Abstract
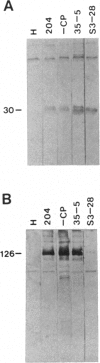
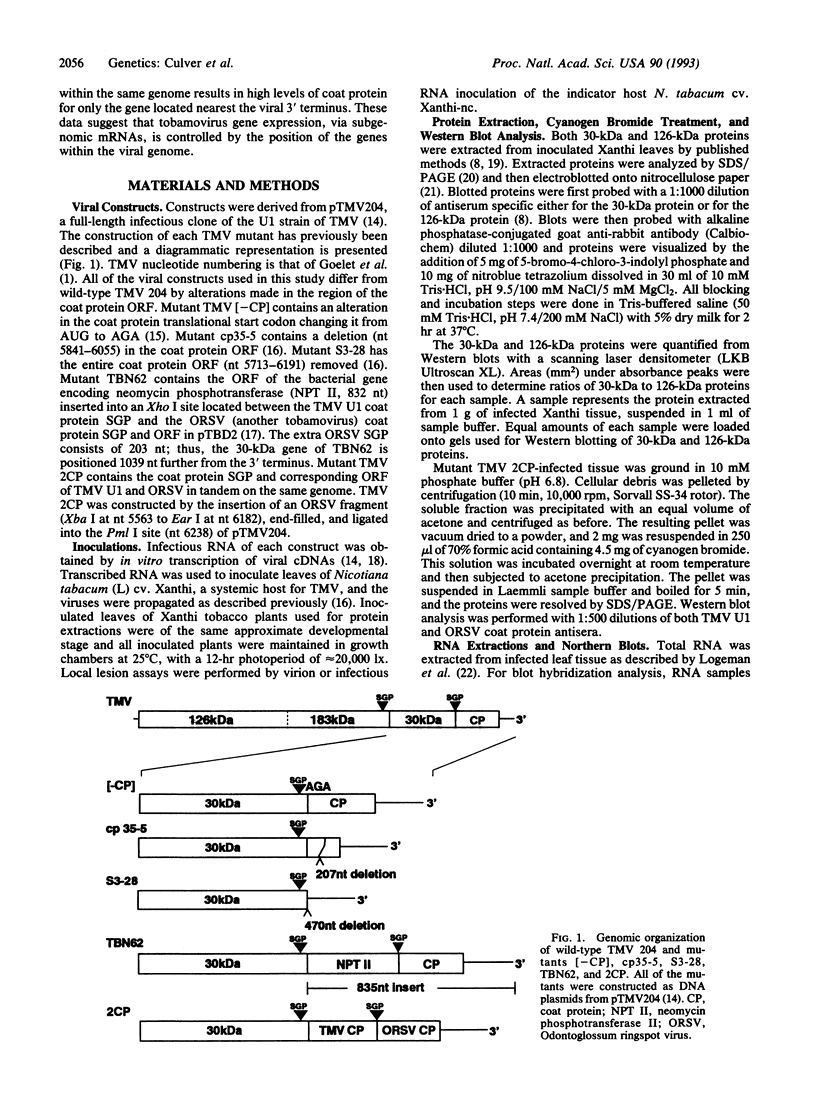
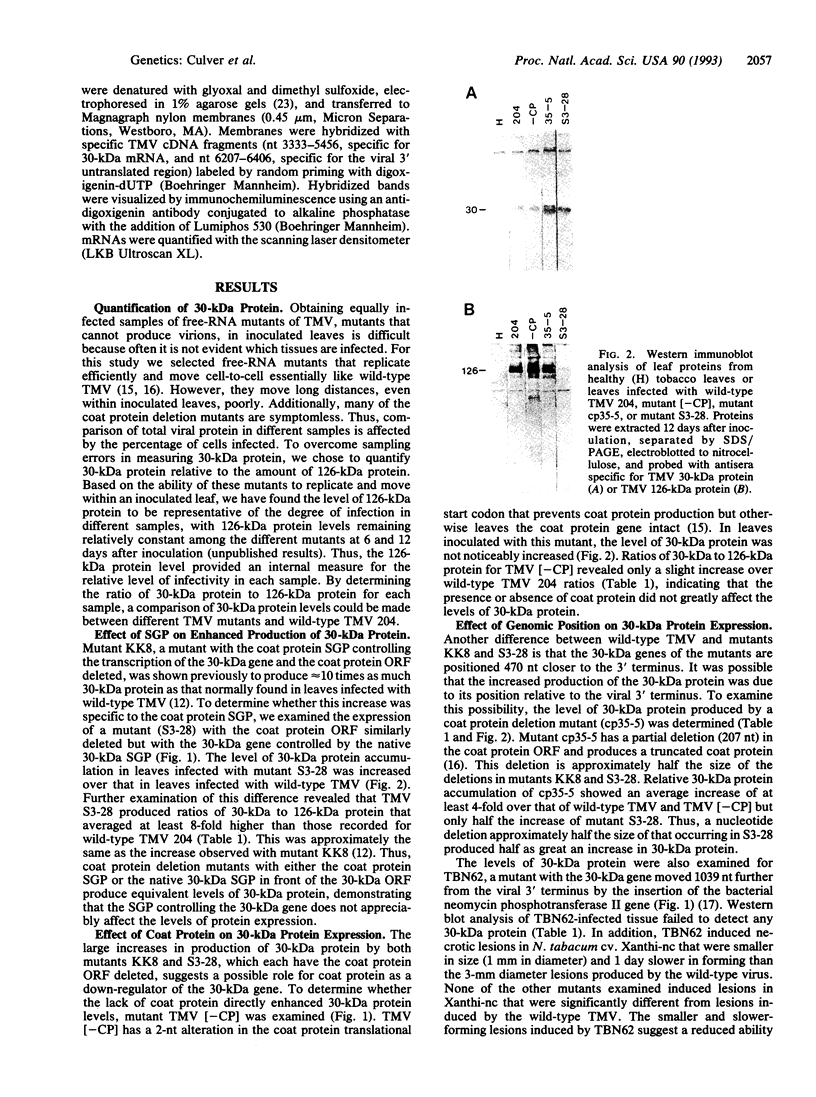
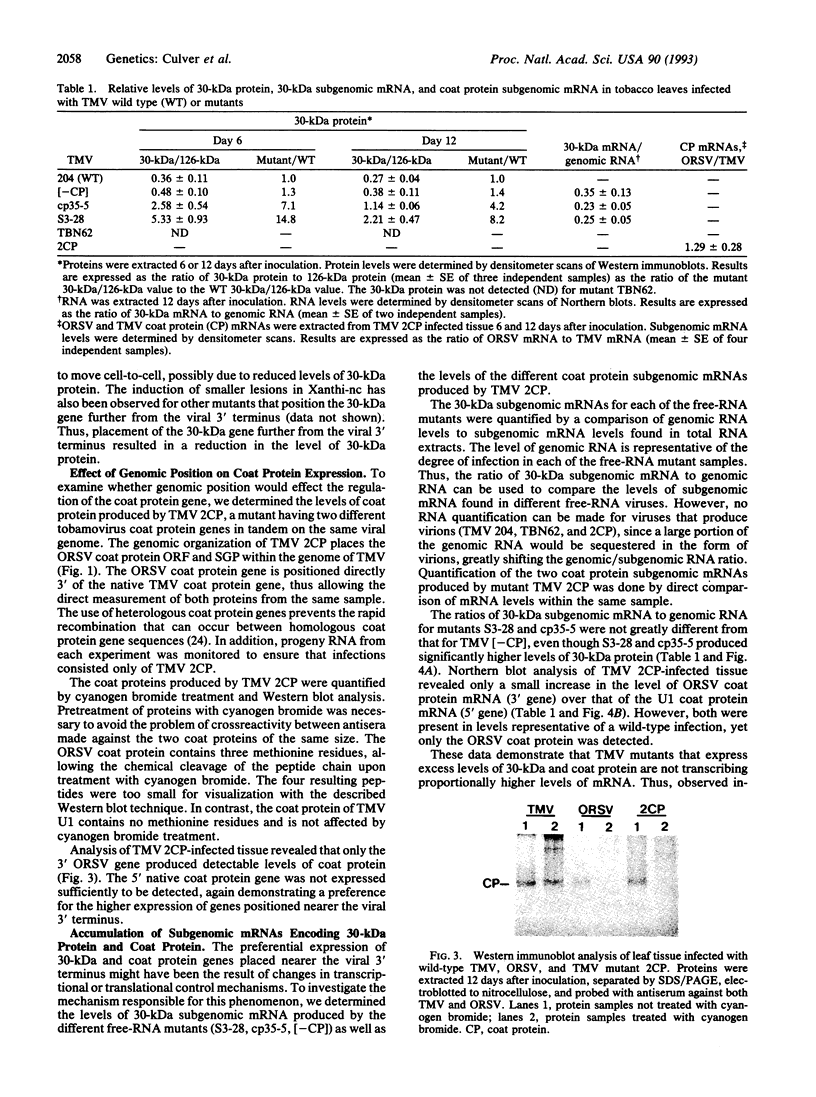
Alterations in the genomic position of the tobacco mosaic virus (TMV) genes encoding the 30-kDa cell-to-cell movement protein or the coat protein greatly affected their expression. Higher production of 30-kDa protein was correlated with increased proximity of the gene to the viral 3' terminus. A mutant placing the 30-kDa open reading frame 207 nucleotides nearer the 3' terminus produced at least 4 times the wild-type TMV 30-kDa protein level, while a mutant placing the 30-kDa open reading frame 470 nucleotides closer to the 3' terminus produced at least 8 times the wild-type TMV 30-kDa protein level. Increases in 30-kDa protein production were not correlated with the subgenomic mRNA promoter (SGP) controlling the 30-kDa gene, since mutants with either the native 30-kDa SGP or the coat protein SGP in front of the 30-kDa gene produced similar levels of 30-kDa protein. Lack of coat protein did not affect 30-kDa protein expression, since a mutant with the coat protein start codon removed did not produce increased amounts of 30-kDa protein. Effects of gene positioning on coat protein expression were examined by using a mutant containing two different tandemly positioned tobamovirus (TMV and Odontoglossum ringspot virus) coat protein genes. Only coat protein expressed from the gene positioned nearest the 3' viral terminus was detected. Analysis of 30-kDa and coat protein subgenomic mRNAs revealed no proportional increase in the levels of mRNA relative to the observed levels of 30-kDa and coat proteins. This suggests that a translational mechanism is primarily responsible for the observed effect of genomic position on expression of 30-kDa movement and coat protein genes.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahlquist P., Janda M. cDNA cloning and in vitro transcription of the complete brome mosaic virus genome. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2876–2882. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beachy R. N., Zaitlin M. Characterization and in vitro translation of the RNAs from less-than-full-length, virus-related, nucleoprotein rods present in tobacco mosaic virus preparations. Virology. 1977 Aug;81(1):160–169. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90068-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck D. L., Dawson W. O. Deletion of repeated sequences from tobacco mosaic virus mutants with two coat protein genes. Virology. 1990 Aug;177(2):462–469. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90510-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruening G., Beachy R. N., Scalla R., Zaitlin M. In vitro and in vivo translation of the ribonucleic acids of a cowpea strain of tobacco mosaic virus. Virology. 1976 Jun;71(2):498–517. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90377-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Culver J. N., Dawson W. O. Tobacco mosaic virus coat protein: an elicitor of the hypersensitive reaction but not required for the development of mosaic symptoms in Nicotiana sylvestris. Virology. 1989 Dec;173(2):755–758. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90592-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson W. O., Beck D. L., Knorr D. A., Grantham G. L. cDNA cloning of the complete genome of tobacco mosaic virus and production of infectious transcripts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1832–1836. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donson J., Kearney C. M., Hilf M. E., Dawson W. O. Systemic expression of a bacterial gene by a tobacco mosaic virus-based vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7204–7208. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn S. D. Effects of the modification of transfer buffer composition and the renaturation of proteins in gels on the recognition of proteins on Western blots by monoclonal antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1986 Aug 15;157(1):144–153. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90207-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- French R., Ahlquist P. Characterization and engineering of sequences controlling in vivo synthesis of brome mosaic virus subgenomic RNA. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2411–2420. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2411-2420.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goelet P., Lomonossoff G. P., Butler P. J., Akam M. E., Gait M. J., Karn J. Nucleotide sequence of tobacco mosaic virus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):5818–5822. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.5818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T. R., Hunt T., Knowland J., Zimmern D. Messenger RNA for the coat protein of tobacco mosaic virus. Nature. 1976 Apr 29;260(5554):759–764. doi: 10.1038/260759a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehto K., Bubrick P., Dawson W. O. Time course of TMV 30K protein accumulation in intact leaves. Virology. 1990 Jan;174(1):290–293. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90077-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehto K., Dawson W. O. Changing the start codon context of the 30K gene of tobacco mosaic virus from "weak" to "strong" does not increase expression. Virology. 1990 Jan;174(1):169–176. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90065-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehto K., Dawson W. O. Replication, stability, and gene expression of tobacco mosaic virus mutants with a second 30K ORF. Virology. 1990 Mar;175(1):30–40. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90183-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehto K., Grantham G. L., Dawson W. O. Insertion of sequences containing the coat protein subgenomic RNA promoter and leader in front of the tobacco mosaic virus 30K ORF delays its expression and causes defective cell-to-cell movement. Virology. 1990 Jan;174(1):145–157. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90063-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logemann J., Schell J., Willmitzer L. Improved method for the isolation of RNA from plant tissues. Anal Biochem. 1987 May 15;163(1):16–20. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90086-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raju R., Huang H. V. Analysis of Sindbis virus promoter recognition in vivo, using novel vectors with two subgenomic mRNA promoters. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2501–2510. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2501-2510.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel A., Hari V., Kolacz K. The effect of tobacco mosaic virus infection on host and virus-specific protein synthesis in protoplasts. Virology. 1978 Apr;85(2):494–503. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90456-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel A., Hari V., Montgomery I., Kolacz K. A messenger RNA for capsid protein isolated from tobacco mosaic virus-infected tissue. Virology. 1976 Sep;73(2):363–371. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90397-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]