Abstract
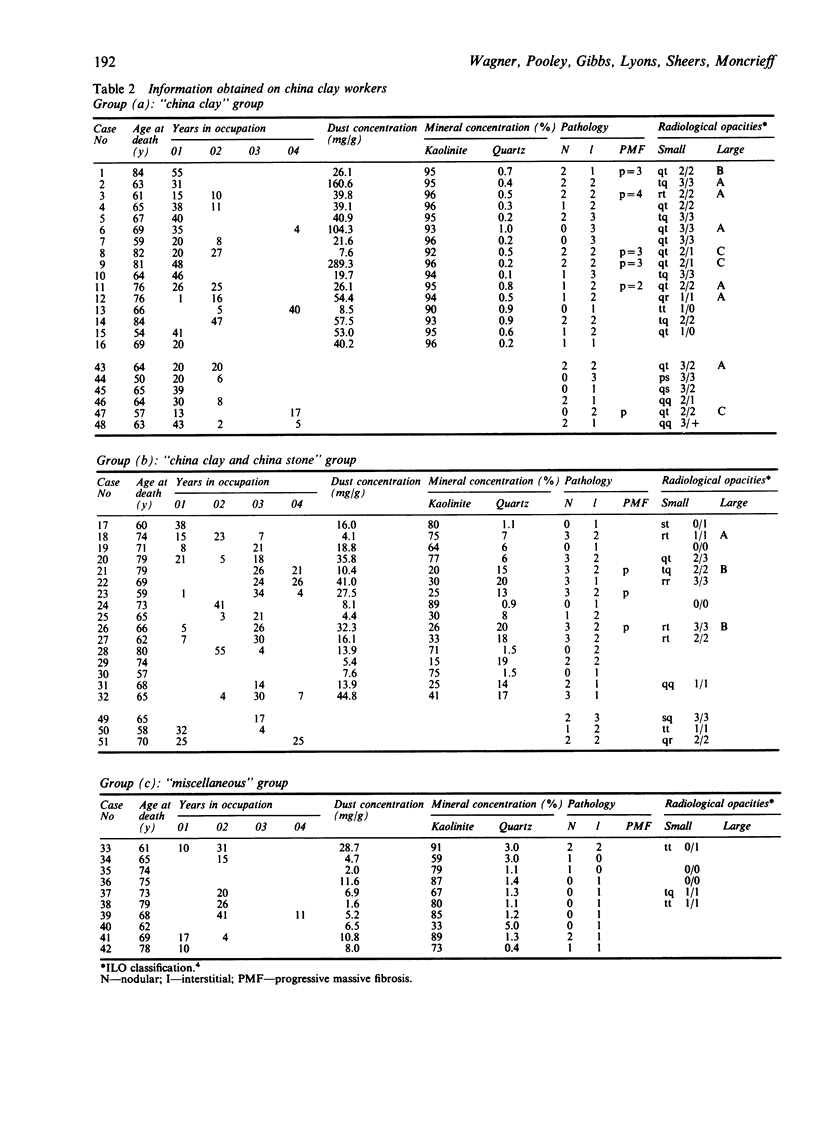
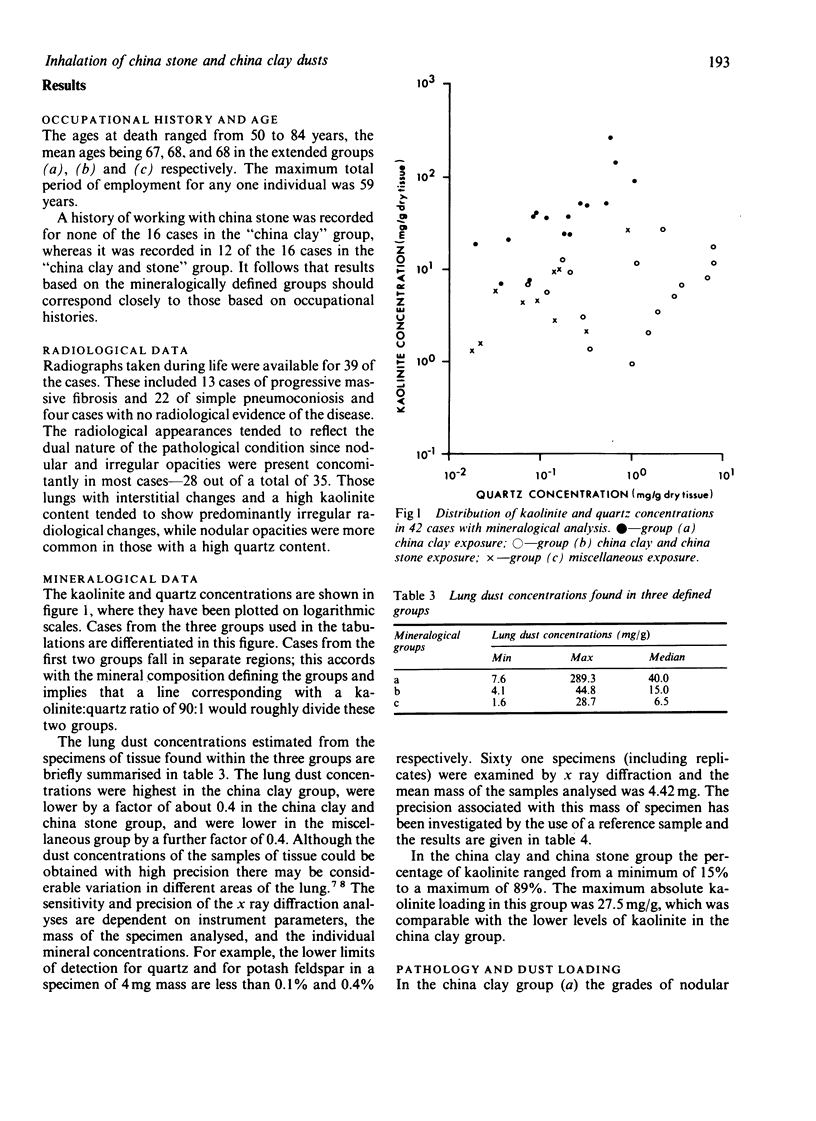
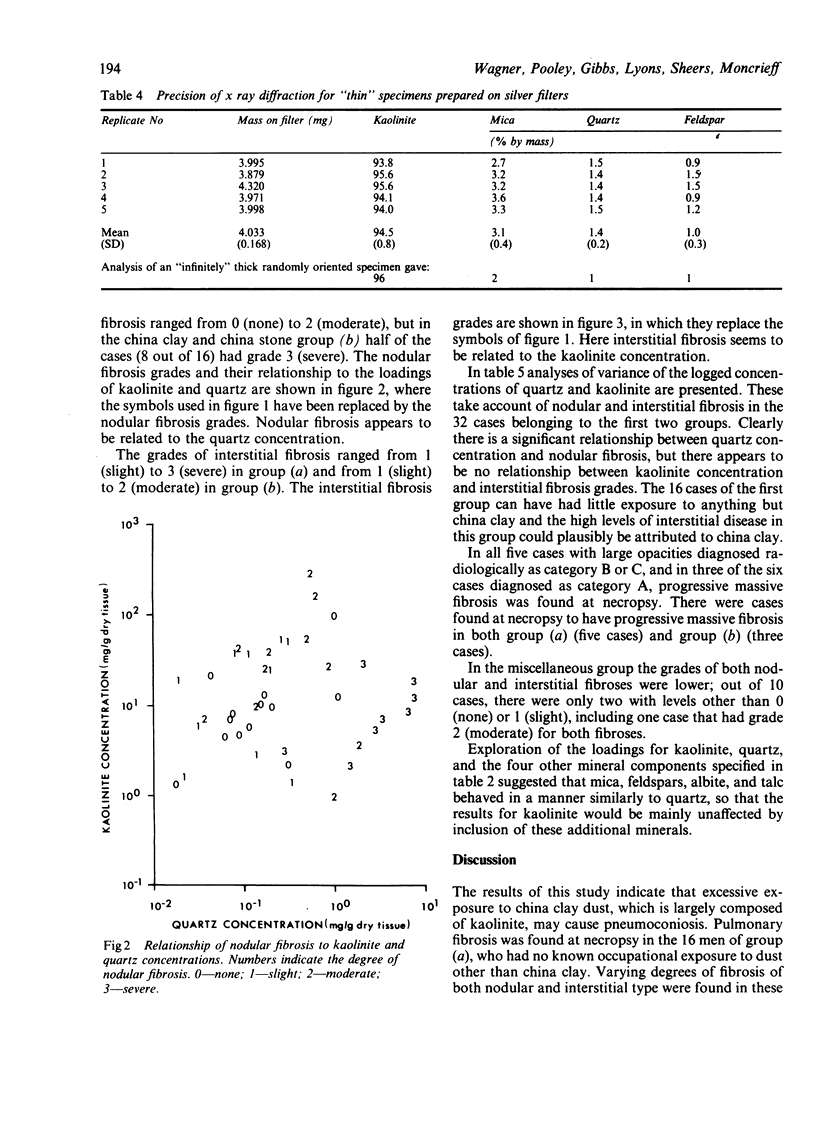
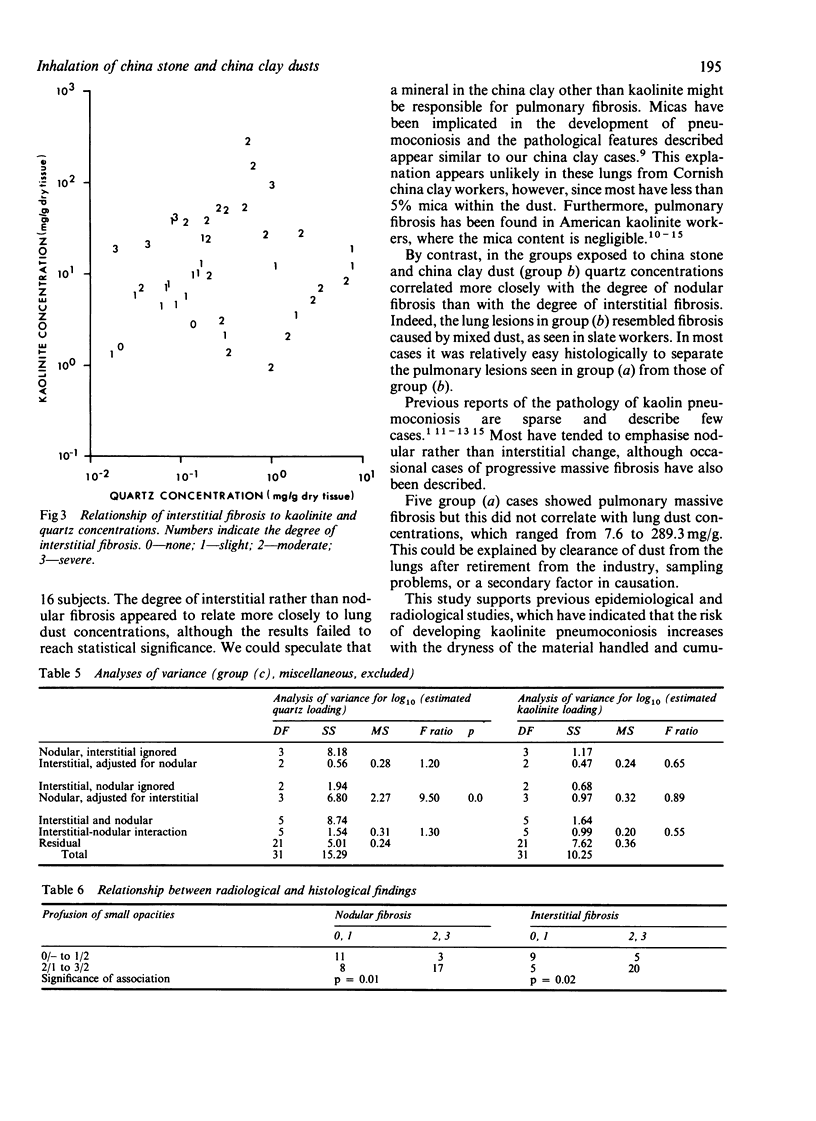
A combined clinical, radiological, pathological, and mineralogical study was undertaken on 62 cases referred to the Medical Research Council Pneumoconiosis Unit by the Cardiff Pneumoconiosis Panel as Cornish china clay workers. Considerable pathological lesions were found in the lungs, both nodular and interstitial fibroses being present. Some men had worked with china stone but others had worked entirely with china clay. Nodular fibrosis appeared to be related to a high quartz content of the dust recovered from the lung, whereas among those with a high content of kaolinite dust in the lungs interstitial fibrosis was observed.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altekruse E. B., Chaudhary B. A., Pearson M. G., Morgan W. K. Kaolin dust concentrations and pneumoconiosis at a kaolin mine. Thorax. 1984 Jun;39(6):436–441. doi: 10.1136/thx.39.6.436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft A. E., Wagner J. C., Seal E. M., Lyons J. P., Campbell M. J. Irregular opacities in coalworkers' pneumoconiosis--correlation with pulmonary function and pathology. Ann Occup Hyg. 1982;26(1-4):767–787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies D., Cotton R. Mica pneumoconiosis. Br J Ind Med. 1983 Feb;40(1):22–27. doi: 10.1136/oem.40.1.22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDENFIELD R. W. A clinical and roentgenological study of kaolin workers. Arch Environ Health. 1960 Nov;1:392–403. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1960.10662713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOUGH J., HALE L. W., KING E. J., NAGELSCHMIDT G. Pneumoconiosis of kaolin workers. Br J Ind Med. 1956 Oct;13(4):251–259. doi: 10.1136/oem.13.4.251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy T., Rawlings W., Jr, Baser M., Tockman M. Pneumoconiosis in Georgia kaolin workers. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 Feb;127(2):215–220. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.127.2.215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LYNCH K. M., McIVER F. A. Pneumoconiosis from exposure to kaolin dust kaolinosis. Am J Pathol. 1954 Nov-Dec;30(6):1117–1127. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapenas D. J., Gale P. N. Kaolin pneumoconiosis. A case report. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1983 Dec;107(12):650–653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapenas D., Gale P., Kennedy T., Rawlings W., Jr, Dietrich P. Kaolin pneumoconiosis. Radiologic, pathologic, and mineralogic findings. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Aug;130(2):282–288. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.130.2.282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldham P. D. Pneumoconiosis in Cornish china clay workers. Br J Ind Med. 1983 May;40(2):131–137. doi: 10.1136/oem.40.2.131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHEERS G. PREVALENCE OF PNEUMOCONIOSIS IN CORNISH KAOLIN WORKERS. Br J Ind Med. 1964 Jul;21:218–225. doi: 10.1136/oem.21.3.218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salt P. D. Quantitative mineralogical analysis of small samples of china clay using x ray diffractometry. Br J Ind Med. 1985 Sep;42(9):635–641. doi: 10.1136/oem.42.9.635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



