Abstract
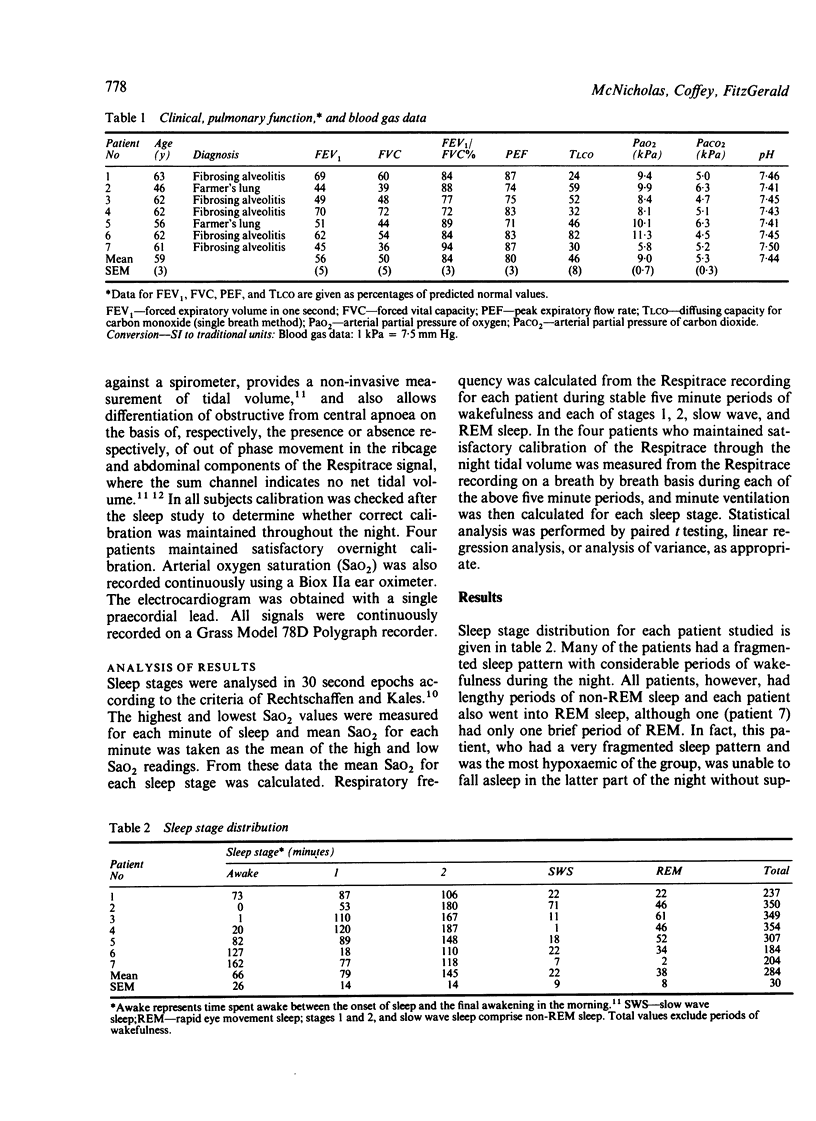
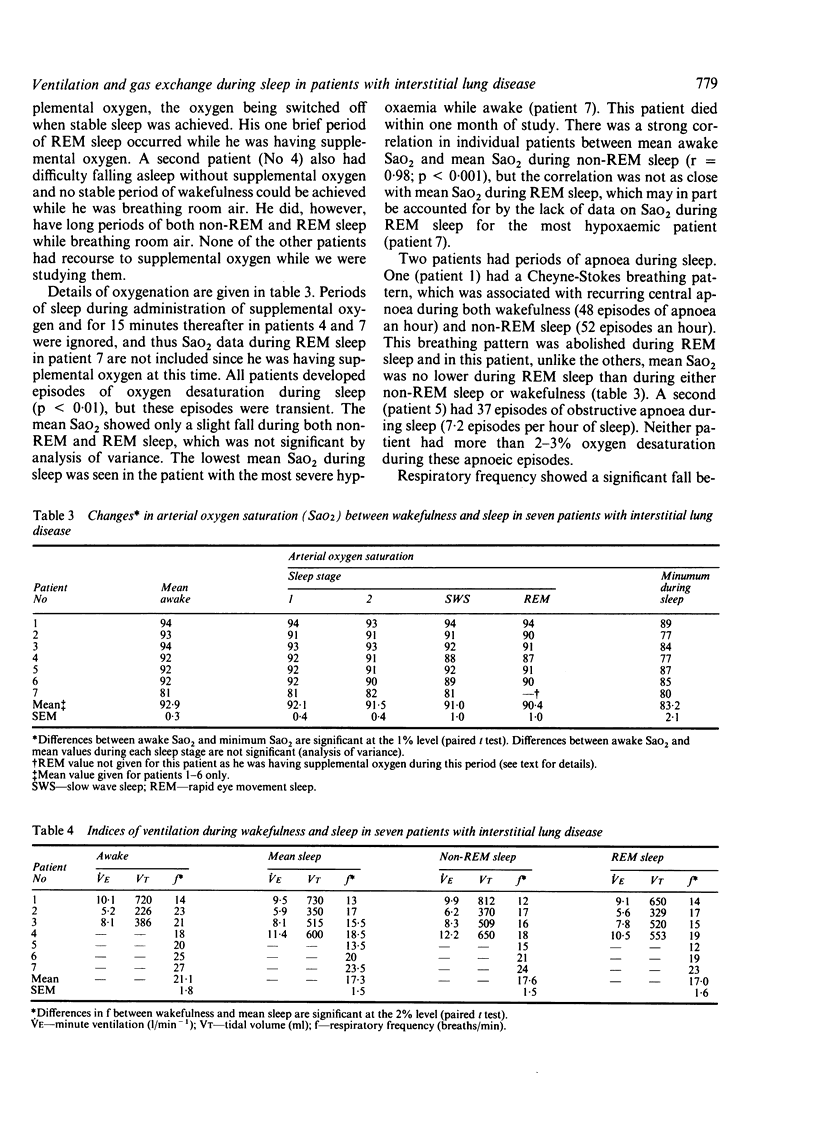
Ventilation and gas exchange during overnight sleep was studied in a group of seven patients with severe interstitial lung disease (mean vital capacity 50%, mean diffusing capacity 46% predicted), to see whether clinically significant oxygen desaturation occurred. Patients with a history of loud snoring or clinically significant airflow obstruction were excluded. Sleep was fragmented in these patients, but all achieved rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. All patients showed episodes of oxygen desaturation during sleep--mean (SEM) awake arterial oxygen saturation (SaO2) was 92.9% (0.3%) compared with a mean minimum SaO2 during sleep of 83.2% (2.1%) (p less than 0.01). These episodes were, however, transient, and mean SaO2 showed only a slight fall between wakefulness and sleep (non-REM 91.5%, REM 90.4%; NS). Furthermore, SaO2 during non-REM sleep correlated well (p less than 0.001) with SaO2 during wakefulness. Respiratory frequency showed a significant fall between wakefulness and sleep--21.1 (1.8) versus 17.3 (1.5) breaths per minute (p less than 0.02). Our data suggest that nocturnal oxygen treatment need not be considered in patients with interstitial lung disease unless the level of oxygenation while they are awake indicates the need for such treatment.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agnew H. W., Jr, Webb W. B., Williams R. L. The first night effect: an EEG study of sleep. Psychophysiology. 1966 Jan;2(3):263–266. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8986.1966.tb02650.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Block A. J., Boysen P. G., Wynne J. W., Hunt L. A. Sleep apnea, hypopnea and oxygen desaturation in normal subjects. A strong male predominance. N Engl J Med. 1979 Mar 8;300(10):513–517. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197903083001001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bye P. T., Issa F., Berthon-Jones M., Sullivan C. E. Studies of oxygenation during sleep in patients with interstitial lung disease. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Jan;129(1):27–32. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.129.1.27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chadha T. S., Watson H., Birch S., Jenouri G. A., Schneider A. W., Cohn M. A., Sackner M. A. Validation of respiratory inductive plethysmography using different calibration procedures. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 Jun;125(6):644–649. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1982.125.6.644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMarco F. J., Jr, Wynne J. W., Block A. J., Boysen P. G., Taasan V. C. Oxygen desaturation during sleep as a determinant of the "Blue and Bloated" syndrome. Chest. 1981 Jun;79(6):621–625. doi: 10.1378/chest.79.6.621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas N. J., Calverley P. M., Leggett R. J., Brash H. M., Flenley D. C., Brezinova V. Transient hypoxaemia during sleep in chronic bronchitis and emphysema. Lancet. 1979 Jan 6;1(8106):1–4. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)90451-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein R. S., Ramcharan V., Bowes G., McNicholas W. T., Bradley D., Phillipson E. A. Effect of supplemental nocturnal oxygen on gas exchange in patients with severe obstructive lung disease. N Engl J Med. 1984 Feb 16;310(7):425–429. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198402163100704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudgel D. W., Martin R. J., Capehart M., Johnson B., Hill P. Contribution of hypoventilation to sleep oxygen desaturation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1983 Sep;55(3):669–677. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1983.55.3.669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudgel D. W., Martin R. J., Johnson B., Hill P. Mechanics of the respiratory system and breathing pattern during sleep in normal humans. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1984 Jan;56(1):133–137. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1984.56.1.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOURENCO R. V., TURINO G. M., DAVIDSON L. A., FISHMAN A. P. THE REGULATION OF VENTILATION IN DIFFUSE PULMONARY FIBROSIS. Am J Med. 1965 Feb;38:199–216. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(65)90174-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littner M. R., McGinty D. J., Arand D. L. Determinants of oxygen desaturation in the course of ventilation during sleep in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980 Dec;122(6):849–857. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.122.6.849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lourenço R. V., Miranda J. M. Drive and performance of the ventilatory apparatus in chronic obstructive lung disease. N Engl J Med. 1968 Jul 11;279(2):53–59. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196807112790201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNicholas W. T., Fitzgerald M. X. Nocturnal deaths among patients with chronic bronchitis and emphysema. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1984 Oct 6;289(6449):878–878. doi: 10.1136/bmj.289.6449.878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Padilla R., West P., Lertzman M., Kryger M. H. Breathing during sleep in patients with interstitial lung disease. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Aug;132(2):224–229. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.132.2.224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillipson E. A. Control of breathing during sleep. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978 Nov;118(5):909–939. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1978.118.5.909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillipson E. A., Murphy E., Kozar L. F. Regulation of respiration in sleeping dogs. J Appl Physiol. 1976 May;40(5):688–693. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1976.40.5.688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stradling J. R., Chadwick G. A., Frew A. J. Changes in ventilation and its components in normal subjects during sleep. Thorax. 1985 May;40(5):364–370. doi: 10.1136/thx.40.5.364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stradling J. R., Lane D. J. Nocturnal hypoxaemia in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Clin Sci (Lond) 1983 Feb;64(2):213–222. doi: 10.1042/cs0640213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tirlapur V. G., Mir M. A. Nocturnal hypoxemia and associated electrocardiographic changes in patients with chronic obstructive airways disease. N Engl J Med. 1982 Jan 21;306(3):125–130. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198201213060301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobin M. J., Chadha T. S., Jenouri G., Birch S. J., Gazeroglu H. B., Sackner M. A. Breathing patterns. 2. Diseased subjects. Chest. 1983 Sep;84(3):286–294. doi: 10.1378/chest.84.3.286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



