Abstract
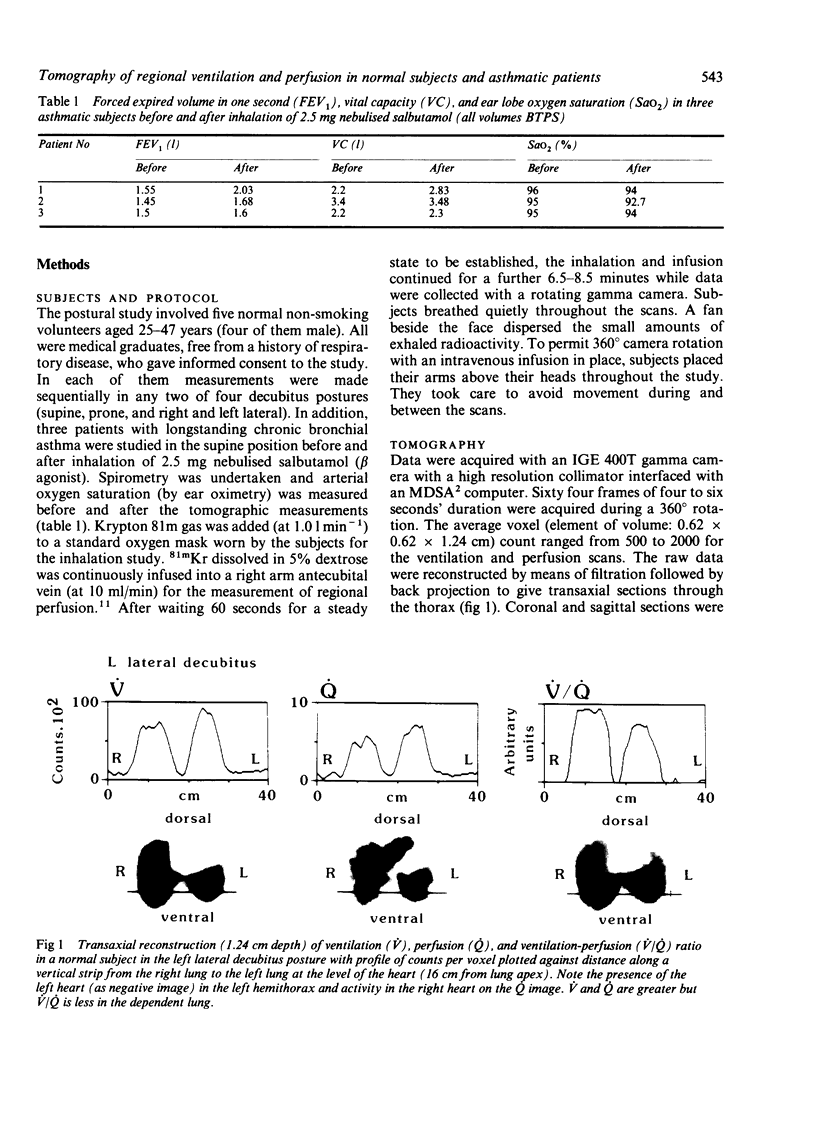
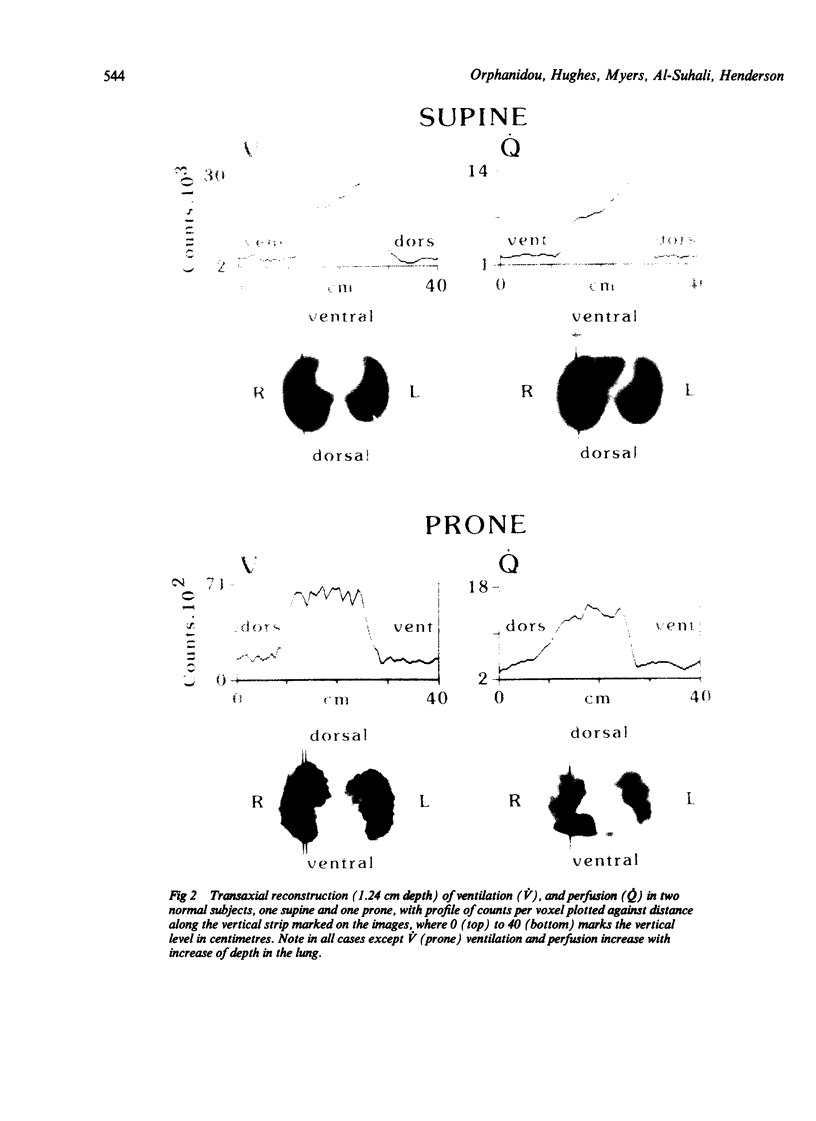
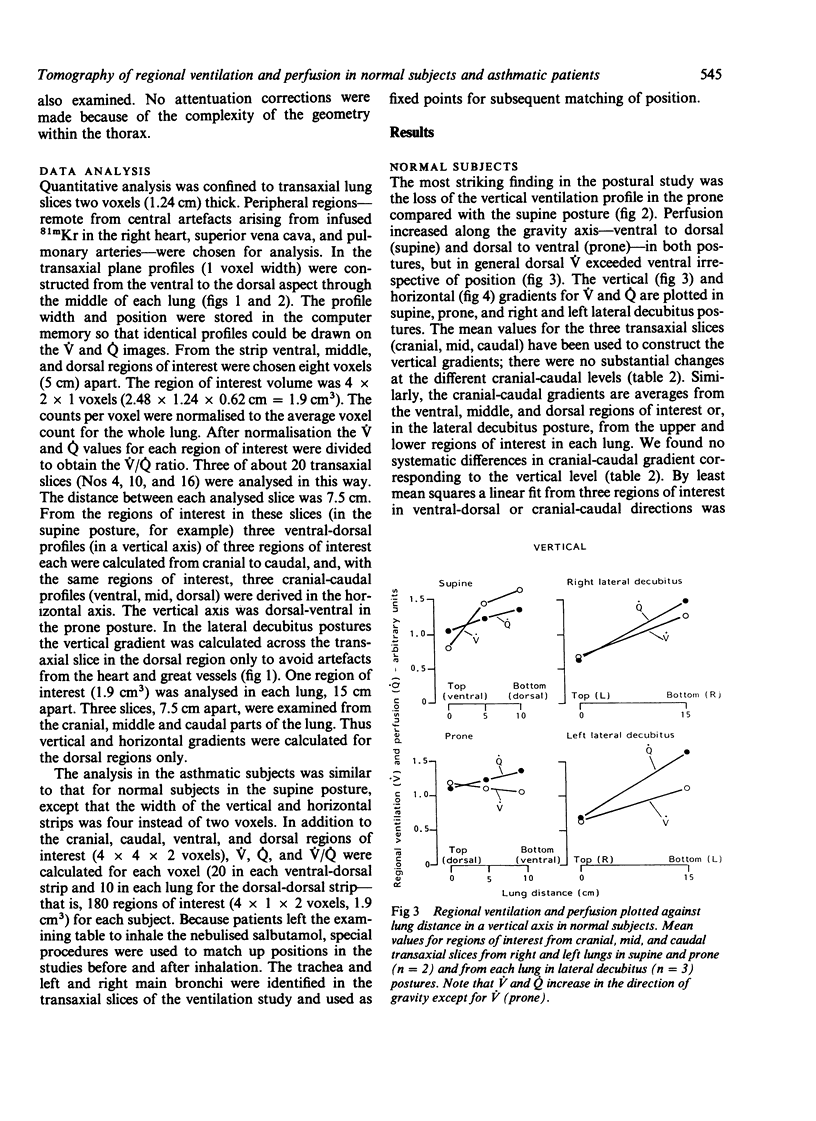
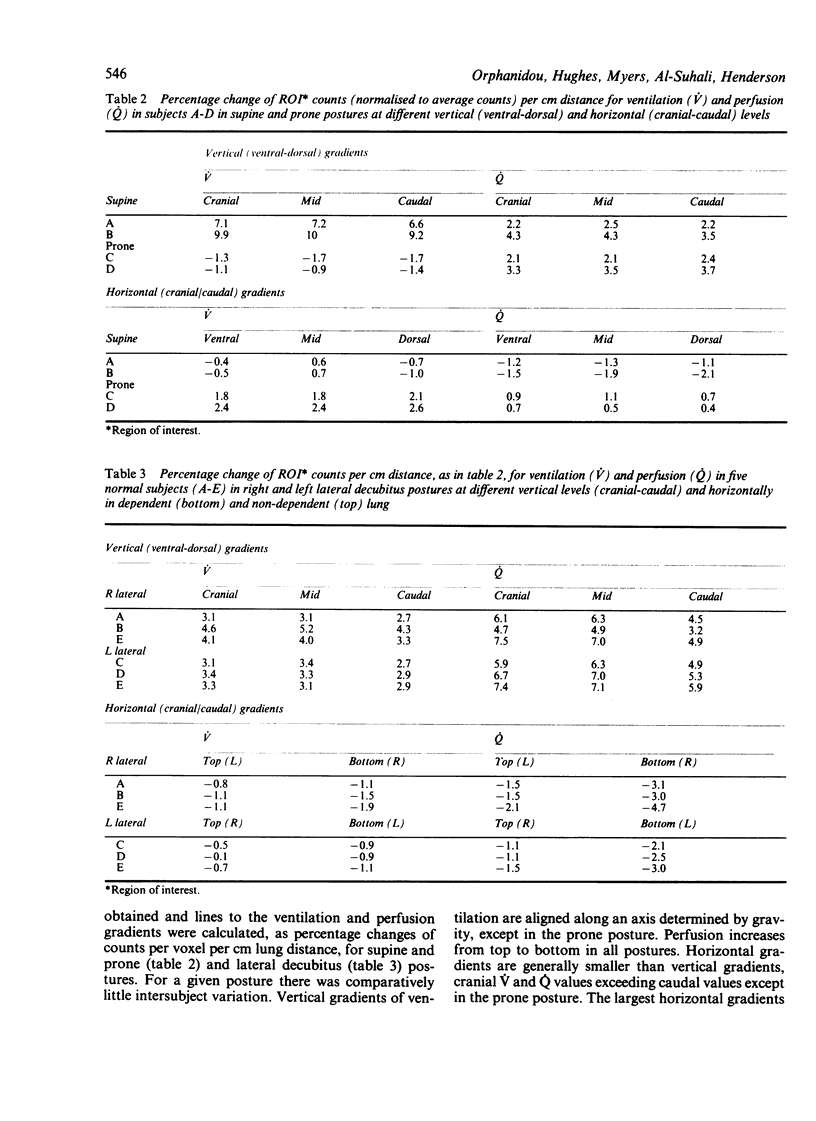
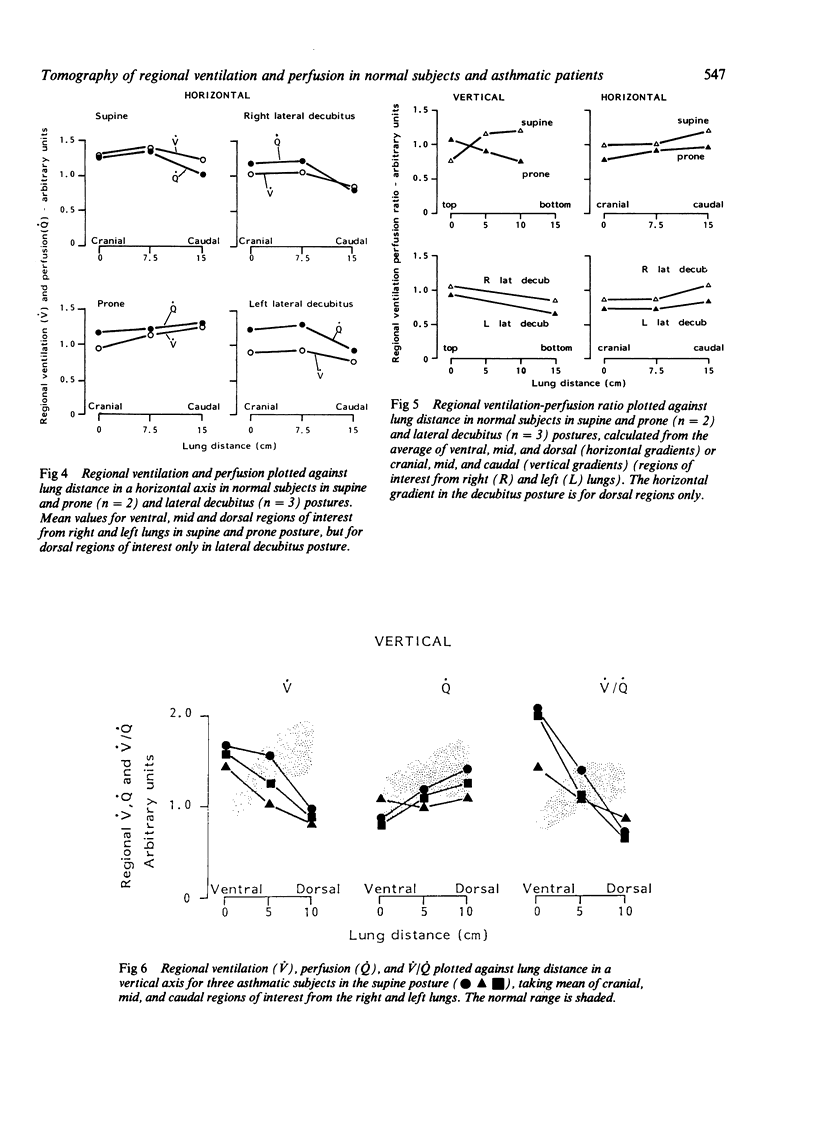
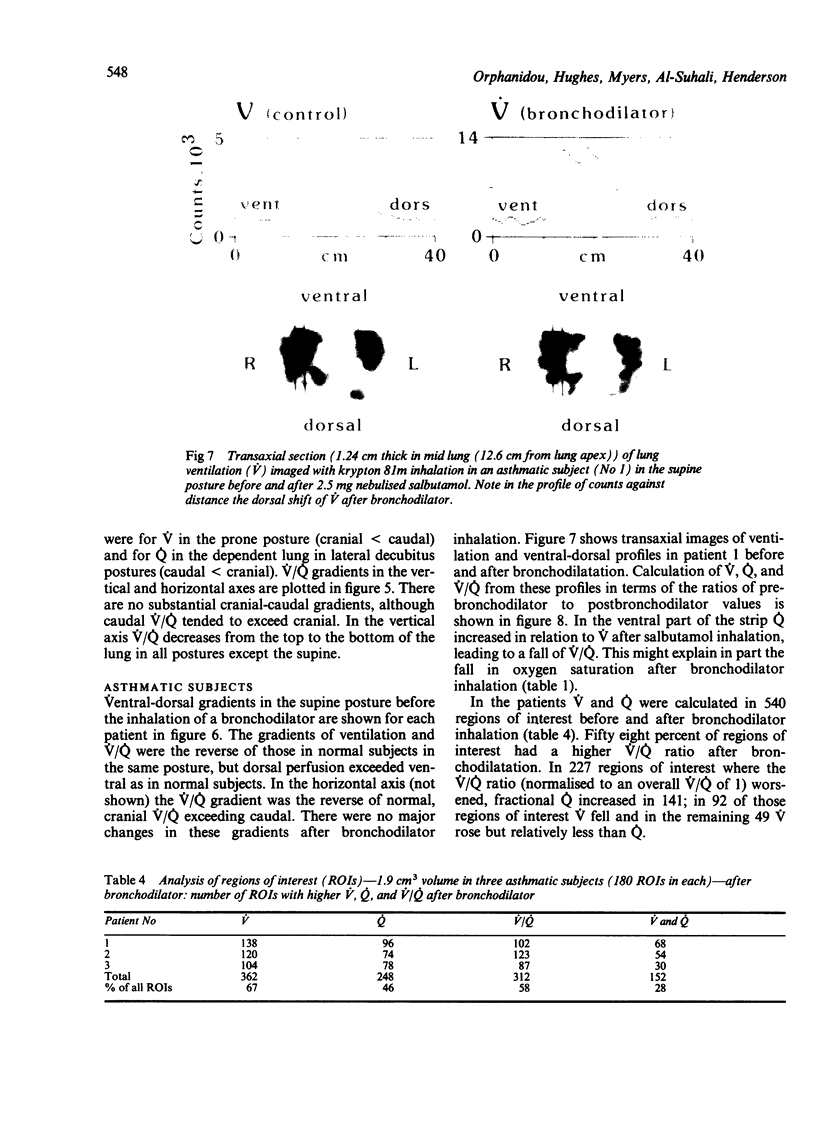
Single photon emission computed tomography, a rotating gamma camera, and continuous inhalation or infusion of krypton 81m (half life 13 seconds) were used to measure regional ventilation (V), perfusion (Q), and ventilation-perfusion (V/Q) ratios in five normal subjects in supine, prone, and lateral decubitus postures and in three asthmatic patients (supine posture only) before and after inhalation of 2.5 mg nebulised salbutamol. Vertical and horizontal gradients of V, Q, and V/Q were examined at three levels in each lung in regions of 1.9 cm3 size. In normal subjects V and Q increased along the axis of gravity in all postures and at all levels in the lung except for V in the prone position. Smaller horizontal gradients were found with an increase in V and Q from caudal to cranial--again except in the prone posture, where the gradient was slightly reversed. Constraint to outward motion of the ventral chest and abdominal wall is the most likely explanation for the different behaviour in the prone posture. In chronic asthma the vertical gradients of V and V/Q were the reverse of normal, but the Q gradient was normal. Bronchodilator treatment did not affect the vertical or horizontal gradients significantly, but analysis of individual regions showed that, relatively, V/Q worsened in 42% of them; this was associated in two thirds with an increase in fractional Q. After inhalation of beta agonist local vasodilatation may influence V/Q ratios in some units more than bronchodilatation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amis T. C., Jones H. A., Hughes J. M. Effect of posture on inter-regional distribution of pulmonary perfusion and VA/Q ratios in man. Respir Physiol. 1984 May;56(2):169–182. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(84)90101-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amis T. C., Jones H. A., Hughes J. M. Effect of posture on inter-regional distribution of pulmonary ventilation in man. Respir Physiol. 1984 May;56(2):145–167. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(84)90100-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amis T. C., Jones T. Krypton-81m as a flow tracer in the lung: theory and quantitation. Bull Eur Physiopathol Respir. 1980 May-Jun;16(3):245–259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciofetta G., Pratt T. A., Hughes J. M. Regional pulmonary perfusion assessed with continuous intravenous infusion of Kr-81m: a comparison with Tc-99m macroaggregates. J Nucl Med. 1978 Oct;19(10):1126–1130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DaCosta J., Hedstrand U. The effect of a new sympathomimetic beta-receptor stimulating drug (terbutaline) on arterial blood gases in bronchial sthma. Scand J Respir Dis. 1970;51(3):212–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel L. A., Prefaut C. Cranio-caudal distribution of inspired gas and perfusion in supine man. Respir Physiol. 1981 Jul;45(1):43–53. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(81)90048-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fazio F., Jones T. Assessment of regional ventilation by continuous inhalation of radioactive krypton-81m. Br Med J. 1975 Sep 20;3(5985):673–676. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5985.673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fazio F., Palla A., Santolicandro A., Solfanelli S., Fornai E., Giuntini C. Studies of regional ventilation in asthma using 81mKr. Lung. 1979;156(3):185–194. doi: 10.1007/BF02714009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glazier J. B., Hughes J. M., Maloney J. E., West J. B. Vertical gradient of alveolar size in lungs of dogs frozen intact. J Appl Physiol. 1967 Nov;23(5):694–705. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1967.23.5.694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harf A., Pratt T., Hughes J. M. Regional distribution of VA/Q in man at rest and with exercise measured with krypton-81m. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1978 Jan;44(1):115–123. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1978.44.1.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J. M. Short-life radionuclides and regional lung function. Br J Radiol. 1979 May;52(617):353–370. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-52-617-353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavender J. P., Al-Nahhas A. M., Myers M. J. Ventilation perfusion ratios of the normal supine lung using emission tomography. Br J Radiol. 1984 Feb;57(674):141–146. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-57-674-141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milic-Emili J., Henderson J. A., Dolovich M. B., Trop D., Kaneko K. Regional distribution of inspired gas in the lung. J Appl Physiol. 1966 May;21(3):749–759. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1966.21.3.749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer K. N., Legge J. S., Hamilton W. F., Diament M. L. Comparison of effect of salbutamol and isoprenaline on spirometry and blood-gas tensions in bronchial asthma. Br Med J. 1970 Apr 4;2(5700):23–24. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5700.23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rehder K., Knopp T. J., Sessler A. D. Regional intrapulmonary gas distribution in awake and anesthetized-paralyzed prone man. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1978 Oct;45(4):528–535. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1978.45.4.528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes C. G., Wollmer P., Fazio F., Jones T. Quantitative measurement of regional extravascular lung density using positron emission and transmission tomography. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1981 Dec;5(6):783–791. doi: 10.1097/00004728-198112000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tai E., Read J. Response of blood gas tensions to aminophylline and isoprenaline in patients with asthma. Thorax. 1967 Nov;22(6):543–549. doi: 10.1136/thx.22.6.543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner P. D., Dantzker D. R., Iacovoni V. E., Tomlin W. C., West J. B. Ventilation-perfusion inequality in asymptomatic asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978 Sep;118(3):511–524. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1978.118.3.511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]