Abstract
Chemotherapy-induced cardiotoxicity is a serious complication that poses a serious threat to life and limits the clinical use of various chemotherapeutic agents, particularly the anthracyclines. Understanding molecular mechanisms of chemotherapy-induced cardiotoxicity is a key to effective preventive strategies and improved chemotherapy regimen. Although no reliable and effective preventive treatment has become available, numerous evidence demonstrates that chemotherapy-induced cardiotoxicity involves the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). This review provides an overview of the roles of oxidative stress in chemotherapy-induced cardiotoxicity using doxorubicin, which is one of the most effective chemotherapeutic agents against a wide range of cancers, as an example. Current understanding in the molecular mechanisms of ROS-mediated cardiotoxicity will be explored and discussed, with emphasis on cardiomyocyte apoptosis leading to cardiomyopathy. The review will conclude with perspectives on model development needed to facilitate further progress and understanding on chemotherapy-induced cardiotoxicity.
1. Introduction
Chemotherapy is a common treatment for various cancers as an adjuvant or a primary therapy; however, it also carries a risk of adverse effects that might leave an unfavorable damage to cancer patients. Chemotherapy-induced cardiotoxicity is a serious complication that limits the clinical use of chemotherapeutic agents, particularly the anthracyclines, since it could eventually culminate in the development of life-threatening cardiomyopathy. Understanding the mechanisms that are responsible for cardiotoxicity could help lessen the undesirable impact on normal tissues and improve the cancer treatment regimen. One of the most widely accepted mechanisms of chemotherapy-induced cardiotoxicity involves the generation of oxidative stress. This review provides an overview of the roles of oxidative stress in chemotherapy-induced cardiotoxicity. Current understanding in the molecular mechanisms of oxidative stress-mediated cardiotoxicity is discussed, with emphasis on cellular apoptosis leading to cardiomyopathy.
2. Chemotherapy-Induced Cardiotoxicity
The basic principle of chemotherapy is to impair mitotic and metabolic process of cancer cells. Unfortunately, certain normal cells and tissues are also affected by the chemotherapy, leading to various mild and severe adverse effects, including nausea and vomiting, bone marrow suppression, and cardiovascular side effects, namely, hypotension, tachycardia, arrhythmias, and heart failure [1]. The National Cancer Institute generally defines toxicity that affects the heart as cardiotoxicity. Although cardiotoxicity could be affected by different chemotherapeutic agents as summarized in Table 1, certain class of chemotherapy, for example, the anthracyclines, induces more common and frequent adverse effects. These drugs should not be administered to patients with high risk of developing cardiac complications. The risk of cardiotoxicity increases in patients with hypertension, diabetes mellitus, liver disease, and previous cardiac diseases [2]. The risk of cardiotoxicity also depends largely on route of administration, duration of chemotherapy (cumulative dose) and the dosage regimen. For example, a combination of anthracyclines with other potential cardiotoxic agents, namely paclitaxel or trastuzumab, would greatly enhance the risk of cardiotoxicity that potentially lead to disastrous congestive heart failure [3–6].
Table 1.
Potential cardiotoxicity induced by numerous chemotherapeutic agents.
| Class | Examples of chemotherapeutic agents | Possible cardiotoxicity |
|---|---|---|
| Anthracyclines and anthraquinones | DOX, mitoxantrone | Congestive heart failure, left ventricular dysfunction, acute myocarditis, and arrhythmia |
|
| ||
| Antimetabolite agents | Capecitabine, 5-fluorouracil, and cytarabine | Ischemia, pericarditis, congestive heart failure, and cardiogenic shock |
|
| ||
| Antimicrotubule agents | Paclitaxel, vinca alkaloids | Sinus bradycardia, ventricular tachycardia, atrioventricular block, hypotension, congestive heart failure, and ischemia |
|
| ||
| Alkylating agents | Cyclophosphamide, ifosfamide | Neurohumoral activation, mild mitral regurgitation |
|
| ||
| Monoclonal antibody against HER2 | Trastuzumab | Arrhythmias, congestive heart failure, angioedema, and left ventricular dysfunction |
|
| ||
| Antiangiogenic and tyrosine kinase inhibitors | Imatinib, sorafenib, and sunitinib | Hypertension, arrhythmias |
|
| ||
| Antivascular endothelial growth factor | Bevacizumab | Hypertension, thromboembolism |
Anthracyclines including doxorubicin (DOX), daunorubicin, epirubicin, and idarubicin are highly effective against acute lymphoblastic and myeloblastic leukemias. DOX in particular has been found to have a much broader spectrum, which includes numerous solid tumors, for example, breast cancer, sarcomas, and childhood solid tumors (e.g., Wilms' tumor) in addition to hematological malignancies, for example, leukemias, Hodgkin's disease, and non-Hodgkin's lymphomas [1]. Anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity can occur in an acute or chronic manner. The acute cardiotoxicity within the course of treatment or immediately afterwards including pericarditis-myocarditis or arrhythmias is normally reversible and generally manageable, while the chronic cardiotoxicity, which may manifest even decades after the completion of treatment, is serious and clinically significant, substantially affecting overall morbidity and mortality and requiring long-term therapy. As DOX is an important component of current cancer treatment that generates high level of ROS, this review mainly emphasizes on the DOX-induced cardiotoxicity.
2.1. DOX-Induced Cardiotoxicity
The cumulative dose of administered DOX is an important factor that dictates its cardiotoxicity; it cannot exceed 500 mg/m2 or else the risk of congestive heart failure (CHF) would increase tremendously [7]. The chance of developing CHF increases from <4% at the cumulative dose of 500–550 mg/m2 to <18% or 36% when the cumulative dose of DOX is 551–600 or over 600 mg/m2, respectively. A retrospective analysis revealed that 30-year childhood cancer survivors had a 15-fold higher rate of heart failure and 10-fold higher rate of other cardiovascular diseases when compared to estimated values in their siblings. Cardiac abnormality can be seen as asymptomatic disturbances in cardiac rhythms [8], changes in blood pressure [9], thickening of pericardium [10], cardiac dilation [11], and cardiomyopathy.
Histologically, areas of patchy and interstitial fibrosis with scattered vacuolated cardiomyocytes can be visualized under microscope [11, 12]. There are also partial loss of myofibrils and the degeneration of myocyte vacuoles [13], resulting in the remaining peripheral Z disks without filaments and the large membrane-bound space accordingly. In the nucleus, chromatin disorganization with partial replacement of the chromatin by pale staining fibers and filaments could be observed [11]. Ultimately, these changes would lead to cardiomyocyte death. Since the turnover rate of cardiomyocytes in the heart is very low, approximately 1% at the age of 20 and lower in older ages [14], the progressive loss of myocytes cannot be reversed. Subsequently, the heart loses its ability to function properly. These pathophysiological changes can lead to dilated cardiomyopathy, cardiac hypertrophy, and eventually heart failure.
DOX is particularly harmful to the heart due to its exceptional effects on mitochondria. Heart as a pump that circulates blood throughout the body requires a great amount of energy and thus contains a large amount of energy producing mitochondria. Generally, mitochondria are the site where most of reactive oxygen species (ROS) are produced as a consequence of electrons escaping from electron transport chain and captured by oxygen, rendering it to be the home of superoxide production. However, DOX can drive these ROS production to another level. Enzymes within mitochondria, including NADPH oxidase (also known as NADPH dehydrogenase), cytochrome P-450 reductase, and xanthine oxidase (XO), can transform DOX and other anthracyclines in the form of quinone to semiquinone via one electron reduction of the quinone moiety in ring C [14–17]. This semiquinone can be readily regenerated back to its parental quinone by reacting with oxygen, generating superoxide anion (O2 ∙−), which could be further changed to other ROS or reactive nitrogen species (RNS) [18, 19]. This redox cycling thus aids in amplifying the production of oxidative stress. Apart from mitochondrial enzymes, endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS), which generates nitric oxide (NO), can also affect the ROS production by DOX [20]. Expression and transcription of eNOS were found to be increased after the DOX administration [19, 21]. By binding to eNOS's reductase domain, DOX veers its production towards more O2 ∙− and less nitric oxide (NO).
The nature of cardiac tissue that exhibits low level of antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase makes it more susceptible to ROS generation and accumulation of oxidative stress [22]. Moreover, DOX is known to bind to cardiolipin, a major phospholipid component of heart mitochondrial inner membranes, with high affinity [23–25]. DOX and its major metabolite doxorubicinol (DOXol) are abundantly retained inside cardiac cells, attributable to cardiotoxicity [26, 27].
3. Oxidative Stress
Major mechanism of chemotherapy-induced cardiotoxicity involves the generation of ROS. Elevated ROS that causes cellular damages and alteration responses, referred to as oxidative stress, occurs when the delicate balance of the ROS-generating system and antioxidant defense system was tipped in favor of the former. Immediate systemic oxidative stress and reduced antioxidant status, as demonstrated by the decrease in glutathione (GSH) and total antioxidant capacity of plasma (TRAP) levels, were observed in cancer patients receiving DOX treatment [28]. To discuss the advances in molecular mechanisms underlying chemotherapy-induced cardiotoxicity, an overview of biochemistry of ROS and antioxidants has provided.
Basically, ROS are reactive molecules that contain oxygen atom and are primarily generated either by metabolic process or by physical irradiation as O2 ∙−. The reaction is catalyzed by NADPH oxidase with electron supplied by NADPH as in the following equations:
| (1) |
In mitochondrial electron transport chain, O2 ∙− is also generated when an electron is transferred from NADH to oxygen molecule by NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase or complex I:
| (2) |
O2 ∙− then undergoes a dismutation, a reaction that is accelerated by SOD enzyme, generating less-reactive specie hydrogen peroxide (H2O2):
| (3) |
The H2O2-removing enzymes include catalase and glutathione peroxidase (GPx):
| (4) |
O2 ∙− may react with H2O2 and form the highly reactive hydroxyl radical (∙OH) by Haber-Weiss reaction:
| (5) |
Since the Haber-Weiss reaction is kinetically slow, transition metals such as iron and copper often serve as its catalysts. The iron-catalyzed Haber-Weiss reaction is called Fenton reaction:
| (6) |
Under stress conditions, O2 ∙− facilitates the release of free iron from iron-containing molecules, for example, [4Fe-4S]-containing enzymes, leading to the generation of ∙OH from Fenton reaction. Moreover, O2 ∙− can facilitate the ∙OH production in the reaction by generating ferrous (Fe(II)) from the reduction of ferric (Fe(III)):
| (7) |
With regard to DOX, iron has been implicated in its redox cycling [29, 30]. When DOX was reduced to semiquinone radical, it can form a complex of semiquinone and iron-free radical, which would spontaneously revert back to DOX while generating O2 ∙− [31], and thus it magnifies the generation of DOX-derived ROS. However, under normal situation, iron is sequestered within the cells by ferritin as polynuclear ferric oxyhydroxide [32]. DOX's metabolite DOXol was shown to remove iron from Fe-S cluster of cytoplasmic aconitase, an enzyme in the Krebs cycle, and turn it into cluster-free iron regulatory proteins-1 (IRP-1) [33]. Then, via redox reaction, DOX was regenerated and formed complex with Fe(II), blocking the conversion of IRP-1 back to aconitase [34]. This IRP-1 then bound to iron-responsive elements (IREs) in ferritin mRNA, inhibiting its translation and resulting in the tremendous release of free iron within the cells [35, 36].
In addition to its direct effects on DNA, RNA, proteins, and lipids, ROS can also act as secondary signaling molecules in various pathways that are involved in homeostasis, including cell proliferation and cell death [37, 38]. Thus, it is imperative to maintain the proper level of ROS in the cellular environment. In the heart, oxidative stress could lead to cellular hypertrophy [39], gene expression alterations [40], cell death activation [41], extracellular matrix (ECM) transformation [42], ventricular remodeling [41], and calcium transient perturbation [43], all of which could result in the pathophysiological changes that lead to cardiomyopathy and heart failure.
4. Experimental Models
Similar to other abnormalities, the ideal and most relevant data for human cardiotoxicity should be obtained from suffering patients. However, due to the limitation in obtaining human myocardial biopsy or necropsy and the complication from patients' multidrug regimen, the meaningful information for chemotherapy-induced cardiotoxicity comes mostly from experimental models. The commonly used animals for in vivo studies include mouse, rat, rabbit, pig, and dog. These whole animal studies enable repeated administration of chemotherapeutic agents, mimicking chronic cardiotoxicity in clinical practice. In addition, transgenic animal models with certain gene modification could aid tremendously to study and model cardiotoxicity. For example, Hfe-deficient mice with excess iron stores exhibited increased susceptibility to DOX-induced cardiotoxicity, suggesting the significance of iron in cardiotoxicity [44]. On the other hand, the simplest and most straightforward approach is the use of in vitro cell culture models, including isolated cardiac myocytes, particularly primary neonatal rat cardiomyocytes and less often adult cardiomyocytes, and cardiomyocyte-derived cell lines, for example, H9c2 rat embryonic cardiomyoblasts [45]. These in vitro models offer the advantages of gene manipulation that provides insight into the molecular mechanisms, high throughput, ease of use, and low cost.
5. Molecular Mechanisms of Chemotherapy-Induced Cardiotoxicity
Extensive researches have been conducted to examine the molecular mechanisms of cardiotoxicity induced by chemotherapy, particularly DOX, and oxidative stress was found to be the major contributor to various potential causes that ultimately lead to cardiomyopathy and heart failure. We will summarize the current understanding of ROS in such phenomena and discuss the alterations of key related genes and/or proteins, with emphasis on cellular apoptosis leading to cardiomyopathy.
5.1. Cellular Hypertrophy
Cellular hypertrophy is characterized by an increase in cell size and volume, enhanced protein synthesis, and content and heightened organization of the sarcomere [46, 47]. At the molecular level, there is an induction of cardiac hypertrophic-associated genes such as ventricular myosin light chain-2 (MLC-2v), alpha-myosin heavy chain (α-MHC), and atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) [48]. Major signaling cascades of cardiac hypertrophy include tyrosine kinases (Src and focal adhesion kinase), protein kinase C (PKC), mitogen activated protein kinases (MAPK; ERK1/2, p38, and JNK), calcineurin, PI3K/Akt, and NF-κB, coupling to the activation of transcriptional expression of hypertrophic-associated genes. It is now evident that ROS are capable of direct modulation of these cascades [39, 41, 49–52]. Additionally, ROS were found to activate apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK-1), which in turn stimulates p38 and JNK MAPK as well as NF-κB pathways [53–55]. Merten et al. reported that DOX-induced H9c2 cardiac hypertrophy involved the activation of PI3K/Akt and to a lesser extent calcineurin [56]. The role of oxidative stress in DOX-induced cardiac hypertrophy was supported by the attenuation of DOX-induced hypertrophy and cardiotoxicity in transgenic mice containing high level of cardiac metallothionein, a potent antioxidant [57].
5.2. ECM Remodeling
Microenvironment is crucial to the proper functions of cardiomyocytes. ECM microenvironment provides a platform for cardiomyocytes to attach, align, and orient, thereby facilitating efficient cellular contraction, proper force transduction, and smooth electrical transmission [58]. An alteration in ECM structure or composition would transform the healthy functional heart to the defected one [59–61]. Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) are enzymes that are responsible for the ECM degradation. It has previously been demonstrated that ROS activated MMPs and ECM degradation via the activation of activator protein-1 (AP-1) and NF-κB, leading to the impairment of cardiac functions [62, 63]. Animal studies in mouse and rat showed that MMPs particularly MMP-2 and MMP-9 mediated DOX-induced cardiotoxicity [64–66]. DOX increased MMP-2 and MMP-9 activities through the mechanisms that involved the activation of p38 MAPK and NADPH oxidase, respectively [67]. Further, Nox2 NADPH oxidase was found to be a major source of DOX-derived ROS. Cardiac remodeling induced by DOX was less pronounced in Nox2-deficient mice (Nox2−/−) compared to the wild-type controls [68]. Additionally, DOX induced nitric oxide (NO) in vitro and in vivo [69, 70], which in the presence of O2 ∙− formed peroxynitrite (ONOO−), leading to an activation of precursors of MMPs (pro-MMPs) and ECM remodeling.
5.3. Impaired Cardiac Contraction
Cardiomyocytes (also known as cardiac muscle cells) are myogenic, having an inherent rhythmic contraction and relaxation. For the whole heart to properly pump and propel blood into the circulation, precise control and synchronization of these cells are imperative. Each cardiomyocyte is composed of bundles of myofibrils, which is a chain of several contractile units called sarcomeres. The sarcomeres contain thick (myosin) and thin (actin) myofilaments that process cardiac contraction. In the relaxed state, tropomyosin wrapped around actin filament and covered the myosin-binding site. Calcium ion, generally resides within sarcomeric reticulum, is a key player for myocyte contraction. Once released to cytosol, calcium ions bind to troponin, which is associated with tropomyosin, and shift tropomyosin position on actin filament, exposing the myosin-binding site for myosin head of thick filament to bind to the thin filament and resulting in sarcomere shortening. That being said, what control cardiac contraction are the myofilaments and calcium flux.
DOX could affect the transcription and expression of cardiac specific proteins [11, 71, 72]. GATA4 is a transcription factor critical for regulation of cardiac differentiation, sarcomere synthesis, and cell survival. GATA4 is expressed in the cardiomyocytes where it functions to regulate many cardiospecific genes, including cardiac adriamycin-responsive protein (CARP). DOX-derived ROS downregulated GATA4 binding activity, leading to myofibrillar deterioration, disruption of sarcomere organization, and reduction of contractile function [73, 74].
DOX has been shown to alter calcium homeostasis [75, 76]. This may be, in part, due to the change of ion channel flux and the functional defect of membrane ion pump [77] as a result of lipid peroxidation by DOX-derived ROS. ∙OH and H2O2 can readily attack polyunsaturated fatty acids of the membrane and initiate a redox chain reaction that destroys membrane lipids [78], thereby disturbing the function of membrane-bound protein including mitochondrial calcium channel [17]. Moreover, DOX could directly affect the expression level of important component of sarcomeric reticulum calcium release or uptake channels, for example, ryanodine receptor (RYR2) and sarco-/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase (SERCA2) [79, 80], leading to an impaired calcium handling and subsequent impaired cardiac contraction [81]. It has been reported that DOX modifies the thiol group (–SH) of RYR2 [82, 83]. This modification enhances the probability of RYR2 channel to adopt its open state [84, 85], making cytosol overloaded with calcium ions. Additionally, DOX could increase the activity of voltage-sensitive L-type calcium channel (VSCC) on cardiac cell membrane [86] as well as inhibiting the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger (NCX) on sarcolemmal membrane [87], resulting in calcium overload.
When cytosolic calcium ions were excessive, the relaxed state after contraction would be undermined, and thus the contraction-relaxation cycle of cardiomyocytes is interrupted. DOX's major metabolite DOXol was shown to have more profound effect on contraction-relaxation cycle as compared to DOX [26]. DOXol could inhibit RYR2, Na+/K+ pump on the cell membrane, and proton pump on mitochondria, resulting in the impairment of relaxation [26, 88].
5.4. Cardiac Cell Death
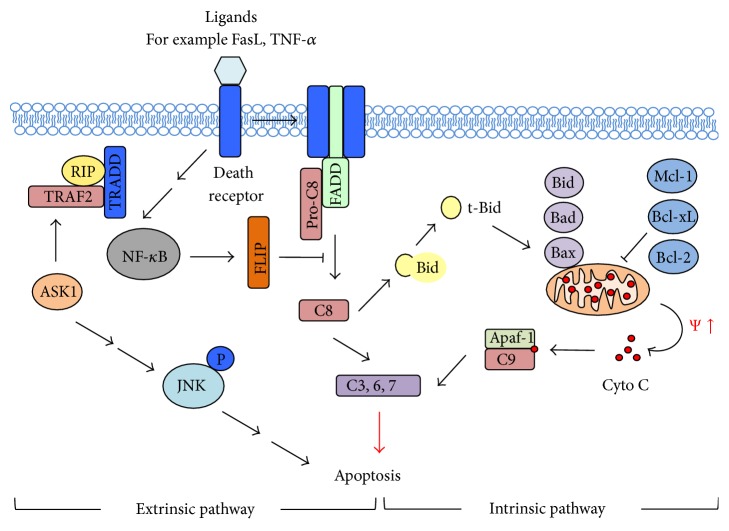
Programmed cell death or apoptosis is a critical cellular process occurring when a cell commits suicide, as it is no longer needed, no longer processes properly or senses the cytotoxic signals. Damage to genetic DNA, proteins, cellular organelles, or membrane integrity that is beyond repair would trigger apoptosis in order to reserve resources and energy for other normal cells and prevent neighboring cells from its death signals. Apoptosis is a tightly regulated process, involving multiple signaling cascades commonly in extrinsic death receptor and intrinsic mitochondrial apoptosis pathways (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
Major pathways of apoptosis. An extrinsic pathway of apoptosis (left) involves the stimulation through binding of death receptor (e.g., FasR and TNFR) to their respective ligands (e.g., FasL and TNF-α), recruiting adaptive proteins such as Fas-associated death-domain (FADD) and pro-caspase-8 (pro-C8), forming death-inducing signaling complex (DISC) and relaying signals to activation of effector caspases such as caspase-3 (C3), C6, and C7. In addition, Bid is also activated, which transduces these death signals to the intrinsic pathway. On the other hand, an intrinsic pathway of apoptosis is induced in response to cellular stresses such as DNA damage and ROS that increase the expression of proapoptotic Bcl-2 family proteins (e.g., Bid, Bad, and Bax), while repressing antiapoptotic Bcl-2 family proteins (e.g., Bcl-2, Bcl-xL, and Mcl-1), leading to an alteration in mitochondrial membrane potential and the release of cytochrome C (Cyto C). Proteins such as Apaf-1 and caspase-9 (C9) are activated, resulting in the formation of an apoptosome, which then stimulate the activation of effector caspases. NF-κB and JNK/ASK-1 also play a role in apoptotic signaling through the regulation of antiapoptotic molecules such as FLIP and Bcl-2.
The death receptor pathway involves the binding of death ligands, for example, Fas ligand (FasL) and TNF-α, to their respective membrane-bound death receptors, for example, Fas receptor or apoptosis antigen-1 (APO-1) or CD95 and TNF-α receptor (TNFR), resulting in the recruitment of secondary proteins that will relay the signals to various proteins mediating the caspase cascade, leading to apoptosis. In particular, when FasL binds to Fas receptor, the receptor oligomerizes and recruits an adaptor protein Fas-associated death-domain (FADD) and pro-caspase-8, assembling the death-inducing signaling complex (DISC) and activating the initiator caspase-8 (FLICE), which in turn activates effector caspase-3 [89]. Caspase-3 catalyzes the cleavage of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP), causing apoptosis as characterized by chromatin condensation, DNA fragmentation, and membrane blebbing [90]. Alternatively, caspase-8 can cleave Bid to become truncated Bid (t-Bid) that will translocate to mitochondria, thus linking the death receptor and mitochondrial pathways [91, 92]. Similar to FasL, the binding of TNF-α to TNFR recruits TNFR-associated death domain protein (TRADD) adaptor protein, which will then recruit either FADD or receptor-interacting protein (RIP). These two pathways result in two different situations that are TRADD/FADD activates caspase-8 and induces apoptosis, while TRADD/RIP/TRAF2 activates NF-κB and prosurvival pathway [93]. NF-κB could induce the expression of antiapoptotic proteins such as FLIP and Bcl-2 [94]. On the other hand, TRAF-2 can activate ASK-1/JNK pathway via an ROS-dependent manner and induce apoptotic signaling cascades [95]. An active phosphorylated JNK can translocate to nucleus and increase the expression of proapoptotic genes. Or else, it can translocate to mitochondria and phosphorylate Bcl-2 to antagonize its activity as well as releasing the cytochrome C and Smac/Diablo (Smac), which is a TRAF2/IAP1 inhibitor.
The mitochondrial pathway relies on the changes in mitochondrial transmembrane potential (ψ), which is a key indicator of mitochondrial membrane permeability. Bcl-2 family proteins includes antiapoptotic proteins, such as Bcl-2, Bcl-XL, and Mcl-1, and proapoptotic proteins, such as Bid, Bad, Bax, Bak, Bok, and Bim. The proapoptotic proteins facilitate the release of cytochrome C from mitochondria by dimerizing and forming transition pores [96]. The released cytochrome C subsequently binds to caspase adaptor molecule Apaf-1 and recruits initiator pro-caspase-9 to form a complex called apoptosome, which activates effector caspase-3. The oligomerization of proapoptotic Bcl-2 family proteins can be prevented by antiapoptotic Bcl-2 family proteins.
When the number of cardiomyocytes available to function in the heart was remarkably reduced, the heart can no longer effectively and efficiently pump blood, sequentially leading to ventricular remodeling and heart failure [97–100]. DOX has been demonstrated to cause cardiomyocyte apoptosis by various means. It can activate mitochondrial apoptosis pathway by disrupting the cardiolipin, an important component of mitochondrial inner membrane [99]. Cardiolipin controls energy metabolism, and thereby its alteration can potentially lead to heart failure [101]. Apoptosis can also be activated by the damage to cellular lipid membrane, DNA, or mitochondrial DNA induced by DOX [102–105]. ROS are believed to be responsible for the apoptotic effect of DOX. An increase in ROS level as measured by electron spin resonance spectroscopy was observed in cardiac cells after exposing to DOX, in agreement with an increase in malondialdehyde, a product of lipid peroxidation driven by ROS [106, 107]. Mitochondrial DNA is particularly vulnerable to DOX toxicity due to its proximity to DOX and sources of ROS generation within mitochondrial membrane [108]. In addition to the amplification of ROS signals, as mentioned earlier, DOX suppressed the antioxidant defense system. DOX reduced the levels and activities of antioxidant GSH, GPx-1, and sulfhydryl groups within enzyme complex as well as the cytosolic SOD, making cells vulnerable to oxidative stress [22, 31, 49, 108–113]. A large amount of O2 ∙− produced within mitochondria cannot pass through its membrane and thus can easily damage mitochondrial DNA that does not have the protective complex chromatin organization like histone proteins and introns and has limited repair capability [114].
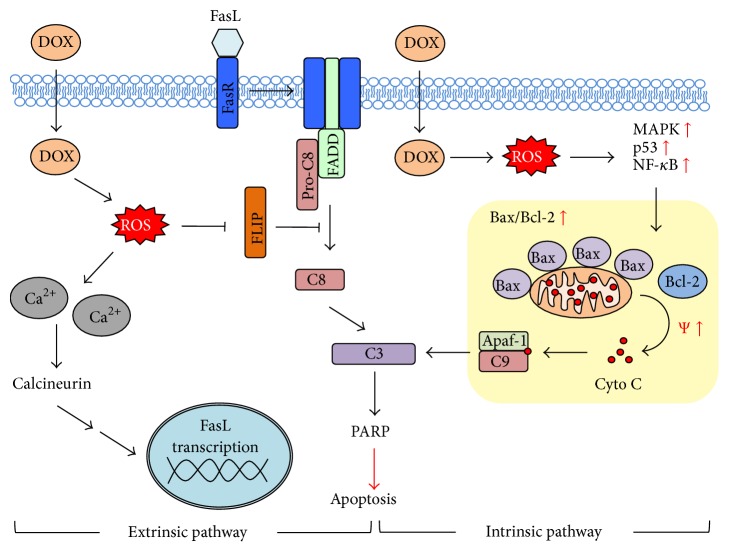
With regard to apoptosis pathways, DOX-derived ROS was reported to activate p53 as well as p38 and JNK MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways, resulting in an imbalance between pro- and anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family proteins, for example, an increase in Bax to Bcl-2 ratio [115, 116] (Figure 2). Such imbalance disrupted mitochondrial membrane potential, causing cytochrome C release. Notably, JNK can also translocate to nucleus after being activated by DOX-derived ROS and phosphorylate c-Jun, that subsequently binds to AP-1 and initiates FasL transcription [95]. Inhibition of FLIP by DOX-derived ROS further rendered cardiac cells to apoptosis induced by FasL, providing another potential mechanism for DOX-mediated apoptosis [117]. Additionally, DOX-derived ROS were shown to cause calcium leakage from sarcoplasmic reticulum, which then activated calcineurin and promoted apoptosis via NFAT/FasL activation or Bcl-XL and Akt pathway inhibition by Bad [118]. Several studies reported that DOX induced the loss of phospholipase C delta-1 (PLCD-1) and PLCD-3 that simultaneously led to cardiomyocyte apoptosis and the development of cardiomyopathy [118, 119]. Additionally, DOX could directly induce the mitochondrial release of cytochrome C and activate caspase-3 or p53 accumulation, leading to the proapoptotic signaling cascades [120, 121].
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of DOX-induced apoptosis and the involvement of ROS. DOX-derived ROS could affect the regulation of calcium homeostasis, resulting in cytosolic calcium (Ca2+) overload that can activate calcineurin and increase the transcription of Fas ligand (FasL). DOX-derived ROS could also inhibit the expression of caspase-8 (C8, also known as FLICE) inhibitory protein FLIP, rendering cells to apoptosis. Additionally, DOX-derived ROS could act as an intrinsic stress that activates mitogen activated protein kinases (MAPK) p38 and JNK and NF-κB pathways as well as intracellular p53 accumulation, leading to an alteration in the ratio of proapoptotic proteins to antiapoptotic proteins (e.g., Bax to Bcl-2), cytochrome C (Cyto C) release, and caspase-9 and -3 (C9/C3) activation.
5.5. Autophagy
The role of autophagy towards cell fate may vary, depending on cellular environment and stimuli. Under normal physiological condition, autophagy enhances cellular function and overall viability by eliminating damaged and/or unnecessary proteins and organelles, while maintaining cellular integrity and inhibiting apoptosis. Under pathological condition, autophagy could either promote cell survival or induce cell death. Several studies demonstrated cardiac autophagy upon DOX administration, as evaluated by an increase of autophagic vacuoles and expression of autophagosome markers [122–127]; however, its precise role in DOX toxicity still remains controversial. Many groups agreed that inhibition of autophagy resulted in a decrease in DOX toxicity [122, 125, 127, 128], in correspondence with a decrease in mitochondrial membrane potential and ROS generation [127]. On the other hand, Kawaguchi et al. and Sishi et al. observed the protective effect of autophagy towards DOX cardiotoxicity [124, 129], likely through the reduction in mitochondrial ROS [129].
6. Preventive Strategies
Cardiotoxicity could be life threatening, and thus several attempts have been made to attenuate and minimize such toxicity induced by chemotherapy, particularly the most common DOX. Clinical practice suggests close monitoring and evaluation of patient risks for developing complications after treatment. Early detection and immediate proper medication could reverse the condition in time that minimizes cardiotoxic effects. Analogues of DOX with some changes in molecular structures, including epirubicin, idarubicin, and mitoxantrone, have been developed and became another appealing alternative as studies in cancer patients showed comparable drug efficacy with lower cardiotoxicity to conventional DOX [130–132]. Liposomal DOX is another strategy to reduce the drug toxicity as encapsulating DOX was restricted to the site with tight capillary junction like in the heart's wall, while readily penetrating through the more fragile tumor vasculature [133].
Dexrazoxane is the only FDA-approved cardioprotective agent against cardiotoxicity induced by anthracyclines. Due to the potential risk of developing secondary tumors and interfering effect of dexrazoxane towards anticancer activity of DOX, Dexrazoxane clinical use is limited only to some certain groups of patients [134, 135], namely, adult patients with breast cancer who have received cumulative dose of at least 300 mg/m2 doxorubicin or 540 mg/m2 epirubicin.
7. Conclusions and Perspectives
Adverse effects of chemotherapeutic agents limit their clinical benefits. For instance, DOX, one of the most effective and frequently used chemotherapeutic agents to treat a variety of cancers, poses serious problem of cardiotoxicity when administered over certain critical dosage. Several studies demonstrate that ROS are the main contributor of DOX-induced cardiotoxicity. DOX-derived ROS affected various major cellular processes leading to cardiomyopathy and eventually congestive heart failure, including cellular hypertrophy, ECM remodeling, impaired cardiac contraction, and remarkable cardiac cell death. Specifically to cell death, DOX-derived ROS served as a secondary signaling molecule engaged in numerous pathways of apoptosis. The protective effect of antioxidants against DOX-induced apoptosis in cell culture and animal models support the notion that DOX-induced cardiotoxicity is caused mainly by ROS. Other chemotherapeutic agents that induce ROS and high degree of cardiotoxicity include all other anthracyclines, alkylating agents, and vinca alkaloids. However, the nonprotective effect of antioxidants against cardiotoxicity induced by DOX and other chemotherapeutic agents was observed, particularly in chronic studies using animal models or in clinical trials. Such failure of antioxidants may be due to (i) a complexity of ROS network that partly interruptions or inhibitions by antioxidants cannot totally reverse its effects and (ii) a variety of different mechanisms governing in chemotherapy-induced cardiotoxicity. A key to effective preventive strategies is a better understanding of molecular mechanisms of chemotherapy-induced cardiotoxicity which requires the development of more predictive experimental models. Much of our understanding on chemotherapy-induced cardiotoxicity was based on animal models and neonatal rat cardiomyocyte culture, thus strengthening the notion that the experimental models that mimic human heart physiology and allow mechanistic studies are currently lacking. The newly developed human induced pluripotent stem- (iPS-) derived cardiomyocytes or three-dimensional (3D) organ culture is promising and might provide us with the different facet of this complicated problem. In addition, the drug concentrations and regimen used during each preventive study should faithfully reflect the real scenario of drug administration during cancer therapy so that its results could be better appreciated and reliable.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Grants from Thailand Research Fund (RTA 488-0007) and the Commission on Higher Education (CHE-RES-RG-49).
Abbreviations
- α-MHC:
Alpha-myosin heavy chain
- 3D:
Three-dimensional
- ANP:
Atrial natriuretic peptide
- AP-1:
Activator protein-1
- APO-1:
Apoptosis antigen-1
- ASK-1:
Apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1
- C3, C8, C9:
Caspase-3, caspase-8, caspase-9
- CARP:
Cardiac adriamycin-responsive protein
- CHF:
Congestive heart failure
- Cyto C:
Cytochrome C
- DISC:
Death-inducing signaling complex
- DOX:
Doxorubicin
- DOXol:
Doxorubicinol
- ECM:
Extracellular matrix
- FADD:
Fas-associated death-domain
- Fe(II):
Ferrous
- Fe(III):
Ferric
- eNOS:
Endothelial nitric oxide synthase
- FasL:
Fas ligand
- GPx:
Glutathione peroxidase
- GSH:
Glutathione
- H2O2:
Hydrogen peroxide
- iPS:
Induced pluripotent stem
- IREs:
Iron-responsive elements
- IRP-1:
Iron regulatory proteins-1
- MAPK:
Mitogen activated protein kinases
- MLC-2v:
Ventricular myosin light chain-2
- MMPs:
Matrix metalloproteinases
- NO:
Nitric oxide
- O2∙−:
Superoxide anion
- ∙OH:
Hydroxyl radical
- ONOO−:
Peroxynitrite
- PARP:
Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase
- PKC:
Protein kinase C
- PLCD:
Phospholipase C delta
- pro-MMPs:
Precursors of matrix metalloproteinases
- RIP:
Receptor-interacting protein
- RNS:
Reactive nitrogen species
- ROS:
Reactive oxygen species
- RYR2:
Ryanodine receptor
- SERCA2:
Sarco-/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase
- SOD:
Superoxide dismutase
- t-Bid:
Truncated Bid
- TNFR:
TNF-α receptor
- TRADD:
TNFR-associated death domain protein
- VSCC:
Voltage-sensitive L-type calcium channel.
Conflict of Interests
No potential conflict of interests was disclosed.
References
- 1.Kufe D. W., Holland J. F., Frei E. American Cancer Society: Cancer Medicine. Hamilton, Canada: BC Decker; 2003. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Hershman D. L., McBride R. B., Eisenberger A., Wei Y. T., Grann V. R., Jacobson J. S. Doxorubicin, cardiac risk factors, and cardiac toxicity in elderly patients with diffuse B-cell non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2008;26(19):3159–3165. doi: 10.1200/jco.2007.14.1242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Gianni L., Munzone E., Capri G., et al. Paclitaxel by 3-hour infusion in combination with bolus doxorubicin in women with untreated metastatic breast cancer: high antitumor efficacy and cardiac effects in a dose-finding and sequence-finding study. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 1995;13(11):2688–2699. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1995.13.11.2688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Eisenhauer E. A., Vermorken J. B. The taxoids. Comparative clinical pharmacology and therapeutic potential. Drugs. 1998;55(1):5–30. doi: 10.2165/00003495-199855010-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Giantris A., Abdurrahman L., Hinkle A., Asselin B., Lipshultz S. E. Anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity in children and young adults. Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology. 1998;27(1):53–68. doi: 10.1016/S1040-8428(97)10007-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Pai V. B., Nahata M. C. Cardiotoxicity of chemotherapeutic agents. Incidence, treatment and prevention. Drug Safety. 2000;22(4):263–302. doi: 10.2165/00002018-200022040-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Lefrak E. A., Pitha J., Rosenheim S., Gottlieb J. A. A clinicopathologic analysis of adriamycin cardiotoxicity. Cancer. 1973;32(2):302–314. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197308)32:2<302::AID-CNCR2820320205>3.0.CO;2-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ferrans V. J., Clark J. R., Zhang J., Yu Z.-X., Herman E. H. Pathogenesis and prevention of doxorubicin cardiomyopathy. Tsitologiya. 1997;39(10):928–936. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Medrano F. L., Munoz A. S., Sánchez V. S., Pérez-Herrero J. R. C. Cardiotoxicity of 5-fluorouracil: ischemia or myocardial toxicity? Revista Clínica Española. 2001;201(2):106–107. doi: 10.1016/s0014-2565(01)71381-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Lestuzzi C. Neoplastic pericardial disease: old and current strategies for diagnosis and management. World Journal of Cardiology. 2010;2(9):p. 270. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v2.i9.270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Takemura G., Fujiwara H. Doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy from the cardiotoxic mechanisms to management. Progress in Cardiovascular Diseases. 2007;49(5):330–352. doi: 10.1016/j.pcad.2006.10.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Buja L. M., Ferrans V. J., Mayer R. J., Roberts W. C., Henderson E. S. Cardiac ultrastructural changes induced by daunorubicin therapy. Cancer. 1973;32(4):771–788. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197310)32:4lt;771::aid-cncr282032040762;3.0.co;2-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Billingham M. E., Mason J. W., Bristow M. R., Daniels J. R. Anthracycline cardiomyopathy monitored by morphologic changes. Cancer Treatment Reports. 1978;62(6):865–872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Bachur N. R., Gordon S. L., Gee M. V., Kon H. NADPH cytochrome P-450 reductase activation of quinone anticancer agents to free radicals. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 1979;76(2):954–957. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Berlin V., Haseltine W. A. Reduction of adriamycin to a semiquinone-free radical by NADPH cytochrome P-450 reductase produces DNA cleavage in a reaction mediated by molecular oxygen. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1981;256(10):4747–4756. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Davies K. J. A., Doroshow J. H. Redox cycling of anthracyclines by cardiac mitochondria. I. Anthracycline radical formation by NADH dehydrogenase. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1986;261(7):3060–3067. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Schimmel K. J. M., Richel D. J., van den Brink R. B. A., Guchelaar H. Complications of treatment: cardiotoxicity of cytotoxic drugs. Cancer Treatment Reviews. 2004;30:181–191. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2003.07.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Doroshow J. H. Effect of anthracycline antibiotics on oxygen radical formation in rat heart. Cancer Research. 1983;43(2):460–472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Vásquez-Vivar J., Martasek P., Hogg N., Masters B. S. S., Pritchard K. A., Jr., Kalyanaraman B. Endothelial nitric oxide synthase-dependent superoxide generation from adriamycin. Biochemistry. 1997;36(38):11293–11297. doi: 10.1021/bi971475e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Weinstein D. M., Mihm M. J., Bauer J. A. Cardiac peroxynitrite formation and left ventricular dysfunction following doxorubicin treatment in mice. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 2000;294(1):396–401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Liu B., Li H., Qu H., Sun B. Nitric oxide synthase expressions in ADR-induced cardiomyopathy in rats. Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. 2006;39(6):759–765. doi: 10.5483/bmbrep.2006.39.6.759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Doroshow J. H., Locker G. Y., Myers C. E. Enzymatic defenses of the mouse heart against reactive oxygen metabolites. Alterations produced by doxorubicin. The Journal of Clinical Investigation. 1980;65(1):128–135. doi: 10.1172/jci109642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Parker M. A., King V., Howard K. P. Nuclear magnetic resonance study of doxorubicin binding to cardiolipin containing magnetically oriented phospholipid bilayers. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 2001;1514(2):206–216. doi: 10.1016/s0005-2736(01)00371-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Hatch G. M., McClarty G. Regulation of cardiolipin biosynthesis in H9c2 cardiac myoblasts by cytidine 5′-triphosphate. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1996;271(42):25810–25816. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.42.25810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Goormaghtigh E., Chatelain P., Caspers J., Ruysschaert J. M. Evidence of a specific complex between adriamycin and negatively-charged phospholipids. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 1980;597(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90145-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Olson R. D., Mushlin P. S., Brenner D. E., et al. Doxorubicin cardiotoxicity may be caused by its metabolite, doxorubicinol. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 1988;85(10):3585–3589. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Stewart D. J., Grewaal D., Green R. M., et al. Concentrations of doxorubicin and its metabolites in human autopsy heart and other tissues. Anticancer Research. 1993;13:1945–1952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Panis C., Herrera A. C. S. A., Victorino V. J., et al. Oxidative stress and hematological profiles of advanced breast cancer patients subjected to paclitaxel or doxorubicin chemotherapy. Breast Cancer Research and Treatment. 2012;133(1):89–97. doi: 10.1007/s10549-011-1693-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Thorn C. F., Oshiro C., Marsh S., et al. Doxorubicin pathways: pharmacodynamics and adverse effects. Pharmacogenetics and Genomics. 2011;21(7):440–446. doi: 10.1097/fpc.0b013e32833ffb56. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Minotti G., Recalcati S., Menna P., Salvatorelli E., Corna G., Cairo G. Doxorubicin cardiotoxicity and the control of iron metabolism: quinone-dependent and independent mechanisms. Methods in Enzymology. 2004;378:340–361. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(04)78025-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Chen Y., Jungsuwadee P., Vore M., Butterfield D. A., Clair D. K. S. Collateral damage in cancer chemotherapy: oxidative stress in nontargeted tissues. Molecular Interventions. 2007;7(3):147–156. doi: 10.1124/mi.7.3.6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Theil E. C., Eichorn G. L., Marzili L. Ferritin: structure, function and regulation in iron binding proteins without cofactors and sulfur clusters. Annual Review of Biochemistry. 1987;56:289–315. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.001445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Minotti G., Ronchi R., Salvatorelli E., Menna P., Cairo G. Doxorubicin irreversibly inactivates iron regulatory proteins 1 and 2 in cardiomyocytes: evidence for distinct metabolic pathways and implications for iron-mediated cardiotoxicity of antitumor therapy. Cancer Research. 2001;61(23):8422–8428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Minotti G., Cairo G., Monti E. Role of iron in anthracycline cardiotoxicity: new tunes for an old song? The FASEB Journal. 1999;13(2):199–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Minotti G., Recalcati S., Mordente A., et al. The secondary alcohol metabolite of doxorubicin irreversibly inactivates aconitase/iron regulatory protein-1 in cytosolic fractions from human myocardium. The FASEB Journal. 1998;12:541–552. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.12.7.541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Minotti G., Mancuso C., Frustaci A., et al. Paradoxical inhibition of cardiac lipid peroxidation in cancer patients treated with doxorubicin: Pharmacologic and molecular reappraisal of anthracycline cardiotoxicity. The Journal of Clinical Investigation. 1996;98(3):650–661. doi: 10.1172/jci118836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Devasagayam T. P. A., Tilak J. C., Boloor K. K., Sane K. S., Ghaskadbi S. S., Lele R. D. Free radicals and antioxidants in human health: current status and future prospects. Journal of Association of Physicians of India. 2004;52:794–804. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Deavall D. G., Martin E. A., Horner J. M., Roberts R. Drug-induced oxidative stress and toxicity. Journal of Toxicology. 2012;2012:13. doi: 10.1155/2012/645460.645460 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Sabri A., Hughie H. H., Lucchesi P. A. Regulation of hypertrophic and apoptotic signaling pathways by reactive oxygen species in cardiac myocytes. Antioxidants and Redox Signaling. 2003;5(6):731–740. doi: 10.1089/152308603770380034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Siwik D. A., Tzortzis J. D., Pimental D. R., et al. Inhibition of copper-zinc superoxide dismutase induces cell growth, hypertrophic phenotype, and apoptosis in neonatal rat cardiac myocytes in vitro. Circulation Research. 1999;85(2):147–153. doi: 10.1161/01.res.85.2.147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Kwon S. H., Pimentel D. R., Remondino A., Sawyer D. B., Colucci W. S. H2O2 regulates cardiac myocyte phenotype via concentration-dependent activation of distinct kinase pathways. Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology. 2003;35(6):615–621. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2828(03)00084-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Siwik D. A., Pagano P. J., Colucci W. S. Oxidative stress regulates collagen synthesis and matrix metalloproteinase activity in cardiac fibroblasts. The American Journal of Physiology—Cell Physiology. 2001;280(1):C53–C60. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.2001.280.1.C53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Dhalla N. S., Temsah R. M., Netticadan T. Role of oxidative stress in cardiovascular diseases. Journal of Hypertension. 2000;18(6):655–673. doi: 10.1097/00004872-200018060-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Miranda C. J., Makui H., Soares R. J., et al. Hfe deficiency increases susceptibility to cardiotoxicity and exacerbates changes in iron metabolism induced by doxorubicin. Blood. 2003;102(7):2574–2580. doi: 10.1182/blood-2003-03-0869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Šimůnek T., Štěrba M., Popelová O., Adamcová M., Hrdina R., Gerši V. Anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity: overview of studies examining the roles of oxidative stress and free cellular iron. Pharmacological Reports. 2009;61(1):154–171. doi: 10.1016/s1734-1140(09)70018-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Frey N., Katus H. A., Olson E. N., Hill J. A. Hypertrophy of the heart: a new therapeutic target? Circulation. 2004;109(13):1580–1589. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.0000120390.68287.bb. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Mouli S., Nanayakkara G. R., Fu R., et al. The role of frataxin in doxorubicin-mediated cardiac hypertrophy. The FASEB Journal. 2014;28(1, supplement 648.6) doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00182.2015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Karagiannis T. C., Lin A. J. E., Ververis K., et al. Trichostatin A accentuates doxorubicin-induced hypertrophy in cardiac myocytes. Aging. 2010;2(10):659–668. doi: 10.18632/aging.100203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Li J.-M., Gall N. P., Grieve D. J., Chen M., Shah A. M. Activation of NADPH oxidase during progression of cardiac hypertrophy to failure. Hypertension. 2002;40(4):477–484. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.0000032031.30374.32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Date M. O., Morita T., Yamashita N., et al. The antioxidant N-2-mercaptopropionyl glycine attenuates left ventricular hypertrophy in in vivo murine pressure-overload model. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 2002;39(5):907–912. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(01)01826-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Higuchi Y., Otsu K., Nishida K., et al. Involvement of reactive oxygen species-mediated NF-κB activation in TNF-α-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology. 2002;34(2):233–240. doi: 10.1006/jmcc.2001.1505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Pimentel D. R., Amin J. K., Xiao L., et al. Reactive oxygen species mediate amplitude-dependent hypertrophic and apoptotic responses to mechanical stretch in cardiac myocytes. Circulation Research. 2001;89(5):453–460. doi: 10.1161/hh1701.096615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Hirotani S., Otsu K., Nishida K., et al. Involvement of nuclear factor-κB and apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 in G-protein-coupled receptor agonist-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. Circulation. 2002;105(4):509–515. doi: 10.1161/hc0402.102863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Nakamura K., Fushimi K., Kouchi H., et al. Inhibitory effects of antioxidants on neonatal rat cardiac myocyte hypertrophy induced by tumor necrosis factor-alpha and angiotensin II. Circulation. 1998;98(8):794–799. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.98.8.794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Izumiya Y., Kim S., Izumi Y., et al. Apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 plays a pivotal role in angiotensin II-induced cardiac hypertrophy and remodeling. Circulation Research. 2003;93(9):874–883. doi: 10.1161/01.res.0000100665.67510.f5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Merten K. E., Jiang Y., Feng W., Kang Y. J. Calcineurin activation is not necessary for doxorubicin-induced hypertrophy in H9c2 embryonic rat cardiac cells: involvement of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase-akt pathway. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 2006;319(2):934–940. doi: 10.1124/jpet.106.108845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Sun X., Zhou Z., Kang Y. J. Attenuation of doxorubicin chronic toxicity in metallothionein-overexpressing transgenic mouse heart. Cancer Research. 2001;61(8):3382–3387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Spreeuwel A. V., Bax N., Bouten C. The relevance of extracellular matrix structure and composition in engineering the diseased cardiac microenvironment. Tissue Engineering & Modeling. 2014;2(1) [Google Scholar]
- 59.McCain M. L., Yuan H., Pasqualini F. S., Campbell P. H., Parker K. K. Matrix elasticity regulates the optimal cardiac myocyte shape for contractility. American Journal of Physiology—Heart and Circulatory Physiology. 2014;306(11):H1525–H1539. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00799.2013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Goetzenich A., Hatam N., Zernecke A., et al. Alteration of matrix metalloproteinases in selective left ventricular adriamycin-induced cardiomyopathy in the pig. Journal of Heart and Lung Transplantation. 2009;28(10):1087–1093. doi: 10.1016/j.healun.2009.06.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Nikitovic D., Juranek I., Wilks M. F., Tzardi M., Tsatsakis A., Tzanakakis G. N. Anthracycline-dependent cardiotoxicity and extracellular matrix remodeling. CHEST Journal. 2014;146(4):p. 1123. doi: 10.1378/chest.14-0460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Mann D. L., Spinale F. G. Activation of matrix metalloproteinases in the failing human heart: breaking the tie that binds. Circulation. 1998;98(17):1699–1702. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.98.17.1699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Spinale F. G., Coker M. L., Thomas C. V., Walker J. D., Mukherjee R., Hebbar L. Time-dependent changes in matrix metalloproteinase activity and expression during the progression of congestive heart failure: relation to ventricular and myocyte function. Circulation Research. 1998;82(4):482–495. doi: 10.1161/01.res.82.4.482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Ivanová M., Dovinová I., Okruhlicová L., et al. Chronic cardiotoxicity of doxorubicin involves activation of myocardial and circulating matrix metalloproteinases in rats. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica. 2012;33(4):459–469. doi: 10.1038/aps.2011.194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Kizaki K., Ito R., Okada M., et al. Enhanced gene expression of myocardial matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9 after acute treatment with doxorubicin in mice. Pharmacological Research. 2006;53(4):341–346. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2006.01.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Bai P., Mabley J., Liaudet L., Virág L., Szabó C., Pacher P. Matrix metalloproteinase activation is an early event in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Oncology Reports. 2004;11(2):505–508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Spallarossa P., Altieri P., Garibaldi S., et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 are induced differently by doxorubicin in H9c2 cells: the role of MAP kinases and NAD(P)H oxidase. Cardiovascular Research. 2006;69(3):736–745. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2005.08.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Zhao Y., McLaughlin D., Robinson E., et al. Nox2 NADPH oxidase promotes pathologic cardiac remodeling associated with doxorubicin chemotherapy. Cancer Research. 2010;70(22):9287–9297. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-2664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Mukhopadhyay P., Rajesh M., Bátkai S., et al. Role of superoxide, nitric oxide, and peroxynitrite in doxorubicin-induced cell death in vivo and in vitro. The American Journal of Physiology: Heart and Circulatory Physiology. 2009;296(5):H1466–H1483. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00795.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Okamoto T., Akaike T., Sawa T., Miyamoto Y., van der Vliet A., Maeda H. Activation of matrix metalloproteinases by peroxynitrite-induced protein s-glutathiolation via disulfide s-oxide formation. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2001;276(31):29596–29602. doi: 10.1074/jbc.m102417200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Ito H., Miller S. C., Billingham M. E., et al. Dexorubicin selectively inhibits muscle gene expression in cardiac muscle cells in vivo and in vitro. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 1990;87(11):4275–4279. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Jeyaseelan R., Poizat C., Wu H.-Y., Kedes L. Molecular mechanisms of doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy. Selective suppression of Reiske iron-sulfur protein, ADP/ATP translocase, and phosphofructokinase genes is associated with ATP depletion in rat cardiomyocytes. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1997;272(9):5828–5832. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.9.5828. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Kim Y., Ma A.-G., Kitta K., et al. Anthracycline-induced suppression of GATA-4 transcription factor: implication in the regulation of cardiac myocyte apoptosis. Molecular Pharmacology. 2003;63(2):368–377. doi: 10.1124/mol.63.2.368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Aries A., Paradis P., Lefebvre C., Schwartz R. J., Nemer M. Essential role of GATA-4 in cell survival and drug-induced cardiotoxicity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2004;101(18):6975–6980. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0401833101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Takahashi S.-S., Denvir M. A., Harder L., et al. Effects of in vitro and in vivo exposure to doxorubicin (adriamycin) on caffeine-induced Ca2+ release from sarcoplasmic reticulum and contractile protein function in 'chemically-skinned' rabbit ventricular trabeculae. Japanese Journal of Pharmacology. 1998;76(4):405–413. doi: 10.1254/jjp.76.405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Dodd D. A., Atkinson J. B., Olson R. D., et al. Doxorubicin cardiomyopathy is associated with a decrease in calcium release channel of the sarcoplasmic reticulum in a chronic rabbit model. The Journal of Clinical Investigation. 1993;91(4):1697–1705. doi: 10.1172/jci116379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Kourie J. I. Interaction of reactive oxygen species with ion transport mechanisms. The American Journal of Physiology—Cell Physiology. 1998;275(1):C1–C24. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1998.275.1.C1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Mylonas C., Kouretas D. Lipid peroxidation and tissue damage. In Vivo. 1999;13(3):295–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Arai M., Tomaru K., Takizawa T., et al. Sarcoplasmic reticulum genes are selectively down-regulated in cardiomyopathy produced by doxorubicin in rabbits. Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology. 1998;30(2):243–254. doi: 10.1006/jmcc.1997.0588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Kaplan P., Babusikova E., Lehotsky J., Dobrota D. Free radical-induced protein modification and inhibition of Ca2+-ATPase of cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry. 2003;248(1-2):41–47. doi: 10.1023/a:1024145212616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Arai M., Yoguchi A., Takizawa T., et al. Mechanism of doxorubicin-induced inhibition of sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase gene transcription. Circulation Research. 2000;86(1):8–14. doi: 10.1161/01.res.86.1.8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Zima A. V., Blatter L. A. Redox regulation of cardiac calcium channels and transporters. Cardiovascular Research. 2006;71(2):310–321. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2006.02.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Xu L., Eu J. P., Meissner G., Stamler J. S. Activation of the cardiac calcium release channel (Ryanodoine receptor) by poly-S-nitrosylation. Science. 1998;279(5348):234–237. doi: 10.1126/science.279.5348.234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Holmberg S. R. M., Williams A. J. Patterns of interaction between anthraquinone drugs and the calcium-release channel from cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum. Circulation Research. 1990;67(2):272–283. doi: 10.1161/01.res.67.2.272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Saeki K., Obi I., Ogiku N., Shigekawa M., Imagawa T., Matsumoto T. Doxorubicin directly binds to the cardiac-type ryanodine receptor. Life Sciences. 2002;70(20):2377–2389. doi: 10.1016/s0024-3205(02)01524-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Keung E. C., Toll L., Ellis M., Jensen R. A. L-type cardiac calcium channels in doxorubicin cardiomyopathy in rats morphological, biochemical, and functional correlations. Journal of Clinical Investigation. 1991;87(6):2108–2113. doi: 10.1172/JCI115241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Caroni P., Villani F., Carafoli E. The cardiotoxic antibiotic doxorubicin inhibits the Na+/Ca2+ exchange of dog heart sarcolemmal vesicles. FEBS Letters. 1981;130(2):184–186. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)81115-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Boucek R. J., Jr., Olson R. D., Brenner D. E., Ogunbunmi E. M., Inui M., Fleischer S. The major metabolite of doxorubicin is a potent inhibitor of membrane-associated ion pumps: a correlative study of cardiac muscle with isolated membrane fractions. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1987;262(33):15851–15856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Lavrik I. N., Krammer P. H. Regulation of CD95/Fas signaling at the DISC. Cell Death and Differentiation. 2012;19(1):36–41. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2011.155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Porter A. G., Jänicke R. U. Emerging roles of caspase-3 in apoptosis. Cell Death and Differentiation. 1999;6(2):99–104. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4400476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Kantari C., Walczak H. Caspase-8 and Bid: caught in the act between death receptors and mitochondria. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 2011;1813(4):558–563. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2011.01.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Kaufmann T., Strasser A., Jost P. J. Fas death receptor signalling: roles of Bid and XIAP. Cell Death & Differentiation. 2012;19(1):42–50. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2011.121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Van Herreweghe F., Festjens N., Declercq W., Vandenabeele P. Tumor necrosis factor-mediated cell death: to break or to burst, that's the question. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences. 2010;67(10):1567–1579. doi: 10.1007/s00018-010-0283-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Wajant H., Scheurich P. TNFR1-induced activation of the classical NF-κB pathway. The FEBS Journal. 2011;278(6):862–876. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2011.08015.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Dhanasekaran D. N., Reddy E. P. JNK signaling in apoptosis. Oncogene. 2008;27(48):6245–6251. doi: 10.1038/onc.2008.301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Brunelle J. K., Letai A. Control of mitochondrial apoptosis by the Bcl-2 family. Journal of Cell Science. 2009;122(4):437–441. doi: 10.1242/jcs.031682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Sawyer D. B., Peng X., Chen B., Pentassuglia L., Lim C. C. Mechanisms of anthracycline cardiac injury: can we identify strategies for cardioprotection? Progress in Cardiovascular Diseases. 2010;53(2):105–113. doi: 10.1016/j.pcad.2010.06.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Kotamraju S., Konorev E. A., Joseph J., Kalyanaraman B. Doxorubicin-induced apoptosis in endothelial cells and cardiomyocytes is ameliorated by nitrone spin traps and ebselen. Role of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2000;275(43):33585–33592. doi: 10.1074/jbc.m003890200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Wang L., Ma W., Markovich R., Chen J.-W., Wang P. H. Regulation of cardiomyocyte apoptotic signaling by insulin-like growth factor I. Circulation Research. 1998;83(5):516–522. doi: 10.1161/01.res.83.5.516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Arola O. J., Saraste A., Pulkki K., Kallajoki M., Parvinen M., Voipio-Pulkki L. M. Acute doxorubicin cardiotoxicity involves cardiomyocyte apoptosis. Cancer Research. 2000;60(7):1789–1792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Houtkooper R. H., Vaz F. M. Cardiolipin, the heart of mitochondrial metabolism. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences. 2008;65(16):2493–2506. doi: 10.1007/s00018-008-8030-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Thollon C., Iliou J. P., Cambarrat C., Robin F., Vilaine J. P. Nature of the cardiomyocyte injury induced by lipid hydroperoxides. Cardiovascular Research. 1995;30(5):648–655. doi: 10.1016/0008-6363(95)00075-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Rathore N., John S., Kale M., Bhatnagar D. Lipid peroxidation and antioxidant enzymes in isoproterenol induced oxidative stress in rat tissues. Pharmacological Research. 1998;38(4):297–303. doi: 10.1006/phrs.1998.0365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Hemnani T., Parihar M. S. Reactive oxygen species and oxidative DNA damage. Indian Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology. 1998;42(4):440–452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Suematsu N., Tsutsui H., Wen J., et al. Oxidative stress mediates tumor necrosis factor-α-induced mitochondrial DNA damage and dysfunction in cardiac myocytes. Circulation. 2003;107(10):1418–1423. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.0000055318.09997.1f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Costa L., Malatesta V., Morazzoni F., Scotti R., Monti E., Paracchini L. Direct detection of paramagnetic species in adriamycin perfused rat hearts. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 1988;153(1):275–280. doi: 10.1016/S0006-291X(88)81218-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Singal P. K., Pierce G. N. Adriamycin stimulates low-affinity Ca2+ binding and lipid peroxidation but depresses myocardial function. American Journal of Physiology—Heart and Circulatory Physiology. 1986;250(3):H419–H425. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1986.250.3.H419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Singal P. K., Segstro R. J., Singh R. P., Kutryk M. J. Changes in lysosomal morphology and enzyme activities during the development of adriamycin-induced cardiomyopathy. Canadian Journal of Cardiology. 1985;1(2):139–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Serrano J., Palmeira C. M., Kuehl D. W., Wallace K. B. Cardioselective and cumulative oxidation of mitochondrial DNA following subchronic doxorubicin administration. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 1999;1411(1):201–205. doi: 10.1016/s0005-2728(99)00011-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Olson R. D., MacDonald J. S., van Boxtel C. J., et al. Regulatory role of glutathione and soluble sulfhydryl groups in the toxicity of adriamycin. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 1980;215(2):450–454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Pereira G. C., Silva A. M., Diogo C. V., Carvalho F. S., Monteiro P., Oliveira P. J. Drug-induced cardiac mitochondrial toxicity and protection: from doxorubicin to carvedilol. Current Pharmaceutical Design. 2011;17(20):2113–2129. doi: 10.2174/138161211796904812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Odom A. L., Hatwig C. A., Stanley J. S., Benson A. M. Biochemical determinants of adriamycin toxicity in mouse liver, heart and intestine. Biochemical Pharmacology. 1992;43(4):831–836. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(92)90250-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Abd El-Gawad H. M., El-Sawalhi M. M. Nitric oxide and oxidative stress in brain and heart of normal rats treated with doxorubicin: role of aminoguanidine. Journal of Biochemical and Molecular Toxicology. 2004;18(2):69–77. doi: 10.1002/jbt.20013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Wallace D. C. Mitochondrial defects in cardiomyopathy and neuromuscular disease. American Heart Journal. 2000;139(2):S70–S85. doi: 10.1067/mhj.2000.103934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Venkatakrishnan C. D., Tewari A. K., Moldovan L., et al. Heat shock protects cardiac cells from doxorubicin-induced toxicity by activating p38 MAPK and phosphorylation of small heat shock protein 27. The American Journal of Physiology—Heart and Circulatory Physiology. 2006;291(6):H2680–H2691. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00395.2006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Ghosh J., Das J., Manna P., Sil P. C. The protective role of arjunolic acid against doxorubicin induced intracellular ROS dependent JNK-p38 and p53-mediated cardiac apoptosis. Biomaterials. 2011;32(21):4857–4866. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.03.048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Nitobe J., Yamaguchi S., Okuyama M., et al. Reactive oxygen species regulate FLICE inhibitory protein (FLIP) and susceptibility to Fas-mediated apoptosis in cardiac myocytes. Cardiovascular Research. 2003;57(1):119–128. doi: 10.1016/S0008-6363(02)00646-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Lien Y.-C., Noel T., Liu H., Stromberg A. J., Chen K.-C., St. Clair D. K. Phospholipase C-δ1 is a critical target for tumor necrosis factor receptor-mediated protection against adriamycin-induced cardiac injury. Cancer Research. 2006;66(8):4329–4338. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.can-05-3424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Nakamura Y., Kanemaru K., Kojima R., et al. Simultaneous loss of phospholipase Cδ1 and phospholipase Cδ3 causes cardiomyocyte apoptosis and cardiomyopathy. Cell Death and Disease. 2014;5(5. article e1215) doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Childs A. C., Phaneuf S. L., Dirks A. J., Phillips T., Leeuwenburgh C. Doxorubicin treatment in vivo causes cytochrome c release and cardiomyocyte apoptosis, as well as increased mitochondrial efficiency, superoxide dismutase activity, and Bcl-2:Bax ratio. Cancer Research. 2002;62(16):4592–4598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Ueno M., Kakinuma Y., Yuhki K.-I., et al. Doxorubicin induces apoptosis by activation of caspase-3 in cultured cardiomyocytes in vitro and rat cardiac ventricles in vivo. Journal of Pharmacological Sciences. 2006;101(2):151–158. doi: 10.1254/jphs.FP0050980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Lu L., Wu W., Yan J., Li X., Yu H., Yu X. Adriamycin-induced autophagic cardiomyocyte death plays a pathogenic role in a rat model of heart failure. International Journal of Cardiology. 2009;134(1):82–90. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2008.01.043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Dimitrakis P., Romay-Ogando M.-I., Timolati F., Suter T. M., Zuppinger C. Effects of doxorubicin cancer therapy on autophagy and the ubiquitin-proteasome system in long-term cultured adult rat cardiomyocytes. Cell and Tissue Research. 2012;350(2):361–372. doi: 10.1007/s00441-012-1475-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Kawaguchi T., Takemura G., Kanamori H., et al. Prior starvation mitigates acute doxorubicin cardiotoxicity through restoration of autophagy in affected cardiomyocytes. Cardiovascular Research. 2012;96(3):456–465. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvs282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Kobayashi S., Volden P., Timm D., Mao K., Xu X., Liang Q. Transcription factor GATA4 inhibits doxorubicin-induced autophagy and cardiomyocyte death. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2010;285(1):793–804. doi: 10.1074/jbc.m109.070037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Smuder A. J., Kavazis A. N., Min K., Powers S. K. Doxorubicin-induced markers of myocardial autophagic signaling in sedentary and exercise trained animals. Journal of Applied Physiology. 2013;115(2):176–185. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00924.2012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Zhang Y., Meng C., Zhang X., et al. Ophiopogonin D attenuates doxorubicin-induced autophagic cell death by relieving mitochondrial damage in vitro and in vivo . The Journal of Pharmacology & Experimental Therapeutics. 2014;352(1):166–174. doi: 10.1124/jpet.114.219261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Xu X., Chen K., Kobayashi S., Timm D., Liang Q. Resveratrol attenuates doxorubicin-induced cardiomyocyte death via inhibition of p70 S6 kinase 1-mediated autophagy. The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 2012;341(1):183–195. doi: 10.1124/jpet.111.189589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Sishi B. J. N., Loos B., van Rooyen J., Engelbrecht A.-M. Autophagy upregulation promotes survival and attenuates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Biochemical Pharmacology. 2013;85(1):124–134. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2012.10.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Hortobagyi G. N., Yap H.-Y., Kau S. W., et al. A comparative study of doxorubicin and epirubicin in patients with metastatic breast cancer. American Journal of Clinical Oncology: Cancer Clinical Trials. 1989;12(1):57–62. doi: 10.1097/00000421-198902000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Weiss R. B. The anthracyclines: will we ever find a better doxorubicin? Seminars in Oncology. 1992;19(6):670–686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Smith L. A., Cornelius V. R., Plummer C. J., et al. Cardiotoxicity of anthracycline agents for the treatment of cancer: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. BMC Cancer. 2010;10, article 337 doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Gabizon A. A. Stealth liposomes and tumor targeting: one step further in the quest for the magic bullet. Clinical Cancer Research. 2001;7(2):223–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Tebbi C. K., London W. B., Friedman D., et al. Dexrazoxane-associated risk for acute myeloid leukemia/myelodysplastic syndrome and other secondary malignancies in pediatric Hodgkin's disease. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2007;25(5):493–500. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2005.02.3879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Swain S. M., Whaley F. S., Gerber M. C., et al. Cardioprotection with dexrazoxane for doxorubicin-containing therapy in advanced breast cancer. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 1997;15(4):1318–1332. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1997.15.4.1318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]