Abstract
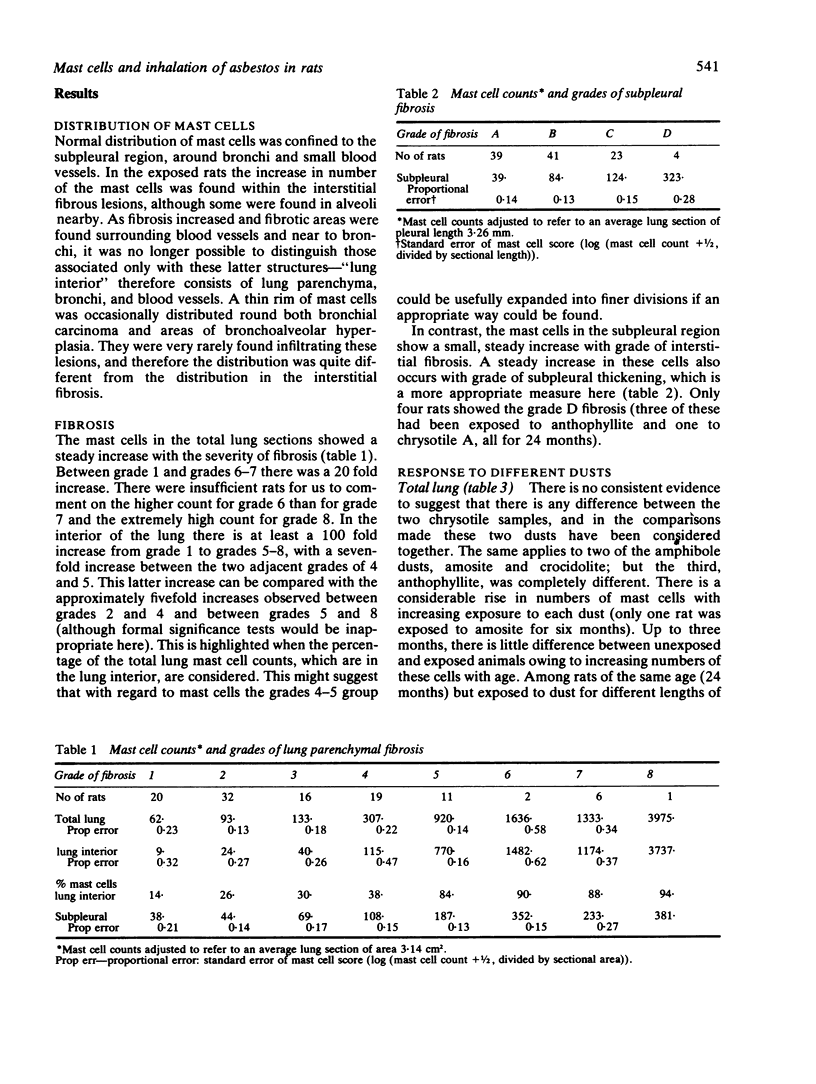
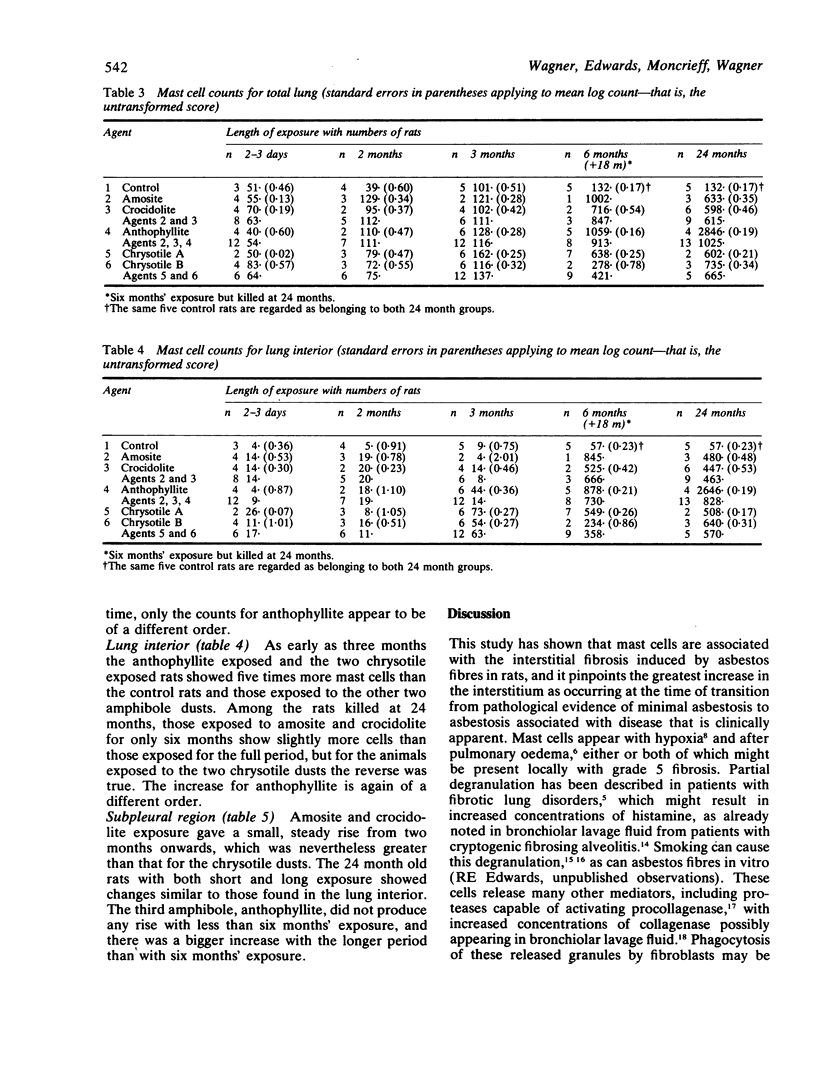
Mast cell counts were performed on sections taken from the lungs of rats exposed by inhalation to different UICC samples of asbestos fibres for periods ranging from a few days to two years. A comparison of mast cell counts with grades of fibrosis showed that there is a sevenfold increase when there is interlobular linking of the fibrotic lesions (grade 5). Submesothelial mast cells showed a trend of increasing numbers with increasing exposure and with increasing subpleural thickening. Each type of asbestos produced a steady increase in mast cell numbers with increasing exposure. Two samples from animals exposed to chrysotile and two from animals exposed to amphiboles (crocidolite and amosite respectively) had 10 times as many cells as the control group after six and 24 months' exposure. Another amphibole, anthophyllite, produced 50 times more cells than were present in the control specimen appropriate for the heaviest exposure. These results are briefly discussed in relation to further exposure, smoking, and characteristics of the dusts.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bateman E. D., Turner-Warwick M., Adelmann-Grill B. C. Immunohistochemical study of collagen types in human foetal lung and fibrotic lung disease. Thorax. 1981 Sep;36(9):645–653. doi: 10.1136/thx.36.9.645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkedal-Hansen H., Cobb C. M., Taylor R. E., Fullmer H. M. Activation of fibroblast procollagenase by mast cell proteases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jun 7;438(1):273–286. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90243-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csaba G. Mechanism of the formation of mast-cell granules. II. Cell-free model. Acta Biol Acad Sci Hung. 1969;20(2):205–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P., Allison A. C., Ackerman J., Butterfield A., Williams S. Asbestos induces selective release of lysosomal enzymes from mononuclear phagocytes. Nature. 1974 Oct 4;251(5474):423–425. doi: 10.1038/251423a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadek J. E., Kelman J. A., Fells G., Weinberger S. E., Horwitz A. L., Reynolds H. Y., Fulmer J. D., Crystal R. G. Collagenase in the lower respiratory tract of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 1979 Oct 4;301(14):737–742. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197910043011401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein R. H., Miller K., Glassroth J., Linscott R., Snider G. L., Franzblau C., Polgar P. Influence of asbestos fibers on collagen and prostaglandin production in fibroblast and macrophage co-cultures. J Lab Clin Med. 1982 Nov;100(5):778–785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslam P. L., Cromwell O., Dewar A., Turner-Warwick M. Evidence of increased histamine levels of lung lavage fluids from patients with cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Jun;44(3):587–593. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heath D., Trueman T., Sukonthamarn P. Pulmonary mast cells in mitral stenosis. Cardiovasc Res. 1969 Oct;3(4):467–471. doi: 10.1093/cvr/3.4.467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaurand M. C., Bignon J., Sebastien P., Goni J. Leaching of chrysotile asbestos in human lungs. Correlation with in vitro studies using rabbit alveolar macrophages. Environ Res. 1977 Oct;14(2):245–254. doi: 10.1016/0013-9351(77)90036-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawanami O., Ferrans V. J., Fulmer J. D., Crystal R. G. Ultrastructure of pulmonary mast cells in patients with fibrotic lung disorders. Lab Invest. 1979 Jun;40(6):717–734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay J. M., Waymire J. C., Grover R. F. Lung mast cell hyperplasia and pulmonary histamine-forming capacity in hypoxic rats. Am J Physiol. 1974 Jan;226(1):178–184. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1974.226.1.178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb D., Lumsden A. Intra-epithelial mast cells in human airway epithelium: evidence for smoking-induced changes in their frequency. Thorax. 1982 May;37(5):334–342. doi: 10.1136/thx.37.5.334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meurman L. O., Kiviluoto R., Hakama M. Mortality and morbidity among the working population of anthophyllite asbestos miners in Finland. Br J Ind Med. 1974 Apr;31(2):105–112. doi: 10.1136/oem.31.2.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newball H. H., Lichtenstein L. Mast cells and basophils: effector cells of inflammatory disorders in the lung. Thorax. 1981 Oct;36(10):721–725. doi: 10.1136/thx.36.10.721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenberger C. I., Hunninghake G. W., Kawanami O., Ferrans V. J., Crystal R. G. Role of alveolar macrophages in asbestosis: modulation of neutrophil migration to the lung after acute asbestos exposure. Thorax. 1982 Nov;37(11):803–809. doi: 10.1136/thx.37.11.803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subba Rao P. V., Friedman M. M., Atkins F. M., Metcalfe D. D. Phagocytosis of mast cell granules by cultured fibroblasts. J Immunol. 1983 Jan;130(1):341–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner J. C., Berry G., Skidmore J. W., Timbrell V. The effects of the inhalation of asbestos in rats. Br J Cancer. 1974 Mar;29(3):252–269. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1974.65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter A., Walter S. Mast cell density in isolated monkey lungs on exposure to cigarette smoke. Thorax. 1982 Sep;37(9):699–702. doi: 10.1136/thx.37.9.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman S. I. The lung mast cell: its physiology and potential relevance to defense of the lung. Environ Health Perspect. 1980 Apr;35:153–164. doi: 10.1289/ehp.8035153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe S., Watanabe K., Oishi T., Aiba M., Kageyama K. Mast cells in the rat alveolar septa undergoing fibrosis after ionizing irradiation. Ultrastructural and histochemical studies. Lab Invest. 1974 Nov;31(5):555–567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



