Abstract
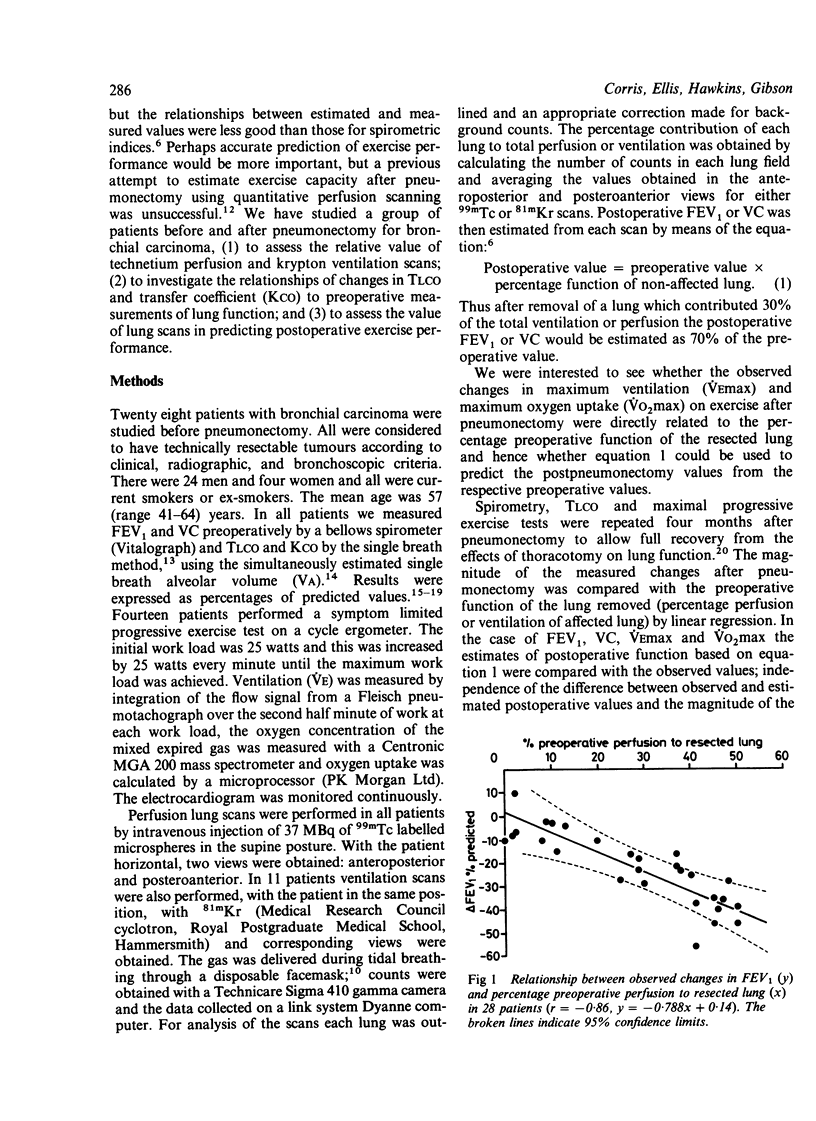
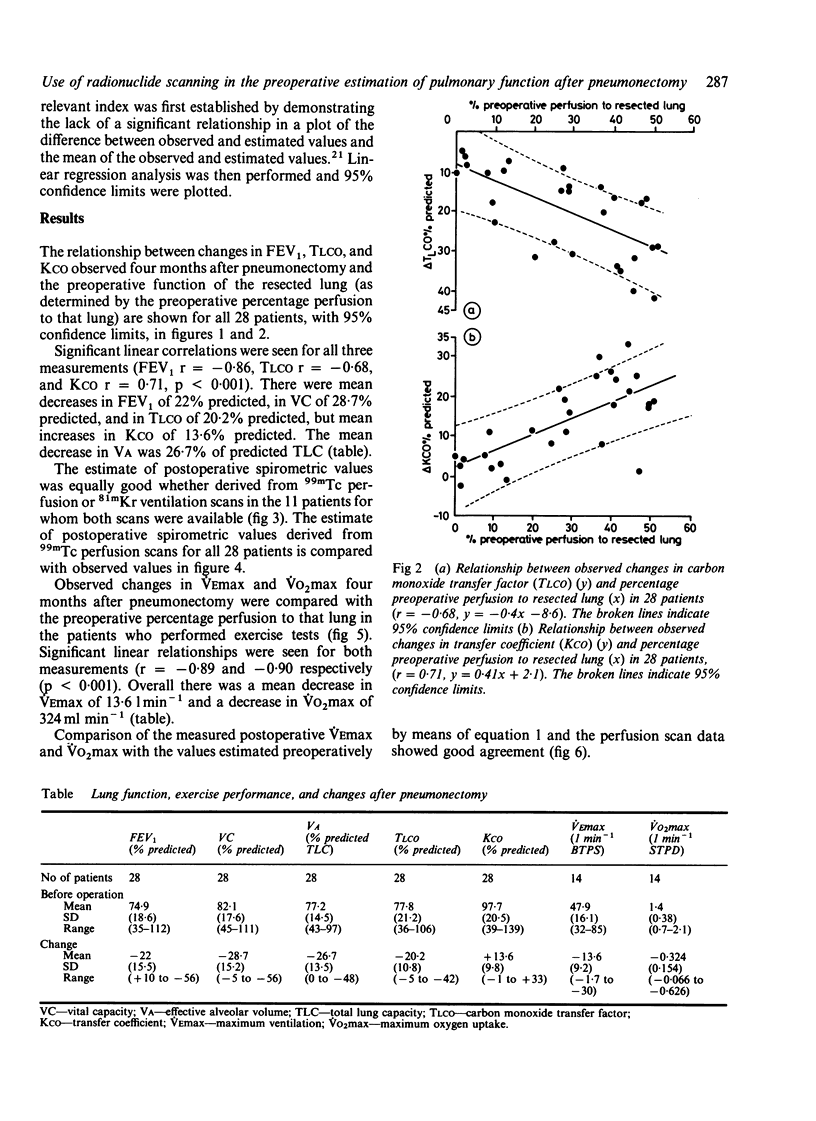
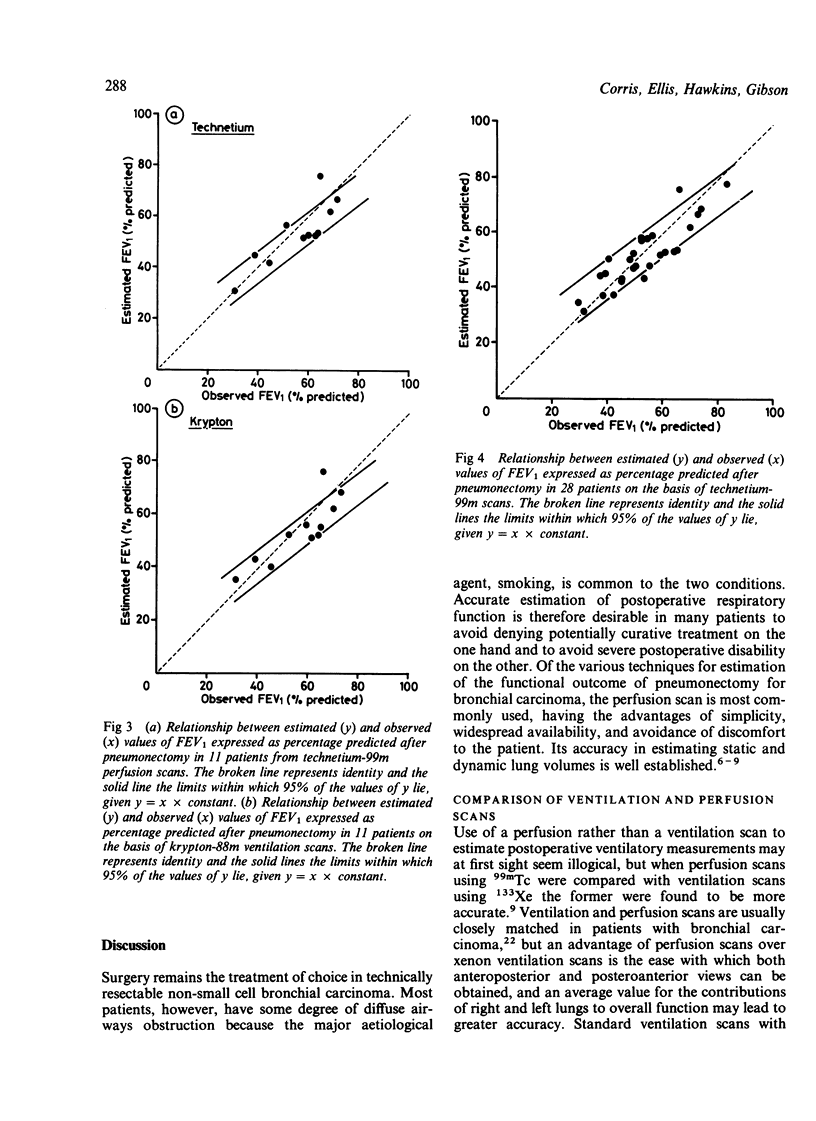
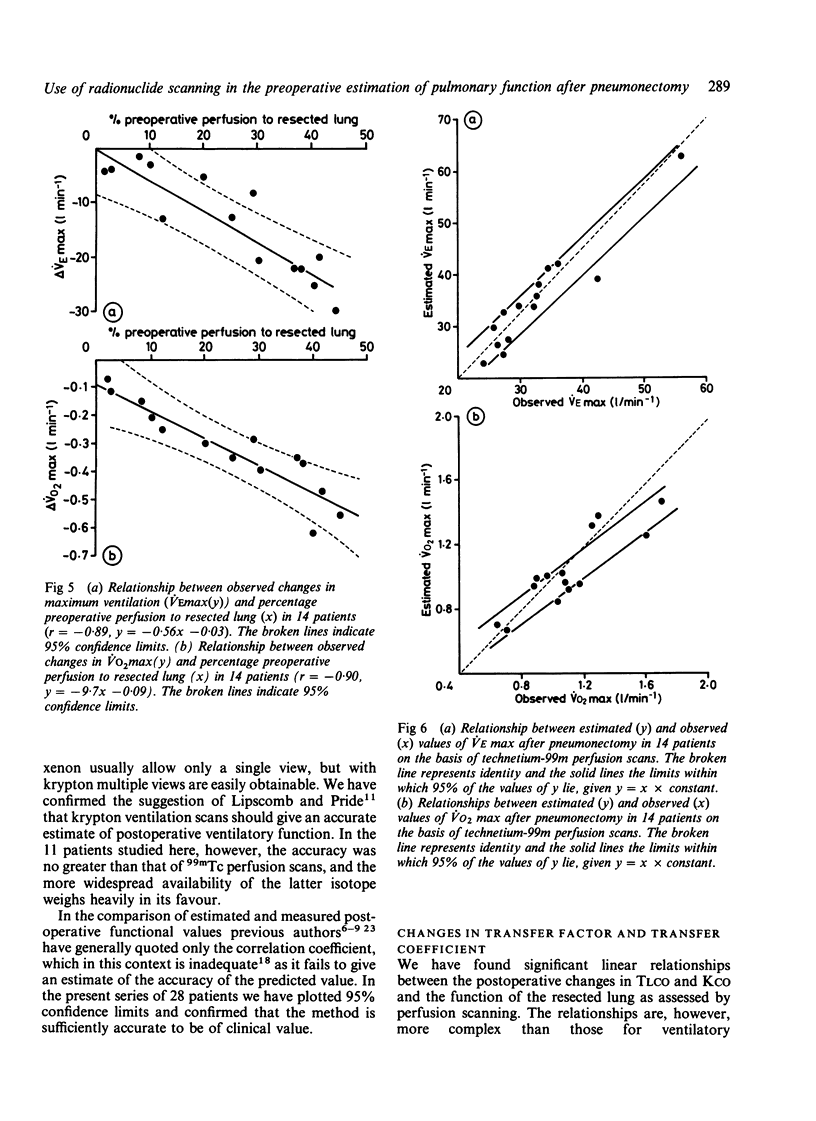
Twenty eight patients with bronchial carcinoma were studied before pneumonectomy. Measurement of spirometric indices, static lung volumes, transfer factor (TLCO), and transfer coefficient (KCO) was undertaken before and four months after pneumonectomy. Fourteen of the patients also performed a symptom limited progressive exercise test on a cycle ergometer before and four months after pneumonectomy. All patients had standard xenon-133 ventilation and technetium-99m perfusion scans performed before operation. Eleven patients had krypton-81m ventilation scans in addition. Significant correlations were seen between changes in FEV1, TLCO and KCO and the preoperative function of the resected lung as determined by percentage preoperative perfusion to that lung (p less than 0.001). There were mean decreases in FEV1 of 22% and in vital capacity (VC) of 28.7% predicted. Estimation of postoperative FEV1 from the preoperative values showed equally good agreement with measured postoperative values whether 99mTc perfusion or 81mKr ventilation scans were used in the 11 patients in whom both scans were available. Significant correlations were seen between change in maximum exercise ventilation (VEmax) or maximum oxygen uptake (VO2max) after pneumonectomy and percentage preoperative perfusion to the resected lung (p less than 0.001). Estimation of postoperative maximum ventilation and maximum oxygen uptake from the postoperative values on the basis of 99mTc perfusion scans showed good agreement with observed values. Perfusion scans are useful in estimating not only the changes in spirometric indices that follow pneumonectomy for bronchial carcinoma but also changes in carbon monoxide transfer and exercise capacity.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ali M. K., Mountain C. F., Ewer M. S., Johnston D., Haynie T. P. Predicting loss of pulmonary function after pulmonary resection for bronchogenic carcinoma. Chest. 1980 Mar;77(3):337–342. doi: 10.1378/chest.77.3.337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERGAN F. A simple method for determination of the relative function of the right and left lung. Acta Chir Scand Suppl. 1960;Suppl 253:58–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERGLUND E., BIRATH G., BJURE J., GRIMBY G., KJELLMER I., SANDQVIST L., SODERHOLM B. Spirometric studies in normal subjects. I. Forced expirograms in subjects between 7 and 70 years of age. Acta Med Scand. 1963 Feb;173:185–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLAKEMORE W. S., FORSTER R. E., MORTON J. W., OGILVIE C. M. A standardized breath holding technique for the clinical measurement of the diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide. J Clin Invest. 1957 Jan;36(1 Pt 1):1–17. doi: 10.1172/JCI103402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boysen P. G., Block A. J., Olsen G. N., Moulder P. V., Harris J. O., Rawitscher R. E. Prospective evaluation for pneumonectomy using the 99mtechnetium quantitative perfusion lung scan. Chest. 1977 Oct;72(4):422–425. doi: 10.1378/chest.72.4.422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley J., Bye C., Hayden S. P., Hughes D. T. Normal values of transfer factor and transfer coefficients in healthy males and females. Respiration. 1979;38(4):221–226. doi: 10.1159/000194084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis D. A., Hawkins T., Gibson G. J., Nariman S. Role of lung scanning in assessing the resectability of bronchial carcinoma. Thorax. 1983 Apr;38(4):261–266. doi: 10.1136/thx.38.4.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fazio F., Jones T. Assessment of regional ventilation by continuous inhalation of radioactive krypton-81m. Br Med J. 1975 Sep 20;3(5985):673–676. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5985.673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDMAN H. I., BECKLAKE M. R. Respiratory function tests; normal values at median altitudes and the prediction of normal results. Am Rev Tuberc. 1959 Apr;79(4):457–467. doi: 10.1164/artpd.1959.79.4.457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORLIN R., KNOWLES J. H., STOREY C. F. Effects of thoracotomy on pulmonary function; patients with localized pulmonary disease. J Thorac Surg. 1957 Aug;34(2):242–249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORY R. C., CALLAHAN R., BOREN H. G., SYNER J. C. The Veterans Administration-Army cooperative study of pulmonary function. I. Clinical spirometry in normal men. Am J Med. 1961 Feb;30:243–258. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(61)90096-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristersson S., Lindell S. E., Svanberg L. Prediction of pulmonary function loss due to pneumonectomy using 133 Xe-radiospirometry. Chest. 1972 Dec;62(6):694–698. doi: 10.1378/chest.62.6.694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laros C. D., Swierenga J. Temporary unilateral pulmonary artery occlusion in the preoperative evaluation of patients with bronchial carcinoma. Comparison of pulmonary artery pressure measurements, pulmonary function tests and early postoperative mortality. Med Thorac. 1967;24(5):269–283. doi: 10.1159/000192532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipscomb D. J., Pride N. B. Ventilation and perfusion scans in the preoperative assessment of bronchial carcinoma. Thorax. 1977 Dec;32(6):720–725. doi: 10.1136/thx.32.6.720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGRATH M. W., THOMSON M. L. The effect of age, body size and lung volume change on alveolar-capillary permeability and diffusing capacity in man. J Physiol. 1959 Jun 11;146(3):572–582. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuhaus H., Cherniack N. S. A bronchospirometric method of estimating the effect of pneumonectomy on the maximum breathing capacity. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1968 Jan;55(1):144–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen G. N., Block A. J., Tobias J. A. Prediction of postpneumonectomy pulmonary function using quantitative macroaggregate lung scanning. Chest. 1974 Jul;66(1):13–16. doi: 10.1378/chest.66.1.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SNIDER G. L. A CRITICAL EVALUATION OF BRONCHOSPIROMETRIC MEASUREMENT IN PREDICTING LOSS OF VENTILATORY FUNCTION DUE TO THORACIC SURGERY. J Lab Clin Med. 1964 Aug;64:321–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wernly J. A., DeMeester T. R., Kirchner P. T., Myerowitz P. D., Oxford D. E., Golomb H. M. Clinical value of quantitative ventilation-perfusion lung scans in the surgical management of bronchogenic carcinoma. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1980 Oct;80(4):535–543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A. J., Cayton R. M., Harding L. K., Mostafa A. B., Matthews H. R. Quantitative lung scintigrams and lung function in the selection of patients for pneumonectomy. Br J Dis Chest. 1984 Apr;78(2):105–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



