Abstract
Proliferative verrucous leukoplakia is an intriguing disease, which occurs particularly in women aged greater than 60 years, is not associated with tobacco and alcohol, and has a high risk of recurrence and malignant transformation. Although it is well known that the typical presentation is characterized by multifocal and verrucous white lesions, there is no description that its initial clinical presentation may simulate a lichenoid reaction.
Keywords: Proliferative verrucous leukoplakia, Lichenoid reactions, Diagnosis
Core tip: Although uncommon, it is important for the clinician to recognize the main features of proliferative verrucous leukoplakia in order to provide the correct diagnosis and appropriate management.
PROLIFERATIVE VERRUCOUS LEUKOPLAKIA WITH LICHENOID ASPECT
Proliferative verrucous leukoplakia (PVL) was first described in 1985 as a rare form of oral leukoplakia with a distinct clinical presentation and outcome[1]. This condition more commonly affects non-smoking and non-drinking women, aged greater than 60 years. PVL clinically begins as flat homogenous leukoplakia, becomes multifocal and tends to develop exophytic, wart-like and verrucous areas. Besides this clinical progression, PVL also has a high tendency to recur after treatment and has a high risk of malignant transformation. According to several reports, malignant transformation rates vary between 33.3% and 100% and depend on many factors, particularly the number of patients and time of follow-up[2-4].
The characteristics reported above are well known and well accepted by the scientific community. However, there are many doubts and controversies particularly regarding etiology, diagnostic criteria and treatment[5]. The diagnosis of PVL is based on the retrospective association of clinical and histopathological features, which basically consist of observing progressive evolution of the lesions from a homogeneous and isolated area to a multifocal presentation with a verrucous appearance. As these manifestations take time, the diagnosis of PVL is often late.
In order to better recognize this condition, diagnostic criteria were recently proposed, which included 5 major and 4 minor criteria, as well as various combinations of these criteria[6]. In this proposal, one of the major criteria is “the presence of verrucous area”. However, according to Aguirre-Urizar[7], the diagnosis of PVL may be delayed if verrucous appearance is considered a main diagnostic feature. In this author’s opinion, the most important diagnostic criteria for this type of leukoplakia are the “proliferative” and the “multifocal” aspects. Thus, he proposed a new name for this entity: “Proliferative Multifocal Leukoplakia” with the aim of reducing under-diagnosis[7].
When attending patients with this disorder we observed that in some cases it was very clear and simple to establish the diagnosis of PVL as the patients had lesions with peculiar aspects. However, in other situations the lesions may have different clinical features such as erythroplakic changes[8], which may cause some difficulty in diagnosis. In this scenario, close follow-up is necessary and will permit observation of the development of more characteristic lesions such as in the patient presented below.
In May 2011, a non-smoking and non-drinking 64-year-old female patient was referred to our oral diagnosis service complaining of a painful area on the tongue. She reported the onset of a white lesion on the left lateral border of the tongue 3 years before attending our Clinic. At that time, she had been seen by another dental team and it was initially thought to be a fungal infection and she received treatment based on topical antifungals. As no improvement was observed, a lichenoid reaction was suspected and her dental metallic (gold) restorations were replaced and a partial fixed prosthesis was inserted. However, no improvement was observed. As the lesion persisted, an incisional biopsy was performed by an otorhinolaryngologist. Microscopically, the lesion showed moderate epithelial dysplasia and a chronic inflammatory infiltrate in the underlying connective tissue. The patient was then referred for our evaluation and the first visit to our service revealed white striations with atrophic areas on the buccal mucosa bilaterally. She also had similar alterations on the left lateral border of the tongue (Figure 1). An incisional biopsy was performed on the left lateral border of the tongue and another on the right buccal mucosa. Histopathological analysis of both sites revealed hyperkeratosis and acanthosis with mild epithelial dysplasia. According to these clinical features and the patient’s symptoms, she was treated with topical clobetasol 0.05% three times a day. After 3 wk, pain relief was observed. During the follow-up period, areas of leukoplakia were observed on the left lateral border of the tongue (Figure 1). Taking these findings into account, the diagnosis of possible PVL was suggested and the patient was advised about the need for close observation. The patient remained on regular follow-up without clinical modifications. However, after 15 mo the white lesion on the left lateral border of the tongue became more diffuse and another incisional biopsy was performed and the diagnosis of squamous cell carcinoma was established. The patient was then referred to a head and neck surgeon and a partial glossectomy was performed disclosing free surgical margins.
Figure 1.
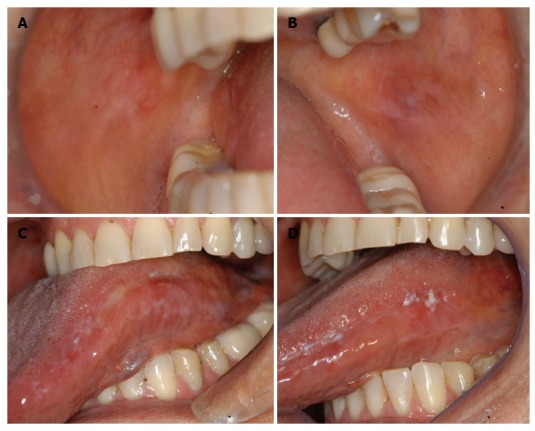
Lichenoid aspect on the right buccal mucosa (A), left buccal mucosa (B) and on the left lateral border of the tongue (C), leukoplakic lesions on the lateral border of the tongue (D).
Recently, it was reported that the clinical presentation of oral lichen planus (OLP) has similarities to PVL based on the facts that most patients are females, without a history of tobacco or alcohol use and the presence of multifocal white lesions. In addition, as in OLP, the lesions have a predilection for the gingiva, tongue and buccal mucosa[9]. In addition to the above-mentioned similarities, we noted that some older female patients without tobacco or alcohol habits had lesions that were similar to lichenoid reactions, but the histopathological analysis proved to be hyperkeratosis and acanthosis with variable degrees of epithelial dysplasia. However, the diagnosis of lichen planus or lichenoid reaction was ruled out microscopically, and these patients later developed more leukoplakic lesions consistent with multifocal leukoplakia.
Therefore, we suggest that the initial clinical manifestation in some cases of PVL may mimic OLP or oral lichenoid reaction, and both biopsy and microscopic analysis are mandatory in order to avoid misdiagnosis, and consequently provide better patient management.
Footnotes
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare no conflict-of-interest.
Open-Access: This article is an open-access article which was selected by an in-house editor and fully peer-reviewed by external reviewers. It is distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution Non Commercial (CC BY-NC 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt, build upon this work non-commercially, and license their derivative works on different terms, provided the original work is properly cited and the use is non-commercial. See: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/
Peer-review started: February 12, 2015
First decision: May 13, 2015
Article in press: September 8, 2015
P- Reviewer: Hu R, Teoh AYB, Voutsas V S- Editor: Tian YL L- Editor: A E- Editor: Jiao XK
References
- 1.Hansen LS, Olson JA, Silverman S. Proliferative verrucous leukoplakia. A long-term study of thirty patients. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1985;60:285–298. doi: 10.1016/0030-4220(85)90313-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bagan JV, Jimenez Y, Sanchis JM, Poveda R, Milian MA, Murillo J, Scully C. Proliferative verrucous leukoplakia: high incidence of gingival squamous cell carcinoma. J Oral Pathol Med. 2003;32:379–382. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0714.2003.00167.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Morton TH, Cabay RJ, Epstein JB. Proliferative verrucous leukoplakia and its progression to oral carcinoma: report of three cases. J Oral Pathol Med. 2007;36:315–318. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0714.2007.00499.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Gouvêa AF, Vargas PA, Coletta RD, Jorge J, Lopes MA. Clinicopathological features and immunohistochemical expression of p53, Ki-67, Mcm-2 and Mcm-5 in proliferative verrucous leukoplakia. J Oral Pathol Med. 2010;39:447–452. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0714.2010.00889.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Bishen KA, Sethi A. Proliferative Verrucous Leukoplakia--diagnostic pitfalls and suggestions. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2009;14:E263–E264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Cerero-Lapiedra R, Baladé-Martínez D, Moreno-López LA, Esparza-Gómez G, Bagán JV. Proliferative verrucous leukoplakia: a proposal for diagnostic criteria. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2010;15:e839–e845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Aguirre-Urizar JM. Proliferative multifocal leukoplakia better name that proliferative verrucous leukoplakia. World J Surg Oncol. 2011;9:122. doi: 10.1186/1477-7819-9-122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Bagan J, Scully C, Jimenez Y, Martorell M. Proliferative verrucous leukoplakia: a concise update. Oral Dis. 2010;16:328–332. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-0825.2009.01632.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Müller S. Oral manifestations of dermatologic disease: a focus on lichenoid lesions. Head Neck Pathol. 2011;5:36–40. doi: 10.1007/s12105-010-0237-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


