Abstract
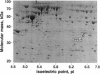
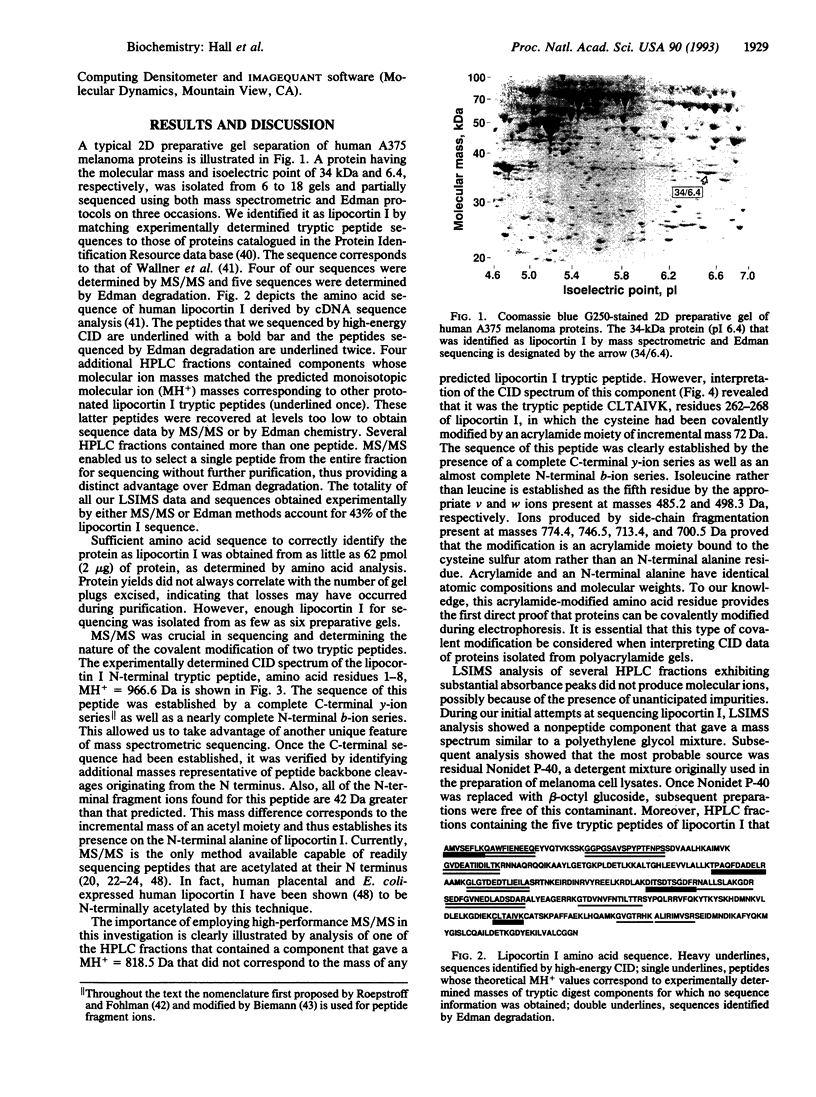
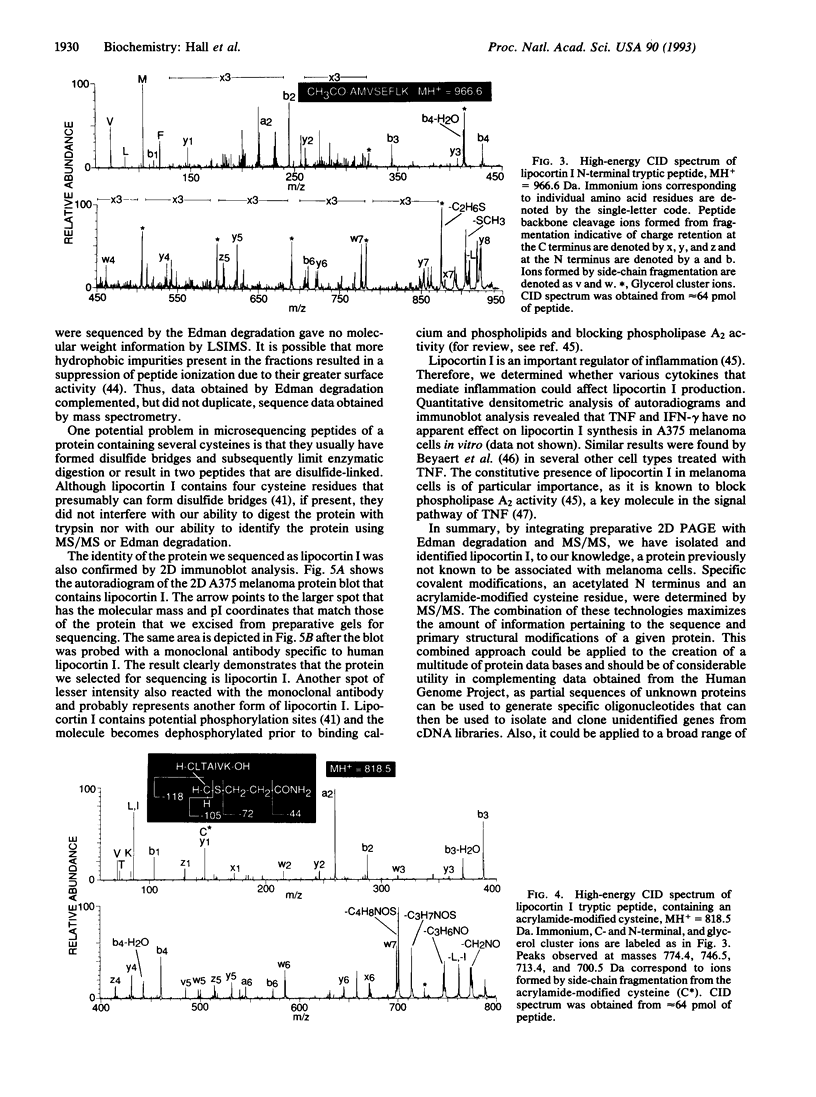
We have integrated preparative two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis with high-performance tandem mass spectrometry and Edman degradation. By using this approach, we have isolated and identified, by partial sequencing, a human melanoma protein (34 kDa, pI 6.4) as lipocortin I. To our knowledge, this protein was not previously known to be associated with melanoma cells. The identity of the protein was confirmed by two-dimensional immunoblot analysis. High-energy collision-induced dissociation analysis revealed the sequence and acetylation of the N-terminal tryptic peptide and an acrylamide-modified cysteine in another tryptic peptide. Thus, knowledge concerning both the primary structure and covalent modifications of proteins isolated from two-dimensional gels can be obtained directly by this approach, which is applicable to a broad range of biological problems.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aebersold R., Leavitt J. Sequence analysis of proteins separated by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis: towards an integrated protein database. Electrophoresis. 1990 Jul;11(7):517–527. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150110702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beresini M. H., Lempert M. J., Epstein L. B. Overlapping polypeptide induction in human fibroblasts in response to treatment with interferon-alpha, interferon-gamma, interleukin 1 alpha, interleukin 1 beta, and tumor necrosis factor. J Immunol. 1988 Jan 15;140(2):485–493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beresini M. H., Sugarman B. J., Shepard H. M., Epstein L. B. Synergistic induction of polypeptides by tumor necrosis factor and interferon-gamma in cells sensitive or resistant to tumor necrosis factor: assessment by computer based analysis of two-dimensional gels using the PDQUEST system. Electrophoresis. 1990 Mar;11(3):232–241. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150110307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beyaert R., Suffys P., Van Roy F., Fiers W. Inhibition by glucocorticoids of tumor necrosis factor-mediated cytotoxicity. Evidence against lipocortin involvement. FEBS Lett. 1990 Mar 12;262(1):93–96. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80161-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biemann K. Mass spectrometry of peptides and proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:977–1010. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.004553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biemann K., Scoble H. A. Characterization by tandem mass spectrometry of structural modifications in proteins. Science. 1987 Aug 28;237(4818):992–998. doi: 10.1126/science.3303336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burlingame A. L., Baillie T. A., Russell D. H. Mass spectrometry. Anal Chem. 1992 Jun 15;64(12):467R–502R. doi: 10.1021/ac00036a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celis J. E., Gesser B., Rasmussen H. H., Madsen P., Leffers H., Dejgaard K., Honore B., Olsen E., Ratz G., Lauridsen J. B. Comprehensive two-dimensional gel protein databases offer a global approach to the analysis of human cells: the transformed amnion cells (AMA) master database and its link to genome DNA sequence data. Electrophoresis. 1990 Dec;11(12):989–1071. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150111202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celis J. E., Ratz G. P., Madsen P., Gesser B., Lauridsen J. B., Kwee S., Rasmussen H. H., Nielsen H. V., Crüger D., Basse B. Comprehensive, human cellular protein databases and their implication for the study of genome organization and function. FEBS Lett. 1989 Feb 27;244(2):247–254. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80538-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driessen H. P., de Jong W. W., Tesser G. I., Bloemendal H. The mechanism of N-terminal acetylation of proteins. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1985;18(4):281–325. doi: 10.3109/10409238509086784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flower R. J. Eleventh Gaddum memorial lecture. Lipocortin and the mechanism of action of the glucocorticoids. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Aug;94(4):987–1015. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11614.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrels J. I., Franza B. R., Chang C., Latter G. Quantitative exploration of the REF52 protein database: cluster analysis reveals the major protein expression profiles in responses to growth regulation, serum stimulation, and viral transformation. Electrophoresis. 1990 Dec;11(12):1114–1130. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150111204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrels J. I. Two dimensional gel electrophoresis and computer analysis of proteins synthesized by clonal cell lines. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 25;254(16):7961–7977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George D. G., Barker W. C., Hunt L. T. The protein identification resource (PIR). Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 10;14(1):11–15. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson B. W., Daley D. J., Williams D. H. Structural elucidation of N-terminal post-translational modifications by mass spectrometry: application to chicken enolase and the alpha- and beta-subunits of bovine mitochondrial F1-ATPase. Anal Biochem. 1988 Mar;169(2):217–226. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90277-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson B. W., Yu Z. G., Aberth W., Burlingame A. L., Bass N. M. Revision of the blocked N terminus of rat heart fatty acid-binding protein by liquid secondary ion mass spectrometry. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 25;263(9):4182–4185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris C. A., Derbin K. S., Hunte-McDonough B., Krauss M. R., Chen K. T., Smith D. M., Epstein L. B. Manganese superoxide dismutase is induced by IFN-gamma in multiple cell types. Synergistic induction by IFN-gamma and tumor necrosis factor or IL-1. J Immunol. 1991 Jul 1;147(1):149–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris C. A., Hunte B., Krauss M. R., Taylor A., Epstein L. B. Induction of leucine aminopeptidase by interferon-gamma. Identification by protein microsequencing after purification by preparative two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 5;267(10):6865–6869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunkapiller M. W., Hewick R. M., Dreyer W. J., Hood L. E. High-sensitivity sequencing with a gas-phase sequenator. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:399–413. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91038-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunkapiller M. W., Lujan E., Ostrander F., Hood L. E. Isolation of microgram quantities of proteins from polyacrylamide gels for amino acid sequence analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:227–236. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91019-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy T. E., Gawinowicz M. A., Barzilai A., Kandel E. R., Sweatt J. D. Sequencing of proteins from two-dimensional gels by using in situ digestion and transfer of peptides to polyvinylidene difluoride membranes: application to proteins associated with sensitization in Aplysia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):7008–7012. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.7008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klose J. Systematic analysis of the total proteins of a mammalian organism: principles, problems and implications for sequencing the human genome. Electrophoresis. 1989 Feb;10(2):140–152. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150100208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konigsberg W. H., Henderson L. Removal of sodium dodecyl sulfate from proteins by ion-pair extraction. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:254–259. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91022-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medzihradszky K. F., Gibson B. W., Kaur S., Yu Z. H., Medzihradszky D., Burlingame A. L., Bass N. M. The primary structure of fatty-acid-binding protein from nurse shark liver. Structural and evolutionary relationship to the mammalian fatty-acid-binding protein family. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Feb 1;203(3):327–339. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16553.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neale M. L., Fiera R. A., Matthews N. Involvement of phospholipase A2 activation in tumour cell killing by tumour necrosis factor. Immunology. 1988 May;64(1):81–85. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otter T., King S. M., Witman G. B. A two-step procedure for efficient electrotransfer of both high-molecular-weight (greater than 400,000) and low-molecular-weight (less than 20,000) proteins. Anal Biochem. 1987 May 1;162(2):370–377. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90406-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patton W. F., Pluskal M. G., Skea W. M., Buecker J. L., Lopez M. F., Zimmermann R., Belanger L. M., Hatch P. D. Development of a dedicated two-dimensional gel electrophoresis system that provides optimal pattern reproducibility and polypeptide resolution. Biotechniques. 1990 May;8(5):518–527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepinsky R. B., Sinclair L. K., Dougas I., Liang C. M., Lawton P., Browning J. L. Monoclonal antibodies to lipocortin-1 as probes for biological function. FEBS Lett. 1990 Feb 26;261(2):247–252. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80564-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulter L., Ang S. G., Gibson B. W., Williams D. H., Holmes C. F., Caudwell F. B., Pitcher J., Cohen P. Analysis of the in vivo phosphorylation state of rabbit skeletal muscle glycogen synthase by fast-atom-bombardment mass spectrometry. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Aug 15;175(3):497–510. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14222.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulter L., Earnest J. P., Stroud R. M., Burlingame A. L. Structure, oligosaccharide structures, and posttranslationally modified sites of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6645–6649. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roepstorff P., Fohlman J. Proposal for a common nomenclature for sequence ions in mass spectra of peptides. Biomed Mass Spectrom. 1984 Nov;11(11):601–601. doi: 10.1002/bms.1200111109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roepstorff P., Nielsen P. F., Klarskov K., Højrup P. Applications of plasma desorption mass spectrometry in peptide and protein chemistry. Biomed Environ Mass Spectrom. 1988 Oct;16(1-12):9–18. doi: 10.1002/bms.1200160103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders D. A., Gillece-Castro B. L., Stock A. M., Burlingame A. L., Koshland D. E., Jr Identification of the site of phosphorylation of the chemotaxis response regulator protein, CheY. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21770–21778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VanBogelen R. A., Hutton M. E., Neidhardt F. C. Gene-protein database of Escherichia coli K-12: edition 3. Electrophoresis. 1990 Dec;11(12):1131–1166. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150111205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallner B. P., Mattaliano R. J., Hession C., Cate R. L., Tizard R., Sinclair L. K., Foeller C., Chow E. P., Browing J. L., Ramachandran K. L. Cloning and expression of human lipocortin, a phospholipase A2 inhibitor with potential anti-inflammatory activity. Nature. 1986 Mar 6;320(6057):77–81. doi: 10.1038/320077a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward L. D., Reid G. E., Moritz R. L., Simpson R. J. Strategies for internal amino acid sequence analysis of proteins separated by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Chromatogr. 1990 Oct 19;519(1):199–216. doi: 10.1016/0021-9673(90)85148-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb J. W., Jiang K., Gillece-Castro B. L., Tarentino A. L., Plummer T. H., Byrd J. C., Fisher S. J., Burlingame A. L. Structural characterization of intact, branched oligosaccharides by high performance liquid chromatography and liquid secondary ion mass spectrometry. Anal Biochem. 1988 Mar;169(2):337–349. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90293-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wen D. X., Livingston B. D., Medzihradszky K. F., Kelm S., Burlingame A. L., Paulson J. C. Primary structure of Gal beta 1,3(4)GlcNAc alpha 2,3-sialyltransferase determined by mass spectrometry sequence analysis and molecular cloning. Evidence for a protein motif in the sialyltransferase gene family. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 15;267(29):21011–21019. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]