Abstract
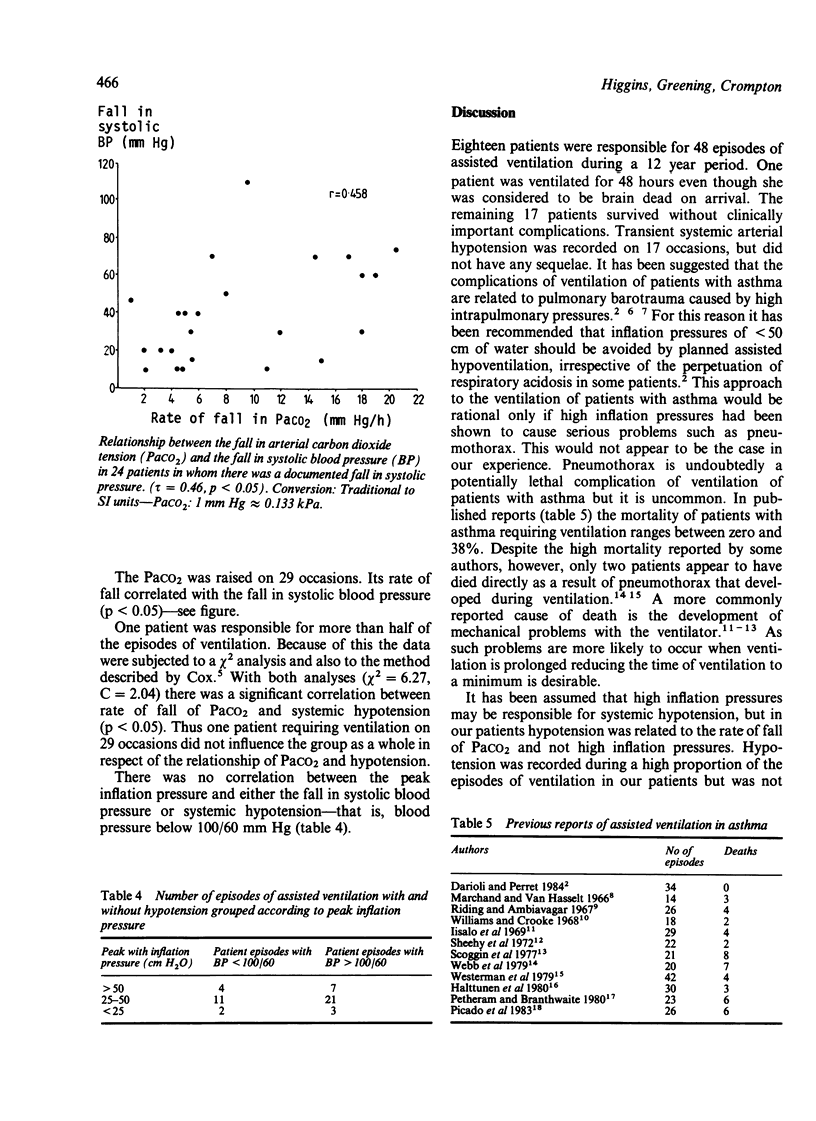
During the period 1973-85 assisted ventilation was used for the treatment of severe asthma on 48 occasions in 18 patients (one patient was ventilated 29 times). On each occasion arterial blood gas abnormalities were restored to normal as quickly as possible irrespective of peak inflation pressures. One patient was thought to be brain dead on transfer from another hospital but was ventilated for 48 hours while this diagnosis was confirmed. There was one episode of mediastinal emphysema. There were no other complications apart from transient hypotension (blood pressure less than 100/60 mm Hg), which occurred on 17 occasions but did not have any sequelae. There was no relationship between hypotension and inflation pressure but there was an association between hypotension and rate of fall of arterial carbon dioxide tension. It is concluded that the risks of barotrauma during the ventilation of patients with severe asthma are theoretical or extremely small. Rapid correction of respiratory acidosis abolishes hypercapnic respiratory drive, allowing ventilation without use of muscle relaxants. It may also enable a shorter duration of ventilation, thus decreasing the likelihood of complications.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Darioli R., Perret C. Mechanical controlled hypoventilation in status asthmaticus. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Mar;129(3):385–387. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.129.3.385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fergusson R. J., Crompton G. K., Grant I. W. Severe acute asthma--a problem patient. Br J Dis Chest. 1982 Jul;76(3):301–302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halttunen P. K., Luomanmäki K., Takkunen O., Viljanen A. A. Management of severe bronchial asthma in an intensive care unit. Ann Clin Res. 1980 Jun;12(3):109–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iisalo E. U., Iisalo E. I., Vapaavuori M. J. Prolonged artificial ventilation in severe status asthmaticus. Acta Med Scand. 1969 Jan-Feb;185(1-2):51–55. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1969.tb07297.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karetzky M. S. Asthma mortality: an analysis of one years experience, review of the literature and assessment of current modes of therapy. Medicine (Baltimore) 1975 Nov;54(6):471–484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEONHARDT K. O. Resuscitation of the moribund asthmatic and emphysematous patient. N Engl J Med. 1961 Apr 20;264:785–790. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196104202641602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchand P., Van Hasselt H. Last-resort treatment of status asthmaticus. Lancet. 1966 Jan 29;1(7431):227–230. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)90050-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petheram I. S., Branthwaite M. A. Mechanical ventilation for pulmonary disease. A six year survey. Anaesthesia. 1980 May;35(5):467–473. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.1980.tb03824.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picado C., Montserrat J. M., Roca J., Rodríguez-Roisín R., Estopá R., Xaubet A., Marín A., Agustí-Vidal A. Mechanical ventilation in severe exacerbation of asthma. Study of 26 cases with six deaths. Eur J Respir Dis. 1983 Feb;64(2):102–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riding W. D., Ambiavagar M. Resuscitation of the moribund asthmatic. Postgrad Med J. 1967 Apr;43(498):234–243. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.43.498.234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scoggin C. H., Sahn S. A., Petty T. L. Status asthmaticus. A nine-year experience. JAMA. 1977 Sep 12;238(11):1158–1162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheehy A. F., DiBenedetto R., Lefrak S., Lyons H. A. Treatment of status asthmaticus. A report of 70 episodes. Arch Intern Med. 1972 Jul;130(1):37–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb A. K., Bilton A. H., Hanson G. C. Severe bronchial asthma requiring ventilation. A review of 20 cases and advice on management. Postgrad Med J. 1979 Mar;55(641):161–170. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.55.641.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westerman D. E., Benatar S. R., Potgieter P. D., Ferguson A. D. Identification of the high-risk asthmatic patient. Experience with 39 patients undergoing ventilation for status asthmaticus. Am J Med. 1979 Apr;66(4):565–572. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(79)91165-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams N. E., Crooke J. W. The practical management of severe status asthmaticus. Lancet. 1968 May 18;1(7551):1081–1083. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)91426-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



