Abstract
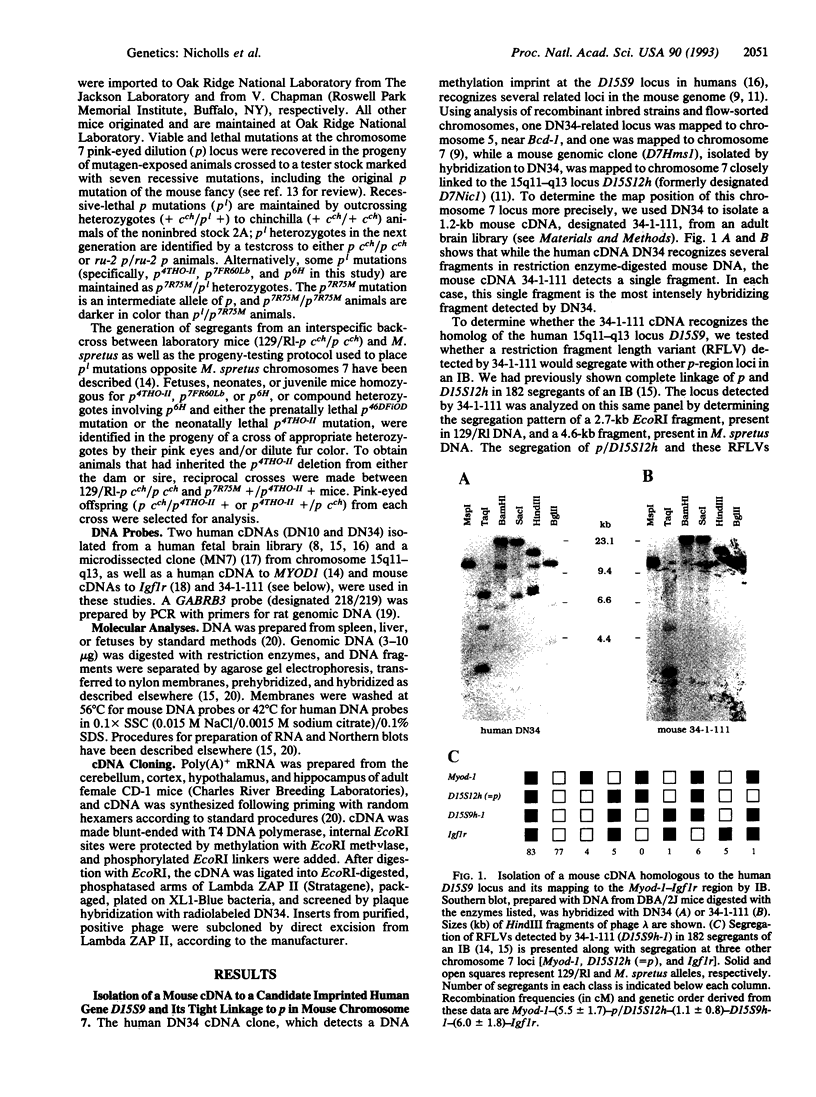
Prader-Willi and Angelman syndromes are complex neurobehavioral contiguous gene syndromes whose expression depends on the unmasking of genomic imprinting for different genetic loci in human chromosome 15q11-q13. The homologous chromosomal region in the mouse genome has been fine-mapped by using interspecific (Mus spretus) crosses and overlapping, radiation-induced deletions to evaluate potential animal models for both imprinted and nonimprinted components of these syndromes. Four evolutionarily conserved sequences from human 15q11-q13, including two cDNAs from fetal brain (DN10, D15S12h; DN34, D15S9h-1), a microdissected clone (MN7; D15F37S1h) expressed in mouse brain, and the gene for the beta 3 subunit of the gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptor (Gabrb3), were mapped in mouse chromosome 7 by analysis of deletions at the pink-eyed dilution (p) locus. Three of these loci are deleted in pre- and postnatally lethal p-locus mutations, which extend up to 5.5 +/- 1.7 centimorgans (cM) proximal to p; D15S9h-1, which maps 1.1 +/- 0.8 cM distal to p and is the mouse homolog of the human gene D15S9 (which shows a DNA methylation imprint), is not deleted in any of the p-locus deletion series. A transcript from the Gabrb3 gene, but not the transcript detected by MN7 at the D15F37S1h locus, is expressed in mice homozygous for the p6H deletion, which have an abnormal neurological phenotype. Furthermore, the Gabrb3 transcript is expressed equally well from the maternal or paternal chromosome 7 and, therefore, its expression is not imprinted in mouse brain. Deletions at the mouse p locus should serve as intermediate genetic reagents and models with which to analyze the genetics and etiology of individual components of human 15q11-q13 disorders.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buiting K., Greger V., Brownstein B. H., Mohr R. M., Voiculescu I., Winterpacht A., Zabel B., Horsthemke B. A putative gene family in 15q11-13 and 16p11.2: possible implications for Prader-Willi and Angelman syndromes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5457–5461. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler M. G. Hypopigmentation: a common feature of Prader-Labhart-Willi syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Jul;45(1):140–146. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler M. G. Prader-Willi syndrome: current understanding of cause and diagnosis. Am J Med Genet. 1990 Mar;35(3):319–332. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320350306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattanach B. M., Barr J. A., Evans E. P., Burtenshaw M., Beechey C. V., Leff S. E., Brannan C. I., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A., Jones J. A candidate mouse model for Prader-Willi syndrome which shows an absence of Snrpn expression. Nat Genet. 1992 Dec;2(4):270–274. doi: 10.1038/ng1292-270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaillet J. R., Knoll J. H., Horsthemke B., Lalande M. The syntenic relationship between the critical deletion region for the Prader-Willi/Angelman syndromes and proximal mouse chromosome 7. Genomics. 1991 Nov;11(3):773–776. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90090-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherubini E., Gaiarsa J. L., Ben-Ari Y. GABA: an excitatory transmitter in early postnatal life. Trends Neurosci. 1991 Dec;14(12):515–519. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(91)90003-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton-Smith J., Pembrey M. E. Angelman syndrome. J Med Genet. 1992 Jun;29(6):412–415. doi: 10.1136/jmg.29.6.412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton-Smith J., Webb T., Robb S. A., Dijkstra I., Willems P., Lam S., Cheng X. J., Pembrey M. E., Malcolm S. Further evidence for dominant inheritance at the chromosome 15q11-13 locus in familial Angelman syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1992 Sep 15;44(2):256–260. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320440236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll D. J., Waters M. F., Williams C. A., Zori R. T., Glenn C. C., Avidano K. M., Nicholls R. D. A DNA methylation imprint, determined by the sex of the parent, distinguishes the Angelman and Prader-Willi syndromes. Genomics. 1992 Aug;13(4):917–924. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90001-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fryburg J. S., Breg W. R., Lindgren V. Diagnosis of Angelman syndrome in infants. Am J Med Genet. 1991 Jan;38(1):58–64. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320380114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galán F., Aguilar M. S., González J., Clemente F., Sánchez R., Tapia M., Moya M. Interstitial 15q deletion without a classic Prader-Willi phenotype. Am J Med Genet. 1991 Mar 15;38(4):532–534. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320380406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner J. M., Nakatsu Y., Gondo Y., Lee S., Lyon M. F., King R. A., Brilliant M. H. The mouse pink-eyed dilution gene: association with human Prader-Willi and Angelman syndromes. Science. 1992 Aug 21;257(5073):1121–1124. doi: 10.1126/science.257.5073.1121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt D. M., Johnson D. R. Abnormal spermiogenesis in two pink-eyed sterile mutants in the mouse. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1971 Aug;26(1):111–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwano A., Mutirangura A., Dittrich B., Buiting K., Horsthemke B., Saitoh S., Niikawa N., Ledbetter S. A., Greenberg F., Chinault A. C. Molecular dissection of the Prader-Willi/Angelman syndrome region (15q11-13) by YAC cloning and FISH analysis. Hum Mol Genet. 1992 Sep;1(6):417–425. doi: 10.1093/hmg/1.6.417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leff S. E., Brannan C. I., Reed M. L., Ozçelik T., Francke U., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A. Maternal imprinting of the mouse Snrpn gene and conserved linkage homology with the human Prader-Willi syndrome region. Nat Genet. 1992 Dec;2(4):259–264. doi: 10.1038/ng1292-259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyon M. F., King T. R., Gondo Y., Gardner J. M., Nakatsu Y., Eicher E. M., Brilliant M. H. Genetic and molecular analysis of recessive alleles at the pink-eyed dilution (p) locus of the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):6968–6972. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.6968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakatsu Y., Gondo Y., Brilliant M. H. The p locus is closely linked to the mouse homolog of a gene from the Prader-Willi chromosomal region. Mamm Genome. 1992;2(1):69–71. doi: 10.1007/BF00570442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinchik E. M., Bultman S. J., Horsthemke B., Lee S. T., Strunk K. M., Spritz R. A., Avidano K. M., Jong M. T., Nicholls R. D. A gene for the mouse pink-eyed dilution locus and for human type II oculocutaneous albinism. Nature. 1993 Jan 7;361(6407):72–76. doi: 10.1038/361072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitoh S., Kubota T., Ohta T., Jinno Y., Niikawa N., Sugimoto T., Wagstaff J., Lalande M. Familial Angelman syndrome caused by imprinted submicroscopic deletion encompassing GABAA receptor beta 3-subunit gene. Lancet. 1992 Feb 8;339(8789):366–367. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)91686-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmickel R. D. Contiguous gene syndromes: a component of recognizable syndromes. J Pediatr. 1986 Aug;109(2):231–241. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(86)80377-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz S., Max S. R., Panny S. R., Cohen M. M. Deletions of proximal 15q and non-classical Prader-Willi syndrome phenotypes. Am J Med Genet. 1985 Feb;20(2):255–263. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320200208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scrable H. J., Johnson D. K., Rinchik E. M., Cavenee W. K. Rhabdomyosarcoma-associated locus and MYOD1 are syntenic but separate loci on the short arm of human chromosome 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2182–2186. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Gray A., Tam A. W., Yang-Feng T., Tsubokawa M., Collins C., Henzel W., Le Bon T., Kathuria S., Chen E. Insulin-like growth factor I receptor primary structure: comparison with insulin receptor suggests structural determinants that define functional specificity. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2503–2512. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04528.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagstaff J., Chaillet J. R., Lalande M. The GABAA receptor beta 3 subunit gene: characterization of a human cDNA from chromosome 15q11q13 and mapping to a region of conserved synteny on mouse chromosome 7. Genomics. 1991 Dec;11(4):1071–1078. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90034-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagstaff J., Knoll J. H., Fleming J., Kirkness E. F., Martin-Gallardo A., Greenberg F., Graham J. M., Jr, Menninger J., Ward D., Venter J. C. Localization of the gene encoding the GABAA receptor beta 3 subunit to the Angelman/Prader-Willi region of human chromosome 15. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Aug;49(2):330–337. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagstaff J., Knoll J. H., Glatt K. A., Shugart Y. Y., Sommer A., Lalande M. Maternal but not paternal transmission of 15q11-13-linked nondeletion Angelman syndrome leads to phenotypic expression. Nat Genet. 1992 Jul;1(4):291–294. doi: 10.1038/ng0792-291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y., Tycko B. Monoallelic expression of the human H19 gene. Nat Genet. 1992 Apr;1(1):40–44. doi: 10.1038/ng0492-40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







