Fig. 7. A 77-year-old male who has plaque ulceration.
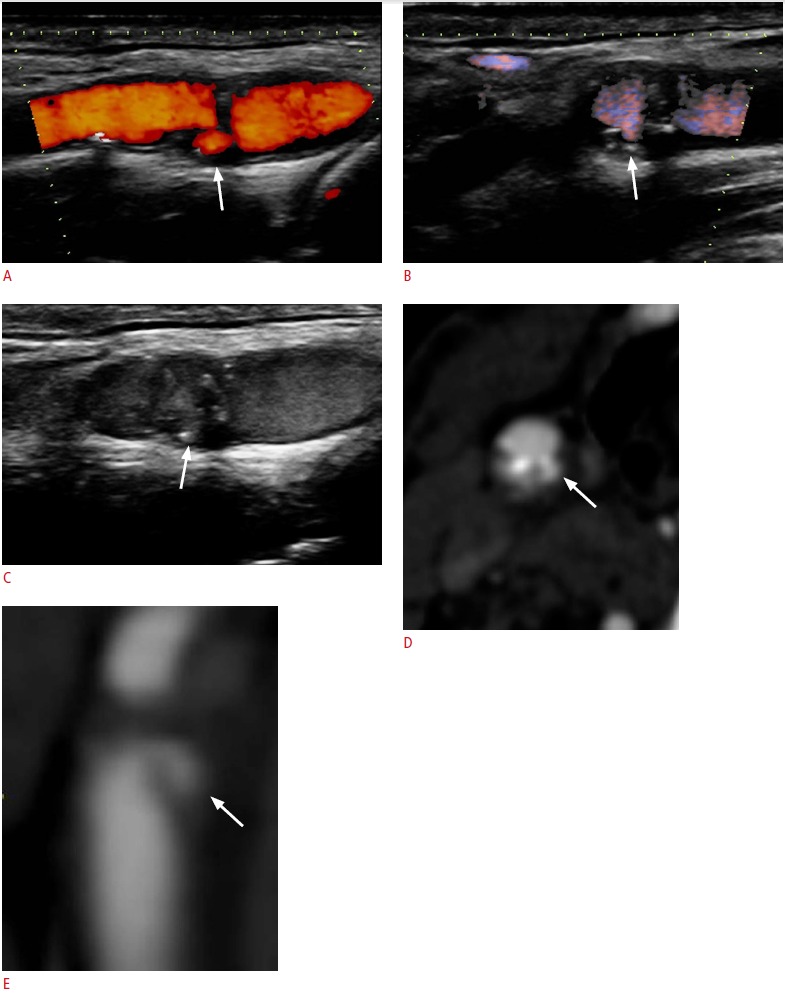
A, B. Power Doppler imaging (A) and directional-eFLOW imaging (B) adequately identify an ulcer in the carotid plaque located in the distal carotid wall (arrows). However, there are interruptions in the color flow signals due to calcifications. C. The contrast-enhanced ultrasonography examination provided better delineation of the carotid plaque surface, the blood flow, and better filling of the ulcer (arrow). D, E. Contrast-enhanced multidetector computed tomographic angiography confirmed the presence of an ulcerated plaque (arrows) in both transverse (D) and sagittal reformatted planes (E).
