Abstract
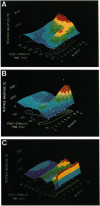
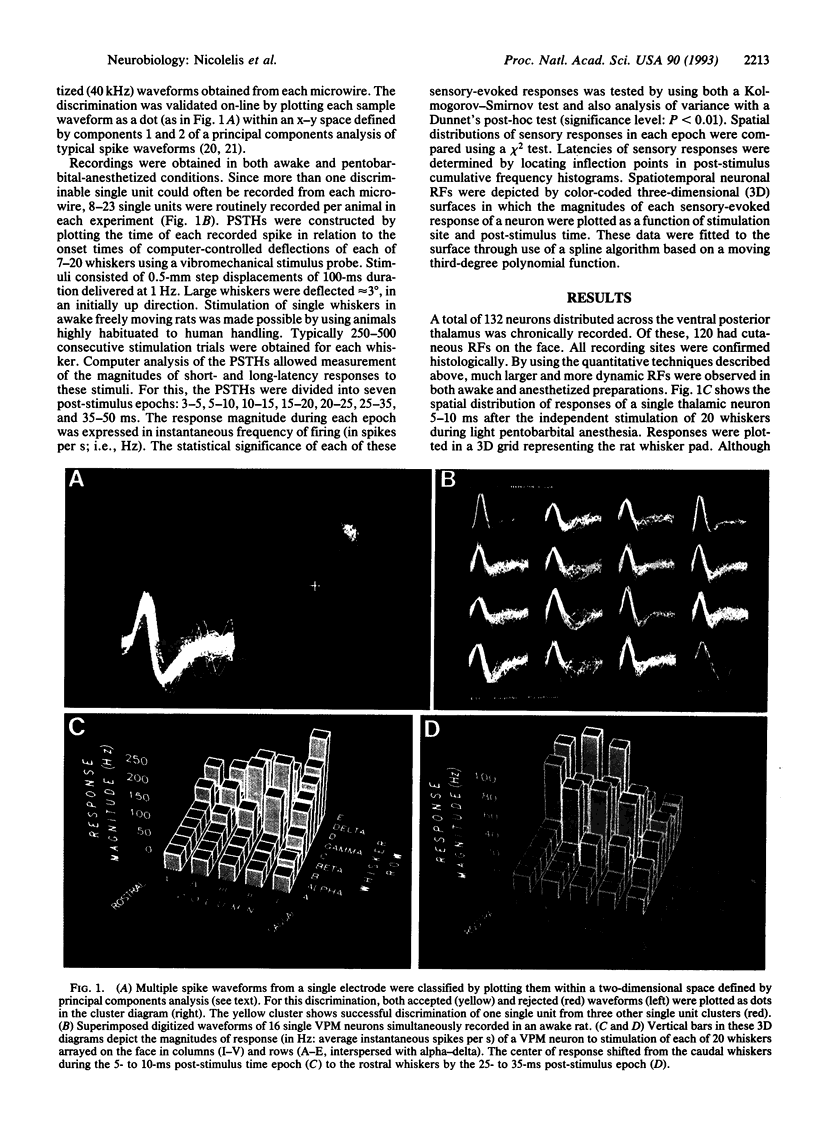
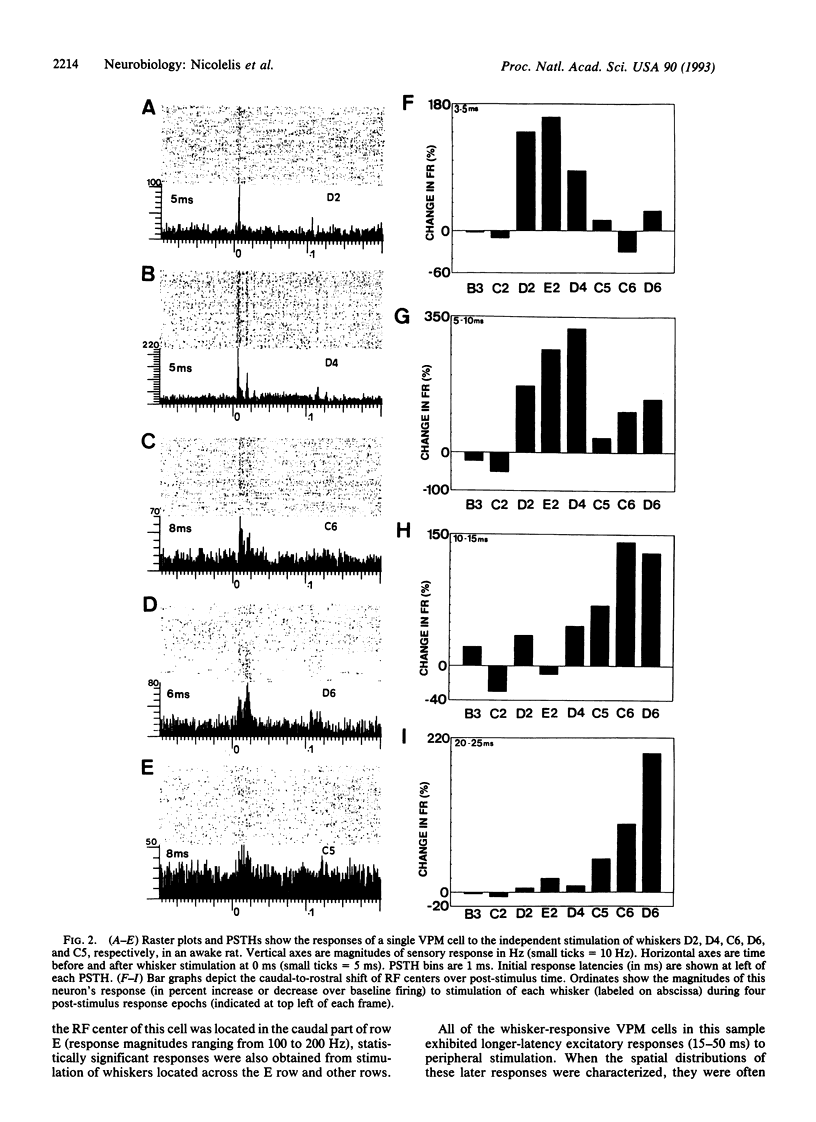
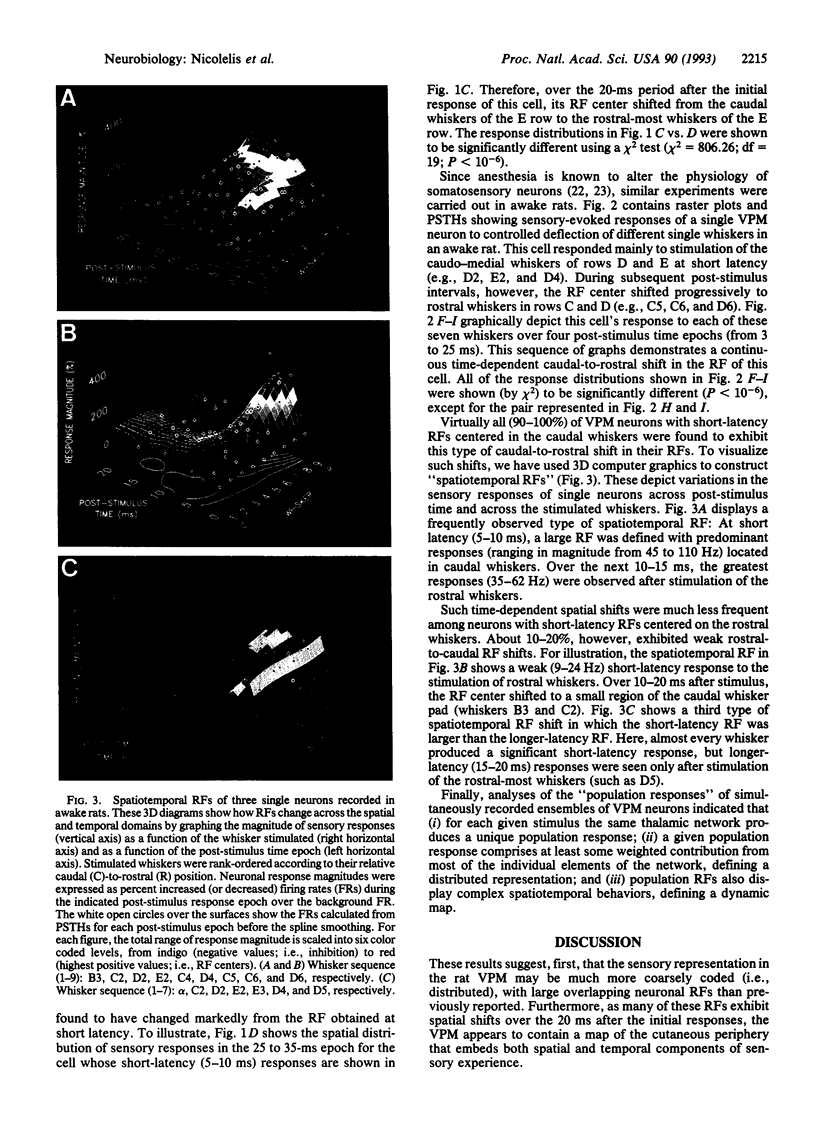
The traditional view that the map of the face in the ventral posterior medial thalamus (VPM) is static and highly discrete was derived largely from qualitative studies that reported only small, robust, and nonoverlapping receptive fields (RFs). Here, by using more quantitative techniques, we have provided evidence for an alternative hypothesis: the RFs in the VPM are large and overlapping and tend to shift as a function of post-stimulus time. These results were obtained through simultaneous recordings of up to 23 single neurons across the whisker representation in the VPM of rats. Under both awake and anesthetized conditions, these neurons responded robustly at short (4-6 ms) and/or long (15-25 ms) latencies to discrete vibromechanical stimulation of single facial whiskers. Computer graphics were used to construct three-dimensional plots depicting the magnitudes of neuronal responses to stimulation of each of several whiskers as a function of post-stimulus time. These "spatiotemporal RFs" demonstrated that (i) the RFs of VPM neurons are quite large, covering up to 20 whiskers and (ii) the spatial locations of these RFs may shift dramatically over the first 35 ms of post-stimulus time, especially from the caudal-most to the rostral-most whiskers on the face. These results suggest that the VPM contains a dynamic and distributed representation of the face, in which stimulus information is coded in both spatial and temporal domains.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong-James M., Callahan C. A. Thalamo-cortical processing of vibrissal information in the rat. II. spatiotemporal convergence in the thalamic ventroposterior medial nucleus (VPm) and its relevance to generation of receptive fields of S1 cortical "barrel" neurones. J Comp Neurol. 1991 Jan 8;303(2):211–224. doi: 10.1002/cne.903030204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carvell G. E., Simons D. J. Biometric analyses of vibrissal tactile discrimination in the rat. J Neurosci. 1990 Aug;10(8):2638–2648. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-08-02638.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapin J. K., Lin C. S. Mapping the body representation in the SI cortex of anesthetized and awake rats. J Comp Neurol. 1984 Oct 20;229(2):199–213. doi: 10.1002/cne.902290206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapin J. K., Waterhouse B. D., Woodward D. J. Differences in cutaneous sensory response properties of single somatosensory cortical neurons in awake and halothane anesthetized rats. Brain Res Bull. 1981 Jan;6(1):63–70. doi: 10.1016/s0361-9230(81)80069-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chmielowska J., Carvell G. E., Simons D. J. Spatial organization of thalamocortical and corticothalamic projection systems in the rat SmI barrel cortex. J Comp Neurol. 1989 Jul 15;285(3):325–338. doi: 10.1002/cne.902850304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond M. E., Armstrong-James M., Budway M. J., Ebner F. F. Somatic sensory responses in the rostral sector of the posterior group (POm) and in the ventral posterior medial nucleus (VPM) of the rat thalamus: dependence on the barrel field cortex. J Comp Neurol. 1992 May 1;319(1):66–84. doi: 10.1002/cne.903190108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond M. E., Armstrong-James M., Ebner F. F. Somatic sensory responses in the rostral sector of the posterior group (POm) and in the ventral posterior medial nucleus (VPM) of the rat thalamus. J Comp Neurol. 1992 Apr 22;318(4):462–476. doi: 10.1002/cne.903180410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erzurumlu R. S., Bates C. A., Killackey H. P. Differential organization of thalamic projection cells in the brain stem trigeminal complex of the rat. Brain Res. 1980 Oct 6;198(2):427–433. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90756-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgopoulos A. P., Schwartz A. B., Kettner R. E. Neuronal population coding of movement direction. Science. 1986 Sep 26;233(4771):1416–1419. doi: 10.1126/science.3749885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris R. M. Morphology of physiologically identified thalamocortical relay neurons in the rat ventrobasal thalamus. J Comp Neurol. 1986 Sep 22;251(4):491–505. doi: 10.1002/cne.902510405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacquin M. F., Mooney R. D., Rhoades R. W. Morphology, response properties, and collateral projections of trigeminothalamic neurons in brainstem subnucleus interpolaris of rat. Exp Brain Res. 1986;61(3):457–468. doi: 10.1007/BF00237571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins W. M., Merzenich M. M., Ochs M. T., Allard T., Guíc-Robles E. Functional reorganization of primary somatosensory cortex in adult owl monkeys after behaviorally controlled tactile stimulation. J Neurophysiol. 1990 Jan;63(1):82–104. doi: 10.1152/jn.1990.63.1.82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOUNTCASTLE V. B., HENNEMAN E. The representation of tactile sensibility in the thalamus of the monkey. J Comp Neurol. 1952 Dec;97(3):409–439. doi: 10.1002/cne.900970302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merzenich M. M., Kaas J. H., Wall J., Nelson R. J., Sur M., Felleman D. Topographic reorganization of somatosensory cortical areas 3b and 1 in adult monkeys following restricted deafferentation. Neuroscience. 1983 Jan;8(1):33–55. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90024-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POGGIO G. F., MOUNTCASTLE V. B. A study of the functional contributions of the lemniscal and spinothalamic systems to somatic sensibility. Central nervous mechanisms in pain. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1960 May;106:266–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POWELL T. P., MOUNTCASTLE V. B. Some aspects of the functional organization of the cortex of the postcentral gyrus of the monkey: a correlation of findings obtained in a single unit analysis with cytoarchitecture. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1959 Sep;105:133–162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peschanski M., Lee C. L., Ralston H. J., 3rd The structural organization of the ventrobasal complex of the rat as revealed by the analysis of physiologically characterized neurons injected intracellularly with horseradish peroxidase. Brain Res. 1984 Apr 9;297(1):63–74. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90543-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peschanski M., Mantyh P. W., Besson J. M. Spinal afferents to the ventrobasal thalamic complex in the rat: an anatomical study using wheat-germ agglutinin conjugated to horseradish peroxidase. Brain Res. 1983 Nov 14;278(1-2):240–244. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)90245-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoades R. W., Belford G. R., Killackey H. P. Receptive-field properties of rat ventral posterior medial neurons before and after selective kainic acid lesions of the trigeminal brain stem complex. J Neurophysiol. 1987 May;57(5):1577–1600. doi: 10.1152/jn.1987.57.5.1577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarna M. F., Gochin P., Kaltenbach J., Salganicoff M., Gerstein G. L. Unsupervised waveform classification for multi-neuron recordings: a real-time, software-based system. II. Performance comparison to other sorters. J Neurosci Methods. 1988 Oct;25(3):189–196. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(88)90133-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons D. J., Carvell G. E. Thalamocortical response transformation in the rat vibrissa/barrel system. J Neurophysiol. 1989 Feb;61(2):311–330. doi: 10.1152/jn.1989.61.2.311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. L. The ascending fiber projections from the principal sensory trigeminal nucleus in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1973 Apr 15;148(4):423–445. doi: 10.1002/cne.901480403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens J. K., Gerstein G. L. Spatiotemporal organization of cat lateral geniculate receptive fields. J Neurophysiol. 1976 Mar;39(2):213–238. doi: 10.1152/jn.1976.39.2.213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waite P. M. Somatotopic organization of vibrissal responses in the ventro-basal complex of the rat thalamus. J Physiol. 1973 Jan;228(2):527–540. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young M. P., Yamane S. Sparse population coding of faces in the inferotemporal cortex. Science. 1992 May 29;256(5061):1327–1331. doi: 10.1126/science.1598577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]