G. Ouabain binding sites and (Na+,K+)-ATPase activity in rat cardiac hypertrophy. Expression of the neonatal forms. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):185–189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeTomaso A. W., Xie Z. J., Liu G., Mercer R. W. Expression, targeting, and assembly of functional Na,K-ATPase polypeptides in baculovirus-infected insect cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 15;268(2):1470–1478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eakle K. A., Kim K. S., Kabalin M. A., Farley R. A. High-affinity ouabain binding by yeast cells expressing Na+, K(+)-ATPase alpha subunits and the gastric H+, K(+)-ATPase beta subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2834–2838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmann M. ATPase and phosphatase activity of Na+,K+-ATPase: molar and specific activity, protein determination. Methods Enzymol. 1988;156:105–115. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)56013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geering K. The functional role of the beta-subunit in the maturation and intracellular transport of Na,K-ATPase. FEBS Lett. 1991 Jul 22;285(2):189–193. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80801-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Good P. J., Richter K., Dawid I. B. A nervous system-specific isotype of the beta subunit of Na+,K(+)-ATPase expressed during early development of Xenopus laevis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9088–9092. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara Y., Nikamoto A., Kojima T., Matsumoto A., Nakao M. Expression of sodium pump activities in BALB/c 3T3 cells transfected with cDNA encoding alpha 3-subunits of rat brain Na+,K+-ATPase. FEBS Lett. 1988 Sep 26;238(1):27–30. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80218-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara Y., Ohtsubo M., Kojima T., Noguchi S., Nakao M., Kawamura M. Expression of active alpha-3 subunit of rat brain Na+,K+-ATPase from the messenger RNA injected into Xenopus oocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Aug 30;163(1):102–105. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92104-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horisberger J. D., Lemas V., Kraehenbühl J. P., Rossier B. C. Structure-function relationship of Na,K-ATPase. Annu Rev Physiol. 1991;53:565–584. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.53.030191.003025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz B., Eakle K. A., Scheiner-Bobis G., Randolph G. R., Chen C. Y., Hitzeman R. A., Farley R. A. Synthesis and assembly of functional mammalian Na,K-ATPase in yeast. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 15;265(8):4189–4192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hundal H. S., Marette A., Mitsumoto Y., Ramlal T., Blostein R., Klip A. Insulin induces translocation of the alpha 2 and beta 1 subunits of the Na+/K(+)-ATPase from intracellular compartments to the plasma membrane in mammalian skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 15;267(8):5040–5043. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolansky D. M., Brines M. L., Gilmore-Hebert M., Benz E. J., Jr The A2 isoform of rat Na+,K(+)-adenosine triphosphatase is active and exhibits high ouabain affinity when expressed in transfected fibroblasts. FEBS Lett. 1992 Jun 1;303(2-3):147–153. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80507-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingrel J. B., Orlowski J., Shull M. M., Price E. M. Molecular genetics of Na,K-ATPase. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1990;38:37–89. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60708-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercer R. W., Schneider J. W., Savitz A., Emanuel J., Benz E. J., Jr, Levenson R. Rat-brain Na,K-ATPase beta-chain gene: primary structure, tissue-specific expression, and amplification in ouabain-resistant HeLa C+ cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3884–3890. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi S., Mishina M., Kawamura M., Numa S. Expression of functional (Na+ + K+)-ATPase from cloned cDNAs. FEBS Lett. 1987 Dec 10;225(1-2):27–32. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81125-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider J. W., Mercer R. W., Caplan M., Emanuel J. R., Sweadner K. J., Benz E. J., Jr, Levenson R. Molecular cloning of rat brain Na,K-ATPase alpha-subunit cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6357–6361. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz A., Grupp G., Wallick E., Grupp I. L., Ball W. J., Jr Role of the Na+K+-ATPase in the cardiotonic action of cardiac glycosides. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1988;268B:321–338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shyjan A. W., Ceña V., Klein D. C., Levenson R. Differential expression and enzymatic properties of the Na+,K(+)-ATPase alpha 3 isoenzyme in rat pineal glands. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1178–1182. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweadner K. J. Isozymes of the Na+/K+-ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 May 9;988(2):185–220. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(89)90019-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeyasu K., Lemas V., Fambrough D. M. Stability of Na(+)-K(+)-ATPase alpha-subunit isoforms in evolution. Am J Physiol. 1990 Oct;259(4 Pt 1):C619–C630. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.259.4.C619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeyasu K., Tamkun M. M., Siegel N. R., Fambrough D. M. Expression of hybrid (Na+ + K+)-ATPase molecules after transfection of mouse Ltk-cells with DNA encoding the beta-subunit of an avian brain sodium pump. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10733–10740. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urayama O., Sweadner K. J. Ouabain sensitivity of the alpha 3 isozyme of rat Na,K-ATPase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Oct 31;156(2):796–800. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80914-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]