Abstract
We show that the two most important properties needed for a tRNA to function in initiation in Escherichia coli are its ability to be formylated and its ability to bind to the ribosomal P site. This conclusion is based on conversion of two different elongator tRNAs to ones that can act as initiators in E. coli. We transplanted the features unique to E. coli and eubacterial initiator tRNAs to E. coli elongator methionine tRNA (tRNA(Met)) along with an anticodon sequence change and analyzed their activities in initiation in E. coli. Introduction of a C1.A72 mismatch at the end of the acceptor stem of tRNA(Met), which generates the minimal features necessary for formylation, produces a tRNA with very low activity in initiation. Subsequent introduction of three consecutive G.C base pairs at the bottom of the anticodon stem, which is necessary for ribosomal P site binding, produces a tRNA with significant activity in initiation. Furthermore, introduction of the features necessary for formylation and for ribosomal P site binding into E. coli elongator glutamine tRNA produces a tRNA that initiates protein synthesis in E. coli.
Full text
PDF
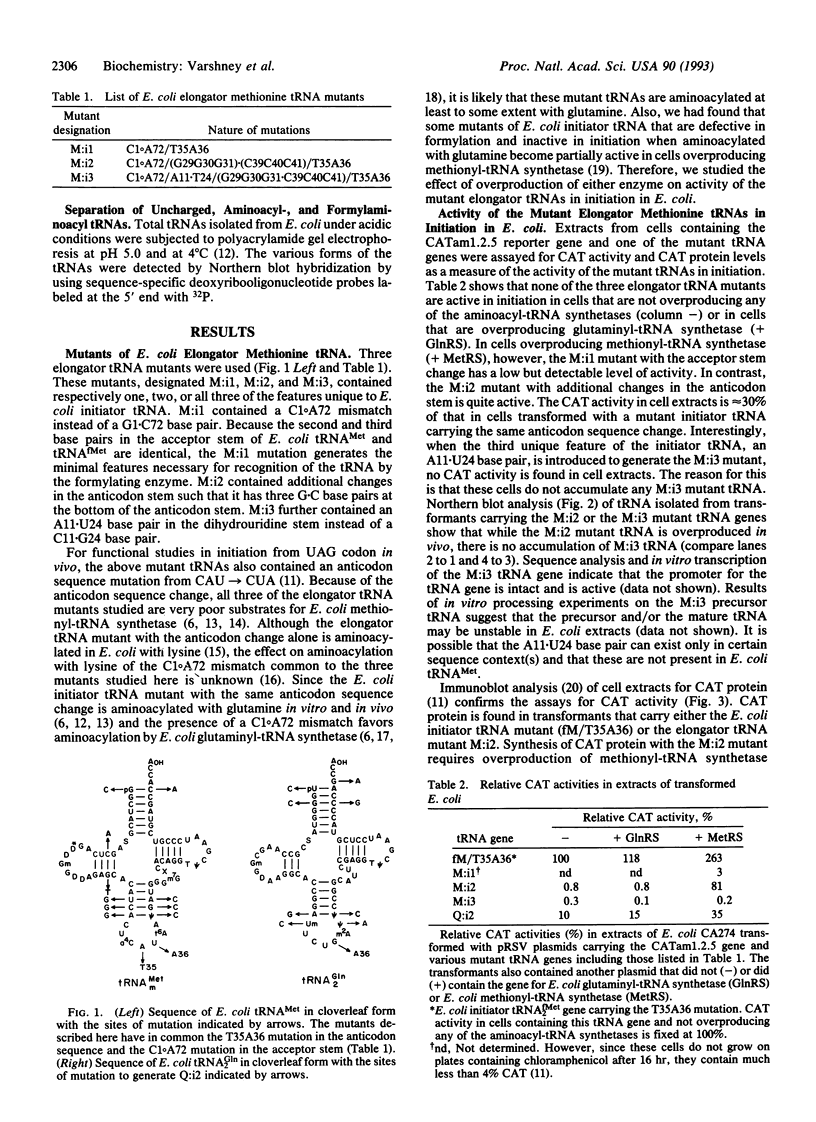
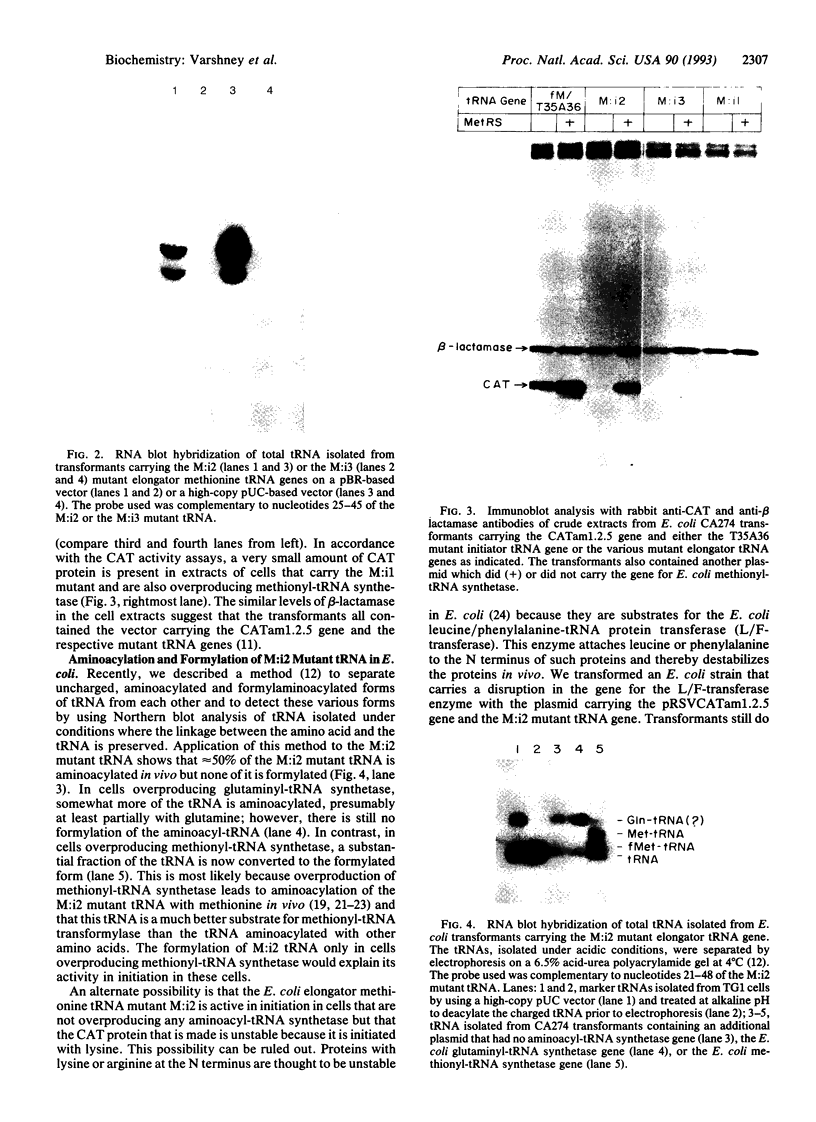


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gold L. Posttranscriptional regulatory mechanisms in Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:199–233. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.001215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gualerzi C. O., Pon C. L. Initiation of mRNA translation in prokaryotes. Biochemistry. 1990 Jun 26;29(25):5881–5889. doi: 10.1021/bi00477a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillon J. M., Mechulam Y., Schmitter J. M., Blanquet S., Fayat G. Disruption of the gene for Met-tRNA(fMet) formyltransferase severely impairs growth of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jul;174(13):4294–4301. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.13.4294-4301.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillon J. M., Meinnel T., Mechulam Y., Lazennec C., Blanquet S., Fayat G. Nucleotides of tRNA governing the specificity of Escherichia coli methionyl-tRNA(fMet) formyltransferase. J Mol Biol. 1992 Mar 20;224(2):359–367. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)91000-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hou Y. M., Schimmel P. Modeling with in vitro kinetic parameters for the elaboration of transfer RNA identity in vivo. Biochemistry. 1989 Jun 13;28(12):4942–4947. doi: 10.1021/bi00438a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahn M., Rogers M. J., Söll D. Anticodon and acceptor stem nucleotides in tRNA(Gln) are major recognition elements for E. coli glutaminyl-tRNA synthetase. Nature. 1991 Jul 18;352(6332):258–260. doi: 10.1038/352258a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Comparison of initiation of protein synthesis in procaryotes, eucaryotes, and organelles. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Mar;47(1):1–45. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.1.1-45.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. P., Dyson M. R., Mandal N., Varshney U., Bahramian B., RajBhandary U. L. Striking effects of coupling mutations in the acceptor stem on recognition of tRNAs by Escherichia coli Met-tRNA synthetase and Met-tRNA transformylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):9262–9266. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.9262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. P., Seong B. L., RajBhandary U. L. Structural and sequence elements important for recognition of Escherichia coli formylmethionine tRNA by methionyl-tRNA transformylase are clustered in the acceptor stem. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 25;266(27):18012–18017. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClain W. H., Foss K., Jenkins R. A., Schneider J. Nucleotides that determine Escherichia coli tRNA(Arg) and tRNA(Lys) acceptor identities revealed by analyses of mutant opal and amber suppressor tRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9260–9264. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normanly J., Kleina L. G., Masson J. M., Abelson J., Miller J. H. Construction of Escherichia coli amber suppressor tRNA genes. III. Determination of tRNA specificity. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jun 20;213(4):719–726. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80258-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rould M. A., Perona J. J., Söll D., Steitz T. A. Structure of E. coli glutaminyl-tRNA synthetase complexed with tRNA(Gln) and ATP at 2.8 A resolution. Science. 1989 Dec 1;246(4934):1135–1142. doi: 10.1126/science.2479982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulman L. H., Pelka H. In vitro conversion of a methionine to a glutamine-acceptor tRNA. Biochemistry. 1985 Dec 3;24(25):7309–7314. doi: 10.1021/bi00346a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulman L. H. Recognition of tRNAs by aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1991;41:23–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seong B. L., Lee C. P., RajBhandary U. L. Suppression of amber codons in vivo as evidence that mutants derived from Escherichia coli initiator tRNA can act at the step of elongation in protein synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 15;264(11):6504–6508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seong B. L., RajBhandary U. L. Escherichia coli formylmethionine tRNA: mutations in GGGCCC sequence conserved in anticodon stem of initiator tRNAs affect initiation of protein synthesis and conformation of anticodon loop. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(2):334–338. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.2.334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seong B. L., RajBhandary U. L. Mutants of Escherichia coli formylmethionine tRNA: a single base change enables initiator tRNA to act as an elongator in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8859–8863. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprinzl M., Hartmann T., Weber J., Blank J., Zeidler R. Compilation of tRNA sequences and sequences of tRNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989;17 (Suppl):r1–172. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.suppl.r1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson R., Hoben P., Sumner-Smith M., Uemura H., Watson L., Söll D. Accuracy of in vivo aminoacylation requires proper balance of tRNA and aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase. Science. 1988 Dec 16;242(4885):1548–1551. doi: 10.1126/science.3144042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobias J. W., Shrader T. E., Rocap G., Varshavsky A. The N-end rule in bacteria. Science. 1991 Nov 29;254(5036):1374–1377. doi: 10.1126/science.1962196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varshney U., Lee C. P., RajBhandary U. L. Direct analysis of aminoacylation levels of tRNAs in vivo. Application to studying recognition of Escherichia coli initiator tRNA mutants by glutaminyl-tRNA synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 25;266(36):24712–24718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varshney U., Lee C. P., Seong B. L., RajBhandary U. L. Mutants of initiator tRNA that function both as initiators and elongators. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 25;266(27):18018–18024. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varshney U., RajBhandary U. L. Initiation of protein synthesis from a termination codon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1586–1590. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varshney U., RajBhandary U. L. Role of methionine and formylation of initiator tRNA in initiation of protein synthesis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1992 Dec;174(23):7819–7826. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.23.7819-7826.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarus M. Intrinsic precision of aminoacyl-tRNA synthesis enhanced through parallel systems of ligands. Nat New Biol. 1972 Sep 27;239(91):106–108. doi: 10.1038/newbio239106a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]