Abstract
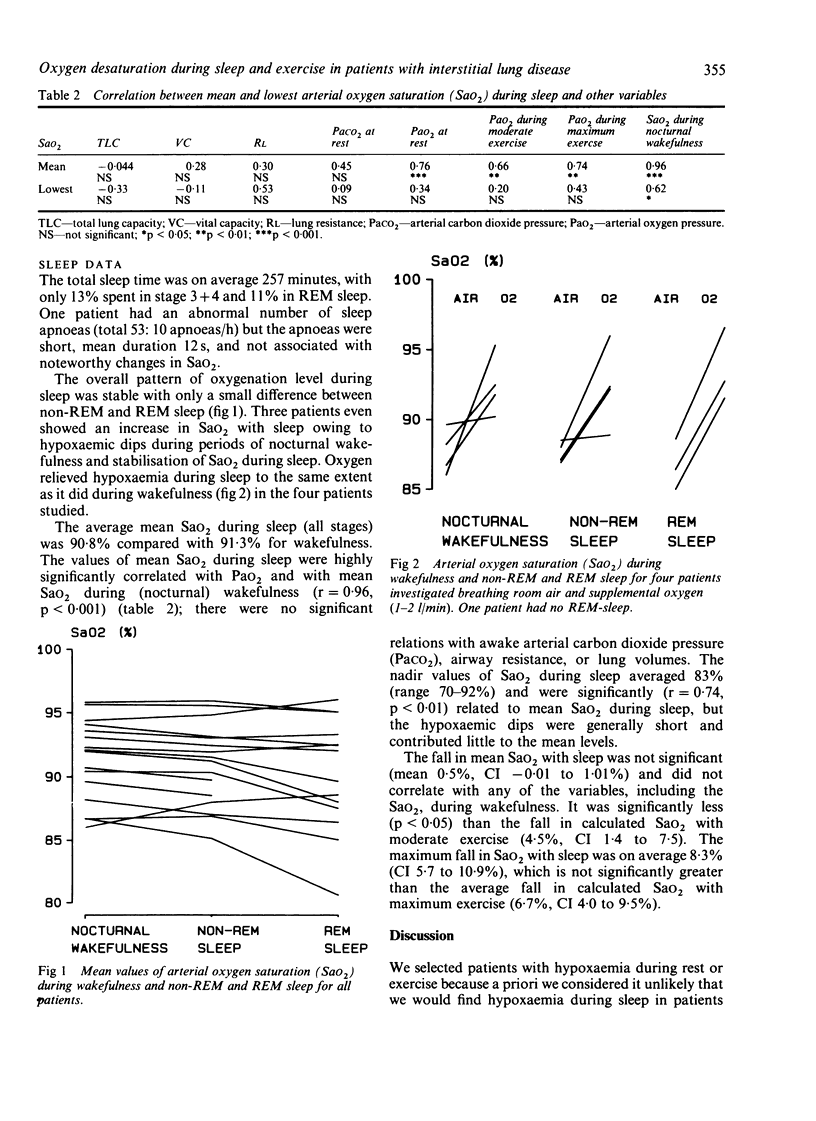
The relations between mean and maximum fall in arterial oxygen saturation (SaO2) during sleep, hypoxaemia during moderate and maximum exercise, and lung mechanics were studied in 16 patients with interstitial lung disease. Mean and minimum SaO2 during sleep were significantly related to each other and to daytime oxygenation but not to lung mechanics. Although the maximum fall in SaO2 during sleep was similar to the fall during maximum exercise (a level seldom achieved during normal daily activities), profound hypoxaemic episodes during sleep were rare and brief and therefore contributed little to the mean SaO2. The fall in mean SaO2 during sleep was not significant and was considerably less than during moderate exercise (average 0.5 v an estimated 4.5%, p less than 0.05). It is therefore concluded that in patients with interstitial lung disease oxygen desaturation during sleep is mild and less severe than hypoxaemia during exercise.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERGLUND E., BIRATH G., BJURE J., GRIMBY G., KJELLMER I., SANDQVIST L., SODERHOLM B. Spirometric studies in normal subjects. I. Forced expirograms in subjects between 7 and 70 years of age. Acta Med Scand. 1963 Feb;173:185–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bye P. T., Issa F., Berthon-Jones M., Sullivan C. E. Studies of oxygenation during sleep in patients with interstitial lung disease. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Jan;129(1):27–32. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.129.1.27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall J. R., Douglas N. J., Calverley P. M., Shapiro C. M., Brezinova V., Brash H. M., Flenley D. C. Transient hypoxemia during sleep in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is not a sleep apnea syndrome. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 Jul;128(1):24–29. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.128.1.24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman K. R., D'Urzo A., Rebuck A. S. The accuracy and response characteristics of a simplified ear oximeter. Chest. 1983 Jun;83(6):860–864. doi: 10.1378/chest.83.6.860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crystal R. G., Fulmer J. D., Roberts W. C., Moss M. L., Line B. R., Reynolds H. Y. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Clinical, histologic, radiographic, physiologic, scintigraphic, cytologic, and biochemical aspects. Ann Intern Med. 1976 Dec;85(6):769–788. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-85-6-769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonson B. A method for determination of pulmonary elastic recoil and resistance at a regulated flow rate. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1969 Sep;24(2):115–125. doi: 10.3109/00365516909080141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelman G. R., Nunn J. F. Nomograms for correction of blood Po2, Pco2, pH, and base excess for time and temperature. J Appl Physiol. 1966 Sep;21(5):1484–1490. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1966.21.5.1484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNicholas W. T., Coffey M., Fitzgerald M. X. Ventilation and gas exchange during sleep in patients with interstitial lung disease. Thorax. 1986 Oct;41(10):777–782. doi: 10.1136/thx.41.10.777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Midgren B., White T., Petersson K., Bryhn M., Airikkala P., Elmqvist D. Nocturnal hypoxaemia and cor pulmonale in severe chronic lung disease. Bull Eur Physiopathol Respir. 1985 Nov-Dec;21(6):527–533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Padilla R., West P., Lertzman M., Kryger M. H. Breathing during sleep in patients with interstitial lung disease. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Aug;132(2):224–229. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.132.2.224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philipson L., Risberg A. M., Ingvar D. H. Normal sleep pattern analyzed statistically and studied by color "dormograms". Sleep. 1980;2(4):437–451. doi: 10.1093/sleep/2.4.437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutland J., Griffin W. M., Cole P. J. Human ciliary beat frequency in epithelium from intrathoracic and extrathoracic airways. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 Jan;125(1):100–105. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1982.125.1.100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stradling J. R., Lane D. J. Nocturnal hypoxaemia in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Clin Sci (Lond) 1983 Feb;64(2):213–222. doi: 10.1042/cs0640213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tweeddale P. M., Douglas N. J. Evaluation of Biox IIA ear oximeter. Thorax. 1985 Nov;40(11):825–827. doi: 10.1136/thx.40.11.825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


