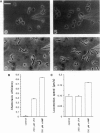
Abstract
The naturally occurring phospholipid lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) can induce a number of physiological responses in vertebrate cells, including platelet aggregation, smooth muscle contraction, and fibroblast proliferation. LPA is thought to activate a specific G-protein-coupled receptor, thereby triggering classic second messenger pathways such as stimulation of phospholipase C and inhibition of adenylate cyclase. Here we report that 1-oleoyl-LPA, at submicromolar concentrations, evokes a chemotactic response in amoebae of the cellular slime mold Dictyostelium discoideum. LPA-induced chemotaxis is specific in that other lysophospholipids, phosphatidic acid, and monoacylglycerol have no effect. We show that the response to LPA is not secondary to the accumulation of extracellular cAMP, a well-established chemoattractant for nutrient-starved D. discoideum. Compared with cAMP-induced chemotaxis, LPA-induced chemotaxis has a somewhat lower efficiency and is not accompanied by the characteristic cellular elongation and orientation along the gradient. These results indicate that LPA has a previously unsuspected role as a chemoattractant for D. discoideum and imply that its biological function as a "first messenger" is not restricted to vertebrate cells.
Full text
PDF
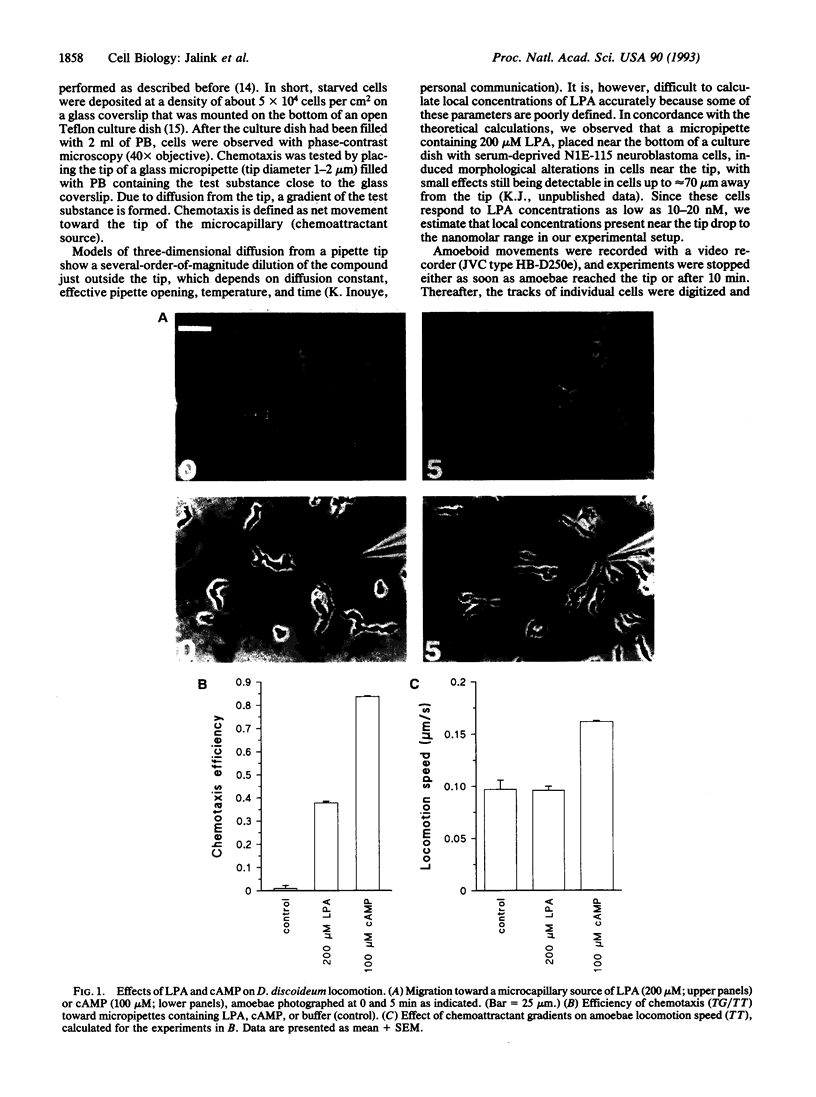
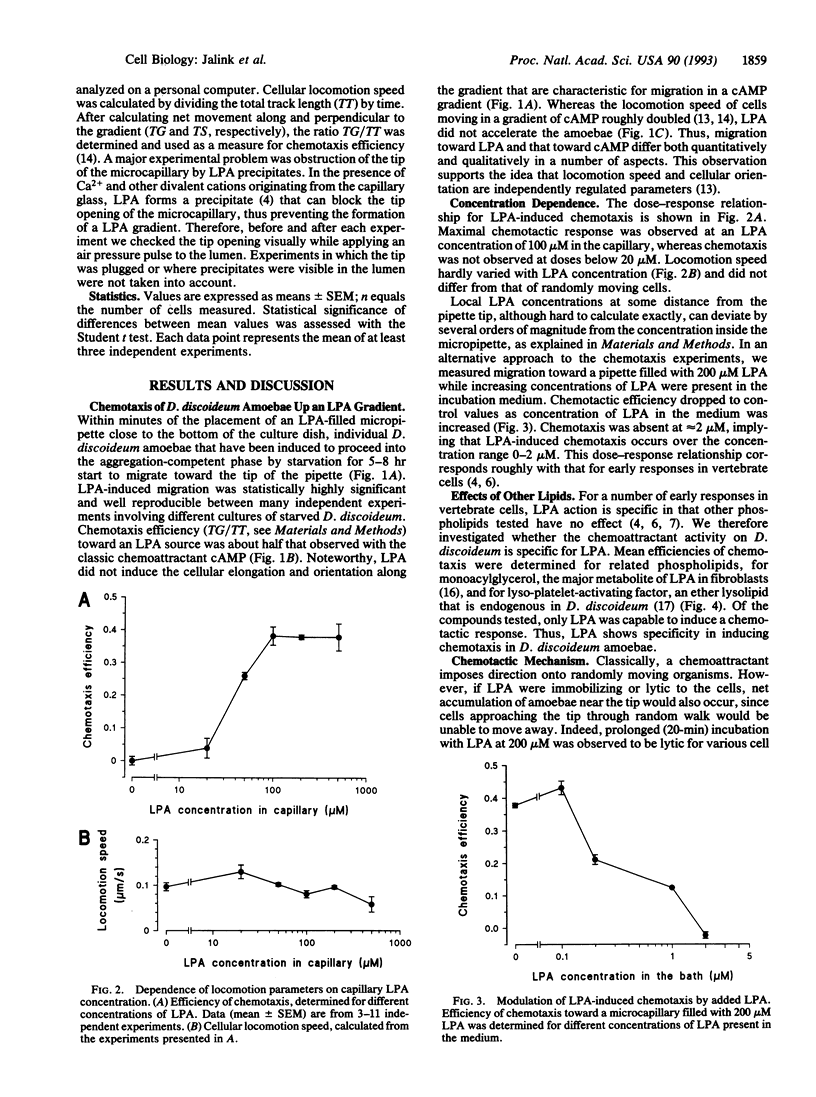
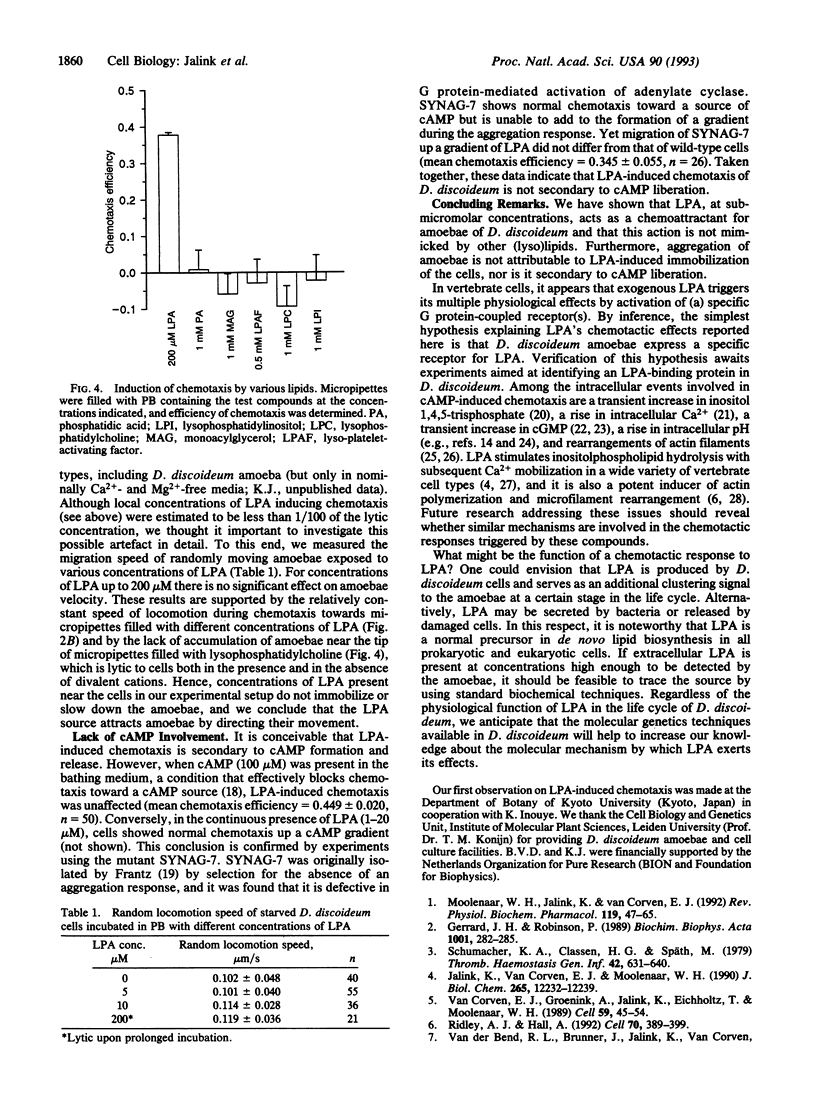

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe T., Maeda Y., Iijima T. Transient increase of the intracellular Ca2+ concentration during chemotactic signal transduction in Dictyostelium discoideum cells. Differentiation. 1988 Dec;39(2):90–96. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1988.tb00085.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aerts R. J., De Wit R. J., Van Lookeren Campagne M. M. Cyclic AMP induces a transient alkalinization in Dictyostelium. FEBS Lett. 1987 Aug 17;220(2):366–370. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80848-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bussolino F., Sordano C., Benfenati E., Bozzaro S. Dictyostelium cells produce platelet-activating factor in response to cAMP. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Mar 28;196(3):609–615. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb15856.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caterina M. J., Devreotes P. N. Molecular insights into eukaryotic chemotaxis. FASEB J. 1991 Dec;5(15):3078–3085. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devreotes P. N., Zigmond S. H. Chemotaxis in eukaryotic cells: a focus on leukocytes and Dictyostelium. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:649–686. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.04.110188.003245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Europe-Finner G. N., Newell P. C. GTP analogues stimulate inositol trisphosphate formation transiently in Dictyostelium. J Cell Sci. 1987 May;87(Pt 4):513–518. doi: 10.1242/jcs.87.4.513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerrard J. M., Robinson P. Identification of the molecular species of lysophosphatidic acid produced when platelets are stimulated by thrombin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Feb 20;1001(3):282–285. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(89)90112-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ince C., van Dissel J. T., Diesselhoff M. M. A teflon culture dish for high-magnification microscopy and measurements in single cells. Pflugers Arch. 1985 Mar;403(3):240–244. doi: 10.1007/BF00583594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jalink K., van Corven E. J., Moolenaar W. H. Lysophosphatidic acid, but not phosphatidic acid, is a potent Ca2(+)-mobilizing stimulus for fibroblasts. Evidence for an extracellular site of action. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 25;265(21):12232–12239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konijn T. M., Van De Meene J. G., Bonner J. T., Barkley D. S. The acrasin activity of adenosine-3',5'-cyclic phosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Sep;58(3):1152–1154. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.3.1152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mato J. M., Van Haastert P. J., Krens F. A., Rhijnsburger E. H., Dobbe F. C., Konijn T. M. Cyclic AMP and folic acid mediated cyclic GMP accumulation in Dictyostelium discoideum. FEBS Lett. 1977 Jul 15;79(2):331–336. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80814-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McRobbie S. J., Newell P. C. Changes in actin associated with the cytoskeleton following chemotactic stimulation of dictyostelium discoideum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Aug 30;115(1):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McRobbie S. J., Newell P. C. Chemoattractant-mediated changes in cytoskeletal actin of cellular slime moulds. J Cell Sci. 1984 Jun;68:139–151. doi: 10.1242/jcs.68.1.139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moolenaar W. H., Jalink K., van Corven E. J. Lysophosphatidic acid: a bioactive phospholipid with growth factor-like properties. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1992;119:47–65. doi: 10.1007/3540551921_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan P., Hall E. M., Bonner J. T. Determination of the active portion of the folic acid molecule in cellular slime mold chemotaxis. J Bacteriol. 1975 Apr;122(1):185–191. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.1.185-191.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan P., Hall E. M., Bonner J. T. Folic acid as second chemotactic substance in the cellular slime moulds. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jun 7;237(75):181–182. doi: 10.1038/newbio237181a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plevin R., MacNulty E. E., Palmer S., Wakelam M. J. Differences in the regulation of endothelin-1- and lysophosphatidic-acid-stimulated Ins(1,4,5)P3 formation in rat-1 fibroblasts. Biochem J. 1991 Dec 15;280(Pt 3):609–615. doi: 10.1042/bj2800609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley A. J., Hall A. The small GTP-binding protein rho regulates the assembly of focal adhesions and actin stress fibers in response to growth factors. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):389–399. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90163-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher K. A., Classen H. G., Späth M. Platelet aggregation evoked in vitro and in vivo by phosphatidic acids and lysoderivatives: identity with substances in aged serum (DAS). Thromb Haemost. 1979 Aug 31;42(2):631–640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Duijn B., Inouye K. Regulation of movement speed by intracellular pH during Dictyostelium discoideum chemotaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4951–4955. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Duijn B., Van Haastert P. J. Independent control of locomotion and orientation during Dictyostelium discoideum chemotaxis. J Cell Sci. 1992 Aug;102(Pt 4):763–768. doi: 10.1242/jcs.102.4.763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Haastert P. J. Sensory adaptation of Dictyostelium discoideum cells to chemotactic signals. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;96(6):1559–1565. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.6.1559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wurster B., Schubiger K., Wick U., Gerisch G. Cyclic GMP in Dictyostelium discoideum, Oscillations and pulses in response to folic acid and cyclic AMP signals. FEBS Lett. 1977 Apr 15;76(2):141–144. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80139-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Corven E. J., Groenink A., Jalink K., Eichholtz T., Moolenaar W. H. Lysophosphatidate-induced cell proliferation: identification and dissection of signaling pathways mediated by G proteins. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):45–54. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90868-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Bend R. L., Brunner J., Jalink K., van Corven E. J., Moolenaar W. H., van Blitterswijk W. J. Identification of a putative membrane receptor for the bioactive phospholipid, lysophosphatidic acid. EMBO J. 1992 Jul;11(7):2495–2501. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05314.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Bend R. L., de Widt J., van Corven E. J., Moolenaar W. H., van Blitterswijk W. J. Metabolic conversion of the biologically active phospholipid, lysophosphatidic acid, in fibroblasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Apr 8;1125(1):110–112. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(92)90163-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]