Background: The transduction of the GLP1 receptor (GLP1R) requires interactions with accessory proteins.
Results: ATP6ap2, also known as the renin receptor, was shown to interact with GLP1R and to regulate both GLP1 and glucose-stimulated insulin secretion.
Conclusion: ATP6ap2 is a novel GLP1R interactor that modulates insulin secretion.
Significance: Our study provides new insights into the fine-tuning GLP1R signaling in beta cells.
Keywords: cyclic AMP (cAMP), insulin secretion, receptor, receptor-interacting protein (RIP), yeast two-hybrid
Abstract
GLP1 activates its receptor, GLP1R, to enhance insulin secretion. The activation and transduction of GLP1R requires complex interactions with a host of accessory proteins, most of which remain largely unknown. In this study, we used membrane-based split ubiquitin yeast two-hybrid assays to identify novel GLP1R interactors in both mouse and human islets. Among these, ATP6ap2 (ATPase H+-transporting lysosomal accessory protein 2) was identified in both mouse and human islet screens. ATP6ap2 was shown to be abundant in islets including both alpha and beta cells. When GLP1R and ATP6ap2 were co-expressed in beta cells, GLP1R was shown to directly interact with ATP6ap2, as assessed by co-immunoprecipitation. In INS-1 cells, overexpression of ATP6ap2 did not affect insulin secretion; however, siRNA knockdown decreased both glucose-stimulated and GLP1-induced insulin secretion. Decreases in GLP1-induced insulin secretion were accompanied by attenuated GLP1 stimulated cAMP accumulation. Because ATP6ap2 is a subunit required for V-ATPase assembly of insulin granules, it has been reported to be involved in granule acidification. In accordance with this, we observed impaired insulin granule acidification upon ATP6ap2 knockdown but paradoxically increased proinsulin secretion. Importantly, as a GLP1R interactor, ATP6ap2 was required for GLP1-induced Ca2+ influx, in part explaining decreased insulin secretion in ATP6ap2 knockdown cells. Taken together, our findings identify a group of proteins that interact with the GLP1R. We further show that one interactor, ATP6ap2, plays a novel dual role in beta cells, modulating both GLP1R signaling and insulin processing to affect insulin secretion.
Introduction
GLP12 is an incretin hormone secreted from enteroendocrine L cells in the intestines. The ability of GLP1 to enhance insulin secretion upon stimulation by the uptake of glucose has been well documented (1–5). Furthermore, GLP1 has been shown to increase beta cell proliferation possibly through the TCF7l2/Wnt pathway (6–8). In addition to its effects in pancreatic beta cells, GLP1 also has diverse functions in a variety of extrapancreatic tissues. In the heart, the cardiac effects of GLP1 analogs have led to the amelioration of myocardial ischemia and to the restriction of infarct size (9), and GLP1 infusion could improve heart function (10). GLP1 in plasma was associated with blood pressure levels in a human population study (11). Further, GLP1 or its analogs were shown to lower blood pressure in rodents and human subjects (12–14). In the brain, GLP1 analogs induced the proliferation of neuronal progenitor cells, implicating a potential involvement in the repair of neurons (15–17).
The physiological and pharmacological effects of GLP1 are mediated by the GLP1 receptor (GLP1R), a member of the B class G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) family (18). GLP1R is widely expressed in pancreatic islets, as well as in the brain, heart, kidney, and gastrointestinal tract (19–21). Specifically in the pancreas, GLP1R expression was confirmed in beta and delta cells; however, it was 10-fold lower in delta cells when quantified by quantitative real time PCR (qPCR) (21). In the alpha cell population, very low expression of GLP1R was detected (21). Like other B class GPCRs, GLP1R signals through the Gs protein complex and activates adenylyl cyclase, which converts ATP into cAMP (22, 23). The increased intracellular accumulation of cAMP triggers both the PKA and Epac2 pathways that are the common downstream pathways responsible for a number of GLP1-induced intracellular actions (24–26). In addition to classical PKA and Epac2 signaling, GLP1R is also found to activate PI3K signaling by transactivating the EGF receptor (27, 28).
As is the case with many GPCRs, a wide number of receptor activities and modes of signal transduction have been described for the GLP1R. This phenomenon may be explained in part by an interaction of the receptor with a large number of G protein-dependent and independent accessory proteins (interactors). Receptor accessory proteins are reported to regulate GPCRs to target subcellular trafficking and intracellular signaling (29). For instance, KCTD isoforms 8, 12, 12b, and 16 are accessory proteins of the GABAB receptor and are indispensable for its function. These isoforms associate tightly with the GABAB2 receptor C terminus to increase agonist potency and markedly alter G protein signaling, thus accelerating the onset of signaling and promoting desensitization of the receptor in a subtype-specific manner (30). However, very little is known thus far on GLP1R accessory proteins. It has been reported that the GLP1R interactor scaffolding protein β-arrestin-1, a protein involved in GPCR agonist-induced desensitization and endocytosis, is required to stimulate cAMP production and insulin secretion in INS-1 beta cell lines upon physical association with the GLP1R (31). Furthermore, the GLP1 interactor caveolin-1 directly interacts with GLP1R, which may in part be directing the trafficking of GLP1R to lipid rafts (32). In another study, β-arrestin-1 was shown to associate with GLP1R and c-Src as a complex, which is required for the proliferative action of GLP1 (33). According to our model, these reports raise the possibility that GLP1R could be coupled to many accessory/interacting proteins to form multimeric protein interactome complexes capable of transducing context-specific downstream signaling pathways that lead to an increasing number of cellular actions.
Recently, using a novel membrane-based split-ubiquitin yeast two-hybrid system (MYTH), we discovered a series of GLP1R interacting proteins in human fetal brain that were shown to attenuate GLP1R activity (34). In this current study, we used MYTH to reveal a GLP1R interactome in both mouse and human islets: two tissues where GLP1R agonists have profound and clinically relevant effects. This MYTH screen identified a host of novel putative GLP1R interacting proteins with major differences seen between human and mouse islet libraries. However, one interactor, ATP6ap2 (ATPase H+-transporting lysosomal accessory protein 2), identified in both mouse and human islet screens was shown to be abundantly expressed in pancreatic islets. Further work demonstrated that ATP6ap2 regulated insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells in both glucose and GLP1R dependent modalities.
Experimental Procedures
Cell Culture
MIN6 cells (a gift from Dr. Susumu Seino from Kobe University, Kobe, Japan) were maintained in DMEM (Life Technologies Inc.) containing 10% FBS, 100 units/ml penicillin G sodium, and 100 μg/ml streptomycin sulfate at 37 °C in 5% CO2. INS-1 832/3 cells (from Dr. Chris Newgard, Duke University, Durham, NC) were maintained in RPMI 1640 (11.1 mm d-glucose) supplemented with 10% FBS, 100 units/ml penicillin, 100 μg/ml streptomycin, 10 mm HEPES, 2 mm l-glutamine, 1 mm sodium pyruvate, and 50 μm mercaptoethanol. Human GLP1R overexpressing CHO cells (RC2) were maintained in DMEM containing 10% FBS, 100 units/ml penicillin G sodium, and 100 μg/ml streptomycin sulfate at 37 °C in 5% CO2. cDNA plasmids and siRNA were transfected into cells using Lipofectamine 2000 and Lipofectamine RNAiMAX (Invitrogen) according to the manufacturer's instructions. After transfection for 48 h, cells were used for analysis.
Isolation and Disperse of Mouse Islet
Mouse islets were isolated and dispersed from male CD-1 mice (∼2 months of age) as described previously (35, 36). The intact islets were cultured in RPMI 1640 medium containing 11.1 mm glucose supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum, 10 mm HEPES, 1% l-glutamate, 100 units/ml penicillin, and 100 μg/ml streptomycin at 37 °C in 5% CO2.
The Split Ubiquitin Membrane Yeast Two-hybrid System
The MYTH system (Fig. 1) methodology was described in detail in previous studies (34, 37). Briefly, MYTH is based on the “split ubiquitin system” (38–41) in which ubiquitin can be split into N-terminal (Nub) and C-terminal (Cub) halves. The reconstitution of the two halves forms pseudoubiquitin, which is recognized by ubiquitin specific proteases leading to proteasomal degradation. In the MYTH system, the receptor (in this case GLP1R) is fused with Cub followed by a transcription factor (TF) to form the “bait,” whereas the interactor protein is fused with NubG (mutational Nub Ile13 → Gly to reduce the affinity of Nub for Cub and avoid self-activation) to form the “prey.” When NubG interactors (prey) are transformed into yeast expressing GSRs-Cub-TF (bait), the interaction between bait and prey brings NubG and Cub to proximity with one another to form a functional pseudoubiquitin, resulting in the release of the TF upon recognition and cleavage of the pseudoubiquitin by ubiquitin specific proteases. The TF further translocates into the nucleus and induces the expression of reporter genes that serves as a readout of protein-protein interaction.
FIGURE 1.
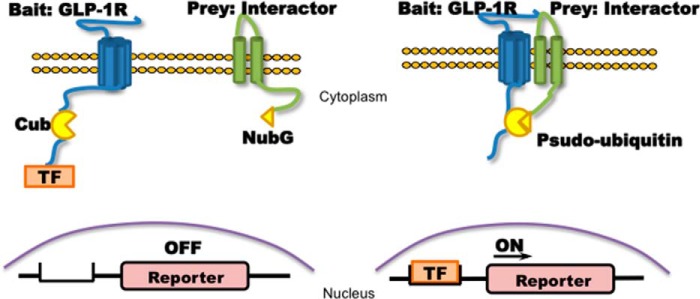
Membrane-based split ubiquitin yeast two-hybrid. Left panel, membrane-bound ubiquitin protein was split into two halves: C terminus (Cub) and N terminus (Nub, NubG is point mutation of Nub to avoid self-activation). Cub is associated with a TF that was fused to the bait GLP1R as GLP1R-Cub, and NubG was fused to the prey interactors as interactor-NubG. Right panel, if the bait interacts with the prey, the resulting proximity of the ubiquitin halves induced by the interaction will enable the reconstitution of Cub and NubG to form a functional pseudoubiquitin protein. Reconstitution recruits ubiquitin-specific proteases that cleave TF downstream of Cub, allowing the TF to translocate into the nucleus to initiate the transcription of reporter genes, which serve as readout of MYTH. As a result, the MYTH system does not rely on protein expression within the nucleus as does the traditional yeast two-hybrid system and can be used to study membrane-bound proteins such as GLP1R and its interactors.
Construction of Human and Mouse Islet cDNA Libraries Compatible with MYTH
Mouse islets were isolated from CD-1 mice (∼2 months of age) as described previously (35, 36, 42). Human islets from review board-approved healthy donors were provided by the Clinical Islet Laboratory (University of Alberta, Edmonton, Canada). The total RNA of human and mouse islets was prepared using the RNeasy mini kit (Qiagen) and were used to produce a cDNA library that was compatible to the MYTH system by Dualsystems Biotech, Inc. (Schlieren, Switzerland). pPR3-N (Dualsystems Biotech, Inc.) was used as the prey vector for generating the cDNA library.
MYTH Analysis of GLP1R in Human and Mouse Islet cDNA Library
The MYTH analysis was performed by Dualsystems Biotech Inc. The technology and the bait vector pCCW-ste-hGLP1R-cub were described in previous studies (34, 37). Briefly, the bait and prey vector were co-transformed into Saccharomyces cerevisiae host THY.AP4 strain, and colony selection was performed on yeast minimal media/synthetic defined agar plates deficient of tryptophan, leucine, histidine, andadenine negative (−Trp/−Leu/−His/−Ade). All positively selected colonies were inoculated in yeast, and the plasmids harboring the interactor sequence were purified. The purified plasmids were amplified in Escherichia coli strain XL-10 Gold. All the plasmids were validated by sequencing. The candidates were compared against pre-existing MYTH screening databases from Dualsystem Biotech Inc., and only unique candidates identified in our current screen were chosen as putative interactors of GLP1R for further study.
cDNA Plasmids, siRNA, and qPCR
The cDNA plasmid pcDNA-ATP6ap2 was purchased from Origene (Rockville, MD) and the Midi-Prep Kit (Qiagen) was used for plasmid purification. Short interfering RNA (SMARTpool siRNA) or scrambled siRNA (control) were purchased from Dharmacon, Thermo Scientific (Waltham, MA). Total RNA from cells was prepared using the RNeasy mini kit (Qiagen) according to the manufacturer's instructions. Purified RNA was converted to cDNA using a Moloney murine leukemia virus reverse transcriptase cDNA kit (Sigma), and real time PCR was performed using an ViiA7 real time PCR system (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA) according to the same protocol described in previous studies (43). A standard curve was generated using mouse genomic DNA for quantification purposes. The measurements of gene expression were normalized to β-actin transcripts within the same sample. The sequences of the primers are shown in Table 1.
TABLE 1.
Sequence of primers
| Name | Access number | Species | Primer sequences |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Forward | Reverse | |||
| Atp6ap2 | NM_027439 | Mouse | 5′-GTTTTGCAGTTGGCTCCCAG-3′ | 5′-GCCGCAATGTGACTGAAAGG-3′ |
| Aig1 | NM_025446 | Mouse | 5′-TTCTTCGGCATCTGTGTGCT-3′ | 5′-CTGTCGTTCTTGCTCCTGGT-3′ |
| Aph1b | NM_177583 | Mouse | 5′-TCATGGGCATCTGGGCATTT-3′ | 5′-TCCTTGTCTTGGCAGAGCAG-3′ |
| Gnas | NM_001077507 | Mouse | 5′-CAGCCTGAAGCAATGGATGC-3′ | 5′-CGTAGGAGCTCCAGCATCAG-3′ |
| Gpr108 | NM_030084 | Mouse | 5′-TCGTGCTCACTGGCTACAAG-3′ | 5′-TCCTCCTCATCCTCCTGTGG-3′ |
| Iftm3 | NM_025378 | Mouse | 5′-GGATCGGAAGATGGTGGGTG-3′ | 5′-CCATCAGGATGCTGAGGACC-3′ |
| ZIP13 | NM_026721 | Mouse | 5′-TGACTGTAACAGGGTCCCCA-3′ | 5′-CTGCCTGTCGCCTGGATAAT-3′ |
| ZIP7 | NM_008202 | Mouse | 5′-GACAGTGTCCAGGTGGTGTT-3′ | 5′-CATGGCCACTCCCACGATAG-3′ |
| Ly6e | NM_001164040 | Mouse | 5′-TGTCAACCTTGGCTACACCC-3′ | 5′-CGCCACACCGAGATTGAGAT-3′ |
| Syngr4 | NM_021482 | Mouse | 5′-CTCTCCATCATCCACCAGCC-3′ | 5′-AGTCGTCATGTAGGGGGACA-3′ |
| Selk | NM_019979 | Mouse | 5′-CCAGGAAACCCTCCACGAAG-3′ | 5′-TCATCCACCAGCCATTGGAG-3′ |
| Vamp3 | NM_009498 | Mouse | 5′-TGCCTCGCAGTTTGAAACAAG-3′ | 5′-CACTGATCCCTATCGCCCAC-3′ |
| Slc2a5 | NM_019741 | Mouse | 5′-CGAAAAACCTACGAGGGGCT-3′ | 5′-GAGACTCCGAAGGCCAAACA-3′ |
| Leprotl1 | NM_026609 | Mouse | 5′-ATGAGCAACGCGTGTAAGGA-3′ | 5′-GCTCTGGCAAACACAACAGG-3′ |
| Kcnj11 | NM_010602 | Mouse | 5′-GACATCCCCATGGAGAATGG-3′ | 5′-TCGATGACGTGGTAGATGATGAG-3′ |
| β-Actin | NM_007393.3 | Mouse | 5′-CTGAATGGCCCAGGTCTGA-3′ | 5′-CCCTGGCTGCCTCAACAC-3′ |
| Zip7 | NM_001008885 | Rat | 5′-CGGCGCTTTCCATGCTTTTA-3′ | 5′-GCTCTAGCCTTTGATCCGCA-3′ |
| Zip13 | NM_001039196 | Rat | 5′-CCACTGTCACCTAGCAGCAA-3′ | 5′-TGGGGCTGGTTTCTTTGTCA-3′ |
| Leprotl1 | NM_001013188 | Rat | 5′-GAGCAACGCTTGTAAGGAGC-3′ | 5′-TGGCAAACACTACAGGGAGC-3′ |
| Selk | NM_207589 | Rat | 5′-CGGTCTTCTCTGTCGCTAGG-3′ | 5′-CCGGCTGTCTAACACCTGAC-3′ |
| Gpr108 | NM_199399 | Rat | 5′-CGCAGTGTCGATGGGAATACT-3′ | 5′-GAGAGTCAGCCGGTGGATAC-3′ |
| Syngr4 | NM_001025644 | Rat | 5′-AGCTGGCTTCCTGTCCTTTC-3′ | 5′-TCTTAAAGCGGGTGCCTACC-3′ |
| Iftm3 | NM_001136124 | Rat | 5′-CTGATCCTGACGTGCTCCAC-3′ | 5′-AGTGTTACACCTGCGTGTCG-3′ |
| Aph1b | NM_001047090 | Rat | 5′-TGCTCCGCCCTCTTCTCTAA-3′ | 5′-GTGCATGGGACGCTGTCTTA-3′ |
| Ly6e | NM_001017467 | Rat | 5′-TGTCAACCTTGGCTACACCC-3′ | 5′-TAGCTATTCACGGACGCCAC-3′ |
| Slc2a5 | NM_031741 | Rat | 5′-GACACCTACTACGACAGAAACAA-3′ | 5′-CCAAGAATCCAACCATGAGAGA-3′ |
| Gnas | NM_021845 | Rat | 5′-AACTGCCTCCACGGCAATAA-3′ | 5′-CCCTTGGGCTTCCAAAGGTT-3′ |
| Atp6ap2 | NM_001007091 | Rat | 5′-TGCTGTGGGCAACCTATTC-3′ | 5′-CTGCATTCTCCAAAGGGTAAGA-3′ |
| Aig1 | NM_001134425 | Rat | 5′-GGCTGTATTCTTCGGCATCT-3′ | 5′-TTCCTGAGCTGTCGTTCTTG-3′ |
| Vamp3 | NM_009498 | Rat | 5′-AACTTTGGTGCTGTCTCCTC-3′ | 5′-CGGGAACATTCCCAGCTAAA-3′ |
| PC1/3 | NM_017091 | Rat | 5′-AGAGGTCTCTGTGGGTCGAA-3′ | 5′-ACAAGGCACAAAGGGGGAAA-3′ |
| PC2 | NM_012746.1 | Rat | 5′-TGGCGAGACATGCAACATCT-3′ | 5′-AATTCCAGGCCAACCCCATT-3′ |
| CPE | NM_013128.1 | Rat | 5′-TGCTTGCGCCTGGAAACTAT-3′ | 5′-AACAGCAGGGCTGAAAGGAA-3′ |
| KCNJ11 | NM_031358 | Rat | 5′-AGTGTGGCTGTGGCAAAGG-3′ | 5′-GGACCGCAACTCAGGACAA-3′ |
| β-Actin | NM_031144 | Rat | 5′-TAGCCATCCAGGCTGTGTTG-3′ | 5′-GGAGCGCGTAACCCTCATAG-3′ |
Co-immunoprecipitation and Immunoblotting
INS-1 cells co-transfected with GLP1R-His-V5-tagged and FLAG-tagged interactor were washed with ice-cold PBS containing 137 mm NaCl, 2.7 mm KCl, 10 mm Na2HPO4, and 1.76 mm KH2PO4 to a pH of 7.4. Cells were harvested in lysis buffer containing 10% glycerol, 50 mm HEPES, 150 mm NaCl, 2 mm EDTA, 0.25% n-dodecyl-β-d-maltoside with complete protease inhibitor mixture (Hoffmann-La Roche Limited, Ltd., Mississauga, Canada). M2 Anti-FLAG affinity gel (Sigma-Aldrich) was used to pull down FLAG-tagged interactor proteins. Briefly, the cell extract (supernatant) was incubated with anti-FLAG-agarose that was equilibrated with wash buffer (0.1% digitonin, 5 mm imidazole with protease inhibitor mixture) for 2 h at 4 °C. The anti-FLAG affinity beads were washed three times with wash buffer and eluted in 2× SDS loading buffer. The precipitated proteins from each sample were loaded and separated on a 10% polyacrylamide gel and transferred to PVDF-plusTM membrane for immunoblotting. Anti-V5 (Invitrogen, 1:2500 dilution), anti-FLAG primary antibodies (Sigma-Aldrich, 1:2000 dilution), and HRP-conjugated mouse secondary antibody were used, and the fluorescence signal was detected by Amersham Biosciences enhanced chemiluminescence (GE Healthcare Lifesciences) with images acquired by the Kodak Image Station 4000 Pro (Carestream Health Inc., Rochester, NY).
Immunohistochemistry
Tissues and cells were fixed in 10% neutral buffered formalin, dehydrated in 70% ethanol, and embedded in paraffin. Paraffinized samples were sliced (5 μm) and adhered to glass slides, rehydrated, and blocked with 3% H2O2 for 30 min. Following PBS washing, sections were incubated in nonimmune serum-free protein block solution (Dako Canada Inc., Burlington, Canada) for 30 min. Sections were blotted to remove excess blocking solution prior to overnight application of primary anti-ATP6ap2 antibody (Sigma-Aldrich, 1:500 dilution) and anti-insulin (Invitrogen, 1:100 dilution) at 4 °C. Images of each section were acquired using Aperio Imagescope version 11.0.2.725 (Aperio Technologies, Vista, CA).
Immunofluorescence and Confocal Microscopy
The expression of ATP6ap2 was determined in dispersed human islets from both normal and type 2 diabetic donors (44) with primary anti-ATP6ap2 (1:125, Sigma), and the cells were co-stained with anti-insulin (1:100, Dako) and anti-glucagon (1:2000, Sigma), followed by Alexa Fluor® 488 goat anti-mouse (1:500, Molecular Probes, Life Technologies), Alexa Fluor® 555 donkey anti-rabbit (1:500, Molecular Probes, Life Technologies), or Alexa Fluor® 488 donkey anti-guinea pig (1:500, Jackson ImmunoResearch, West Grove, PA) secondary antibody. Images were acquired on LSM510 Zeiss confocal microscope (Zeiss) at 40× magnification with an oil lens. The relative fluorescence intensity was quantified using LSM510 software and normalized by area.
Glucose-stimulated Insulin Secretion and Intracellular cAMP Assays
Glucose-stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS) studies were carried out as previously described (43). Briefly, cells were preincubated for 2 h in 2.5 mm glucose HEPES balanced salt solution (114 mm NaCl, 4.7 mm KCl, 1.2 mm KH2PO4, 1.16 mm MgSO4, 2.5 mm CaCl2, 25.5 mm NaHCO3, 20 mm HEPES, and 0.2% (w/v) bovine serum albumin, essentially fatty-acid free, pH7.2) and then in the same HEPES balanced salt solution buffer containing different indicated glucose concentrations for 1 h with 30 nm GLP1 (GLP1-induced insulin secretion) (Bachem Inc., Torrance, CA). Insulin secreted was measured using the homogenous time-resolved fluorescence kit (Cisbio Bioassays, Bedford, MA) and normalized to total protein content. Intracellular cAMP content was measured as previously described (42, 34) by using the homogenous time-resolved fluorescence assay kit (Cisbio Bioassays). Cells were incubated for 1 h with cryptate anti-cAMP antibody and D2-labeled cAMP. Fluorescence signals in both insulin and cAMP assays were measured using the PHERAstar Plus microplate reader (BMG LABTECH, Guelph, Canada).
Transmission Electron Microscopy
Cells were fixed, and images were acquired as previously described (45). Briefly, the samples were observed under a Philips CM100 electron microscope operating at 75 kV. Images were recorded digitally using Kodak 1.6 Megaplus camera system operated using AMT software (Advanced Microscopy Techniques Corporation). Granule numbers were manually quantified using ImageJ software (45).
High Content Imaging
Images were acquired and analyzed on a Thermo Fisher Cellomics ArrayScan® VTI HCS reader using iDEVTM software. The filter settings for each dye were excitation/emission: 577/590 nm for LysoTracker Red DND-99, excitation/emission: 494/516 nm for Fluo4AM, and excitation/emission: 350/461 nm for Hoechst 33342 (Molecular Probes, Life Technologies). Each dye was loaded into live INS-1 cells or dispersed mouse islet cells according to the manufacturer's recommendation.
Statistics
Paired t tests were performed to determine statistical significance. p values less than 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
Results
Generation and Analysis of Human and Mouse Islet cDNA Libraries
To better understand the mechanisms through which GLP1R fine tunes the regulation of insulin secretion, we generated cDNA libraries from both human and mouse islets that were equipped with the physiological machinery necessary for insulin secretion. GLP1R was shown to be abundantly expressed in islet beta cells, less in delta cells, and very low in alpha cells (21). As such, we reasoned that isolated human and mouse islets would serve as reasonable models to study the GLP1R interactome in the setting of the pancreatic beta cell. Using purified RNA from isolated human and mouse islets, we generated human and mouse islet cDNA libraries with the complexity and titer required for MYTH screening. The human islet cDNA library generated contained ∼5.6 × 106 independent clones, ranging in sizes from 0.5 to 5.0 kb with 100% of all vectors containing cDNA inserts. The mouse islet library contained 6.9 × 106 independent clones with a size range equal to that of the human islet library generated (Table 2).
TABLE 2.
cDNA libraries of mouse and human islets
| Human islet library | Mouse islet library | |
|---|---|---|
| Islet source | Nondiabetic human | CD1 mouse |
| Library prey vector | pPR3-N | pPR3-N |
| Cloning site | Directional/Sfi I | Directional/Sfi I |
| First strand synthesis | Oligo(dT) | Oligo(dT) |
| Complexity | 5.6 × 106 independent clones | 6.9 × 106 independent clones |
| Average insert size | 1.04 kb | 1.26 kb |
| Size range | 0.5–5 kb | 0.5–5 kb |
| Vectors with insert | 100% | 100% |
| Inserts > 250 bp | 100% | 100% |
MYTH Analysis of GLP1R in Human and Mouse Islets (Functional Involvement)
The structure of the bait vector overexpressing human GLP1R and its ability to respond to GLP1 was previously described by Huang et al. (34). By using the bait GLP1R vector, we observed 43 positive interactor proteins from the human islet library and 37 such interactor proteins from the mouse islet library. By eliminating highly abundant proteins and common nonspecific MYTH screen interactors (those interactors that appeared in over 50% and 20–50% of all performed MYTH screens done by Dualsystems Biotech Inc.), we obtained 31 and 29 unique interacting proteins from the human (Table 3) and the mouse islet libraries (Table 4), respectively. Apart from Gαs, which is known to be linked to GLP1R function, these putative interactors identified in the MYTH screen have not previously been described with GLP1R. Collectively they represent many known functional groups such as intracellular transport, metabolism and ion transport, or signal transduction (Fig. 2). Some interactors were suggested to be relevant to pancreatic beta cell function, such as zinc transporters (SLC39A7 and SLC39A13), fructose transporters (SLC2A5), and insulin exocytotic SNARE proteins (VAMP3) etc. Among the putative interactors, ATP6ap2 and SELK were identified as two proteins present in both the human and mouse islet library screens (Fig. 2).
TABLE 3.
GLP1R interactors identified from human islet cDNA library by MYTH
| Uniprot ID | Protein | Gene | Biological process | Molecular function | Subcellular localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P55061 | Bax inhibitor 1 | TMBIM6 | Suppressor of apoptosis; modulates unfolded protein response signaling; modulates endoplasmic reticulum calcium homeostasis by acting as a calcium leak channel | Calcium binding | Membrane |
| Q8N3C7 | CAP-Gly domain-containing linker protein 4 | CLIP4 | No information | No information | No information |
| P08861 | Chymotrypsin-like elastase family member 3B | CELA3B | Cholesterol metabolic process, proteolysis | Serine-type endopeptidase activity | No information |
| O95471 | Claudin-7 | CLDN7 | Calcium-independent cell-cell adhesion | Identical protein binding, structural molecule activity | Integral component of membrane |
| Q9P0B6 | Coiled-coil domain-containing protein 167 | CCDC167 | No information | No information | Membrane |
| P04118 | Colipase | CLPS | Lipid catabolic process, small molecule metabolic process | Enzyme activator activity | Secreted, extracellular region |
| P61803 | Dolichyl-diphosphooligosaccharide protein glycosyltransferase subunit DAD1 | DAD1 | Apoptosis | Dolichyl-diphosphooligosaccharide protein | Membrane |
| P63092 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein Gs subunit alpha isoforms short | GNAS | Activation of adenylate cyclase activity, GTPase activity | Signal transducer | Cell membrane |
| Q01628 | Interferon-induced transmembrane protein 3 | IFITM3 | Immunity, IFN-induced antiviral protein which disrupts intracellular cholesterol homeostasis | Antiviral protein | Cell membrane |
| O75556 | Mammaglobin-B | SCGB2A1 | Androgen binding, transcriptional regulation of steroid hormones | Steroid binding | Extracellular region |
| Q9Y6C9 | Mitochondrial carrier homolog 2 | MTCH2 | Transport, induces mitochondrial depolarization | Transporter | Mitochondrion inner membrane |
| P55259 | Pancreatic secretory granule membrane major glycoprotein GP2 | GP2 | Antigen transcytosis by M cells in mucosal-associated lymphoid tissue | Antigen binding | Cell membrane, secreted |
| P19021 | Peptidyl-glycine α-amidating monooxygenase | PAM | Peptidylamidoglycolate lyase activity, peptidylglycine monooxygenase activity, protein binding, peptide metabolic process, protein modification process | Ion/protein binding | Membrane |
| Q9NPR9 | Protein GPR108 | GPR108 | No information | No information | Membrane |
| Q8N2A0 | Putative uncharacterized protein encoded by LINC00269 | LINC00269 | No information | No information | No information |
| Q9NQC3 | Reticulon-4 | RTN4 | Neurogenesis, developmental neurite growth regulatory factor with a role as a negative regulator of axon-axon adhesion and growth, and as a facilitator of neurite branching | Regulatory factor | Endoplasmic reticulum membrane |
| Q9BY50 | Signal peptidase complex catalytic subunit SEC11C | SEC11C | Serine-type peptidase activity, proteolysis, regulation of insulin secretion, signal peptide processing, SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane | Serine-type peptidase activity | Integral component of membrane |
| O95473 | Synaptogyrin-4 | SYNGR4 | No information | No information | Membrane |
| P48230 | Transmembrane 4 L6 family member 4 | TM4SF4 | No information | No information | Integral component of membrane |
| Q6UWJ1 | Transmembrane and coiled-coil domain-containing protein 3 | TMCO3 | Hydrogen ion transmembrane transport; probable Na+/H+ antiporter | Solute:hydrogen antiporter activity | Membrane |
| P07478 | Trypsin-2 | PRSS2 | Calcium ion binding, protein binding, serine-type endopeptidase activity, regulation of cell adhesion, regulation of cell growth, proteolysis | Calcium binding | Secreted, extracellular region |
| Q8WVX3 | Uncharacterized protein C4orf3 | C4orf3 | No information | No information | Membrane |
| Q9NVV5 | Androgen-induced gene 1 protein | AIG1 | No information | No information | Membrane |
| P0C6T2 | Dolichyl-diphosphooligosaccharide protein glycosyltransferase subunit 4 | OST4 | Involved in N-glycosylation | Component of the oligosaccharyltransferase complex | Membrane |
| P54851 | Epithelial membrane protein 2 | EMP2 | Cell proliferation, adhesion | Regulatory factor | Membrane |
| P03901 | NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase chain 4L | MT-ND4L | Mitochondrial electron transport, NADH to ubiquinone, small molecule metabolic process | NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) activity | Integral component of membrane |
| Q9P003 | Protein cornichon homolog 4 | CNIH4 | Intracellular signal transduction | Signal transducer | Membrane |
| O75787 | Renin receptor | ATP6AP2 | Protein binding, receptor activity, angiotensin maturation, positive regulation of transforming growth factor β1 production, regulation of MAPK cascade | Aspartic-type endopeptidase activity, receptor activity | Membrane |
| O95197 | Reticulon-3 | RTN3 | Apoptotic process, response to stress, vesicle-mediated transport | Protein binding | Endoplasmic reticulum membrane, Golgi apparatus membrane |
| Q9Y6D0 | Selenoprotein K | SELK | Calcium, ion transport | Transporter | Integral component of membrane |
| Q96B49 | Mitochondrial import receptor subunit TOM6 homolog | TOMM6 | Protein transport, cellular protein metabolic process | Transporter | Mitochondrion outer membrane |
TABLE 4.
GLP1R interactors identified from mouse islet cDNA library by MYTH
| Uniprot ID | Protein | Gene | Biological process | Molecular function | Subcellular localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q9CXR1 | Dehydrogenase/reductase SDR family member 7 | DHRS7 | Nucleotide binding, oxidoreductase | Oxidoreductase activity | No information |
| Q9D0P0 | Emopamil-binding protein-like | EBPL | Cholestenol delta-isomerase activity, sterol metabolic process | Cholestenol delta-isomerase activity | Integral component of membrane |
| Q8C7N7 | γ-Secretase subunit APH-1B | APH1B | Endopeptidase activity, Notch signaling pathway, positive regulation of catalytic activity, protein processing | Endopeptidase activity | Membrane |
| Q9Z186 | Glucose-6-phosphatase 2 | G6PC2 | Glucose-6-phosphatase activity, gluconeogenesis, regulation of insulin secretion | Hydrolase activity | Integral component of membrane |
| Q64253 | Lymphocyte antigen 6E | LY6E | Adrenal gland development, epinephrine secretion, in utero embryonic development, organ growth, ventricular cardiac muscle tissue morphogenesis | Antigen | Cell membrane |
| Q99N07 | Membrane-spanning 4-domains subfamily A member 6D | MS4A6D | Involved in signal transduction as a component of a multimeric receptor complex. | Receptor | Cell membrane |
| Q9DCL9 | Multifunctional protein ADE2 | PAICS | Purine biosynthesis | Decarboxylase, ligase, lyase | No information |
| Q9Z2U0 | Proteasome subunit α type-7 | PSMA7 | Ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process | Threonine-type endopeptidase activity | Cytoplasm, nucleus, proteasome |
| Q9DA39 | Protein lifeguard 4 | TMBIM4 | Anti-apoptosis, apoptotic process, regulation of calcium-mediated signaling | Anti-apoptotic protein | Integral component of membrane |
| Q9Z2E9 | Seipin | BSCL2 | Lipid metabolism and degradation, regulator of lipid catabolism essential for adipocyte differentiation | Regulator protein | Integral component of endoplasmic reticulum membrane |
| Q8R207 | Serine palmitoyltransferase small subunit A | SPTSSA | Sphingolipid metabolism, lipid metabolism | Serine C-palmitoyltransferase activity | Integral component of membrane |
| Q9WV38 | Solute carrier family 2, facilitated glucose transporter member 5 | SLC2A5 | Hexose transmembrane transport, cellular response to fructose stimulus | Glucose/fructose transmembrane transporter activity | Integral component of membrane |
| Q922J6 | Tetraspanin-2 | TSPAN2 | Brain development | Signal transduction | Integral component of membrane |
| P63024 | Vesicle-associated membrane protein 3 | VAMP3 | SNARE involved in vesicular transport from the late endosomes to the trans-Golgi network | SNAP receptor activity, SNARE binding | Integral component of membrane |
| Q31125 | Zinc transporter SLC39A7 | SLC39A7 | Zinc ion transport | Metal ion transmembrane transporter activity | Integral component of membrane |
| Q8BZH0 | Zinc transporter ZIP13 | SLC39A13 | Zinc influx transporter, cellular zinc ion homeostasis | Zinc ion transmembrane transporter activity | Integral component of membrane |
| P27659 | 60 S ribosomal protein L3 | RPL3 | Translation, cellular response to interleukin-4 | Structrual constituent of ribosome | Nucleus, cytoplasm |
| P01887 | β2-Microglobulin | B2M | MHC class I protein complex, antigen processing and presentation of peptide antigen via MHC class I, immune response | Antigen presentation | Secreted, extracellular region |
| P00158 | Cytochrome b | MT-CYB | Component of the ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase complex (complex III or cytochrome b-c1 complex), respiratory electron transport chain | Electron carrier activity, oxidoreductase activity | Mitochondrion inner membrane |
| Q9Z324 | Dolichol phosphate-mannose biosynthesis regulatory protein | DPM2 | Biosynthetic process of dolichol phosphate-mannose | Dolichyl-phosphate β-d-mannosyltransferase activity | Endoplasmic reticulum membrane |
| Q9CQE7 | Endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment protein 3 | ERGIC3 | Endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi vesicle-mediated transport | Transport protein | Endoplasmic reticulum membrane, Golgi apparatus |
| Q9CQ74 | Leptin receptor overlapping transcript-like 1 | LEPROTL1 | Regulates growth hormone receptor cell surface expression in liver | Regulartor protein | Membrane |
| Q60961 | Lysosomal-associated transmembrane protein 4A | LAPTM4A | Transport of nucleosides and/or nucleoside derivatives between the cytosol and the lumen of an intracellular membrane-bound compartment | Transport protein | Endomembrane system, plasma mem brane |
| P03925 | NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase chain 6 | MTND6 | Core subunit of the mitochondrial membrane respiratory chain NADH dehydrogenase (complex I) | NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) activity | Integral component of membrane, mitochondria membrane |
| Q9CQS8 | Protein transport protein Sec61 subunit β | SEC61B | Protein translocation, transport | Ribosome binding | Endoplasmic reticulum and membrane |
| Q9CYN9 | Renin receptor | ATP6AP2 | Protein binding, receptor activity, angiotensin maturation, positive regulation of transforming growth factor β1 production, regulation of MAPK cascade | Aspartic-type endopeptidase activity, receptor activity | Membrane |
| Q9JLJ1 | Selenoprotein K | SELK | Calcium, ion transport | Transporter | Integral component of membrane |
| P97858 | Solute carrier family 35 member B1 | SLC35B1 | Carbohydrate transport | Transport protein | Endoplasmic reticulum membrane |
| Q9CQ56 | Vesicle transport protein USE1 | USE1 | Endoplasmic reticulum tubular network organization, regulation of endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi vesicle-mediated transport | Endoplasmic reticulum membrane |
FIGURE 2.
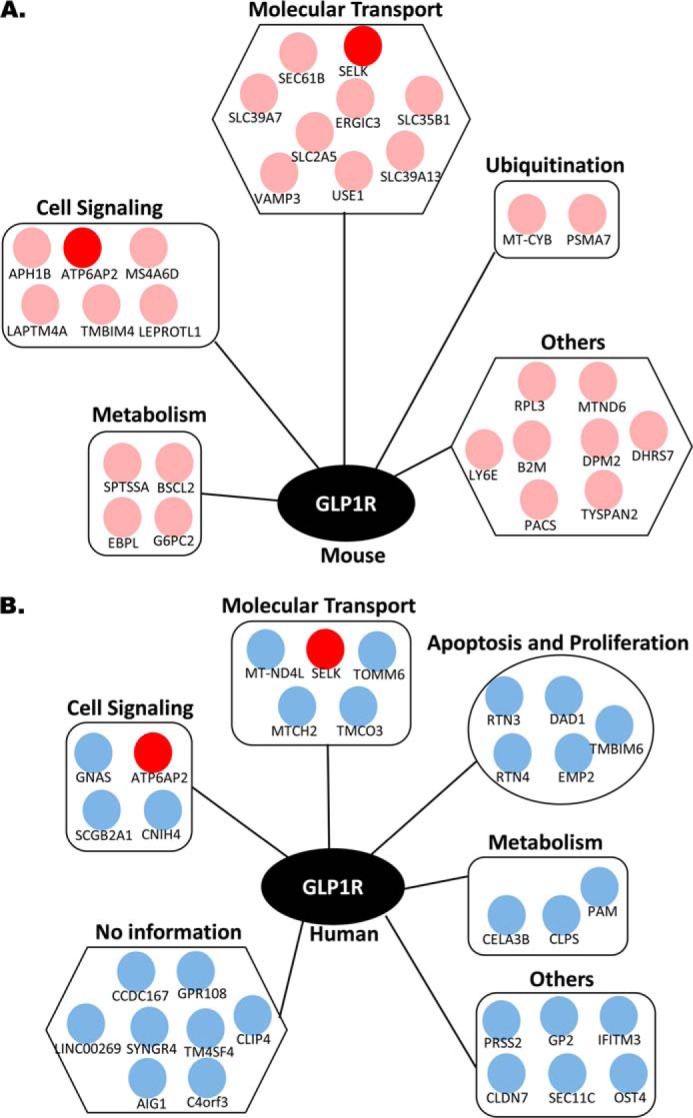
Interactor networks of GLP1R identified from human and mouse islet MYTH screens. A and B, mouse islet (A) and human islet (B) cDNA libraries. Each interactor is represented by a separate dot. Pink dots represent interactors identified in mouse islets, and blue dots represent interactors identified in human islets. Interactors common to both mouse and human islets are identified in red.
Expression of Selected Interactors in Pancreatic Beta Cells
Because ATP6ap2 and SELK were identified from both libraries, we examined their expression using qPCR in three distinct sources of pancreatic beta cells (MIN6, INS1, and isolated mouse islets). Since the GLP1R is primarily expressed at the plasma membrane, we also included 11 membrane-bound putative interactors in addition to ATP6ap2 and SELK found in our screens. Among the 13 interactors examined, ATP6ap2 was consistently the most abundant (Fig. 3) in all three cell types, whereas SELK was not. Some other membrane-bound interactors such as SYNGR4, APH1B, and GNAS showed only very low abundance compared with our control, Kcnj11, the subunit of the KATP channel required for glucose-stimulated insulin secretion (Fig. 3). The transcript expression profile pattern of these interactors was comparable among all three cell types, whereas only SLC39A7 and Leprotl1 had relatively higher expression levels compared with other interactors in mouse islets. Taken together, based on the expression pattern, ATP6ap2 identified from both islet MYTH screening was most highly expressed across all three cell types and was therefore chosen for further functional analysis.
FIGURE 3.
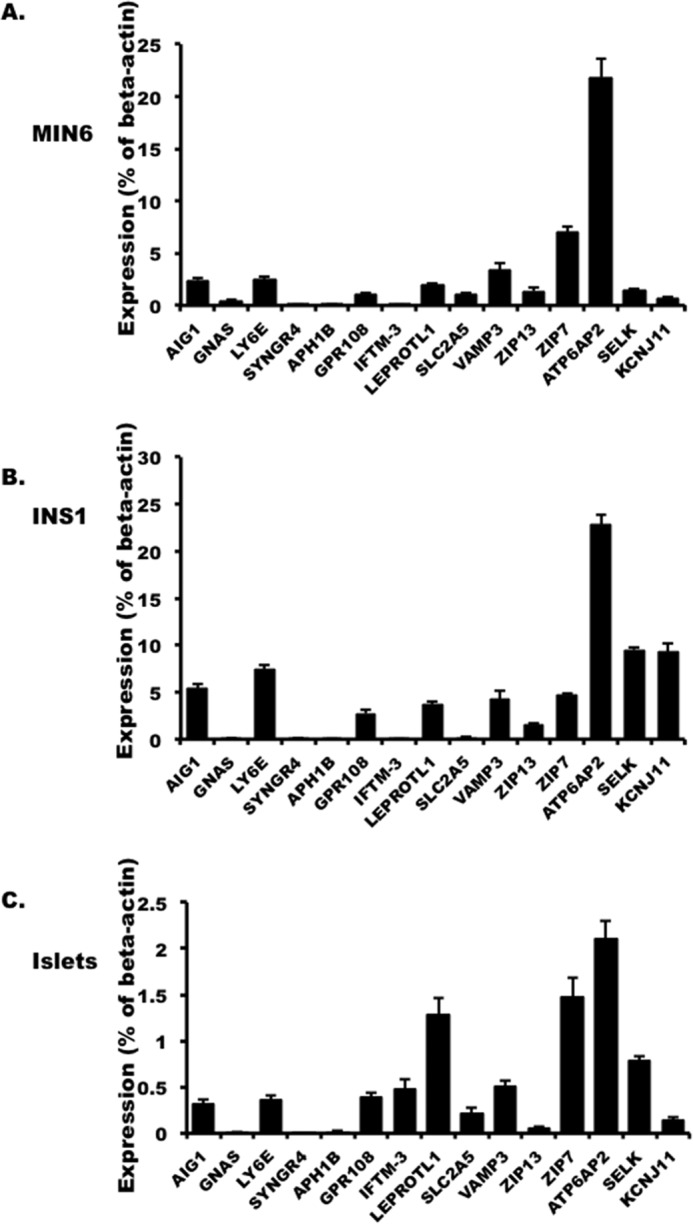
The expression of selected interactors in MIN6 (A), INS1 832/3 cells (B), and mouse islets (C) presented as the percentage of β-actin in the cell. The values are represented by the averages ± S.E. from triplicates in three independent experiments.
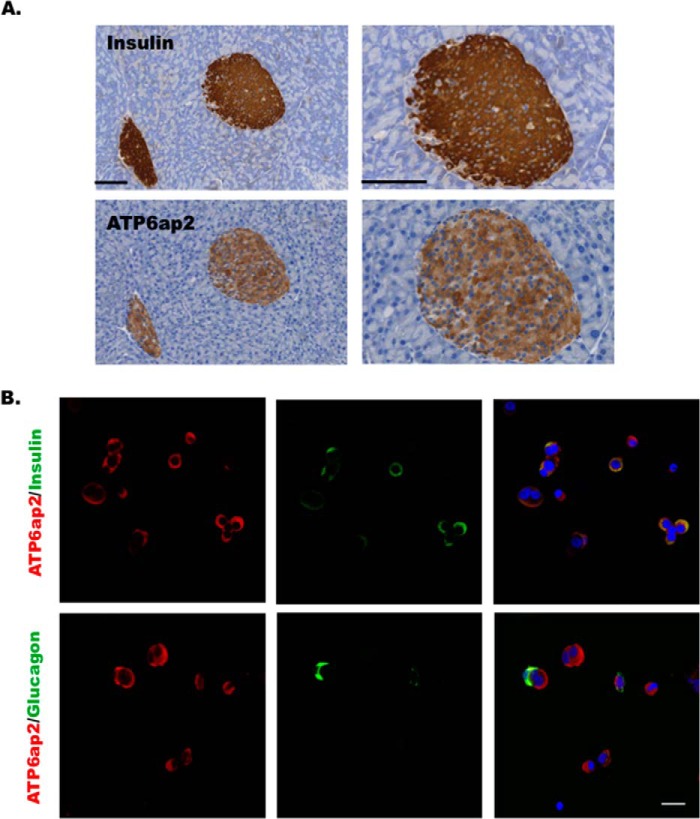
ATP6ap2 has been shown to be expressed in several tissue including brain, heart, kidney, liver, pancreas, and adipose tissues (43, 44) with the highest levels reported in MIN6 cells (BioGPS (46, 47)). To localize ATP6ap2 expression within the pancreas, both immunohistochemistry and immunofluorescence staining were performed on mouse pancreatic slices and dispersed human islet cells, respectively. In mouse pancreata, ATP6ap2 was expressed in insulin immunopositive cells but not in acinar tissue (Fig. 4A). Further, in dispersed human islet cells, ATP6ap2 was shown to be expressed in both alpha and beta cells (Fig. 4B).
FIGURE 4.
ATP6ap2 expression in the pancreas and islets. A, immunohistochemistry showing ATP6ap2 localization in the mouse pancreatic sections. The right panels show the enlarged images of the left panels. Bar, 100 μm. B, immunofluorescence showing ATP6ap2 localization in dispersed human islets. Bar, 20 μm. Representative images are from three independent experiments.
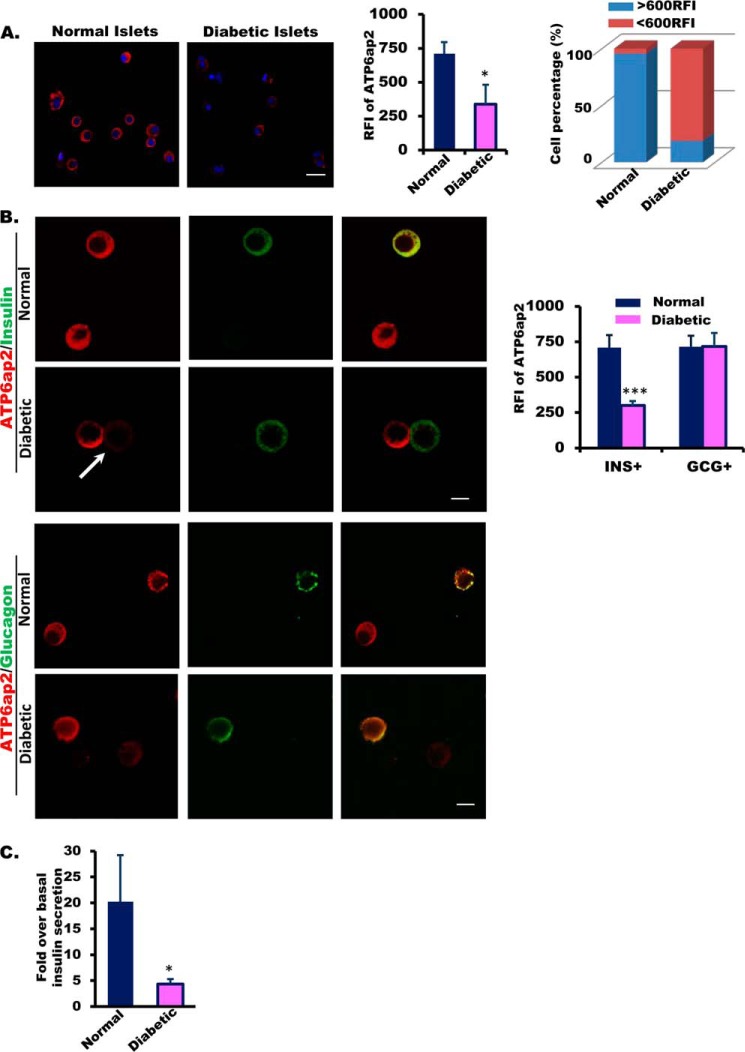
Interestingly, we found that the intensity of ATP6ap2 staining appeared weaker in islets from diabetic donors (Fig. 5A). The percentage of islet cells with strong fluorescence (>600 relative fluorescence intensity) decreased remarkably in diabetic islet cells compared with normal islet cells, whereas the percentage of those with weak fluorescence increased (Fig. 5A). These observations suggested decreased ATP6ap2 expression in diabetic islets. Further, we examined whether or not there was decreased expression in both alpha and beta cells. After co-staining with insulin or glucagon, we showed that ATP6ap2 expression was decreased primarily in beta cells (Fig. 5B). Importantly, correlating with ATP6ap2, islets from diabetic donors had impaired glucose-stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS) compared with controls (Fig. 5C).
FIGURE 5.
ATP6ap2 expression and GSIS in human islets from normal and diabetic donors. A, representative images and quantitative analysis (quantification of fluorescence intensity and distribution of fluorescence intensity within cell population) of ATP6ap2 expression in human islets from normal and diabetic donors. Bar, 20 μm. B, ATP6ap2 expression in human dispersed islets from diabetic donors. Arrow indicates reduced ATP6ap2 expression in insulin-positive cells. Bar, 10 μm. Quantitative analysis of ATP6ap2 expression in both insulin- and glucagon-positive cells is shown (normal donors, n = 3; diabetic donors, n = 2). C, glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in human islets from diabetic donors.
Effect of Overexpressing ATP6ap2 on Insulin Secretion and cAMP Accumulation in INS-1 Cells
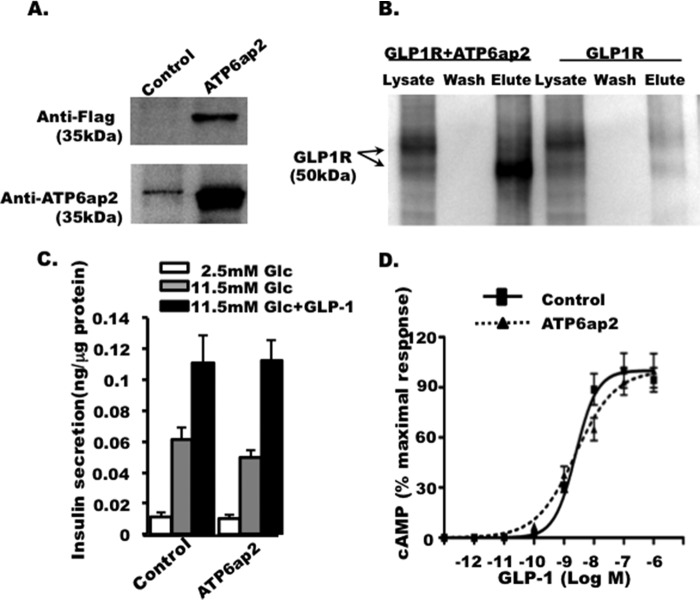
To further validate the interaction of GLP1R with ATP6ap2 employing the INS-1 cell line, we co-expressed epitope tagged GLP1R-V5 and ATP6ap2-FLAG. ATP6ap2 overexpression was detected using both anti-FLAG and anti-ATP6ap2 (Fig. 6A). GLP1R was detected after affinity purification of ATP6ap2-FLAG but not in GLP1R-expressing cell lysates alone, suggesting the interaction between two proteins in pancreatic beta cells (Fig. 6B) validating the MYTH assay results.
FIGURE 6.
Effect of ATP6ap2 overexpression on insulin secretion and cAMP. A, overexpression of ATP6ap2, detected by anti-FLAG and anti-ATP6ap2. B, immunoprecipitation showing the interaction between GLP1R and ATP6ap2 in INS-1 cells. GLP1R overexpression alone was used as negative control to validate the specificity of immunoprecipitation. Representative images are from three independent experiments. C, effect of ATP6ap2 on glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in INS-1 cells. D, effect of ATP6ap2 overexpression on cAMP accumulation stimulated by GLP1 in CHO cells with GLP1R overexpressed.
ATP6ap2 has been found to act as an adapter protein of the V-ATPase receptor complex (48) that maintains the acidic environment within vesicles required for the maturation and priming of insulin protein in pancreatic beta cells (49, 50). We further examined the effect of overexpressing ATP6ap2 in INS-1 cells. Interestingly, ATP6ap2 overexpresssion did not have any significant effect on insulin secretion under basal glucose conditions nor upon glucose or GLP1-induced insulin secretion (Fig. 6C) under the conditions studied. ATP6ap2 overexpression had no effect on GLP1-induced cAMP formation (Fig. 6D), which is a key second messenger molecule in GLP1 signaling.
Effect of Knocking Down ATP6ap2 on Insulin Secretion and cAMP in INS-1 Cells
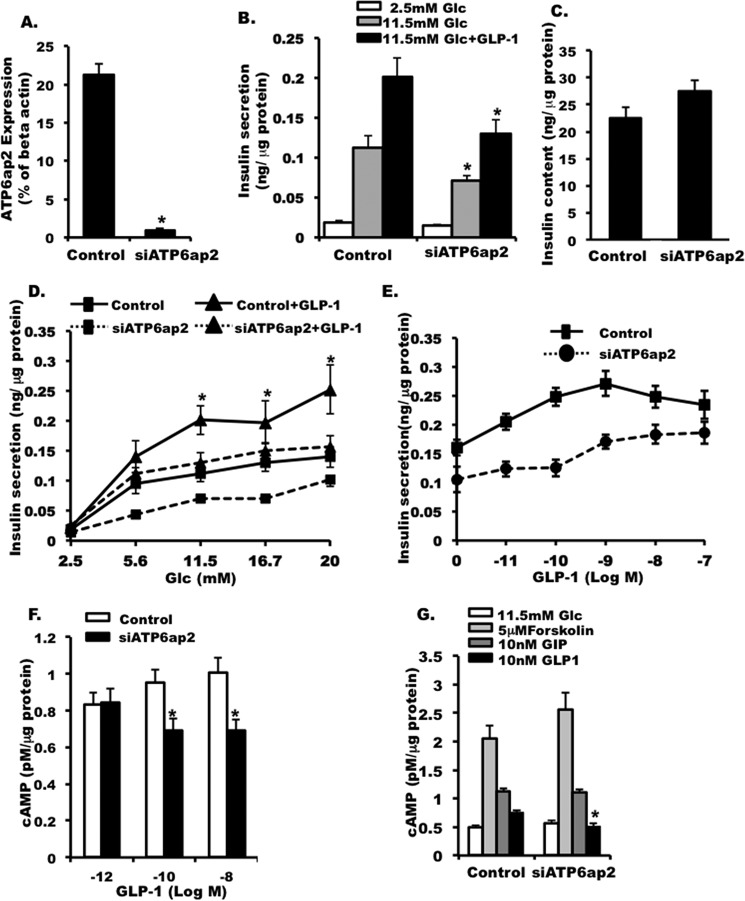
Because we did not observe significant effects in cells overexpressing ATP6ap2, to further elucidate the role of ATP6ap2 within pancreatic beta cells, we knocked down ATP6ap2 by siRNA (Fig. 7A). When ATP6ap2 was effectively knocked down (Fig. 7A), insulin secretion was decreased significantly under high glucose conditions (11.5 mm; Fig. 7B), as was GLP1-induced insulin secretion (Fig. 7B). This reduction in insulin secretion was not associated with cell death (data not shown) nor decreases in total insulin content (Fig. 7C). Furthermore, we showed that this attenuating effect only occurred at stimulatory glucose concentrations (11.5, 16.7, and 20 mm), not at low or moderate glucose levels (2.8 or 5.6 mm) (Fig. 7D). The inhibitory effect of ATP6ap2 knockdown was seen across a range of GLP1 concentrations (Fig. 7E).
FIGURE 7.
Effect of ATP6ap2 in INS-1 cells. A, qPCR showing the efficiency of siATP6ap2 in knocking down ATP6ap2 in INS-1 cells. B, effect of ATP6ap2 knockdown on insulin secretion in INS-1 cells. C, insulin content in INS-1 cells transfected with siATP6ap2. D, insulin secretion in INS-1 cells transfected with scrambled siRNA (Control) and siATP6ap2 at different glucose concentration. E, insulin secretion in cells transfected with siATP6ap2 at 11.5 mm glucose in the presence of incremental doses of GLP1. F, cAMP accumulation in INS-1 cells transfected with siATP6ap2 at different doses of GLP1. G, cAMP accumulation in siATP6ap2 transfected cells that were treated with forskolin, GIP, and GLP1, respectively. The values are represented by the averages ± S.E. from triplicates in at least three independent experiments. *, p < 0.05 (n = 4–6).
GLP1R signaling effects are primarily mediated by the second messenger cAMP. In line with this, we found that down-regulation of ATP6ap2 led to a decrease in GLP1-stimulated cAMP accumulation in INS-1 cells (Fig. 7F). However, this effect was only observed at 0.1 and 10 nm GLP1 concentrations but not at a 1 pm GLP1 concentration (Fig. 7F), suggesting that the decrease in cAMP accumulation might be concentration-dependent. To confirm that the observation was specific, we also treated the siATP6ap2 transfected cells with forskolin (direct stimulation on adenylyl cyclase) and GIP (incretin acting on beta cells and sharing similar structure and signaling pathways with GLP1R). We did not observe any difference in cAMP accumulation between control and ATP6ap2 knockdown cells (Fig. 7G). This suggested that down-regulation of ATP6ap2 specifically decreased GLP1R stimulated cAMP accumulation. The fact that we did not observe an ATP6ap2 effect in the overexpression model is likely due to the high abundance of native ATP6ap2 in INS-1 cells. Conversely, knocking down endogenous ATP6ap2 would likely exhibit more profound effects on the cells.
Effect of Knocking Down ATP6ap2 on Insulin Granule Morphology and Acidification
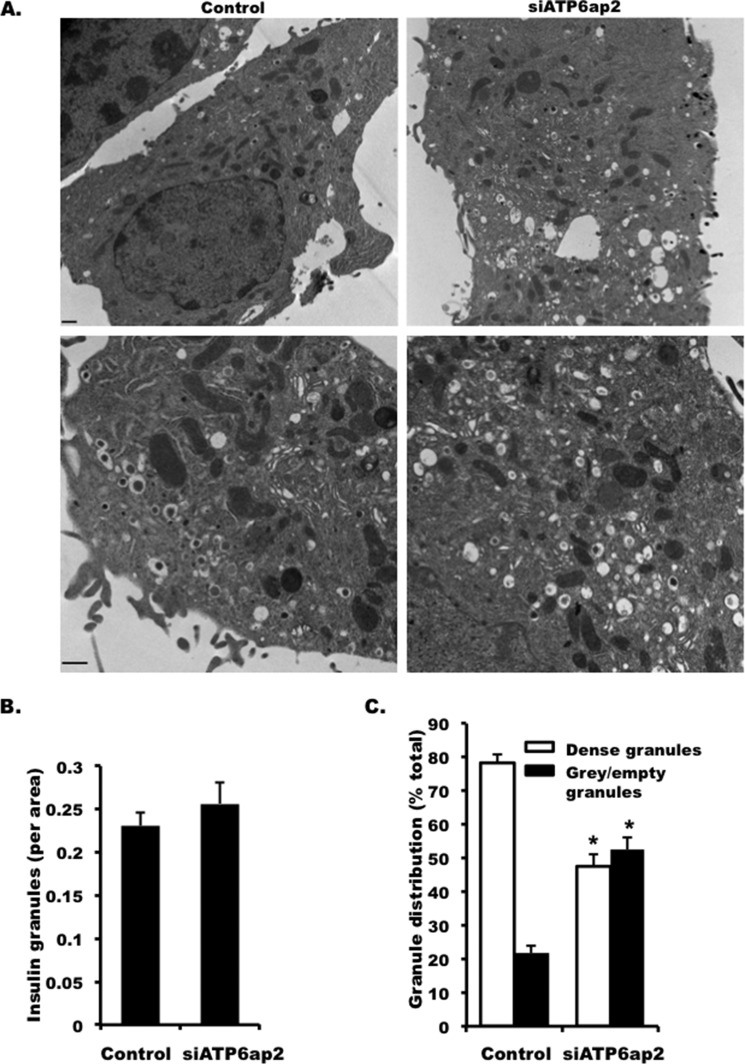
Because decreased insulin secretion and impaired insulin processing were observed in ATP6ap2 knockdown INS-1 cells, we next examined whether there were defects in insulin granule morphology using electron microscopy. We did not observe any change in granule morphology (Fig. 8A) or the number of insulin granules in siRNA treated INS1 cells (Fig. 8B), but the percentage of gray and empty granules was increased by more than 2-fold in ATP6ap2 knockdown cells (Fig. 8C). These results indicated that decreased insulin secretion was not due to the reduction of insulin granules per se but was possibly due to impaired insulin biosynthesis.
FIGURE 8.
Effect of knocking down ATP6ap2 on insulin granules. A, representative images of electron microscopy showing insulin granules in INS-1 cells transfected with siATP6ap2. The lower panel is shown in higher magnification. Bar, 500 nm. B, granule numbers in INS-1 cells transfected with siATP6ap2. C, percentages of dense (mature) and gray/empty (immature) granules in INS-1 cells transfected with siATP6ap2. Representative images are from at least three independent experiments. *, p < 0.05 (n = 3–5).
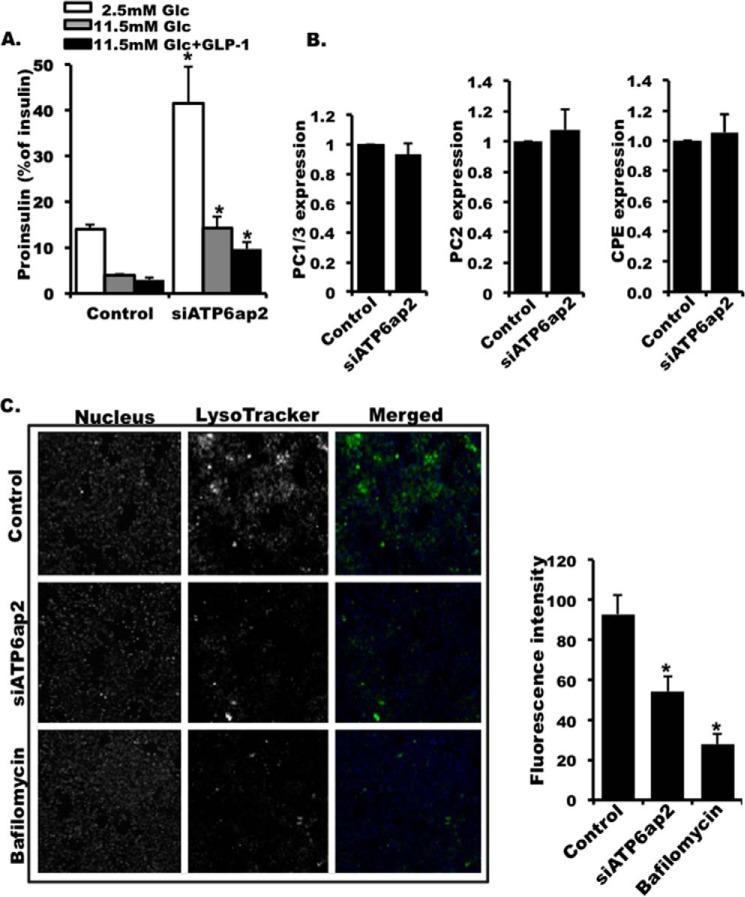
To further explore a processing defect, we detected an increased ratio of proinsulin versus insulin peptide in ATP6ap2 knockdown cells under all conditions including basal glucose, stimulated glucose, and GLP1 stimulation (Fig. 9A). This also suggested a possible impairment of insulin processing in ATP6ap2 knockdown cells. To address this, the expression of the prohormone convertases involved in insulin processing including PC1/3, PC2, and CPE (51–55) were examined. There was no difference in the transcript expression of these three key enzymes (Fig. 9B), suggesting that other factors are contributing to impaired insulin processing. It was reported that acidification within insulin granules was critical for their maturation and priming (56). To examine whether ATP6ap2 is involved in the acidification of the insulin granules, we loaded the cells with acidotropic LysoTracker, a dye that accumulates specifically in acidic organelles. In pancreatic beta cells, the majority of cellular acidic structures are indeed insulin granules; therefore LysoTracker staining can be used to evaluate the acidity of the granule given the fact that insulin granule number did not change in ATP6ap2 knockdown cells compared with the control (Fig. 8B). Consistent with previous studies (57), the cells treated with V-ATPase inhibitor bafilomycin were barely stained with LysoTracker, suggesting that granule acidification was blocked (Fig. 9C). Similarly, LysoTracker staining in ATP6ap2 knockdown cells was shown to be decreased significantly when compared with control cells, suggesting that insulin granule acidification was impaired (Fig. 9C). Taken together, these results suggest that decreased insulin processing and secretion upon ATP6ap2 knockdown could be due to impairment of acidification within individual insulin granules.
FIGURE 9.
Effect of knocking down ATP6ap2 on insulin granule acidification and proinsulin processing. A, ratio of proinsulin versus insulin in cells transfected with siATP6ap2. B, expression of PC1/3, PC2, and CPE in INS-1 cells transfected with siATP6ap2. The expression was presented as ratio over control. C, representative images and quantitative analysis of LysoTracker staining of INS1 cells transfected with scramble siRNA (control), siATP6ap2, and treated with bafilomycin A (10 nm). The values are represented by the averages ± S.E. from triplicates in three independent experiments. *, p < 0.05 (n = 3).
ATP6ap2 Effects on GLP1-stimulated Ca2+ Influx
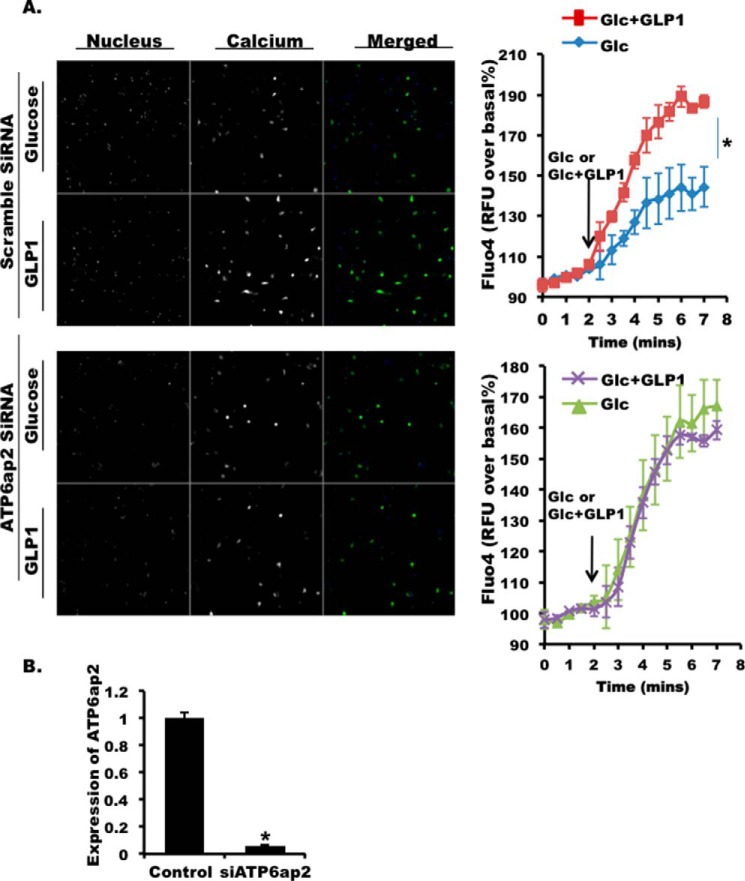
GLP1 R activation increases intracellular Ca2+ mediated by PKA and Epac (cAMP) (26, 58). We observed a robust increase in intracellular Ca2+ in control dispersed mouse islets upon GLP1 stimulation (Fig. 10A, upper two panels). However, when we knock down ATP6ap2 in dispersed islet cells (Fig. 10B), the GLP1-induced increase in Ca2+ was completely diminished, suggesting that ATP6ap2 was required for GLP1-induced Ca2+ influx (Fig. 10A, lower two panels).
FIGURE 10.
Effect of ATP6ap2 knockdown on intracellular Ca2+ in dispersed mouse islets. A, representative images (5 min after GLP1stimulation) and quantitative analysis of Fluo4 in dispersed mouse islets transfected with scramble siRNA (control, upper panels) or siATP6ap2 (lower panels). Nuclear staining in blue and Fluo4 in green for merged images. B, qPCR showing the efficiency of ATP6ap2 knockdown in dispersed mouse islets. The values are represented by the averages ± S.E. from triplicates in three independent experiments. *, p < 0.05 (n = 3).
Discussion
The GLP1R and its associated signaling pathways have gained much attention over the past several years because they are targets for current and future medications to treat type 2 diabetes. In this study, we have used a novel MYTH assay (Fig. 1) to screen mouse and human islet cDNA libraries, enabling us to discover over 50 novel putative interactors of GLP1R. Each of these interactors has the potential to regulate pancreatic beta cell function through GLP1R. The interactor, ATP6ap2, was identified in both mouse and human islet screens and pursued in further studies because of its consistently high expression across beta cell lines and primary islets. Our results showed that ATP6ap2 plays an important dual role; first, it regulates GLP1R signaling through cAMP, and second, it likely facilitates the processing of insulin through granule acidification. We realize that the latter effect appears GLP-1R-independent and may be a more global permissive effect of ATP6ap2 on insulin secretion. Future studies will further delineate the mechanistic link between GLP1R signaling and more general permissive beta cell effects.
In this study, we chose to identify potential interactors of GLP1R from MYTH screens on mouse and human islet cDNA libraries. Previous studies conducted by us have focused on a human fetal brain cDNA library, using a similar approach. However, we reasoned that pancreatic islet tissue is a more appropriate model from which to screen for interactors of GLP1R with the intension of understanding GLP1R signaling in the beta cell specifically. The pancreatic islet consists of a composition of cells including beta, alpha, and delta cells; however, the expression pattern of GLP1R predominantly in beta cells has been widely accepted (19–21), much less in alpha or delta cells (21). However, it is possible that other glucagon receptor subfamily or GPCR interactors that normally are not found in GLP1R-expressing cells may in islet tissue interact with GLP1R, requiring rigorous testing for specificity. Notwithstanding this possibility, the pancreatic islet appears to be a good model tissue in which to study the GLP1R interactome in a beta cell specific setting.
Our study was able to identify a series of novel interactors involved in a variety of intracellular functions (Fig. 2), supporting the dynamic role that GLP1R plays in the regulation of pancreatic beta cell function. Of the common interactors identified from both mouse and human islet screens, the interactor ATP6ap2 was expressed at abundant levels in MIN6, INS-1, and mouse islets. Furthermore, by immunohistochemistry in mouse pancreatic sections, we showed that ATP6ap2 was expressed in endocrine islets but not acinar cells (Fig. 4A). Further analysis on human dispersed islets revealed ATP6ap2 expression in both pancreatic beta and alpha cells (Fig. 4B).
ATP6ap2 is known as an accessory protein of the V-ATPase (59) composed of a transmembrane proton-translocation domain (V0) and extramembrane pump domain (V1 sectors) (60). Although there is no direct evidence demonstrating the effect of ATP6ap2 on insulin secretion in pancreatic beta cells, previous studies have demonstrated that the ATP6V0B subunit of V-ATPase increased 2.38-fold in human diabetic versus normal islets by microarray analysis (61). Also, the islet tropic a3 isoform (membrane-intrinsic subunit) of V-ATPase was reported to regulate insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells (12). We observed reduced expression of ATP6ap2 in human diabetic versus normal islets, and the reduction was not in alpha but beta cells (Fig. 5). The reduced expression of ATP6ap2 was accompanied by an impaired GSIS in the human diabetic islets. In line with these observations, we showed that the down-regulation of ATP6ap2 resulted in decreased GSIS and GLP1-induced insulin secretion, suggesting a regulatory role of ATP6ap2 in insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells. cAMP-PKA is an important pathway for GLP1-induced insulin secretion, and V-ATPase is required for the full activation of PKA in response to glucose stimulation (14). In our studies, cAMP accumulation was significantly decreased at GLP1 concentrations of 0.1 and 10 nm but not at 1 pm, and this effect was not observed in forskolin- or GIP-treated cells (Fig. 7G), suggesting that the cAMP-PKA pathway might be involved in GLP1-induced insulin secretion. The downstream molecules of cAMP are PKA and Epac. Because GLP1R activation increases intracellular Ca2+ via PKA and Epac (26, 58), one would expect ATP6ap2 knockdown could affect Ca2+ influx associated with GLP1. Indeed, we found that the GLP1-induced increase in Ca2+ was abolished in ATP6ap2 knockdown cells, suggesting a requirement of ATP6ap2 for GLP1R Ca2+ signaling. This could also in part explain the decreased insulin secretion in cells with ATP6ap2 knocked down.
ATP6ap2 has been shown to be involved in the maintenance of acidity within secretory vesicles (62). Previously, it was demonstrated that whole body knock-out of ATP6ap2 was lethal in mice (63); whereas, tissue specific knock-out studies of ATP6ap2 in cardiomyocytes or in podocytes resulted in detrimental defects after birth including heart failure or renal failure, respectively (64, 65). These studies confirmed the requirement of ATP6ap2 association with V-ATPase, as well as the functional role of ATP6ap2 in maintaining the acidity of microenvironments within intracellular vesicles. Previous studies have shown the involvement of acidic secretory vesicles in insulin processing and maturation (66). Specifically, proprotein convertases 3 (PC1/3) and 2 (PC2) responsible for insulin processing from proinsulin are strictly pH-dependent (51, 67). In line with this, the gene expression of insulin-processing enzymes PC1/3, PC2, and CPE were not changed in ATP6ap2 knockdown cells. However, granule acidification was impaired, causing increased pH, which might inhibit the activity of the insulin-processing enzymes. Furthermore, an increased proinsulin versus insulin ratio was detected, suggesting impairment in insulin processing and maturation within secretory vesicles from ATP6ap2 knockdown cells. To support this, we observed reduced expression of ATP6ap2 in islets from type 2 diabetic donors, whose GSIS was largely decreased. Our data provided a link between ATP6ap2 and diabetes where loss of ATP6ap2 impaired insulin processing via increasing granule pH.
In summary, our study provided a novel insight into GLP1R signaling and was the first to identify GLP1R interactors in pancreatic islets. Our data also suggested that these interacting proteins of GLP1R could be involved in the regulation of insulin secretion and GLP1R signaling in pancreatic beta cells. Because GLP1R has been used as potent drug target in the treatment of diabetes, our findings could contribute to the development of novel effective therapeutic strategies for this disease.
Author Contributions
F. F. D. designed experiments and analyzed the data, coordinated the study, and wrote the paper. A. B., Y. L., B. B., X. W., and M. Z. contributed to the acquisition of data, analysis, and interpretation of data. X. H., L. L., D. Z., and H. G. provided technical assistance with specific studies and contributed to the preparation of relevant figures. M. B. W. designed the overall study. All authors reviewed the results and approved the final version of the manuscript submitted.
Acknowledgments
We thank both the Alberta Islet Distribution Program and the Alberta Diabetes Institute IsletCore at the University of Alberta (with the assistance of the Human Organ Procurement and Exchange Program and the Trillium Gift of Life Network in the procurement of donor pancreata for research) for generously providing human islets.
This work was supported by a grant from a Novo Nordisk Innovation Award and Canadian Institutes of Health Research MOP-102588 (to M. B. W.), Banting and Best Diabetes Center (BBDC) postdoctoral fellowships (to Y. L. and M. Z.), a BBDC graduate student award (to X. H.), and a BBDC summer student award (to X. W.). The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
- GLP1
- glucagon-like peptide 1
- GLP1R
- GLP1 receptor
- ATP6ap2
- ATPase H+-transporting lysosomal accessory protein 2
- MYTH
- membrane-based split ubiquitin yeast two-hybrid
- GPCR
- G protein-coupled receptor
- qPCR
- quantitative real time PCR
- TF
- transcription factor
- GSIS
- glucose-stimulated insulin secretion.
References
- 1. Drucker D. J., Nauck M. A. (2006) The incretin system: glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes. Lancet 368, 1696–1705 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Edwards C. M., Todd J. F., Mahmoudi M., Wang Z., Wang R. M., Ghatei M. A., Bloom S. R. (1999) Glucagon-like peptide 1 has a physiological role in the control of postprandial glucose in humans: studies with the antagonist exendin 9–39. Diabetes 48, 86–93 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Kreymann B., Williams G., Ghatei M. A., Bloom S. R. (1987) Glucagon-like peptide-1 7–36: a physiological incretin in man. Lancet 2, 1300–1304 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Salehi M., Vahl T. P., D'Alessio D. A. (2008) Regulation of islet hormone release and gastric emptying by endogenous glucagon-like peptide 1 after glucose ingestion. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 93, 4909–4916 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Woerle H. J., Carneiro L., Derani A., Göke B., Schirra J. (2012) The role of endogenous incretin secretion as amplifier of glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in healthy subjects and patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 61, 2349–2358 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Boutant M., Ramos O. H., Tourrel-Cuzin C., Movassat J., Ilias A., Vallois D., Planchais J., Pégorier J. P., Schuit F., Petit P. X., Bossard P., Maedler K., Grapin-Botton A., Vasseur-Cognet M. (2012) COUP-TFII controls mouse pancreatic β-cell mass through GLP-1-β-catenin signaling pathways. PLoS One 7, e30847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Heller C., Kühn M. C., Mülders-Opgenoorth B., Schott M., Willenberg H. S., Scherbaum W. A., Schinner S. (2011) Exendin-4 upregulates the expression of Wnt-4, a novel regulator of pancreatic β-cell proliferation. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 301, E864–E872 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Liu Z., Habener J. F. (2008) Glucagon-like peptide-1 activation of TCF7L2-dependent Wnt signaling enhances pancreatic β cell proliferation. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 8723–8735 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Ye Y., Keyes K. T., Zhang C., Perez-Polo J. R., Lin Y., Birnbaum Y. (2010) The myocardial infarct size-limiting effect of sitagliptin is PKA-dependent, whereas the protective effect of pioglitazone is partially dependent on PKA. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 298, H1454–H1465 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Sokos G. G., Nikolaidis L. A., Mankad S., Elahi D., Shannon R. P. (2006) Glucagon-like peptide-1 infusion improves left ventricular ejection fraction and functional status in patients with chronic heart failure. J. Card. Fail. 12, 694–699 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Krisai P., Aeschbacher S., Schoen T., Bossard M., van der Stouwe J. G., Dörig L., Todd J., Estis J., Risch M., Risch L., Conen D. (2015) Glucagon-like peptide-1 and blood pressure in young and healthy adults from the general population. Hypertension 65, 306–312 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Hirata K., Kume S., Araki S., Sakaguchi M., Chin-Kanasaki M., Isshiki K., Sugimoto T., Nishiyama A., Koya D., Haneda M., Kashiwagi A., Uzu T. (2009) Exendin-4 has an anti-hypertensive effect in salt-sensitive mice model. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 380, 44–49 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. von Scholten B. J., Lajer M., Goetze J. P., Persson F., Rossing P. (2015) Time course and mechanisms of the anti-hypertensive and renal effects of liraglutide treatment. Diabet. Med. 32, 343–352 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Yu M., Moreno C., Hoagland K. M., Dahly A., Ditter K., Mistry M., Roman R. J. (2003) Antihypertensive effect of glucagon-like peptide 1 in Dahl salt-sensitive rats. J. Hypertens. 21, 1125–1135 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. During M. J., Cao L., Zuzga D. S., Francis J. S., Fitzsimons H. L., Jiao X., Bland R. J., Klugmann M., Banks W. A., Drucker D. J., Haile C. N. (2003) Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor is involved in learning and neuroprotection. Nat. Med. 9, 1173–1179 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Hamilton A., Patterson S., Porter D., Gault V. A., Holscher C. (2011) Novel GLP-1 mimetics developed to treat type 2 diabetes promote progenitor cell proliferation in the brain. J. Neurosci. Res. 89, 481–489 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Hunter K., Hölscher C. (2012) Drugs developed to treat diabetes, liraglutide and lixisenatide, cross the blood brain barrier and enhance neurogenesis. BMC Neurosci. 13, 33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Dillon J. S., Tanizawa Y., Wheeler M. B., Leng X. H., Ligon B. B., Rabin D. U., Yoo-Warren H., Permutt M. A., Boyd A. E., 3rd (1993) Cloning and functional expression of the human glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor. Endocrinology 133, 1907–1910 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Jun L. S., Showalter A. D., Ali N., Dai F., Ma W., Coskun T., Ficorilli J. V., Wheeler M. B., Michael M. D., Sloop K. W. (2014) A novel humanized GLP-1 receptor model enables both affinity purification and Cre-LoxP deletion of the receptor. PLoS. One 9, e93746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Pyke C., Heller R. S., Kirk R. K., Ørskov C., Reedtz-Runge S., Kaastrup P., Hvelplund A., Bardram L., Calatayud D., Knudsen L. B. (2014) GLP-1 receptor localization in monkey and human tissue: novel distribution revealed with extensively validated monoclonal antibody. Endocrinology 155, 1280–1290 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Richards P., Parker H. E., Adriaenssens A. E., Hodgson J. M., Cork S. C., Trapp S., Gribble F. M., Reimann F. (2014) Identification and characterization of GLP-1 receptor-expressing cells using a new transgenic mouse model. Diabetes 63, 1224–1233 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Gromada J., Holst J. J., Rorsman P. (1998) Cellular regulation of islet hormone secretion by the incretin hormone glucagon-like peptide 1. Pflugers Arch. 435, 583–594 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Wheeler M. B., Lu M., Dillon J. S., Leng X .H., Chen C., Boyd A. E., III (1993) Functional expression of the rat glucagon-like peptide-I receptor, evidence for coupling to both adenylyl cyclase and phospholipase-C. Endocrinology 133, 57–62 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Seino S., Shibasaki T. (2005) PKA-dependent and PKA-independent pathways for cAMP-regulated exocytosis. Physiol. Rev. 85, 1303–1342 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Gromada J., Bokvist K., Ding W. G., Holst J. J., Nielsen J. H., Rorsman P. (1998) Glucagon-like peptide 1 (7–36) amide stimulates exocytosis in human pancreatic β-cells by both proximal and distal regulatory steps in stimulus-secretion coupling. Diabetes 47, 57–65 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Kang G., Chepurny O. G., Holz G. G. (2001) cAMP-regulated guanine nucleotide exchange factor II (Epac2) mediates Ca2+-induced Ca2+ release in INS-1 pancreatic β-cells. J. Physiol. 536, 375–385 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Buteau J., Foisy S., Rhodes C. J., Carpenter L., Biden T. J., Prentki M. (2001) Protein kinase Czeta activation mediates glucagon-like peptide-1-induced pancreatic β-cell proliferation. Diabetes 50, 2237–2243 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Buteau J., Foisy S., Joly E., Prentki M. (2003) Glucagon-like peptide 1 induces pancreatic β-cell proliferation via transactivation of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Diabetes 52, 124–132 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Bockaert J., Fagni L., Dumuis A., Marin P. (2004) GPCR interacting proteins (GIP). Pharmacol. Ther. 103, 203–221 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Schwenk J., Metz M., Zolles G., Turecek R., Fritzius T., Bildl W., Tarusawa E., Kulik A., Unger A., Ivankova K., Seddik R., Tiao J. Y., Rajalu M., Trojanova J., Rohde V., Gassmann M., Schulte U., Fakler B., Bettler B. (2010) Native GABAB receptors are heteromultimers with a family of auxiliary subunits. Nature 465, 231–235 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Sonoda N., Imamura T., Yoshizaki T., Babendure J. L., Lu J. C., Olefsky J. M. (2008) β-Arrestin-1 mediates glucagon-like peptide-1 signaling to insulin secretion in cultured pancreatic β cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 105, 6614–6619 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Syme C. A., Zhang L., Bisello A. (2006) Caveolin-1 regulates cellular trafficking and function of the glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor. Mol. Endocrinol. 20, 3400–3411 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Talbot J., Joly E., Prentki M., Buteau J. (2012) β-Arrestin1-mediated recruitment of c-Src underlies the proliferative action of glucagon-like peptide-1 in pancreatic β INS832/13 cells. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 364, 65–70 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Huang X., Dai F. F., Gaisano G., Giglou K., Han J., Zhang M., Kittanakom S., Wong V., Wei L., Showalter A. D., Sloop K. W., Stagljar I., Wheeler M. B. (2013) The identification of novel proteins that interact with the GLP-1 receptor and restrain its activity. Mol. Endocrinol. 27, 1550–1563 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Joseph J. W., Koshkin V., Saleh M. C., Sivitz W. I., Zhang C. Y., Lowell B. B., Chan C. B., Wheeler M. B. (2004) Free fatty acid-induced β-cell defects are dependent on uncoupling protein 2 expression. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 51049–51056 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Liu Y., Batchuluun B., Ho L., Zhu D., Prentice K. J., Bhattacharjee A., Zhang M., Pourasgari F., Hardy A. B., Taylor K. M., Gaisano H., Dai F. F., Wheeler M. B. (2015) Characterization of zinc influx transporters (ZIPs) in pancreatic β cells: roles in regulating cytosolic zinc homeostasis and insulin secretion. J. Biol. Chem. 290, 18757–18769 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Wolff N. A., Ghio A. J., Garrick L. M., Garrick M. D., Zhao L., Fenton R. A., Thévenod F. (2014) Evidence for mitochondrial localization of divalent metal transporter 1 (DMT1). FASEB J. 28, 2134–2145 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Dünnwald M., Varshavsky A., Johnsson N. (1999) Detection of transient in vivo interactions between substrate and transporter during protein translocation into the endoplasmic reticulum. Mol. Biol. Cell 10, 329–344 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Johnsson N., Varshavsky A. (1994) Ubiquitin-assisted dissection of protein transport across membranes. EMBO J. 13, 2686–2698 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Stagljar I., Korostensky C., Johnsson N., te Heesen S. (1998) A genetic system based on split-ubiquitin for the analysis of interactions between membrane proteins in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 95, 5187–5192 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Wittke S., Lewke N., Müller S., Johnsson N. (1999) Probing the molecular environment of membrane proteins in vivo. Mol. Biol. Cell 10, 2519–2530 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Dai F. F., Zhang Y., Kang Y., Wang Q., Gaisano H. Y., Braunewell K. H., Chan C. B., Wheeler M. B. (2006) The neuronal Ca2+ sensor protein visinin-like protein-1 is expressed in pancreatic islets and regulates insulin secretion. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 21942–21953 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Zhang M., Robitaille M., Showalter A. D., Huang X., Liu Y., Bhattacharjee A., Willard F. S., Han J., Froese S., Wei L., Gaisano H. Y., Angers S., Sloop K. W., Dai F. F., Wheeler M. B. (2014) Progesterone receptor membrane component 1 is a functional part of the glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor complex in pancreatic β cells. Mol. Cell Proteomics 13, 3049–3062 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Wijesekara N., Dai F. F., Hardy A. B., Giglou P. R., Bhattacharjee A., Koshkin V., Chimienti F., Gaisano H. Y., Rutter G. A., Wheeler M. B. (2010) β Cell-specific Znt8 deletion in mice causes marked defects in insulin processing, crystallisation and secretion. Diabetologia 53, 1656–1668 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Lu H., Koshkin V., Allister E. M., Gyulkhandanyan A. V., Wheeler M. B. (2010) Molecular and metabolic evidence for mitochondrial defects associated with β-cell dysfunction in a mouse model of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 59, 448–459 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Wu C., Orozco C., Boyer J., Leglise M., Goodale J., Batalov S., Hodge C. L., Haase J., Janes J., Huss J. W., 3rd, Su A. I. (2009) BioGPS: an extensible and customizable portal for querying and organizing gene annotation resources. Genome Biol. 10, R130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Wu C., Macleod I., Su A. I. (2013) BioGPS and MyGene.info: organizing online, gene-centric information. Nucleic Acids Res. 41, D561–D565 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Jansen E. J., Martens G. J. (2012) Novel insights into V-ATPase functioning: distinct roles for its accessory subunits ATP6AP1/Ac45 and ATP6AP2/(pro) renin receptor. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 13, 124–133 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Forgac M. (2007) Vacuolar ATPases: rotary proton pumps in physiology and pathophysiology. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 8, 917–929 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Marshansky V., Futai M. (2008) The V-type H+-ATPase in vesicular trafficking: targeting, regulation and function. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 20, 415–426 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Smeekens S. P., Montag A. G., Thomas G., Albiges-Rizo C., Carroll R., Benig M., Phillips L. A., Martin S., Ohagi S., Gardner P.,. (1992) Proinsulin processing by the subtilisin-related proprotein convertases furin, PC2, and PC3. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89, 8822–8826 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Muller L., Lindberg I. (1999) The cell biology of the prohormone convertases PC1 and PC2. Prog. Nucleic Acids Res. Mol. Biol. 63, 69–108 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Naggert J. K., Fricker L. D., Varlamov O., Nishina P. M., Rouille Y., Steiner D. F., Carroll R. J., Paigen B. J., Leiter E. H. (1995) Hyperproinsulinaemia in obese fat/fat mice associated with a carboxypeptidase E mutation which reduces enzyme activity. Nat. Genet. 10, 135–142 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Seidah N. G., Mowla S. J., Hamelin J., Mamarbachi A. M., Benjannet S., Touré B. B., Basak A., Munzer J. S., Marcinkiewicz J., Zhong M., Barale J. C., Lazure C., Murphy R. A., Chrétien M., Marcinkiewicz M. (1999) Mammalian subtilisin/kexin isozyme SKI-1: A widely expressed proprotein convertase with a unique cleavage specificity and cellular localization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 96, 1321–1326 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Zhu X., Orci L., Carroll R., Norrbom C., Ravazzola M., Steiner D. F. (2002) Severe block in processing of proinsulin to insulin accompanied by elevation of des-64,65 proinsulin intermediates in islets of mice lacking prohormone convertase 1/3. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99, 10299–10304 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Rorsman P., Eliasson L., Renström E., Gromada J., Barg S., Göpel S. (2000) The cell physiology of biphasic insulin secretion. News Physiol. Sci. 15, 72–77 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. Sun-Wada G. H., Toyomura T., Murata Y., Yamamoto A., Futai M., Wada Y. (2006) The a3 isoform of V-ATPase regulates insulin secretion from pancreatic β-cells. J. Cell Sci. 119, 4531–4540 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58. Tsuboi T., da, Silva X., Holz G. G., Jouaville L. S., Thomas A. P., Rutter G. A. (2003) Glucagon-like peptide-1 mobilizes intracellular Ca2+ and stimulates mitochondrial ATP synthesis in pancreatic MIN6 β-cells. Biochem. J. 369, 287–299 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59. Ludwig J., Kerscher S., Brandt U., Pfeiffer K., Getlawi F., Apps D. K., Schägger H. (1998) Identification and characterization of a novel 9.2-kDa membrane sector-associated protein of vacuolar proton-ATPase from chromaffin granules. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 10939–10947 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60. Cruciat C. M., Ohkawara B., Acebron S. P., Karaulanov E., Reinhard C., Ingelfinger D., Boutros M., Niehrs C. (2010) Requirement of prorenin receptor and vacuolar H+-ATPase-mediated acidification for Wnt signaling. Science 327, 459–463 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61. Gunton J. E., Kulkarni R. N., Yim S., Okada T., Hawthorne W. J., Tseng Y. H., Roberson R. S., Ricordi C., O'Connell P. J., Gonzalez F. J., Kahn C. R. (2005) Loss of ARNT/HIF1β mediates altered gene expression and pancreatic-islet dysfunction in human type 2 diabetes. Cell 122, 337–349 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62. Riediger F., Quack I., Qadri F., Hartleben B., Park J. K., Potthoff S. A., Sohn D., Sihn G., Rousselle A., Fokuhl V., Maschke U., Purfürst B., Schneider W., Rump L. C., Luft F. C., Dechend R., Bader M., Huber T. B., Nguyen G., Muller D. N. (2011) Prorenin receptor is essential for podocyte autophagy and survival. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 12, 2193–2202 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63. Sihn G., Rousselle A., Vilianovitch L., Burckle C., Bader M. (2010) Physiology of the (pro)renin receptor: Wnt of change? Kidney Int. 78, 246–256 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64. Kinouchi K., Ichihara A., Sano M., Sun-Wada G. H., Wada Y., Kurauchi-Mito A., Bokuda K., Narita T., Oshima Y., Sakoda M., Tamai Y., Sato H., Fukuda K., Itoh H. (2010) The (pro)renin receptor/ATP6AP2 is essential for vacuolar H+-ATPase assembly in murine cardiomyocytes. Circ. Res. 107, 30–34 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65. Oshima Y., Kinouchi K., Ichihara A., Sakoda M., Kurauchi-Mito A., Bokuda K., Narita T., Kurosawa H., Sun-Wada G. H., Wada Y., Yamada T., Takemoto M., Saleem M. A., Quaggin S. E., Itoh H. (2011) Prorenin receptor is essential for normal podocyte structure and function. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 22, 2203–2212 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66. Davidson H., Rhodes C. J., Hutton J. C. (1988) Intraorganellar calcium and pH control proinsulin cleavage in the pancreatic β-cell via two distinct site-specific endopeptidases. Nature 333, 93–96 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67. Orci L., Halban P., Perrelet A., Amherdt M., Ravazzola M., Anderson R. G. (1994) pH-independent and -dependent cleavage of proinsulin in the same secretory vesicle. J. Cell Biol. 126, 1149–1156 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]