Abstract
Objective
Surgery is the only potentially curable treatment for colorectal cancer (CRC), but it is hampered by high mortality. Human serum albumin (HSA) below 35 g/L is associated with poor overall prognosis in patients with CRC, but evidence regarding the impact on postoperative mortality is sparse.
Methods
We performed a population-based cohort study including patients undergoing CRC surgery in North and Central Denmark (1997–2011). We categorised patients according to HSA concentration measured 1–30 days prior to surgery date. We used the Kaplan-Meier method to compute 30-day mortality and Cox regression model to compute HRs as measures of the relative risk of death, controlling for potential confounders. We further stratified patients by preoperative conditions, including cancer stage, comorbidity level, and C reactive protein concentration.
Results
Of the 9339 patients undergoing first-time CRC surgery with preoperative HSA measurement, 26.4% (n=2464) had HSA below 35 g/L. 30-day mortality increased from 4.9% among patients with HSA 36–40 g/L to 26.9% among patients with HSA equal to or below 25 g/L, compared with 2.0% among patients with HSA above 40 g/L. The corresponding adjusted HRs increased from 1.75 (95% CI 1.25 to 2.45) among patients with HSA 36–40 g/L to 7.59 (95% CI 4.95 to 11.64) among patients with HSA equal to or below 25 g/L, compared with patients with HSA above 40 g/L. The negative impact associated with a decrement of HSA was found in all subgroups.
Conclusions
A decrement in preoperative HSA concentration was associated with substantial concentration-dependent increased 30-day mortality following CRC surgery.
Keywords: COLORECTAL CANCER, COLORECTAL SURGERY, EPIDEMIOLOGY
Summary box.
What is already known about this subject?
-
▸
Colorectal cancer (CRC) surgery is hampered by a 30-day mortality of approximately 5%.
-
▸
Hypoalbuminaemia (<35 g/L) in patients undergoing CRC surgery varies from 10% to 57%.
-
▸
Human serum albumin (HSA) below 35 g/L is associated with overall poor survival in patients with CRC, but the impact on short-term survival after CRC surgery is unknown.
What are the new findings?
-
▸
Decrement of preoperative HSA was associated with a concentration-dependent increased risk of 30-day mortality following CRC surgery.
-
▸
Thirty-day crude mortality following CRC surgery increased from 2.0% among patients with HSA above 40 g/L to 26.9% among patients with HSA equal to or below 25 g/L.
-
▸
Compared with patients with HSA above 40 g/L, the 30-day mortality HR increased from 1.75 (95% CI 1.25 to 2.45) among patients with HSA 36–40 g/L to 7.59 (95% CI 4.95 to 11.64) among patients with HSA equal to or below 25 g/L.
-
▸
The negative prognostic impact associated with decrement of HSA persisted independently from other preoperative conditions, including presence of systemic inflammation.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
-
▸
The study highlights the importance of optimise preoperative serum albumin concentration in patients undergoing CRC surgery and aids to evaluate patient's postoperative mortality risk.
Introduction
Surgery is the only potentially curable treatment for colorectal cancer (CRC), but it is hampered by an overall 30-day mortality of approximately 5%.1 2 Advanced cancer stage, presence of comorbidity, and old age at time of CRC surgery are conditions known to impair postoperative mortality.1 3 A common feature associated with these conditions is a decrease in human serum albumin (HSA) concentration.4 5 HSA is the main determinant of plasma oncotic pressure and is a multifunctional protein with a wide range of properties including antioxidant, immunomodulatory, and detoxification functions.6 A previous study showed that a decrease in HSA concentrations from greater than 46 g/L to less than 21 g/L was associated with an increase in 30-day mortality from 1% to 29% among American veterans undergoing major non-cardiac surgery.7 Although it is estimated that hypoalbuminaemia is present in 10–57% of patients undergoing CRC surgery,8–18 the prognostic impact of HSA among these patients has been sparsely examined.8–12 Particularly, no studies have examined the concentration-dependent association between HSA concentrations and mortality among patients with CRC, the prognostic impact among subgroups of patients with CRC, or have been able to properly control for potential confounding.8–12 Moreover, decrement of HSA is often associated with systemic inflammation4 and patients with CRC with hypoalbuminaemia (<35 g/L) and C reactive protein (CRP) concentration above 10 mg/L are at high risk of mortality.19 However, it is not clear if prognostic impact of HSA is independent from the degree of inflammation. Understanding the prognostic impact of HSA will aid with appropriate risk stratification, allocation of patients to intensive perioperative and postoperative care, and better knowledge to inform patients about postoperative risks. We therefore examined, in a population-based setting, the impact of preoperative HSA on 30-day mortality following CRC surgery overall and among patients with different preoperative conditions and CRP levels.
Materials and methods
Setting
We conducted this cohort study using prospectively collected data from medical registries in North and Central Denmark (with approximately 2.15 million inhabitants) from 1 January 1997 to 31 December 2011. Since 1968, a unique civil personal registration (CPR) number has been assigned to every Danish resident at birth or on immigration and allows accurate record linkage at the individual level among all Danish registries.20
Patients with CRC
Our study cohort included patients undergoing first-time CRC surgery in North and Central Denmark during the period 1997–2011. Patients with CRC were identified using the Danish Cancer Registry (DCR), which contains data on date of diagnosis, stage, and other information of incident cases of malignant neoplasms in Denmark since 1943.21 Tumours registered after 1 January 1978 have been reclassified according to the International Classification of Diseases (ICD), 10th revision (ICD-10). To obtain information on surgery, we linked these patients with CRC to the Danish National Patient Registry (DNPR). The DNPR records information from all hospitalisations since 1977 and from outpatient contacts since 1995.22 Each record includes the dates of hospital admission and discharge, up to 20 discharge diagnoses recorded according to the ICD-8 until 1993 and according to the ICD-10 thereafter, type of admission (non-elective or elective), and type and date of surgical procedures. Since 1996, surgical procedures have been coded according to the Nordic Medico-Statistical Committee (NOMESCO) Classification of Surgical Procedures.23 First-time CRC surgery was defined as the first procedure involving colorectal surgery performed during a hospitalisation where CRC was listed as a diagnosis in the DNPR. CRC surgery was categorised according to the intention of eradicating the primary tumour as radical resection and non-eradicative procedures.24 Radical resection included surgeries such as partial and total resections of the colon and/or rectum while non-eradicative procedures included colostomy, stent placement, or excision of a very small part of the colon. Radical resection was further divided into laparoscopic and open surgery. CRC stage was reported as localised (Dukes’ stage A or B), regionally spread (Dukes’ stage C), and metastasised. Surgeries were also categorised as elective and non-elective according to the type of admission.25 We restricted the study population to patients living in the study region at the time of the CRC surgery using data from the Civil Registration System (CRS). This system is updated on a daily basis and tracks the vital status, marital status, and residence of all Danish residents.26 The study population was further restricted to patients undergoing CRC surgery in North Jutland after 1 January 1997, in Aarhus after 1 January 2000, in Viborg after 1 January 2005, and in Ringkjøbing after 1 January 2006, reflecting the availability of laboratory data (see online supplementary table S1).27 The laboratory database contains laboratory tests from inpatient stays, outpatient clinic visits, and visits to general practitioners.27 The National Health Service provides tax-funded medical care covering surgery for all Danish residents and all types of CRC surgery that were provided in the study region during the period investigated.
Preoperative albumin serum concentration
For each patient undergoing CRC surgery, we searched the laboratory database for preoperative measurements of HSA (rounded to the nearest integer). Only measurements 1–30 days prior to surgery date were used. In the event of several preoperative HSA measurements within the same individual, we used the most recent one for analysis. Normal HSA interval was defined as 36–45 g/L for persons aged 40–70 years and 34–45 g/L for those older than 70 years. We categorised HSA levels as follows: ≤25 g/L (severe hypoalbuminaemia), >25 g/L and ≤30 g/L (moderate hypoalbuminaemia), >30 g/L and ≤35 g/L (mild hypoalbuminaemia), >35 g/L and ≤40 g/L (low normal albuminaemia), and >40 g/L (high normal albuminaemia).
Covariates
We quantified patients’ burden of comorbidity using the Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI) that includes 19 diseases, each assigned a score between one and six.28 Using diagnoses registered in the DNPR, we identified the diseases in the CCI at any time prior to or during the CRC surgery admission,29 excluding CRC and CRC metastases. We classified patients as having low (score=0), moderate (score=1–2), or high comorbidity level (score ≥3). We also identified patients with alcohol-related disease defined as alcohol abuse or alcohol-related diseases disregarding alcoholic liver disease.30 Information about marital status was obtained using the CRS.31
Using the laboratory database, we also collected data on other preoperative blood tests from 1 to 30 days prior to surgery including haemoglobin, sodium, potassium, leucocytes, creatinine, CRP, platelets, international normalised ratio (INR), bilirubin, and alanine aminotransferase. Finally, we computed the preoperative Model for End-stage Liver Disease (MELD) scores using values of creatinine, total bilirubin and INR.32 33
Diagnostic and surgical codes are provided in online supplementary appendix.
Thirty-day mortality
We followed patients from date of CRC surgery until death, day 30 postoperatively, or end of study, whichever came first. Information about date of death was obtained from the CRS.
Statistical analysis
We used the Kaplan-Meier method to compute 30-day postoperative mortality of patients with CRC in each HSA category.34 To quantify the excess mortality associated with the decrement of HSA, we computed absolute mortality difference with 95% CIs between patients with HSA above 40 g/L and patients with HSA equal to or below 25 g/L.35 We used Cox regression analysis to compute HRs with 95% CIs as a measure of the relative risk of postoperative mortality using patients with preoperative HSA above 40 g/L as reference and controlling for potential confounding factors.
We stratified patients by elective versus non-elective hospital admissions, age category (0–59, 60–69, 70–79, and 80+ years), gender, cancer site (colon or rectum), cancer stage, type of surgery, comorbidity level, marital status, MELD score (<10 and ≥10), year of surgery (1997–2005, 2006–2011), and by preoperative concentration of CRP (≤10, >10 and ≤20, >20 and ≤50, and >50 mg/L). The regression analysis using categorisation of HSA assumes that the impact of HSA on mortality is equal within the same HSA category and that it is discontinuous as interval boundaries are crossed.36 In order to bridge such limitation, we used fractional polynomial Cox regression analysis to graphically describe adjusted HRs for 30-day mortality associated with preoperative HSA (as continuous variable) overall and stratified by CRP levels, assuming HRs equal to 1 for HSA equal to 40 g/L.37
Finally, we conducted a sensitivity analysis where missing data for type of admission, CRC stage (ie,stage unknown), preoperative HSA, and other laboratory measurements were imputed deterministically with 20 cycles of regression switching assuming data were ‘missing at random’.38 Adjusted HRs and 95% CIs for 30-day mortality for each HSA category compared with HSA above 40 g/L were assessed using the imputed data sets.
Analyses were performed using STATA V.12.0 (StataCorp LP, College Station, Texas, USA). The study was approved by the Danish Data Protection Agency (record number 2009-41-3866). Data obtained from Danish registries are generally available to researchers and their use does not require informed consent.
Results
Descriptive data
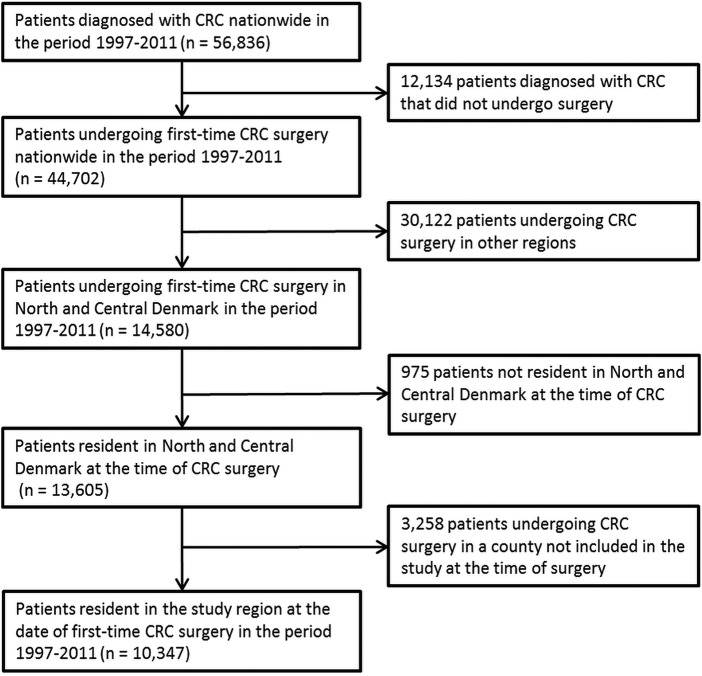
We identified 10 347 patients (median age 71, IQR 62–78) undergoing first-time CRC surgery during the study period (table 1 and figure 1).
Table 1.
Characteristics of patients undergoing surgery for colorectal cancer
| Serum albumin concentration |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hypoalbuminaemia |
Normal albuminaemia |
|||||
| Severe | Moderate | Mild | Low | High | Missing albumin | |
| ≤25 g/L n=401 |
26–30 g/L n=784 |
31–35 g/L n=1742 |
36–40 g/L n=3065 |
>40 g/L n=3347 |
n=1008 | |
| Gender (%) | ||||||
| Male | 143 (35.7) | 371 (47.3) | 844 (48.5) | 1660 (54.2) | 1910 (57.1) | 514 (51.0) |
| Female | 258 (64.3) | 413 (52.7) | 898 (51.6) | 1405 (45.8) | 1437 (42.9) | 494 (49.0) |
| Median age (IQR) | 76 (68–82) | 76 (68–82) | 75 (65–81) | 71 (63–78) | 67 (59–74) | 71 (61–79) |
| Age, years, (%) | ||||||
| <60 | 48 (12.0) | 64 (8.2) | 234 (13.4) | 549 (17.9) | 857 (25.6) | 210 (20.8) |
| 60–69 | 60 (15.0) | 170 (21.7) | 380 (21.8) | 824 (26.9) | 1122 (33.5) | 237 (23.5) |
| 70–79 | 154 (38.4) | 280 (35.7) | 605 (34.7) | 1064 (34.7) | 990 (29.6) | 317 (31.5) |
| ≥80 | 139 (34.7) | 270 (34.4) | 523 (30.0) | 628 (20.5) | 378 (11.3) | 244 (24.1) |
| Type of admission (%) | ||||||
| Elective | 122 (30.4) | 348 (44.4) | 1128 (64.8) | 2544 (83.1) | 3118 (93.2) | 534 (53.5) |
| Non-elective | 279 (69.6) | 435 (55.6) | 612 (35.2) | 516 (16.9) | 227 (6.8) | 465 (46.2) |
| Missing | 0 | 1 (0.1) | 2 (0.1) | 5 (0.16) | 2 (0.1) | 9 (0.9) |
| Cancer site (%) | ||||||
| Colon | 302 (75.3) | 599 (76.4) | 1212 (69.6) | 1856 (60.6) | 1689 (50.5) | 779 (77.3) |
| Rectum | 99 (24.7) | 185 (23.6) | 530 (30.4) | 1209 (39.5) | 1658 (49.5) | 229 (22.7) |
| Cancer stage (%) | ||||||
| Localised | 124 (30.9) | 251 (32.0) | 671 (38.5) | 1287 (42.0) | 1517 (45.3) | 385 (38.2) |
| Regional | 98 (24.4) | 205 (26.2) | 460 (26.4) | 841 (27.4) | 1051 (31.4) | 299 (29.7) |
| Metastasised | 119 (29.7) | 215 (27.4) | 365 (21.0) | 527 (17.2) | 340 (10.2) | 206 (20.4) |
| Unknown | 60 (15.0) | 113 (14.4) | 246 (14.1) | 410 (13.4) | 439 (13.1) | 118 (11.7) |
| Type of surgery (%) | ||||||
| Open radical resection | 266 (66.3) | 579 (73.9) | 1369 (78.6) | 2470 (80.6) | 2546 (76.1) | 721 (71.5) |
| Laparoscopic radical resection | 4 (1.0) | 7 (0.9) | 65 (3.7) | 271 (8.8) | 541 (16.2) | 121 (12.0) |
| Non-eradicative procedures | 131 (32.7) | 198 (25.3) | 308 (17.7) | 324 (10.6) | 260 (7.8) | 166 (16.5) |
| Comorbidity (%) | ||||||
| Low | 205 (51.1) | 375 (47.8) | 928 (53.3) | 1752 (57.2) | 2153 (64.3) | 651 (64.6) |
| Moderate | 134 (33.4) | 279 (35.6) | 585 (33.6) | 969 (31.6) | 916 (27.4) | 271 (26.9) |
| High | 62 (15.5) | 130 (16.6) | 229 (13.2) | 344 (11.2) | 278 (8.3) | 86 (8.5) |
| Alcohol-related disease (%) | ||||||
| No | 386 (96.3) | 764 (97.5) | 1707 (98.0) | 3017 (98.4) | 3290 (98.3) | 988 (98.0) |
| Yes | 15 (3.7) | 20 (2.6) | 35 (2.0) | 48 (1.6) | 57 (1.7) | 20 (2.0) |
| Marital status (%) | ||||||
| Married | 172 (42.9) | 359 (45.8) | 855 (49.1) | 1731 (56.5) | 2139 (63.9) | 516 (51.2) |
| Never married | 40 (10.0) | 55 (7.0) | 137 (7.9) | 218 (7.1) | 214 (6.4) | 82 (8.1) |
| Other | 189 (47.1) | 370 (47.2) | 750 (43.1) | 1116 (36.4) | 994 (29.7) | 410 (40.7) |
Figure 1.
Flow chart showing the selection of patients with colorectal cancer (CRC).
Of those, 9339 (90.3%) had at least one measurement of HSA in the 30 days before surgery and 8381 (81.0%) in the week before surgery. HSA below 35 g/L was present in 26.4% (n=2464) of patients with preoperative HSA measurement. Patients with HSA equal to or below 40 g/L were more likely to be old, female, and to have comorbid conditions including alcohol-related disease as compared with those with HSA above 40 g/L (table 1). Moreover, compared with patients with HSA above 40 g/L, patients with lower HSA were more likely to have metastasised cancer and primary localisation in the colon. The prevalence of non-elective admission increased with the decrease of HSA. The distribution of individual diseases included in the CCI for each HSA category is reported in online supplementary table S2. Information on other preoperative blood tests and MELD score for each HSA category is reported in table 2. Preoperative CRP was available for 66.1% (n=6841) of patients and it was markedly increased among patients with low HSA (table 2). Information about patients with missing preoperative HSA (n=1008) is reported in tables 1 and 2, and online supplementary table S3.
Table 2.
Preoperative blood measurements in patients undergoing surgery for colorectal cancer
| Serum albumin concentration |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hypoalbuminaemia |
Normal albuminaemia |
|||||
| Severe | Moderate | Mild | Low | High | Missing albumin | |
| ≤25 g/L n=401 |
26–30 g/L n=784 |
31–35 g/L n=1742 |
36–40 g/L n=3065 |
>40 g/L n=3347 |
n=1008 | |
| Albumin, g/L | ||||||
| Mean (SD) | 22.0 (3.0) | 28.4 (1.4) | 33.3 (1.4) | 38.1 (1.4) | 43.4 (2.1) | – |
| Median (IQR) | 23 (21–24) | 29 (27–30) | 34 (32–35) | 38 (37–39) | 43 (42–45) | – |
| Haemoglobin, mmol/L | ||||||
| Median (IQR) | 6.6 (6.1–7.6) | 6.9 (6.3–7.6) | 7.3 (6.5–8) | 7.9 (7.1–8.7) | 8.5 (7.8–9.1) | 8.0 (7.1–8.8) |
| Missing, n (%) | 0 | 2 (0.3) | 3 (0.2) | 10 (0.3) | 8 (0.2) | 553 (54.9) |
| Sodium, mmol/L | ||||||
| Median (IQR) | 137 (134–139) | 137 (135–140) | 139 (137–141) | 140 (138–142) | 140 (139–142) | 140 (137–141) |
| Missing, n (%) | 0 | 2 (0.3) | 2 (0.1) | 3 (0.1) | 2 (0.1) | 572 (56.8) |
| Potassium, mmol/L | ||||||
| Median (IQR) | 3.8 (3.4–4.2) | 3.9 (3.5–4.3) | 4 (3.7–4.3) | 4.1 (3.8–4.3) | 4.1 (3.8–4.3) | 4 (3.7–4.3) |
| Missing, n (%) | 0 | 3 (0.4) | 2 (0.1) | 3 (0.1) | 1 (<0.1) | 569 (56.5) |
| Leucocytes, 109/L | ||||||
| Median (IQR) | 11.2 (8.5–15.1) | 10.0 (7.8–13.2) | 8.8 (6.9–11.2) | 8.0 (6.5–9.9) | 7.4 (6.1–9.0) | 9.1 (6.9–11.8) |
| Missing, n (%) | 28 (7.0) | 82 (10.5) | 359 (20.6) | 846 (27.6) | 945 (28.2) | 752 (74.6) |
| Creatinine, µmol/L | ||||||
| Median (IQR) | 68 (55–85) | 74 (61–93) | 78 (66–93) | 79 (68–95) | 77 (67–90) | 78 (67–91) |
| Missing, n (%) | 0 | 1 (0.1) | 0 | 5 (0.2) | 1 (<0.1) | 556 (55.2) |
| C reactive protein, mg/L | ||||||
| Median (IQR) | 85 (41–146) | 51 (24–102) | 26 (10–62) | 10 (10–26) | 10 (8–10) | 19 (10–55) |
| Missing, n (%) | 40 (10.0) | 121 (15.4) | 460 (26.4) | 1019 (33.3) | 1054 (31.5) | 812 (80.6) |
| Platelet, 109/L | ||||||
| Median (IQR) | 411 (309–537) | 392 (300–514) | 353 (278–455) | 316 (250–398) | 290 (242–353) | 324 (253–417) |
| Missing, n (%) | 80 (20.0) | 197 (25.1) | 537 (30.8) | 1027 (33.5) | 1065 (31.8) | 818 (81.2) |
| INR | ||||||
| Median (IQR) | 1.2 (1.1–1.3) | 1.1 (1.0–1.2) | 1.0 (1.0–1.1) | 1.0 (1.0–1.1) | 1.0 (0.9–1.1) | 1.1 (1.0–1.2) |
| Missing, n (%) | 121 (30.2) | 276 (35.2) | 682 (39.2) | 1162 (37.9) | 1123 (33.6) | 845 (83.8) |
| Bilirubin, µmol/L | ||||||
| Median (IQR) | 9 (6–13) | 8 (6–13) | 8 (5–11) | 8 (6–11) | 8 (6–11) | 10 (7–12) |
| Missing, n (%) | 72 (18.0) | 214 (27.3) | 625 (35.9) | 1130 (36.9) | 1036 (31.0) | 821 (81.5) |
| ALAT, U/L | ||||||
| Median (IQR) | 17 (11–28) | 17 (12–28) | 17 (12–25) | 17 (13–25) | 20 (15–27) | 18 (13–28) |
| Missing, n (%) | 135 (33.7) | 324 (41.33) | 812 (46.6) | 1410 (46.0) | 1204 (36.0) | 815 (80.9) |
| MELD | ||||||
| <10, n (%) | 177 (44.1) | 331 (42.2) | 720 (41.3) | 1308 (42.7) | 1742 (52.1) | 100 (9.9) |
| ≥10, n (%) | 76 (19.0) | 97 (12.4) | 120 (6.9) | 200 (6.5) | 127 (3.8) | 20 (2.0) |
| Missing, n (%) | 148 (36.9) | 356 (45.4) | 902 (51.8) | 1557 (50.8) | 1478 (44.16) | 888 (88.1) |
ALAT, alanine aminotransferase; INR, international normalised ratio; MELD, Model for End-Stage Liver Disease.
Postoperative mortality
Overall 30-day mortality increased from 2.0% in patients with HSA above 40 g/L to 26.9% in patients with HSA equal to or below 25 g/L (table 3 and figure 2), corresponding to an absolute mortality difference of 25.0% (95% CI 20.6% to 29.3%).
Table 3.
Thirty-day mortality and corresponding HRs in patients with different preoperative serum albumin concentration undergoing surgery because of colorectal cancer, overall and stratified by type of admission, cancer type, and period of surgery
| HR (95% CI) |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of patients N |
Number of deaths N |
30-Day mortality %* (95% CI) |
Crude | Adjusted† | |
| Colorectal cancer surgery, albumin g/L | |||||
| ≤25 | 401 | 108 | 26.9 (22.9 to 31.6) | 15.89 (11.69 to 21.59) | 7.59 (4.95 to 11.64) |
| 26–30 | 784 | 154 | 19.6 (17.0 to 22.6) | 10.91 (8.18 to 14.56) | 5.19 (3.53 to 7.63) |
| 31–35 | 1742 | 163 | 9.4 (8.1 to 10.8) | 4.92 (3.70 to 6.56) | 2.58 (1.80 to 3.69) |
| 36–40 | 3065 | 149 | 4.9 (4.2 to 5.7) | 2.50 (1.87 to 3.34) | 1.75 (1.25 to 2.45) |
| >40 | 3347 | 66 | 2.0 (1.6 to 2.5) | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Elective admission‡, albumin g/L | |||||
| ≤25 | 122 | 30 | 24.6 (17.9 to 33.2) | 15.32 (9.84 to 23.83) | 8.08 (4.45 to 14.67) |
| 26–30 | 348 | 62 | 17.8 (14.2 to 22.3) | 10.57 (7.38 to 15.15) | 5.31 (3.27 to 8.62) |
| 31–35 | 1128 | 90 | 8.0 (6.5 to 9.7) | 4.50 (3.23 to 6.26) | 2.56 (1.68 to 3.90) |
| 36–40 | 2544 | 99 | 3.9 (3.2 to 4.7) | 2.15 (1.55 to 2.98) | 1.52 (1.04 to 2.21) |
| >40 | 3118 | 57 | 1.8 (1.4 to 2.4) | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Non-elective admission‡, albumin g/L | |||||
| ≤25 | 279 | 78 | 28.0 (23.1 to 33.6) | 8.19 (4.11 to 16.33) | 7.78 (3.17 to 19.12) |
| 26–30 | 435 | 92 | 21.2 (17.6 to 25.3) | 5.83 (2.94 to 11.57) | 5.36 (2.23 to 12.88) |
| 31–35 | 612 | 73 | 11.9 (9.6 to 14.8) | 3.14 (1.57 to 6.28) | 2.68 (1.12 to 6.44) |
| 36–40 | 516 | 50 | 9.7 (7.4 to 12.6) | 2.51 (1.23 to 5.10) | 2.32 (0.97 to 5.55) |
| >40 | 227 | 9 | 4.0 (2.1 to 7.5) | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Age 0–59 years, albumin g/L | |||||
| ≤25 | 48 | 6 | 12.5 (5.8 to 25.7) | 23.03 (7.03 to 75.46) | 7.39 (1.32 to 41.22) |
| 26–30 | 64 | 9 | 14.1 (7.6 to 25.3) | 25.55 (8.56 to 76.24) | 11.84 (2.65 to 52.97) |
| 31–35 | 234 | 9 | 3.9 (2.0 to 7.3) | 6.68 (2.24 to 19.94) | 2.18 (0.51 to 9.35) |
| 36–40 | 549 | 10 | 1.8 (1.0 to 3.4) | 3.15 (1.08 to 9.20) | 2.29 (0.69 to 7.61) |
| >40 | 857 | 5 | 0.6 (0.2 to 1.4) | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Age 60–69 years, albumin g/L | |||||
| ≤25 | 60 | 9 | 15.0 (8.1 to 26.8) | 15.11 (6.37 to 35.87) | 6.63 (2.13 to 20.61) |
| 26–30 | 170 | 26 | 15.3 (10.7 to 21.6) | 15.39 (7.77 to 30.50) | 4.75 (1.77 to 12.76) |
| 31–35 | 380 | 21 | 5.5 (3.6 to 8.4) | 5.26 (2.59 to 10.69) | 2.55 (1.03 to 6.31) |
| 36–40 | 824 | 17 | 2.1 (1.3 to 3.3) | 1.94 (0.92 to 4.05) | 1.34 (0.57 to 3.15) |
| >40 | 1122 | 12 | 1.1 (0.6 to 1.9) | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Age 70–79 years, albumin g/L | |||||
| ≤25 | 154 | 43 | 27.9 (21.5 to 35.7) | 11.89 (7.35 to 19.24) | 8.76 (4.40 to 17.44) |
| 26–30 | 280 | 54 | 19.3 (15.1 to 24.4) | 7.71 (4.86 to 12.24) | 5.23 (2.79 to 9.77) |
| 31–35 | 605 | 46 | 7.6 (5.8 to 10.0) | 2.87 (1.78 to 4.61) | 2.12 (1.19 to 3.80) |
| 36–40 | 1064 | 49 | 4.6 (3.5 to 6.1) | 1.70 (1.06 to 2.72) | 1.41 (0.83 to 2.40) |
| >40 | 990 | 27 | 2.7 (1.9 to 4.0) | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Age 80+ years, albumin g/L | |||||
| ≤25 | 139 | 50 | 36.0 (28.6 to 44.5) | 7.54 (4.56 to 12.45) | 7.09 (3.50 to 14.36) |
| 26–30 | 270 | 65 | 24.1 (19.4 to 29.6) | 4.57 (2.82 to 7.40) | 4.57 (2.40 to 8.68) |
| 31–35 | 523 | 87 | 16.6 (13.7 to 20.1) | 3.03 (1.90 to 4.83) | 2.66 (1.46 to 4.85) |
| 36–40 | 628 | 73 | 11.6 (9.4 to 14.4) | 2.05 (1.28 to 3.31) | 2.17 (1.22 to 3.86) |
| >40 | 378 | 22 | 5.8 (3.9 to 8.7) | 1.00 | 1.00 |
Age and admission type were largely responsible for the change in estimates by adjustment.
*Calculated using the Kaplan-Meier method.
†Mutually adjusted for gender, age (both as a continuous and a categorical variable), type of admission, operation year (calendar year), county, cancer site, cancer stage (excluded patients with stage ‘unknown’), comorbidity level, alcohol-related disease, liver disease, marital status, haemoglobin, sodium, potassium and creatinine (number of observations with complete data=8033).
‡Information on type of admission is missing for some patients. Therefore, the sum of patients with non-elective and elective admissions is not equal to the number of all patients included in the study.
Figure 2.
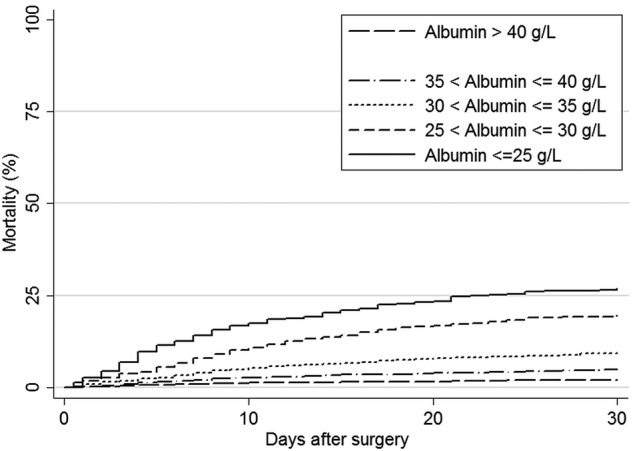
Crude 30-day mortality curves for patients undergoing surgery for colorectal cancer according to preoperative serum albumin concentration.
The adjusted HRs increased from 1.75 (95% CI 1.25 to 2.45) among patients with HSA 35–40 g/L to 7.59 (95% CI 4.95 to 11.64) among patients with HSA equal to or below 25 g/L, compared with patients with HSA above 40 g/L. As expected, in each HSA category 30-day mortality was higher among patients admitted non-electively than among patients with an elective admission. Similarly, elderly patients had higher postoperative mortality than younger patients (table 3). However, adjusted HRs showed that a decrease in HSA was associated with a gradually increased risk of mortality regardless of types of admission or age group (table 3).
Table 4 shows 30-day mortality and corresponding adjusted HRs for subgroups of patients undergoing CRC surgery.
Table 4.
Thirty-day mortality and corresponding adjusted HRs with 95% CIs in subgroups of patients with different preoperative serum albumin concentrations undergoing surgery because of colorectal cancer
| Serum albumin concentration |
||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≤25 g/L |
26–30 g/L |
31–35 g/L |
36–40 g/L |
>40 g/L |
||||||
| 30-Day mortality* % (n) |
Adjusted HR† (95% CI) |
30-DAy mortality* % (n) |
Adjusted HR† (95% CI) |
30-Day mortality* % (n) |
Adjusted HR† (95% CI) |
30-Day mortality* % (n) |
Adjusted HR† (95% CI) |
30-Day mortality* % (n) |
Ref. group |
|
| Gender | ||||||||||
| Male | 30.1 (43) | 8.23 (4.49 to 15.09) | 24.5 (91) | 5.79 (3.45 to 9.71) | 10.3 (87) | 2.68 (1.65 to 4.35) | 5.2 (86) | 1.73 (1.11 to 2.71) | 1.9 (37) | 1.00 |
| Female | 25.2 (65) | 6.79 (3.65 to 12.63) | 15.3 (63) | 4.28 (2.39 to 7.65) | 8.5 (76) | 2.29 (1.39 to 3.92) | 4.5 (63) | 1.64 (0.99 to 2.72) | 2.0 (29) | 1.00 |
| Cancer site | ||||||||||
| Colon | 29.8 (90) | 6.68 (4.01 to 11.14) | 18.4 (110) | 3.96 (2.47 to 6.34) | 9.2 (112) | 2.05 (1.32 to 3.20) | 5.2 (96) | 1.43 (0.94 to 2.19) | 2.4 (41) | 1.00 |
| Rectum | 18.2 (18) | 8.90 (3.77 to 21.05) | 23.8 (44) | 10.76 (5.40 to 21.44) | 9.6 (51) | 3.83 (2.06 to 7.12) | 4.4 (53) | 2.52 (1.44 to 4.41) | 1.5 (25) | 1.00 |
| Cancer stage | ||||||||||
| Localised | 17.7 (22) | 4.22 (2.14 to 8.36) | 16.7 (42) | 4.02 (2.25 to 7.19) | 7.2 (48) | 2.08 (1.24 to 3.46) | 4.8 (62) | 1.74 (1.10 to 2.73) | 2.1 (32) | 1.00 |
| Regional | 25.5 (25) | 11.01 (4.44 to 27.33) | 15.1 (31) | 5.88 (2.65 to 13.07) | 7.8 (36) | 3.90 (1.88 to 8.11) | 3.7 (31) | 2.11 (1.05 to 4.25) | 1.2 (13) | 1.00 |
| Metastasised | 38.7 (46) | 10.61 (4.72 to 23.88) | 27.9 (60) | 6.58 (3.05 to 14.18) | 11.8 (43) | 2.64 (1.25 to 5.58) | 5.7 (30) | 1.53 (0.74 to 3.19) | 2.9 (10) | 1.00 |
| Year of surgery | ||||||||||
| 1997–2005 | 29.8 (78) | 4.40 (2.52 to 7.67) | 20.4 (95) | 3.03 (1.82 to 5.05) | 8.2 (82) | 1.39 (0.85 to 2.28) | 4.5 (68) | 1.05 (0.66 to 1.68) | 3.1 (28) | 1.00 |
| 2006–2011 | 21.6 (30) | 10.11 (5.17 to 19.79) | 18.5 (59) | 8.49 (4.84 to 14.92) | 11.0 (81) | 4.90 (2.94 to 8.15) | 5.2 (81) | 2.81 (1.76 to 4.49) | 1.6 (38) | 1.00 |
| Type of surgery | ||||||||||
| Open radical resection | 24.8 (66) | 5.32 (3.26 to 8.68) | 16.2 (94) | 3.43 (2.21 to 5.30) | 8.6 (118) | 2.03 (1.37 to 3.01) | 4.9 (120) | 1.52 (1.06 to 2.18) | 2.2 (57) | 1.00 |
| Laparoscopic radical resection | 0 | –- | 14.3 (1) | – | 7.7 (5) | 9.13 (1.32 to 63.34) | 3.3 (9) | 3.19 (0.74 to 13.78) | 0.7 (4) | 1,00 |
| Non-eradicative resection | 32.1 (42) | 44.40 (9.48 to 207.97) | 29.8 (59) | 30.81 (6.91 to 41.59) | 13.0 (40) | 9.35 (2.10 to 41.59) | 6.2 (20) | 4.43 (0.98 to 20.05) | 1.9 (5) | 1,00 |
| Comorbidity | ||||||||||
| Low | 23.7 (49) | 7.87 (4.05 to 15.26) | 15.9 (60) | 5.39 (2.96 to 9.82) | 6.6 (61) | 1.91 (1.08 to 3.37) | 2.8 (49) | 1.22 (0.72 to 2.06) | 1.3 (28) | 1.00 |
| Moderate | 29.9 (40) | 9.36 (4.65 to 18.83) | 23.0 (64) | 6.68 (3.59 to 12.45) | 10.9 (64) | 3.31 (1.86 to 5.86) | 6.6 (64) | 2.10 (1.24 to 3.58) | 2.9 (27) | 1.00 |
| High | 31.7 (19) | 6.91 (2.45 to 19.53) | 23.3 (30) | 4.77 (1.91 to 11.94) | 17.0 (38) | 3.55 (1.51 to 8.34) | 10.7 (36) | 2.84 (1.25 to 6.43) | 4.1 (11) | 1.00 |
| Marital status | ||||||||||
| Married | 27.3 (47) | 11.09 (5.95 to 20.66) | 20.1 (72) | 6.70 (3.83 to 11.74) | 8.3 (71) | 3.52 (2.11 to 5.89) | 3.7 (64) | 1.72 (1.06 to 2.79) | 1.5 (31) | 1.00 |
| Never married | 25.0 (10) | 10.50 (1.72 to 64.07) | 27.3 (15) | 5.58 (1.05 to 29.76) | 8.0 (11) | 1.26 (0.27 to 5.87) | 6.0 (13) | 2.29 (0.59 to 8.79) | 2.3 (5) | 1.00 |
| Other | 27.0 (51) | 5.75 (3.03 to 10.92) | 18.1 (67) | 4.15 (2.32 to 7.41) | 10.8 (81) | 2.23 (1.30 to 3.81) | 6.5 (72) | 1.76 (1.06 to 2.91) | 3.0 (30) | 1.00 |
| Creactive protein‡, mg/L | ||||||||||
| ≤10.0 | 14.3 (2) | 5.33 (1.06 to 26.83) | 9.5 (7) | 1.81 (0.57 to 5.76) | 6.2 (20) | 1.88 (0.88 to 4.00) | 4.1 (41) | 1.48 (0.82 to 2.67) | 1.6 (29) | 1.00 |
| 10.1–20.0 | 13.8 (4) | 4.31 (0.87 to 21.32) | 9.7 (7) | 1.91 (0.53 to 6.85) | 12.2 (27) | 3.09 (1.21 to 7.86) | 6.7 (27) | 1.93 (0.83 to 4.50) | 3.6 (11) | 1.00 |
| 20.1–50.0 | 23.6 (17) | 7.47 (2.22 to 25.08) | 21.0 (38) | 7.26 (2.40 to 22.00) | 9.6 (33) | 3.38 (1.18 to 9.70) | 5.6 (22) | 1.88 (0.67 to 5.31) | 2.7 (5) | 1.00 |
| >50.0 | 29.3 (72) | 4.19 (0.97 to 18.12) | 26.5 (89) | 3.63 (0.86 to 15.35) | 13.4 (53) | 1.36 (0.32 to 5.85) | 10.6 (26) | 1.44 (0.33 to 6.25) | 8.1 (3) | 1.00 |
| MELD§ | ||||||||||
| <10 | 23.2 (41) | 7.06 (3.61 to 13.80) | 18.1 (60) | 5.20 (2.87 to 9.42) | 9.2 (66) | 2.74 (1.60 to 4.71) | 4.5 (59) | 1.63 (0.99 to 2.69) | 1.9 (33) | 1.00 |
| ≥10 | 43.4 (33) | 9.22 (3.27 to 25.97) | 43.4 (42) | 8.62 (3.17 to 23.42) | 19.2 (23) | 2.75 (1.03 to 7.32) | 15.5 (31) | 2.36 (0.94 to 5.92) | 6.3 (8) | 1.00 |
*Calculated using the Kaplan-Meier method.
†Mutually adjusted for gender, age (both as a continuous and a categorical variable), type of admission, operation year (calendar year), county, cancer site, cancer stage (excluded patients with stage ‘unknown’), comorbidity level, alcohol-related disease, liver disease, marital status, haemoglobin, sodium, potassium and creatinine (number of observations with complete data=8033).
‡Patients with preoperative C reactive protein measurement=6841.
§Patients with preoperative MELD=5018.
MELD, Model for End-stage Liver Disease; Ref., reference.
For all subgroups, postoperative mortality was lowest among patients with HSA above 40 g/L and gradually increased with decreasing HSA levels. Notably, 30-day mortality was affected even by changes within what is clinically considered the normal HSA range (35–40 g/L as compared with >40 g/L) (tables 3 and 4). Adjusted HRs similarly showed a markedly high mortality associated with a decrease in HSA in most of the subgroups, especially among patients with HSA below 35 g/L. However, 95% CIs reflected imprecise estimates.
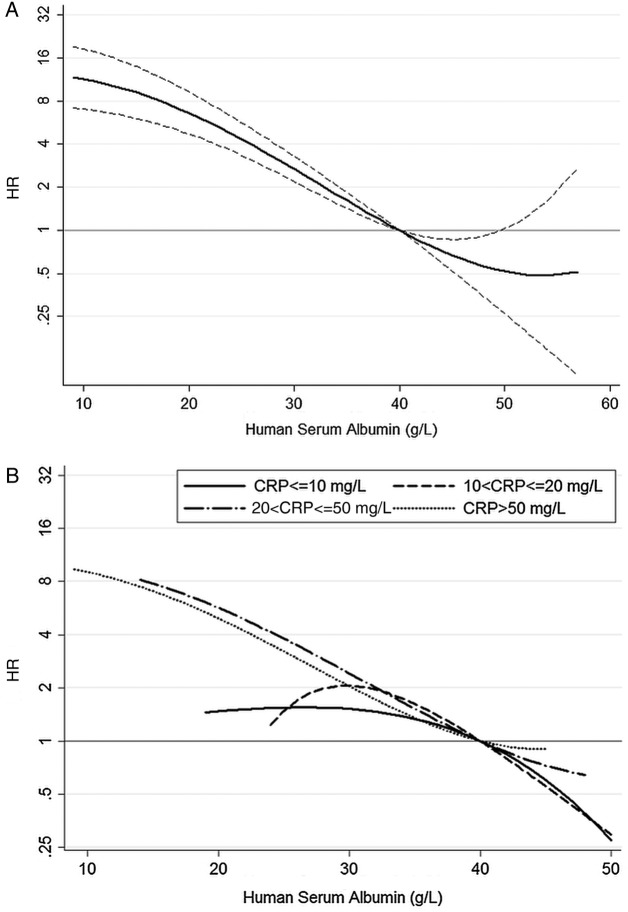
The strong relation between 30-day mortality and preoperative HSA was confirmed from the fractional polynomial analysis (figure 3).
Figure 3.
Adjusted HRs for 30-day mortality, overall (A) and stratified by C reactive protein (CRP) levels (B), associated with preoperative human serum albumin concentration. Adjusted HRs in (A) are provided with 95% CI (dash lines).
Sensitivity analysis
The analysis using data with imputation of missing information on preoperative HSA and other variables revealed results similar to those reported above: the adjusted 30-day HRs were 7.50 (95% CI 5.10 to 11.03) for HSA below 25 g/L, 4.99 (95% CI 3.51 to 7.10) for HSA 26–30 g/L, 2.76 (95% CI 2.00 to 3.79) for HSA 31–35 g/L, and 1.78 (95% CI 1.32 to 2.40) for HSA 36–40 g/L, compared with HSA above 40 g/L.
Discussion
In this cohort study conducted within a population-based hospital setting, we found that 30-day mortality after CRC surgery was inversely associated with preoperative HSA concentration. Even within HSA levels that are clinically considered normal, we found that a decrease in HSA is associated with increased mortality. Moreover, the prognostic impact of decrement of HSA was independent of other preoperative conditions and of different CRP levels.
Our study extends current knowledge by examining the impact of preoperative HSA concentration on 30-day mortality following CRC surgery overall and in subgroups of patients within a population-based setting. Previous studies investigating short-term prognosis in patients undergoing CRC surgery reported increased risk of postoperative complications among patients with HSA below 35 g/L.8–12 14 15 39 40 Lai et al8 found a twofold increased 30-day mortality comparing patients with HSA below 35 g/L to those with HSA above 35 g/L. Our findings showed that the impact of HSA on 30-day mortality had a concentration–response pattern that was not limited to the cut-off of 35 g/L. Moreover, our results showed that the prognostic impact of HSA persisted even in subgroups of patients with different preoperative conditions that are reported to be associated with a decrement of HSA.
Decrement in HSA may have a direct impact on prognosis affecting organ vascularisation, hamper distribution of antibiotics, perpetuate inflammation, and promote intravascular coagulation. Indeed, during the past decade a better understanding of HSA structure and function has led to the concept that HSA has multifunctional properties ranging from provision of oncotic pressure, immune regulation, and endothelial stabilisation to being a molecule that works in the intracellular compartment modifying several key pathophysiological mechanisms.41 A criticism that is often raised regarding causality between decreased HSA concentration and prognosis is that clinical trials provided contradictory results about prognosis following HSA administration, especially among critically ill patients.42–46 However, HSA replacement has been shown beneficial in specific clinical conditions such as spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, patients with ascites receiving paracentesis, hepatic encephalopathy, and hepatorenal syndrome.41 47 Moreover, previous studies showing no benefit from HSA administration were performed in acute patients when their conditions were already worsened and this may have prevented the effect of HSA on prognosis. Finally, the quality of administrated HSA should also be questioned based on previous studies investigating HSA in commercial solutions that reported high prevalence of oxidised forms 48 and in vitro immunosuppressive activity.49
The main strengths of our study include its large size, its population-based design with uniform access to healthcare in Denmark, comprehensive laboratory data, accurate history of preadmission comorbidity,29 and complete follow-up data. However, additional issues should be considered when interpreting our results. Exclusion of patients with CRC with missing data from the main analysis may have introduced selection bias.50 However, the sensitivity analysis using imputed data provided estimates that were similar to those obtained from the complete case analysis. Therefore, it seems unlikely that missing data could have biased our findings. Unmeasured or only partially measured conditions (eg, malnutrition, infection, alcohol consumption, and smoking) known to affect HSA concentration may increase the risk of postoperative mortality also through a non-HSA-related pathway and therefore might have biased our estimates. However, the strength of association and the concentration–response pattern of HRs are unlikely explained only by residual or unmeasured confounding. Finally, we do not have information on cause of death and this prevents us from investigating possible differences in the specific complication leading to death among patients with different preoperative HSA concentrations.
In conclusion, our results showed that a decrement of preoperative HSA was associated with a concentration-dependent increased risk of mortality in the 30 days following CRC surgery even within concentration levels clinically considered normal. Furthermore, we showed that other preoperative conditions and patient characteristics including presence of systemic inflammation did not markedly affect the prognostic impact of HSA on postoperative mortality.
Supplementary Material
Footnotes
Contributors: JM contributed in the study concept and design, statistical analysis, data interpretation, and manuscript preparation. SA contributed in the statistical analysis supervision and manuscript reviewing. RE, TN and HTS contributed in the study concept and design, critical analysis of the data, manuscript reviewing, and study supervision. All the authors approved the final draft submitted for publication.
Funding: The study was supported by a grant from the Danish Cancer Society (R73-A4284-13-S17) and from Aarhus University Research Foundation. JM has received a scholarship from Aarhus University.
Competing interests: None declared.
Ethics approval: The study was approved by the Danish Data Protection Agency (record number 2009-41-3866).
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Data sharing statement: No additional data are available.
References
- 1.Panis Y, Maggiori L, Caranhac G, et al. . Mortality after colorectal cancer surgery: a French survey of more than 84,000 patients. Ann Surg 2011;254:738–43. doi:10.1097/SLA.0b013e31823604ac [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Danish Colorectal Cancer Group. The Danish Colorectal Cancer Group, yearly report 2012 [Landsdækkende database for kræft i tyk- og endetarmen. Årsrapport 2012]. [Report in Danish].
- 3.Morris EJ, Taylor EF, Thomas JD, et al. . Thirty-day postoperative mortality after colorectal cancer surgery in England. Gut 2011;60:806–13. doi:10.1136/gut.2010.232181 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Franch-Arcas G. The meaning of hypoalbuminaemia in clinical practice. Clin Nutr 2001;20:265–9. doi:10.1054/clnu.2001.0438 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Numeroso F, Barilli AL, Delsignore R. Prevalence and significance of hypoalbuminemia in an internal medicine department. Eur J Intern Med 2008;19:587–91. doi:10.1016/j.ejim.2007.04.029 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Fanali G, di Masi A, Trezza V, et al. . Human serum albumin: from bench to bedside. Mol Aspects Med 2012;33:209–90. doi:10.1016/j.mam.2011.12.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Gibbs J, Cull W, Henderson W, et al. . Preoperative serum albumin level as a predictor of operative mortality and morbidity: results from the National VA Surgical Risk Study. Arch Surg 1999;134:36–42. doi:10.1001/archsurg.134.1.36 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Lai CC, You JF, Yeh CY, et al. . Low preoperative serum albumin in colon cancer: a risk factor for poor outcome. Int J Colorectal Dis 2011;26:473–81. doi:10.1007/s00384-010-1113-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Hickman DM, Miller RA, Rombeau JL, et al. . Serum albumin and body weight as predictors of postoperative course in colorectal cancer. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr 1980;4:314–16. doi:10.1177/0148607180004003314 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Özoğul YB, Ulas¸ M, Özer İ, et al. . Short-term outcomes after surgery for colorectal cancer in Turkish patients aged 70 and above. Turk J Gastroenterol 2010;21:257–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Chandrasinghe PC, Ediriweera DS, Kumarage SK, et al. . Pre-operative hypoalbuminaemia predicts poor overall survival in rectal cancer: a retrospective cohort analysis. BMC Clin Pathol 2013;13:12 doi:10.1186/1472-6890-13-12 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ionescu D, Tibrea C, Puia C. Pre-operative hypoalbuminemia in colorectal cancer patients undergoing elective surgery—a major risk factor for postoperative outcome. Chirurgia (Bucur) 2013;108:822–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Sun LC, Chu KS, Cheng SC, et al. . Preoperative serum carcinoembryonic antigen, albumin and age are supplementary to UICC staging systems in predicting survival for colorectal cancer patients undergoing surgical treatment. BMC Cancer 2009;9:288 doi:10.1186/1471-2407-9-288 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Lohsiriwat V, Lohsiriwat D, Boonnuch W, et al. . Pre-operative hypoalbuminemia is a major risk factor for postoperative complications following rectal cancer surgery. World J Gastroenterol 2008;14:1248–51. doi:10.3748/wjg.14.1248 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Ishizuka M, Nagata H, Takagi K, et al. . Inflammation-based prognostic score is a novel predictor of postoperative outcome in patients with colorectal cancer. Ann Surg 2007;246:1047–51. doi:10.1097/SLA.0b013e3181454171 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Cengiz O, Kocer B, Surmeli S, et al. . Are pretreatment serum albumin and cholesterol levels prognostic tools in patients with colorectal carcinoma? Med Sci Monit 2006;12:CR240–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Guthrie GJ, Roxburgh CS, Richards CH, et al. . Circulating IL-6 concentrations link tumour necrosis and systemic and local inflammatory responses in patients undergoing resection for colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer 2013;109:131–7. doi:10.1038/bjc.2013.291 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Crozier JE, McKee RF, McArdle CS, et al. . Preoperative but not postoperative systemic inflammatory response correlates with survival in colorectal cancer. Br J Surg 2007;94:1028–32. doi:10.1002/bjs.5706 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.McMillan DC. The systemic inflammation-based Glasgow Prognostic Score: a decade of experience in patients with cancer. Cancer Treat Rev 2013;39:534–40. doi:10.1016/j.ctrv.2012.08.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Schmidt M, Pedersen L, Sorensen HT. The Danish Civil Registration System as a tool in epidemiology. Eur J Epidemiol 2014;29:541–9. doi:10.1007/s10654-014-9930-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Gjerstorff ML. The Danish Cancer Registry. Scand J Public Health 2011;39:42–5. doi:10.1177/1403494810393562 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Lynge E, Sandegaard JL, Reboli M. The Danish National Patient Register. Scand J Public Health 2011;39:30–3. doi:10.1177/1403494811401482 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Smedby B, Schiøler G. Health classifications in the Nordic countries. Historic development in a national and international perspective 2006. Copenhagen, Denmark: Nordic Medico-Statistical Committee, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Montomoli J, Erichsen R, Christiansen CF, et al. . Liver disease and 30-day mortality after colorectal cancer surgery: a Danish population-based cohort study. BMC Gastroenterol 2013;13:66 doi:10.1186/1471-230X-13-66 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Masoomi H, Kang CY, Chen A, et al. . Predictive factors of in-hospital mortality in colon and rectal surgery. J Am Coll Surg 2012;215:255–61. doi:10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2012.04.019 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Pedersen CB, Gotzsche H, Moller JO, et al. . The Danish Civil Registration System. A cohort of eight million persons. Dan Med Bull 2006;53:441–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Grann AF, Erichsen R, Nielsen AG, et al. . Existing data sources for clinical epidemiology: The clinical laboratory information system (LABKA) research database at Aarhus University, Denmark. Clin Epidemiology 2011;3:133–8. doi:10.2147/CLEP.S17901 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Charlson ME, Pompei P, Ales KL, et al. . A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: development and validation. J Chronic Dis 1987;40:373–83. doi:10.1016/0021-9681(87)90171-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Thygesen SK, Christiansen CF, Christensen S, et al. . The predictive value of ICD-10 diagnostic coding used to assess Charlson Comorbidity Index conditions in the population-based Danish National Registry of Patients. BMC Med Res Methodol 2011;11:83 doi:10.1186/1471-2288-11-83 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Sorensen LT, Jorgensen T, Kirkeby LT, et al. . Smoking and alcohol abuse are major risk factors for anastomotic leakage in colorectal surgery. Br J Surg 1999;86:927–31. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2168.1999.01165.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Aizer AA, Chen MH, McCarthy EP, et al. . Marital status and survival in patients with cancer. J Clin Oncol 2013;31:3869–76. doi:10.1200/JCO.2013.49.6489 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Hedrick TL, Swenson BR, Friel CM. Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) in predicting postoperative mortality of patients undergoing colorectal surgery. Am Surg 2013;79:347–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Northup PG, Wanamaker RC, Lee VD, et al. . Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) predicts nontransplant surgical mortality in patients with cirrhosis. Ann Surg 2005;242:244–51. doi:10.1097/01.sla.0000171327.29262.e0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Seagroatt V, Goldacre M. Measures of early postoperative mortality: beyond hospital fatality rates. BMJ 1994;309:361–5. doi:10.1136/bmj.309.6951.361 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Kirkwood BR, Sterne JAC. Comparing two proportions. In: Kirkwood BR, Sterne JAC, eds. Essential medical statistics. Oxford: Blackwell Science, 2003:148–64. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Bennette C, Vickers A. Against quantiles: categorization of continuous variables in epidemiologic research, and its discontents. BMC Med Res Methodol 2012;12:21 doi:10.1186/1471-2288-12-21 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Royston P, Ambler G, Sauerbrei W. The use of fractional polynomials to model continuous risk variables in epidemiology. Int J Epidemiol 1999;28:964–74. doi:10.1093/ije/28.5.964 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.White IR, Royston P, Wood AM. Multiple imputation using chained equations: issues and guidance for practice. Stat Med 2011;30: 377–99. doi:10.1002/sim.4067 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Lohsiriwat V, Chinswangwatanakul V, Lohsiriwat S, et al. . Hypoalbuminemia is a predictor of delayed postoperative bowel function and poor surgical outcomes in right-sided colon cancer patients. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr 2007;16:213–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Gohil R, Rishi M, Tan BH. Pre-operative serum albumin and neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio are associated with prolonged hospital stay following colorectal cancer surgery. Br J Med Med Res 2014;4:481–7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Garcia-Martinez R, Caraceni P, Bernardi M, et al. . Albumin: pathophysiologic basis of its role in the treatment of cirrhosis and its complications. Hepatology 2013;58:1836–46. doi:10.1002/hep.26338 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Finfer S, Bellomo R, Boyce N, et al. . A comparison of albumin and saline for fluid resuscitation in the intensive care unit. N Engl J Med 2004;350:2247–56. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa040232 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Yuan X, Zhang C, He Y, et al. . Is albumin administration beneficial in early stage of postoperative hypoalbuminemia following gastrointestinal surgery?: a prospective randomized controlled trial. Am J Surg 2008;196:751–5. doi:10.1016/j.amjsurg.2007.10.030 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Caironi P, Tognoni G, Masson S, et al. . Albumin replacement in patients with severe sepsis or septic shock. N Engl J Med 2014;370:1412–21. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1305727 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Mahkovic-Hergouth K, Kompan L. Is replacement of albumin in major abdominal surgery useful? J Clin Anesth 2011;23:42–6. doi:10.1016/j.jclinane.2010.06.007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Vincent JL, Navickis RJ, Wilkes MM. Morbidity in hospitalized patients receiving human albumin: a meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials. Crit Care Med 2004;32:2029–38. doi:10.1097/01.CCM.0000142574.00425.E9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Caraceni P, Domenicali M, Tovoli A, et al. . Clinical indications for the albumin use: still a controversial issue. Eur J Intern Med 2013;24:721–8. doi:10.1016/j.ejim.2013.05.015 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Bar-Or D, Bar-Or R, Rael LT, et al. . Heterogeneity and oxidation status of commercial human albumin preparations in clinical use. Crit Care Med 2005;33:1638–41. doi:10.1097/01.CCM.0000169876.14858.91 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Bar-Or D, Thomas GW, Bar-Or R, et al. . Commercial human albumin preparations for clinical use are immunosuppressive in vitro. Crit Care Med 2006;34:1707–12. doi:10.1097/01.CCM.0000217923.53680.4C [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Greenland S, Rothman KJ. Fundamentals of epidemiologic data analysis. In: Rothman KJ, Greenland S, Lash TL, eds. Modern Epidemiology. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2008:213–37. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.