Abstract
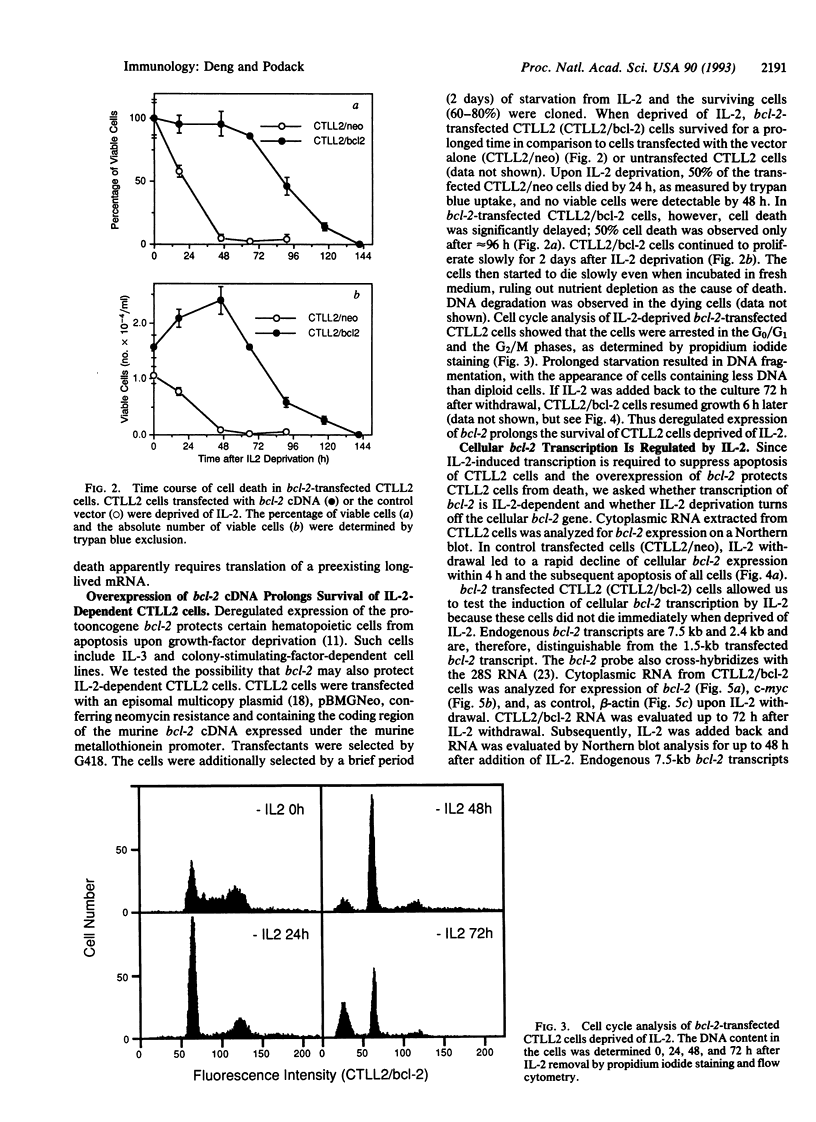
Absence of interleukin 2 (IL-2) from IL-2-dependent cells, such as the cytotoxic T-cell line CTLL2, causes DNA fragmentation and programmed cell death (apoptosis). We found that, upon initiation, DNA degradation proceeds rapidly. IL-2-deprived CTLL2 cells can be rescued from apoptosis by the addition of IL-2 2 h prior to the onset of detectable DNA breakdown. Addition of inhibitors of transcription with IL-2 abolished the IL-2-mediated rescue of CTLL2 cells. Thus it appears that IL-2-mediated gene transcription is necessary for survival. Deregulated expression of a protooncogene, bcl-2, inhibits apoptosis of cells dependent on other hematopoietic growth factors. To determine whether bcl-2 was active in CTLL2 cells, we transfected CTLL2 cells with a plasmid containing bcl-2 cDNA expressed under the metallothionein promoter and observed prolonged survival of the transfected cells upon IL-2 deprivation. Cell growth, however, was arrested in the G0/G1 or G2/M phases of the cell cycle. The prolonged survival of bcl-2 transfectants allowed the analysis of endogenous bcl-2 mRNA levels by Northern blot analysis. The expression of endogenous bcl-2 was down-regulated within 8 h of IL-2 withdrawal and was not detected after 3 days. Addition of IL-2 induced endogenous bcl-2 expression within 8 h. Full recovery of bcl-2 expression was achieved by 24 h after IL-2 addition. We conclude that the survival of death-prone CTLL2 cells may be viewed as IL-2-dependent suppression of suicide, probably by the IL-2-induced expression of the cellular bcl-2 gene.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cohen J. J., Duke R. C., Fadok V. A., Sellins K. S. Apoptosis and programmed cell death in immunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 1992;10:267–293. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.10.040192.001411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. J., Duke R. C. Glucocorticoid activation of a calcium-dependent endonuclease in thymocyte nuclei leads to cell death. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):38–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duke R. C., Cohen J. J. IL-2 addiction: withdrawal of growth factor activates a suicide program in dependent T cells. Lymphokine Res. 1986 Fall;5(4):289–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis H. M., Horvitz H. R. Genetic control of programmed cell death in the nematode C. elegans. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):817–829. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90004-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis R. E., Yuan J. Y., Horvitz H. R. Mechanisms and functions of cell death. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:663–698. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.003311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evan G. I., Wyllie A. H., Gilbert C. S., Littlewood T. D., Land H., Brooks M., Waters C. M., Penn L. Z., Hancock D. C. Induction of apoptosis in fibroblasts by c-myc protein. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):119–128. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90123-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Smith K. A. In vitro generation of tumor-specific cytotoxic lymphocytes. Secondary allogeneic mixed tumor lymphocyte culture of normal murine spleen cells. J Exp Med. 1977 Aug 1;146(2):468–482. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.2.468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gough N. M. Rapid and quantitative preparation of cytoplasmic RNA from small numbers of cells. Anal Biochem. 1988 Aug 15;173(1):93–95. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90164-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hengartner M. O., Ellis R. E., Horvitz H. R. Caenorhabditis elegans gene ced-9 protects cells from programmed cell death. Nature. 1992 Apr 9;356(6369):494–499. doi: 10.1038/356494a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hockenbery D. M., Zutter M., Hickey W., Nahm M., Korsmeyer S. J. BCL2 protein is topographically restricted in tissues characterized by apoptotic cell death. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):6961–6965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.6961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hockenbery D., Nuñez G., Milliman C., Schreiber R. D., Korsmeyer S. J. Bcl-2 is an inner mitochondrial membrane protein that blocks programmed cell death. Nature. 1990 Nov 22;348(6299):334–336. doi: 10.1038/348334a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karasuyama H., Melchers F. Establishment of mouse cell lines which constitutively secrete large quantities of interleukin 2, 3, 4 or 5, using modified cDNA expression vectors. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Jan;18(1):97–104. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr J. F., Wyllie A. H., Currie A. R. Apoptosis: a basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging implications in tissue kinetics. Br J Cancer. 1972 Aug;26(4):239–257. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1972.33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConkey D. J., Hartzell P., Amador-Pérez J. F., Orrenius S., Jondal M. Calcium-dependent killing of immature thymocytes by stimulation via the CD3/T cell receptor complex. J Immunol. 1989 Sep 15;143(6):1801–1806. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConkey D. J., Hartzell P., Nicotera P., Orrenius S. Calcium-activated DNA fragmentation kills immature thymocytes. FASEB J. 1989 May;3(7):1843–1849. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.7.2497041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negrini M., Silini E., Kozak C., Tsujimoto Y., Croce C. M. Molecular analysis of mbcl-2: structure and expression of the murine gene homologous to the human gene involved in follicular lymphoma. Cell. 1987 May 22;49(4):455–463. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90448-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuñez G., London L., Hockenbery D., Alexander M., McKearn J. P., Korsmeyer S. J. Deregulated Bcl-2 gene expression selectively prolongs survival of growth factor-deprived hemopoietic cell lines. J Immunol. 1990 May 1;144(9):3602–3610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim R. W. Cell death during development of the nervous system. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1991;14:453–501. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.14.030191.002321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sentman C. L., Shutter J. R., Hockenbery D., Kanagawa O., Korsmeyer S. J. bcl-2 inhibits multiple forms of apoptosis but not negative selection in thymocytes. Cell. 1991 Nov 29;67(5):879–888. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90361-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. A., Williams G. T., Kingston R., Jenkinson E. J., Owen J. J. Antibodies to CD3/T-cell receptor complex induce death by apoptosis in immature T cells in thymic cultures. Nature. 1989 Jan 12;337(6203):181–184. doi: 10.1038/337181a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strasser A., Harris A. W., Cory S. bcl-2 transgene inhibits T cell death and perturbs thymic self-censorship. Cell. 1991 Nov 29;67(5):889–899. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90362-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ucker D. S., Ashwell J. D., Nickas G. Activation-driven T cell death. I. Requirements for de novo transcription and translation and association with genome fragmentation. J Immunol. 1989 Dec 1;143(11):3461–3469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieland T. The toxic peptides from Amanita mushrooms. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1983 Sep;22(3):257–276. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1983.tb02093.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie A. H. Glucocorticoid-induced thymocyte apoptosis is associated with endogenous endonuclease activation. Nature. 1980 Apr 10;284(5756):555–556. doi: 10.1038/284555a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan J. Y., Horvitz H. R. The Caenorhabditis elegans genes ced-3 and ced-4 act cell autonomously to cause programmed cell death. Dev Biol. 1990 Mar;138(1):33–41. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(90)90174-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






