Abstract
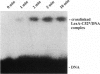
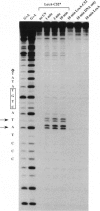
To address the question how the recognition helix of the LexA repressor is positioned within the major groove of operator DNA we have applied a site-specific photocrosslinking approach using a LexA mutant repressor (LexA-C52) that harbors a single cysteine side chain in position 52, close to the COOH terminus of helix 3. The LexA-C52 mutant repressor has been purified and modified site-specifically with the photoreactive azido compound 4-azidophenacyl bromide, giving rise to LexA-C52*. Here we show that LexA-C52* may be selectively photocrosslinked with two adjacent bases within each operator half-site. The crosslinked bases are located, respectively, 10 and 11 base pairs from the dyad axis of the operator. The crosslinking data imply that the LexA recognition helix is oriented opposite to what is generally observed for helix-turn-helix proteins and that this helix should form a steeper angle with respect to the plane of the base pairs than is observed for standard helix-turn-helix proteins.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boelens R., Scheek R. M., van Boom J. H., Kaptein R. Complex of lac repressor headpiece with a 14 base-pair lac operator fragment studied by two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jan 5;193(1):213–216. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90638-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brent R., Ptashne M. Mechanism of action of the lexA gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4204–4208. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodd I. B., Egan J. B. Systematic method for the detection of potential lambda Cro-like DNA-binding regions in proteins. J Mol Biol. 1987 Apr 5;194(3):557–564. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90681-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebright R. H., Ebright Y. W., Pendergrast P. S., Gunasekera A. Conversion of a helix-turn-helix motif sequence-specific DNA binding protein into a site-specific DNA cleavage agent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):2882–2886. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.2882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham K. S., Dervan P. B. Structural motif of the DNA binding domain of gamma delta-resolvase characterized by affinity cleaving. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 25;265(27):16534–16540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison S. C., Aggarwal A. K. DNA recognition by proteins with the helix-turn-helix motif. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:933–969. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.004441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurstel S., Granger-Schnarr M., Daune M., Schnarr M. In vitro binding of LexA repressor to DNA: evidence for the involvement of the amino-terminal domain. EMBO J. 1986 Apr;5(4):793–798. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04283.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurstel S., Granger-Schnarr M., Schnarr M. Contacts between the LexA repressor--or its DNA-binding domain--and the backbone of the recA operator DNA. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):269–275. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02809.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan S. R., Pabo C. O. Structure of the lambda complex at 2.5 A resolution: details of the repressor-operator interactions. Science. 1988 Nov 11;242(4880):893–899. doi: 10.1126/science.3187530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim B., Little J. W. Dimerization of a specific DNA-binding protein on the DNA. Science. 1992 Jan 10;255(5041):203–206. doi: 10.1126/science.1553548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamerichs R. M., Padilla A., Boelens R., Kaptein R., Ottleben G., Rüterjans H., Granger-Schnarr M., Oertel P., Schnarr M. The amino-terminal domain of LexA repressor is alpha-helical but differs from canonical helix-turn-helix proteins: a two-dimensional 1H NMR study. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):6863–6867. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.6863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehming N., Sartorius J., Kisters-Woike B., von Wilcken-Bergmann B., Müller-Hill B. Mutant lac repressors with new specificities hint at rules for protein--DNA recognition. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):615–621. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08153.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. W., Hill S. A. Deletions within a hinge region of a specific DNA-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2301–2305. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. W. Mechanism of specific LexA cleavage: autodigestion and the role of RecA coprotease. Biochimie. 1991 Apr;73(4):411–421. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(91)90108-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. W., Mount D. W. The SOS regulatory system of Escherichia coli. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):11–22. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloubes R., Granger-Schnarr M., Lazdunski C., Schnarr M. Interaction of a regulatory protein with a DNA target containing two overlapping binding sites. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 5;266(4):2303–2312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mack D. P., Sluka J. P., Shin J. A., Griffin J. H., Simon M. I., Dervan P. B. Orientation of the putative recognition helix in the DNA-binding domain of Hin recombinase complexed with the hix site. Biochemistry. 1990 Jul 17;29(28):6561–6567. doi: 10.1021/bi00480a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakley M. G., Dervan P. B. Structural motif of the GCN4 DNA binding domain characterized by affinity cleaving. Science. 1990 May 18;248(4957):847–850. doi: 10.1126/science.2111578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oertel-Buchheit P., Lamerichs R. M., Schnarr M., Granger-Schnarr M. Genetic analysis of the LexA repressor: isolation and characterization of LexA(Def) mutant proteins. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Aug;223(1):40–48. doi: 10.1007/BF00315795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottleben G., Messori L., Rüterjans H., Kaptein R., Granger-Schnarr M., Schnarr M. 1H-NMR investigation of the interaction of the amino terminal domain of the LexA repressor with a synthetic half-operator. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1991 Dec;9(3):447–461. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1991.10507928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pendergrast P. S., Chen Y., Ebright Y. W., Ebright R. H. Determination of the orientation of a DNA binding motif in a protein-DNA complex by photocrosslinking. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10287–10291. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Praseuth D., Chassignol M., Takasugi M., Le Doan T., Thuong N. T., Hélène C. Double helices with parallel strands are formed by nuclease-resistant oligo-[alpha]-deoxynucleotides and oligo-[alpha]-deoxynucleotides covalently linked to an intercalating agent with complementary oligo-[beta]-deoxynucleotides. J Mol Biol. 1987 Aug 20;196(4):939–942. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90416-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Praseuth D., Perrouault L., Le Doan T., Chassignol M., Thuong N., Hélène C. Sequence-specific binding and photocrosslinking of alpha and beta oligodeoxynucleotides to the major groove of DNA via triple-helix formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1349–1353. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnarr M., Granger-Schnarr M., Hurstel S., Pouyet J. The carboxy-terminal domain of the LexA repressor oligomerises essentially as the entire protein. FEBS Lett. 1988 Jul 4;234(1):56–60. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81302-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnarr M., Oertel-Buchheit P., Kazmaier M., Granger-Schnarr M. DNA binding properties of the LexA repressor. Biochimie. 1991 Apr;73(4):423–431. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(91)90109-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnarr M., Pouyet J., Granger-Schnarr M., Daune M. Large-scale purification, oligomerization equilibria, and specific interaction of the LexA repressor of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1985 May 21;24(11):2812–2818. doi: 10.1021/bi00332a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shin J. A., Ebright R. H., Dervan P. B. Orientation of the Lac repressor DNA binding domain in complex with the left lac operator half site characterized by affinity cleaving. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 11;19(19):5233–5236. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.19.5233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sluka J. P., Horvath S. J., Bruist M. F., Simon M. I., Dervan P. B. Synthesis of a sequence-specific DNA-cleaving peptide. Science. 1987 Nov 20;238(4830):1129–1132. doi: 10.1126/science.3120311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thliveris A. T., Mount D. W. Genetic identification of the DNA binding domain of Escherichia coli LexA protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4500–4504. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker G. C. Mutagenesis and inducible responses to deoxyribonucleic acid damage in Escherichia coli. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Mar;48(1):60–93. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.1.60-93.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wertman K. F., Mount D. W. Nucleotide sequence binding specificity of the LexA repressor of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):376–384. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.376-384.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wissmann A., Baumeister R., Müller G., Hecht B., Helbl V., Pfleiderer K., Hillen W. Amino acids determining operator binding specificity in the helix-turn-helix motif of Tn10 Tet repressor. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4145–4152. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04992.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]