Abstract
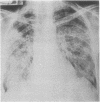
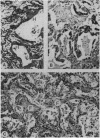
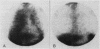
Three further patients are presented who developed evidence of a parenchymal pulmonary disturbance in the course of treatment with amiodarone. In one case the progress of the condition was rapid and ended fatally. Histological examination of the lungs showed evidence of diffuse alveolar damage. The concentration of amiodarone was from four to seven times higher in the lungs than in other organs studied. The concentration of the metabolite desethylamiodarone in the lungs was even higher in relation to other organs studied. The remaining two patients showed a more insidious onset and improvement after withdrawal of amiodarone and treatment with corticosteroids. Gallium 67 scintigraphy appeared to be a sensitive indicator of this adverse effect. Review of published reports revealed 35 cases of amiodarone pneumonitis, including the cases reported in this study. In 11 instances the dose of amiodarone was 400 mg or less. The onset was either insidious or rapidly progressive. Exertional dyspnoea was always present and a nonproductive cough, hypoxaemia, a raised erythrocyte sedimentation rate and diminished carbon monoxide diffusing capacity (transfer factor) were usually noted. Chest radiographs showed either a reticular pattern or diffuse patchy alveolar infiltrates. Discontinuation of amiodarone and an institution of corticosteroid treatment was usually followed by improvement or resolution.
Full text
PDF

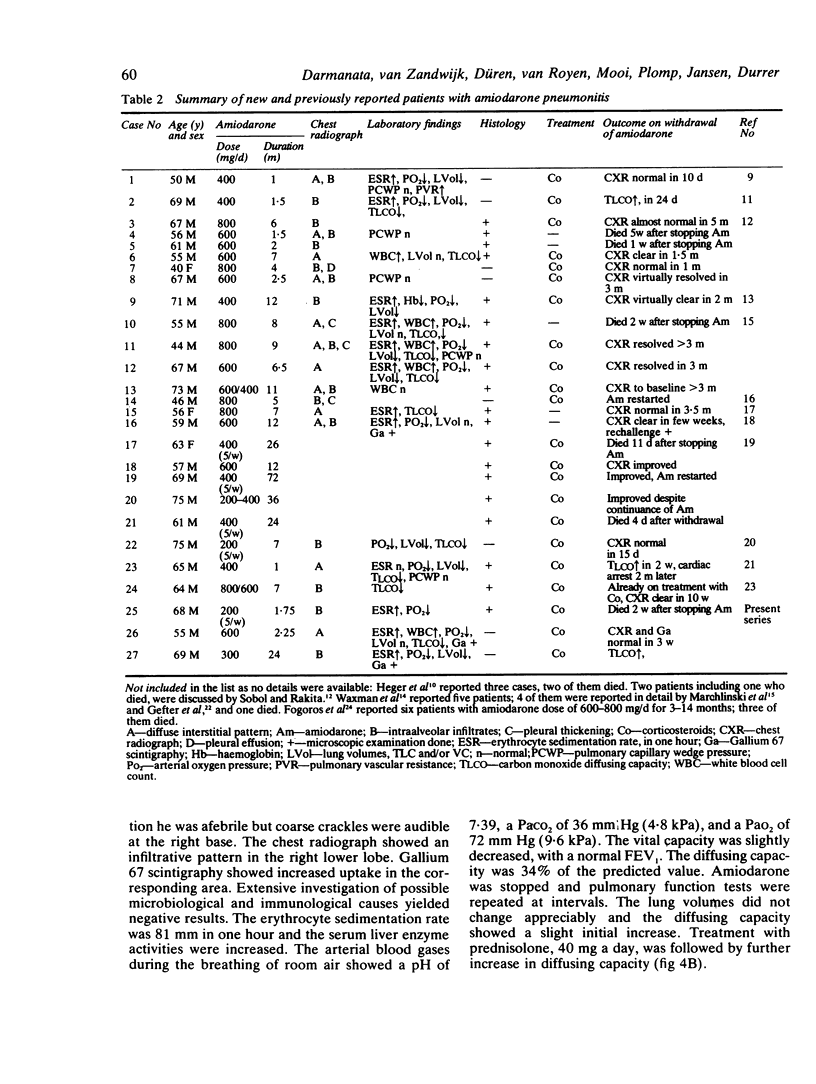
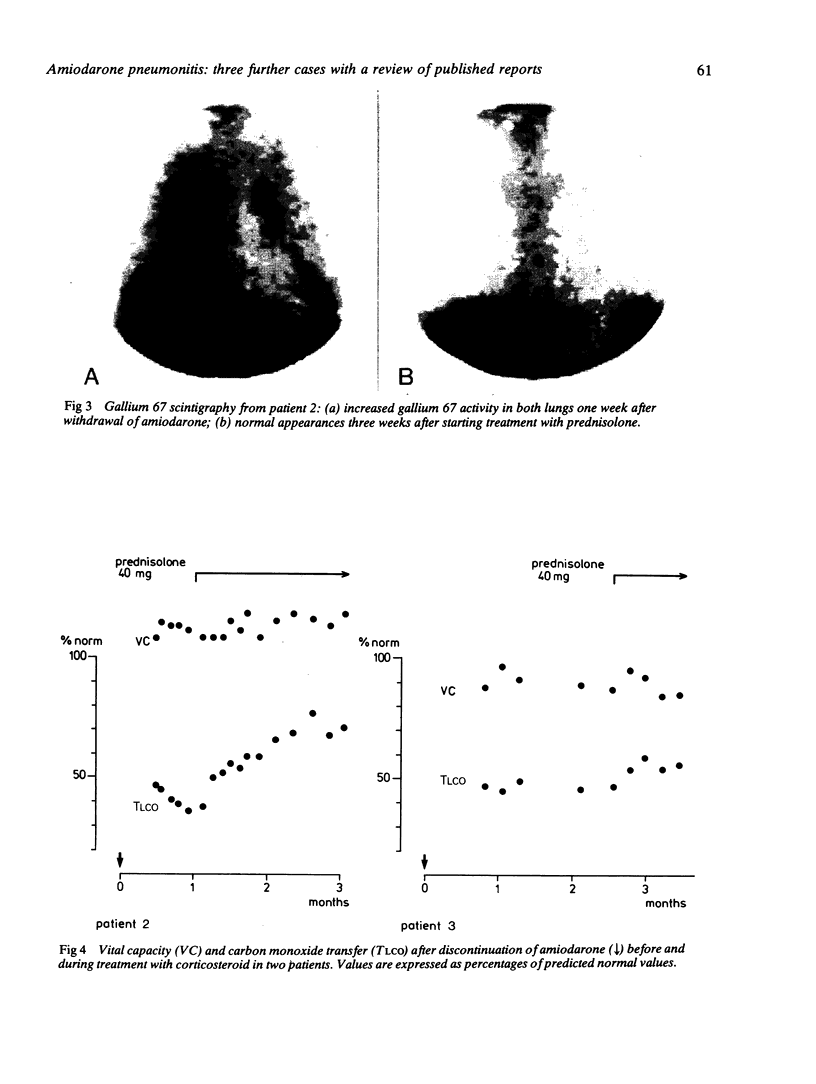



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberts C., van der Schoot J. B., Groen A. S. 67Ga scintigraphy as an index of disease activity in pulmonary sarcoidosis. Eur J Nucl Med. 1981;6(5):205–212. doi: 10.1007/BF00290565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd M. R., Burka L. T. In vivo studies on the relationship between target organ alkylation and the pulmonary toxicity of a chemically reactive metabolite of 4-ipomeanol. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1978 Dec;207(3):687–697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd M. R., Statham C. N., Franklin R. B., Mitchell J. R. Pulmonary bronchiolar alkylation and necrosis by 3-methylfuran, a naturally occurring potential atmospheric contaminant. Nature. 1978 Mar 16;272(5650):270–271. doi: 10.1038/272270a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger A., Dinichert D., Nicod P., Jenny M., Lemarchand-Béraud T., Vallotton M. B. Effect of amiodarone on serum triiodothyronine, reverse triiodothyronine, thyroxin, and thyrotropin. A drug influencing peripheral metabolism of thyroid hormones. J Clin Invest. 1976 Aug;58(2):255–259. doi: 10.1172/JCI108466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chebat J., Caubarrère I. Pneumopathie grave et amiodarone. Therapie. 1983 Jan-Feb;38(1):111–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dake M. D., Golden J. A. Amiodarone and pulmonary effects. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Jun;98(6):1028–1028. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-98-6-1028_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogoros R. N., Anderson K. P., Winkle R. A., Swerdlow C. D., Mason J. W. Amiodarone: clinical efficacy and toxicity in 96 patients with recurrent, drug-refractory arrhythmias. Circulation. 1983 Jul;68(1):88–94. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.68.1.88. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gefter W. B., Epstein D. M., Pietra G. G., Miller W. T. Lung disease caused by amiodarone, a new antiarrythmic agent. Radiology. 1983 May;147(2):339–344. doi: 10.1148/radiology.147.2.6836114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heger J. J., Prystowsky E. N., Jackman W. M., Naccarelli G. V., Warfel K. A., Rinkenberger R. L., Zipes D. P. Clinical efficacy and electrophysiology during long-term therapy for recurrent ventricular tachycardia or ventricular fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 1981 Sep 3;305(10):539–545. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198109033051002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jirik F. R., Henning H., Huckell V. F., Ostrow D. V. Diffuse alveolar damage syndrome associated with amiodarone therapy. Can Med Assoc J. 1983 May 15;128(10):1192–1195. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonckheer M. H., Blockx P., Kaivers R., Wyffels G. Hyperthyroidism as a possible complication of the treatment of ischemic heart disease with amiodarone. Acta Cardiol. 1973;28(2):192–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchlinski F. E., Gansler T. S., Waxman H. L., Josephson M. E. Amiodarone pulmonary toxicity. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Dec;97(6):839–845. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-97-6-839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morera J., Vidal R., Morell F., Ruiz J., Bernadó L., Laporte J. R. Amiodarone and pulmonary fibrosis. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1983;24(5):591–593. doi: 10.1007/BF00542206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plomp T. A., Engels M., Robles de Medina E. O., Maes R. A. Simultaneous determination of amiodarone and its major metabolite desethylamiodarone in plasma, urine and tissues by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1983 Apr 8;273(2):379–392. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)80958-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid W. D., Ilett K. F., Glick J. M., Krishna G. Metabolism and binding of aromatic hydrocarbons in the lung. Relationship to experimental bronchiolar necrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1973 Apr;107(4):539–551. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1973.107.4.539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley S. A., Williams S. E., Cooke N. J. Alveolitis after treatment with amiodarone. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1982 Jan 16;284(6310):161–162. doi: 10.1136/bmj.284.6310.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbaum M. B., Chiale P. A., Halpern M. S., Nau G. J., Przybylski J., Levi R. J., Lázzari J. O., Elizari M. V. Clinical efficacy of amiodarone as an antiarrhythmic agent. Am J Cardiol. 1976 Dec;38(7):934–944. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(76)90807-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbaum M. B., Chiale P. A., Ryba D., Elizari M. V. Control of tachyarrhythmias associated with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome by amiodarone hydrochloride. Am J Cardiol. 1974 Aug;34(2):215–223. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(74)90200-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotmensch H. H., Liron M., Tupilski M., Laniado S. Possible association of pneumonitis with amiodarone therapy. Am Heart J. 1980 Sep;100(3):412–413. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(80)90165-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobol S. M., Rakita L. Pneumonitis and pulmonary fibrosis associated with amiodarone treatment: a possible complication of a new antiarrhythmic drug. Circulation. 1982 Apr;65(4):819–824. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.65.4.819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suárez L. D., Poderoso J. J., Elsner B., Bunster A. M., Esteva H., Bellotti M. Subacute pneumopathy during amiodarone therapy. Chest. 1983 Mar;83(3):566–568. doi: 10.1378/chest.83.3.566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vos A. K., van Ramshorst A. G., Grosfeld J. C., Goossens J. P. A peculiar cutaneous pigmentation from cordarone. Dermatologica. 1972;145(5):297–303. doi: 10.1159/000252057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman H. L., Groh W. C., Marchlinski F. E., Buxton A. E., Sadowski L. M., Horowitz L. N., Josephson M. E., Kastor J. A. Amiodarone for control of sustained ventricular tachyarrhythmia: clinical and electrophysiologic effects in 51 patients. Am J Cardiol. 1982 Nov;50(5):1066–1074. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(82)90419-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellens H. J., Lie K. I., Bär F. W., Wesdorp J. C., Dohmen H. J., Düren D. R., Durrer D. Effect of amiodarone in the Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. Am J Cardiol. 1976 Aug;38(2):189–194. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(76)90148-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright A. J., Brackenridge R. G. Pulmonary infiltration and bone marrow depression complicating treatment with amiodarone. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1982 May 1;284(6325):1303–1303. doi: 10.1136/bmj.284.6325.1303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaher C., Hamer A., Peter T., Mandel W. Low-dose steroid therapy for prophylaxis of amiodarone-induced pulmonary infiltrates. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 31;308(13):779–779. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303313081317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Zandwijk N., Darmanata J. I., Düren D. R., Alberts C., Durrer D., Wagenvoort C. A. Amiodarone pneumonitis. Eur J Respir Dis. 1983 May;64(4):313–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]