Full text
PDF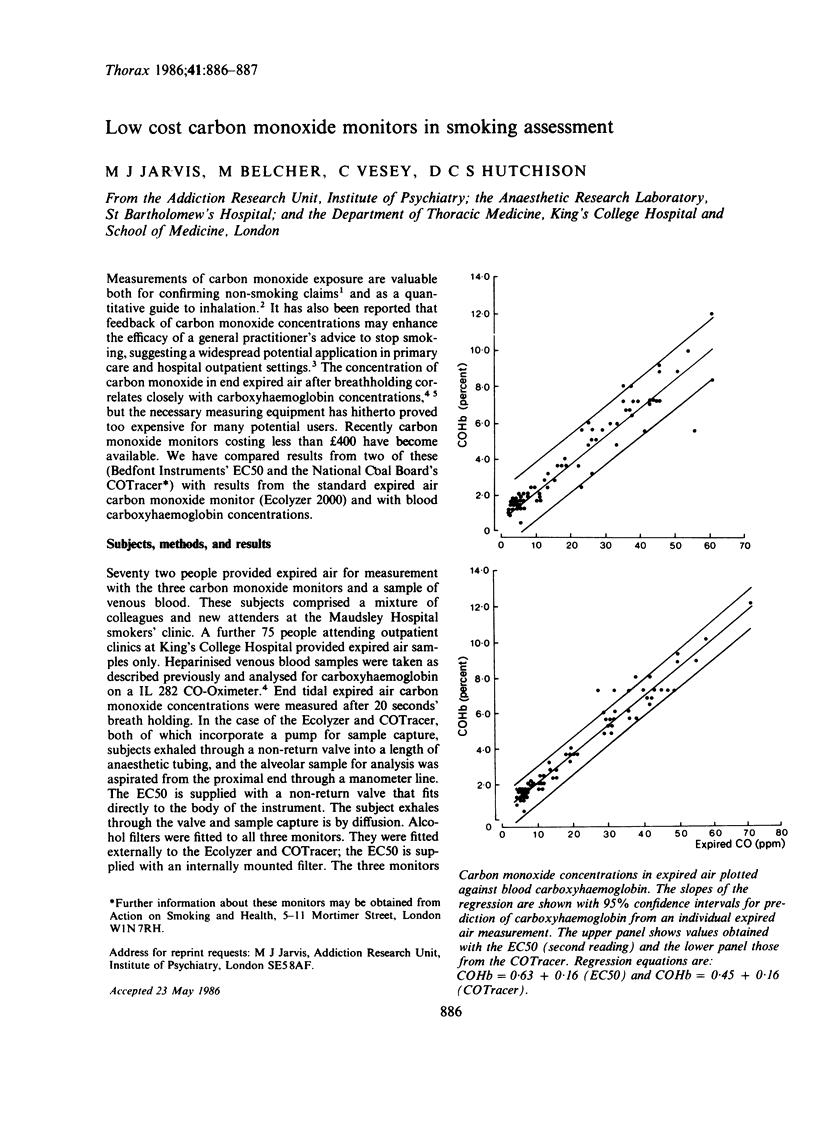

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bland J. M., Altman D. G. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet. 1986 Feb 8;1(8476):307–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamrozik K., Vessey M., Fowler G., Wald N., Parker G., Van Vunakis H. Controlled trial of three different antismoking interventions in general practice. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1984 May 19;288(6429):1499–1503. doi: 10.1136/bmj.288.6429.1499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis M. J., Russell M. A., Saloojee Y. Expired air carbon monoxide: a simple breath test of tobacco smoke intake. Br Med J. 1980 Aug 16;281(6238):484–485. doi: 10.1136/bmj.281.6238.484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis M., Tunstall-Pedoe H., Feyerabend C., Vesey C., Salloojee Y. Biochemical markers of smoke absorption and self reported exposure to passive smoking. J Epidemiol Community Health. 1984 Dec;38(4):335–339. doi: 10.1136/jech.38.4.335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlin P., Lundh B., Westling H. Carbon monoxide blood levels and reported cessation of smoking. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1976 Sep 29;49(3):263–265. doi: 10.1007/BF00426827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wald N. J., Boreham J., Bailey A. Relative intakes of tar, nicotine, and carbon monoxide from cigarettes of different yields. Thorax. 1984 May;39(5):361–364. doi: 10.1136/thx.39.5.361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wald N. J., Idle M., Boreham J., Bailey A. Carbon monoxide in breath in relation to smoking and carboxyhaemoglobin levels. Thorax. 1981 May;36(5):366–369. doi: 10.1136/thx.36.5.366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


