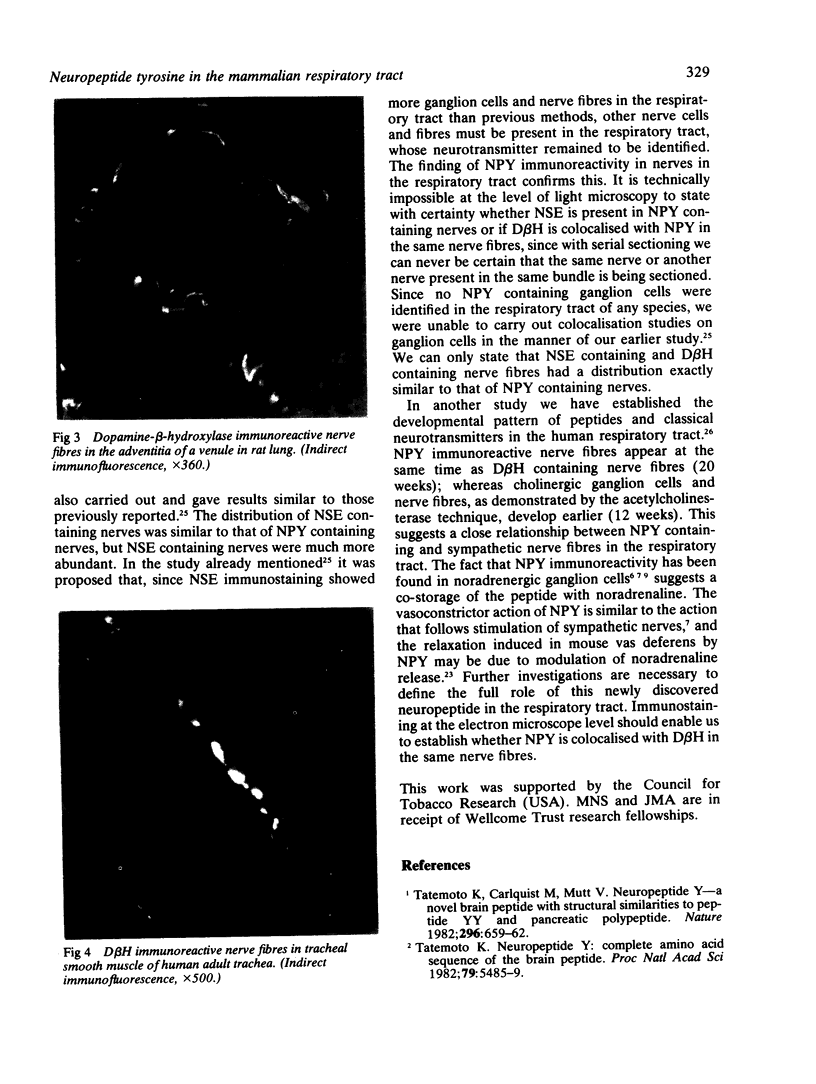
Abstract
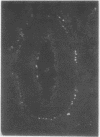
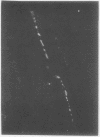
Neuropeptide tyrosine (NPY), a newly discovered peptide known to modulate blood vessel diameter and smooth muscle tone, has been found in many mammalian organs. Its distribution is similar to that of sympathetic nerve fibres and NPY immunoreactivity has been found in noradrenergic ganglion cells. In a study of the respiratory tract of four mammalian species--man, cat, guinea pig, and rat--NPY immunoreactivity has been localised to nerve fibres. NPY immunoreactive nerve fibres were found in the adventitia of blood vessels and in the airway smooth muscle. Its distribution was strikingly similar to that of sympathetic nerve fibres as demonstrated by dopamine-beta-hydroxylase antibodies. The mean (SD) concentrations of NPY in the guinea pig respiratory tract, as determined by radioimmunoassay of tissue extracts, were: upper trachea 3.3 (0.7), lower trachea 2.0 (0.5), and major bronchus 3.5 (1.1) pmol/g. During developmental studies in man NPY immunoreactive nerve fibres were first observed at 20 weeks' gestation in the trachea, and fibres gradually extended down into the intrapulmonary airways after birth. NPY immunoreactive nerve fibres have a distribution and developmental pattern similar to that of sympathetic nerve fibres in the respiratory tract. The finding of NPY immunoreactivity in nerve fibres in the mammalian respiratory tract adds to the growing number of peptides having potent biological actions found in this organ, and shows that the lung possesses a rich peptidergic system, which may influence pulmonary function.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen J. M., Adrian T. E., Tatemoto K., Polak J. M., Hughes J., Bloom S. R. Two novel related peptides, neuropeptide Y (NPY) and peptide YY (PYY) inhibit the contraction of the electrically stimulated mouse vas deferens. Neuropeptides. 1982 Dec;3(2):71–77. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(82)90001-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen J. M., Bircham P. M., Edwards A. V., Tatemoto K., Bloom S. R. Neuropeptide Y (NPY) reduces myocardial perfusion and inhibits the force of contraction of the isolated perfused rabbit heart. Regul Pept. 1983 Jul;6(3):247–253. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(83)90143-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen J. M., McGregor G. P., Adrian T. E., Bloom S. R., Zhang S. Q., Ennis K. W., Unger W. G. Reduction of neuropeptide Y (NPY) in the rabbit iris-ciliary body after chronic sympathectomy. Exp Eye Res. 1983 Aug;37(2):213–215. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(83)90081-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen Y. S., Adrian T. E., Allen J. M., Tatemoto K., Crow T. J., Bloom S. R., Polak J. M. Neuropeptide Y distribution in the rat brain. Science. 1983 Aug 26;221(4613):877–879. doi: 10.1126/science.6136091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker K. L., Monaghan K. G., Silva O. L. Immunocytochemical localization of calcitonin in Kulchitsky cells of human lung. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1980 Apr;104(4):196–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell J. B., Gould R. P., Hyatt P. J., Tait J. F., Tait S. A. Properties of rat adrenal zona reticularis cells: preparation by gravitational sedimentation. J Endocrinol. 1978 Apr;77(1):25–41. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0770025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COONS A. H., LEDUC E. H., CONNOLLY J. M. Studies on antibody production. I. A method for the histochemical demonstration of specific antibody and its application to a study of the hyperimmune rabbit. J Exp Med. 1955 Jul 1;102(1):49–60. doi: 10.1084/jem.102.1.49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dey R. D., Shannon W. A., Jr, Said S. I. Localization of VIP-immunoreactive nerves in airways and pulmonary vessels of dogs, cat, and human subjects. Cell Tissue Res. 1981;220(2):231–238. doi: 10.1007/BF00210505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghatei M. A., Sheppard M. N., O'Shaughnessy D. J., Adrian T. E., McGregor G. P., Polak J. M., Bloom S. R. Regulatory peptides in the mammalian respiratory tract. Endocrinology. 1982 Oct;111(4):1248–1254. doi: 10.1210/endo-111-4-1248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu J., Polak J. M., Adrian T. E., Allen J. M., Tatemoto K., Bloom S. R. Neuropeptide tyrosine (NPY)--a major cardiac neuropeptide. Lancet. 1983 May 7;1(8332):1008–1010. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)92642-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hökfelt T., Lundberg J. M., Tatemoto K., Mutt V., Terenius L., Polak J., Bloom S., Sasek C., Elde R., Goldstein M. Neuropeptide Y (NPY)- and FMRFamide neuropeptide-like immunoreactivities in catecholamine neurons of the rat medulla oblongata. Acta Physiol Scand. 1983 Feb;117(2):315–318. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1983.tb07214.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOOSLI C. G., POTTER E. L. Pre- and postnatal development of the respiratory portion of the human lung with special reference to the elastic fibers. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1959 Jul;80(1 Pt 2):5–23. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1959.80.1P2.5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Terenius L., Hökfelt T., Martling C. R., Tatemoto K., Mutt V., Polak J., Bloom S., Goldstein M. Neuropeptide Y (NPY)-like immunoreactivity in peripheral noradrenergic neurons and effects of NPY on sympathetic function. Acta Physiol Scand. 1982 Dec;116(4):477–480. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1982.tb07171.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheppard M. N., Kurian S. S., Henzen-Logmans S. C., Michetti F., Cocchia D., Cole P., Rush R. A., Marangos P. J., Bloom S. R., Polak J. M. Neurone-specific enolase and S-100: new markers for delineating the innervation of the respiratory tract in man and other mammals. Thorax. 1983 May;38(5):333–340. doi: 10.1136/thx.38.5.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheppard M. N., Marangos P. J., Bloom S. R., Polak J. M. Neuron specific enolase: a marker for the early development of nerves and endocrine cells in the human lung. Life Sci. 1984 Jan 16;34(3):265–271. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(84)90598-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatemoto K., Carlquist M., Mutt V. Neuropeptide Y--a novel brain peptide with structural similarities to peptide YY and pancreatic polypeptide. Nature. 1982 Apr 15;296(5858):659–660. doi: 10.1038/296659a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatemoto K. Isolation and characterization of peptide YY (PYY), a candidate gut hormone that inhibits pancreatic exocrine secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(8):2514–2518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.8.2514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatemoto K. Neuropeptide Y: complete amino acid sequence of the brain peptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5485–5489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terenghi G., Polak J. M., Allen J. M., Zhang S. Q., Unger W. G., Bloom S. R. Neuropeptide Y-immunoreactive nerves in the uvea of guinea pig and rat. Neurosci Lett. 1983 Nov 21;42(1):33–38. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(83)90417-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wharton J., Polak J. M., Bloom S. R., Ghatei M. A., Solcia E., Brown M. R., Pearse A. G. Bombesin-like immunoreactivity in the lung. Nature. 1978 Jun 29;273(5665):769–770. doi: 10.1038/273769a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wharton J., Polak J. M., Bloom S. R., Will J. A., Brown M. R., Pearse A. G. Substance P-like immunoreactive nerves in mammalian lung. Invest Cell Pathol. 1979 Jan-Mar;2(1):3–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]