Abstract
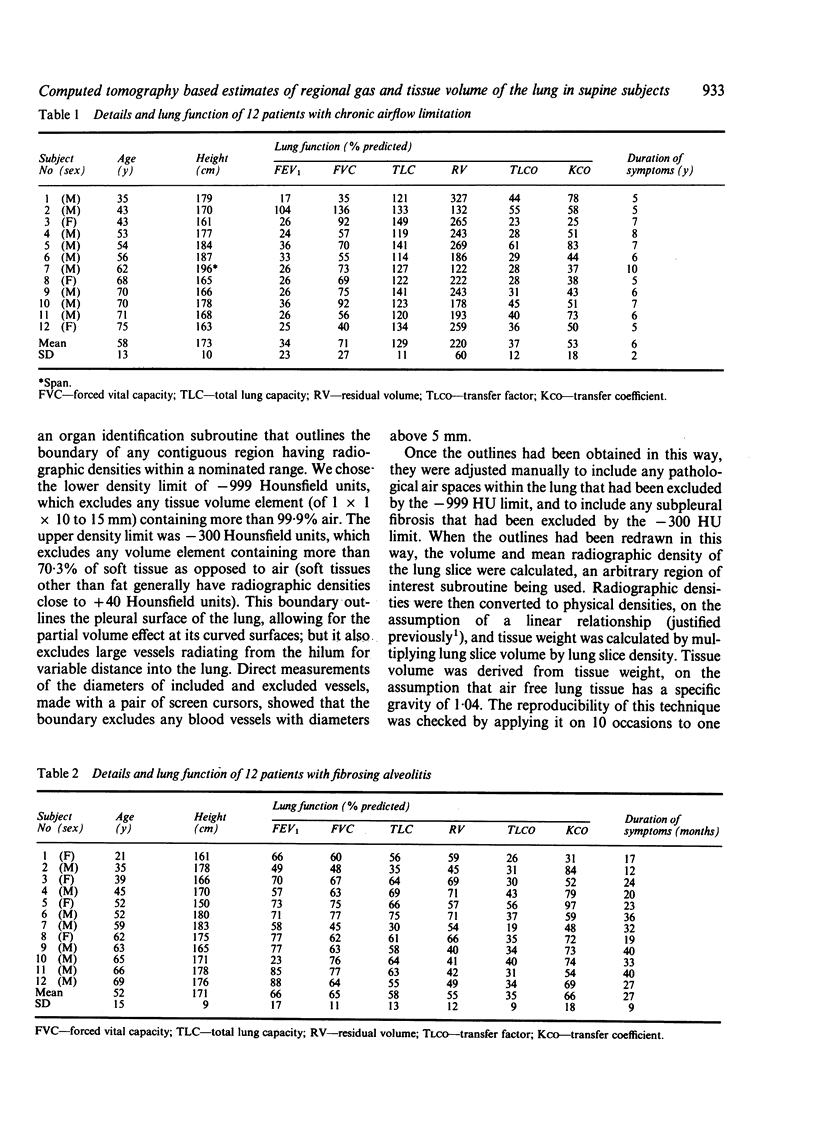
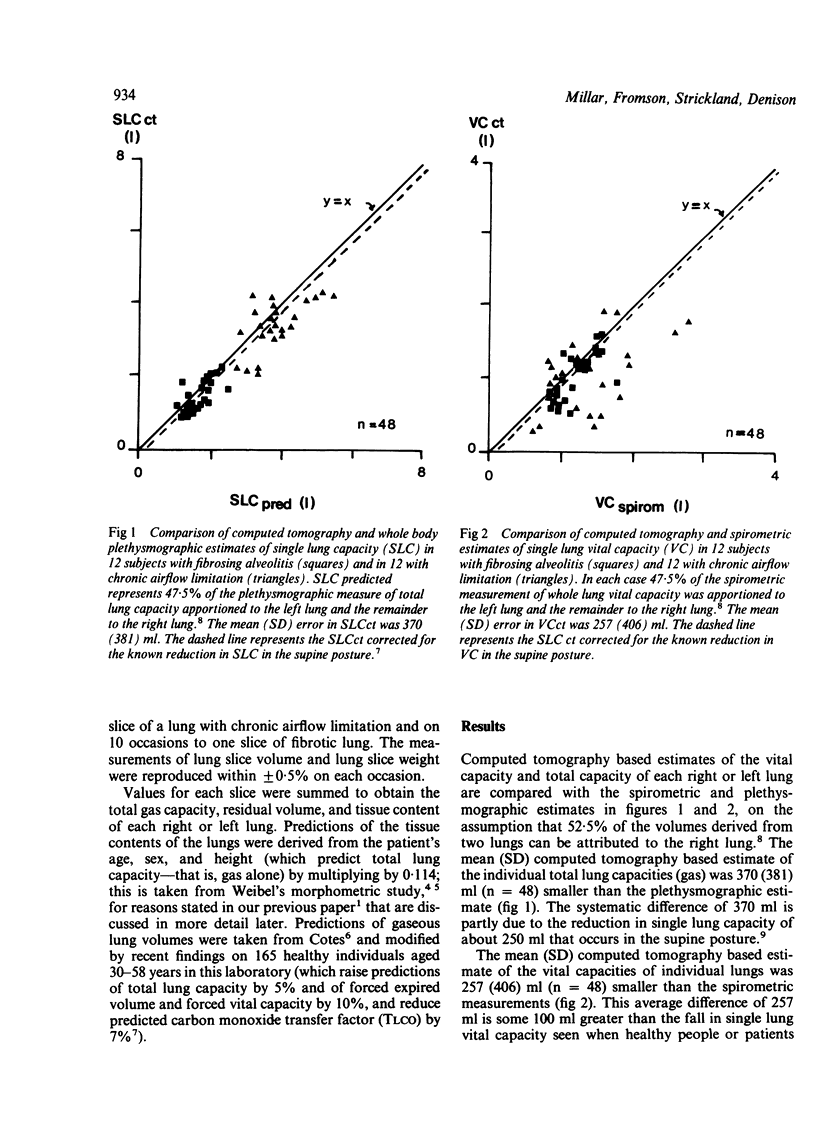
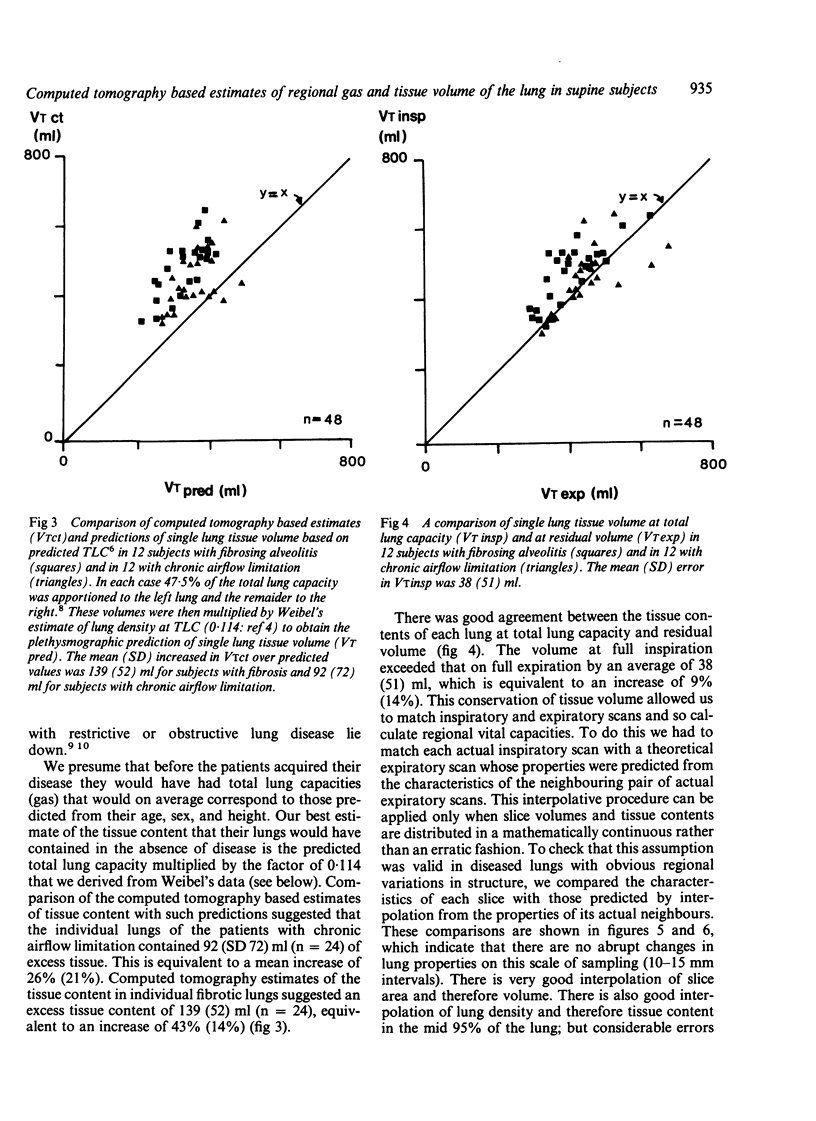
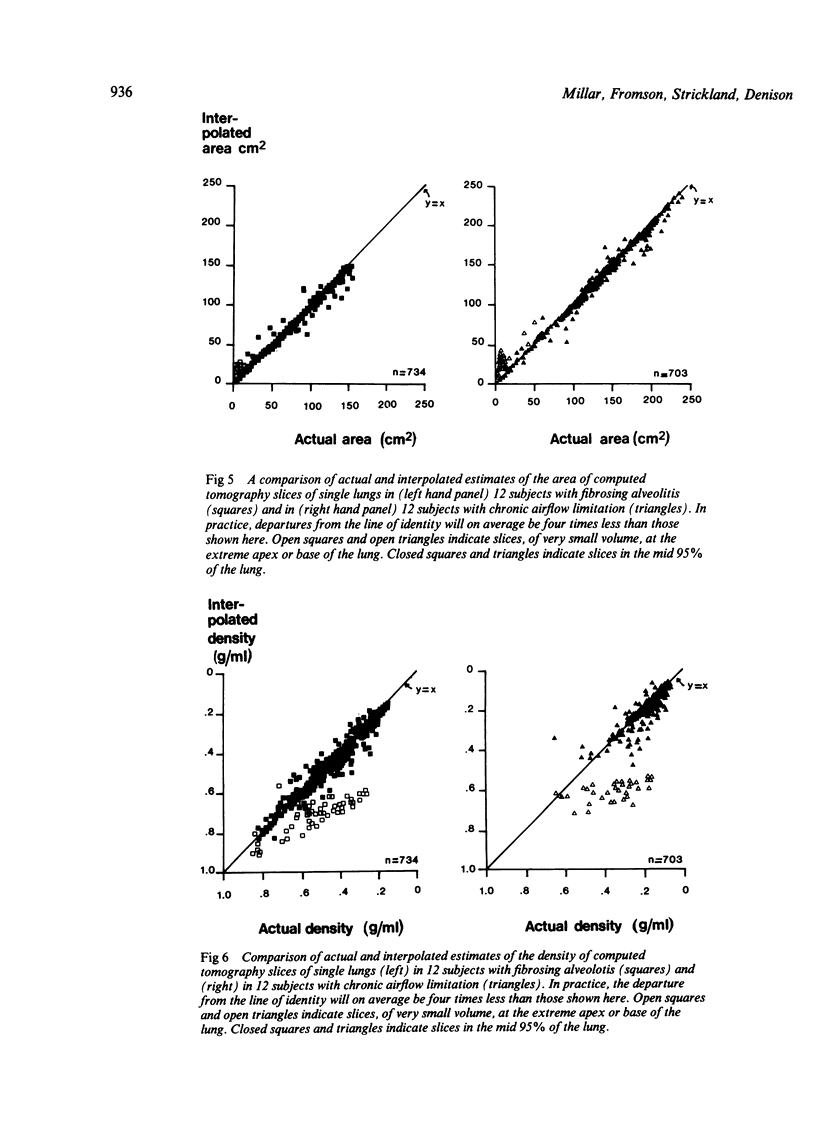
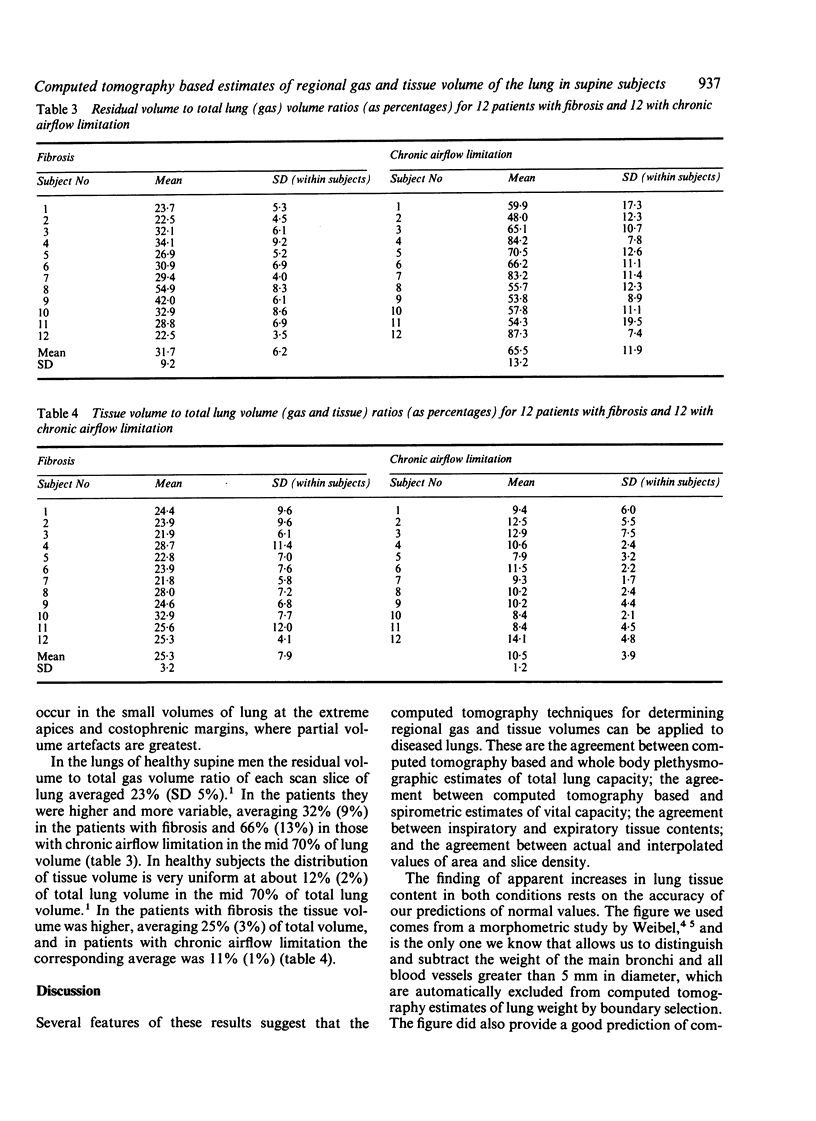
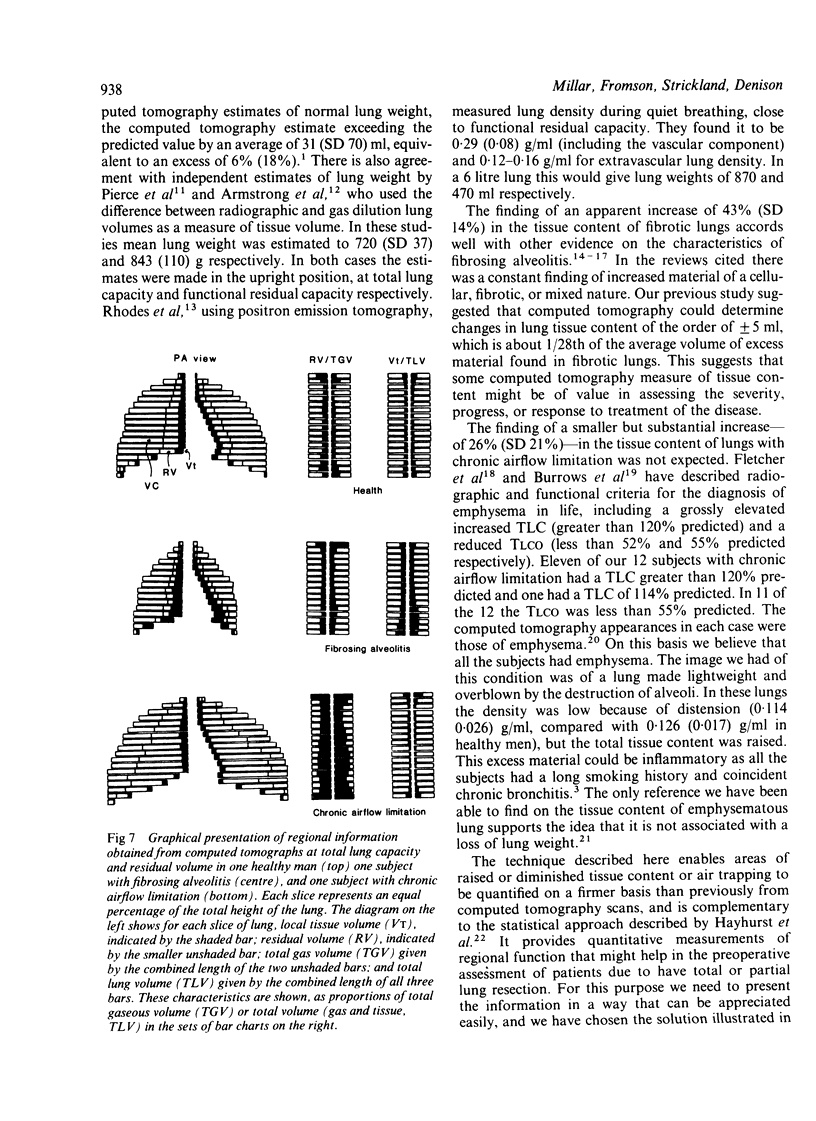
Twelve patients with chronic airflow limitation and 12 patients with a histological diagnosis of fibrosing alveolitis were studied. The calculated mean (SD) tissue volume of a single lung at total lung capacity was 467 (91) ml in the patients with alveolitis, which was 43% (14%) more than predicted for healthy people of the same age, sex, and height. The tissue volume of a single lung at total lung capacity was 436 (82) ml in the patients with chronic airflow limitation, which was 26% (21%) more than predicted. At residual volumes the tissue contents of the fibrotic and the obstructed lungs changed very little (to 407 (84) ml and 433 (84) ml respectively). This allowed tissue volume to be used as a marker of position within the lung, to match inspiratory and expiratory slices and to calculate regional ventilation. In both groups local ventilation was diminished and more variable than in healthy lungs--that is, in the mid 70% of lung volume the local residual volume to total gas volume ratios (RV/TGV) were 32% (10%) in the fibrotic group and 66% (14%) in the group with chronic airflow limitation, compared with 23% (5%) in healthy subjects. As expected, the fibrotic lungs were much denser (0.246 (0.036) g/ml) and the lungs with chronic airflow obstruction were less dense (0.114 (0.026) g/ml) than were healthy lungs (0.126 (0.017) g/ml).
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen S. M., Hunt B., Green M. Fall in vital capacity with posture. Br J Dis Chest. 1985 Jul;79(3):267–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong J. D., Gluck E. H., Crapo R. O., Jones H. A., Hughes J. M. Lung tissue volume estimated by simultaneous radiographic and helium dilution methods. Thorax. 1982 Sep;37(9):676–679. doi: 10.1136/thx.37.9.676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURROWS B., NIDEN A. H., FLETCHER C. M., JONES N. L. CLINICAL TYPES OF CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE LUNG DISEASE IN LONDON AND IN CHICAGO. A STUDY OF ONE HUNDRED PATIENTS. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1964 Jul;90:14–27. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1964.90.1.14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crystal R. G., Fulmer J. D., Roberts W. C., Moss M. L., Line B. R., Reynolds H. Y. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Clinical, histologic, radiographic, physiologic, scintigraphic, cytologic, and biochemical aspects. Ann Intern Med. 1976 Dec;85(6):769–788. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-85-6-769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denison D. M., Morgan M. D., Millar A. B. Estimation of regional gas and tissue volumes of the lung in supine man using computed tomography. Thorax. 1986 Aug;41(8):620–628. doi: 10.1136/thx.41.8.620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLETCHER C. M., HUGH-JONES P., McNICOL M. W., PRIDE N. B. The diagnosis of pulmonary emphysema in the presence of chronic bronchitis. Q J Med. 1963 Jan;32:33–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulmer J. D., Roberts W. C., von Gal E. R., Crystal R. G. Morphologic-physiologic correlates of the severity of fibrosis and degree of cellularity in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 1979 Apr;63(4):665–676. doi: 10.1172/JCI109349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goddard P. R., Nicholson E. M., Laszlo G., Watt I. Computed tomography in pulmonary emphysema. Clin Radiol. 1982 Jul;33(4):379–387. doi: 10.1016/s0009-9260(82)80301-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan M. D., Denison D. M., Strickland B. Value of computed tomography for selecting patients with bullous lung disease for surgery. Thorax. 1986 Nov;41(11):855–862. doi: 10.1136/thx.41.11.855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PIERCE J. A., HOCOTT J. B., EBERT R. V. The collagen and elastin content of the lung in emphysema. Ann Intern Med. 1961 Aug;55:210–222. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-55-2-210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes C. G., Wollmer P., Fazio F., Jones T. Quantitative measurement of regional extravascular lung density using positron emission and transmission tomography. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1981 Dec;5(6):783–791. doi: 10.1097/00004728-198112000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SVANBERG L. Influence of posture on the lung volumes, ventilation and circulation in normals; a spirometric-bronchospirometric investigation. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1957;9 (Suppl 25):1–195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Transcutaneous oxygen measurement in skin ischaemia. Lancet. 1984 Aug 11;2(8398):329–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner-Warwick M., Burrows B., Johnson A. Cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis: clinical features and their influence on survival. Thorax. 1980 Mar;35(3):171–180. doi: 10.1136/thx.35.3.171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright P. H., Buxton-Thomas M., Kreel L., Steel S. J. Cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis: pattern of disease in the lung. Thorax. 1984 Nov;39(11):857–861. doi: 10.1136/thx.39.11.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



