Abstract
Background
Candidatus Neoehrlichia came under the focus of recent research in terms of human and pet relevance. Candidatus Neoehrlichia mikurensis seems to be relatively abundant in animals and humans from Central European countries, whereas Candidatus Neoehrlichia lotoris was found solely in raccoons from the USA.
Findings
Spleen samples from a total of 164 red foxes, originating from two western provinces in Austria (Tyrol and Vorarlberg), were collected and examined for the presence of tick-borne bacteria of the family Anaplasmataceae by PCR and sequencing. In a fox sample originating from Vorarlberg Candidatus Neoehrlichia sp. was found, which is genetically (16S rRNA, groEL) closely related to Candidatus Neoehrlichia lotoris but clearly distinct from Candidatus Neoehrlichia mikurensis.
Conclusions
The present study revealed, for the first time, the occurrence of Candidatus Neoehrlichia sp. in a red fox worldwide. A continuing screening of wild carnivores, especially foxes, and ticks for this potential pathogen is required to evaluate the actual occurrence and distribution of these bacteria. Further research is needed to elucidate the relationships of Neoehrlichia, as well as their reservoir and impact on wildlife, pets and humans.
Keywords: Candidatus Neoehrlichia sp, 16S rRNA, GroEL, Red fox, Austria, Phylogenetic analysis
Findings
Candidatus Neoehrlichia came under the focus of recent research in terms of human and pet relevance [1]. The coccoid Gram-negative bacteria Candidatus Neoehrlichia mikurensis (CNM) and Candidatus Neoehrlichia lotoris (CNL) are supposed to be mainly associated with rodents and raccoons, respectively [1, 2]. Moreover, CNM was found in humans, dogs, hedgehogs, shrews, bears, badgers, chamois, mouflons and ticks collected from various wild animals [1, 3–5]. CNL was solely found in raccoons in the USA [2, 6] and trials to experimentally infect laboratory mice, rats or rabbits failed [7]. The vectors of CNM are supposed to be mainly Ixodes ricinus and other Ixodes species, but the pathogen was also detected in Dermacentor reticulatus, Rhipicephalus sanguineus, Haemaphysalis concinna and H. leachi [1]. For CNL Ixodes spp. are assumed to be potential vectors [7], but further research is needed to confirm the vector competence of different tick species. Until now several studies, mainly on the groEL gene, indicated a considerable genetic variation within CNM in Europe [8], whereas for CNL only a single variant has been described yet [2].
In the year 2014 spleen samples were collected from 164 foxes in two western provinces of Austria (Tyrol and Vorarlberg). DNA was extracted from ~20 mg of spleen tissue using the DNeasy Blood & Tissue Kit (QIAGEN, Netherlands) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. All samples were screened for Anaplasma spp., Ehrlichia spp. and Candidatus Neoehrlichia using the Anaplasmataceae-specific primers EHR16SD and EHR16SR, which amplify a ~345 bp section of the 16S rRNA (16S) [9]. PCR analysis of the spleen of one female fox (FU98) originating from Feldkirch (Vorarlberg) gave a positive signal. For a more integral approach we designed primers amplifying a longer (~1,053 bp) fragment of the 16S and a 806 bp section of the groEL gene. The DNA fragments were amplified with the GoTaq® G2 Polymerase (Promega, USA). The PCR started with 2 min at 95 °C, followed by 35 cycles with 1 min at 95 °C, 1 min at the particular annealing temperature (Table 1), 1 min at 72 °C, and a final extension for 5 min at 72 °C.
Table 1.
PCR conditions for identification of Candidatus Neoehrlichia used in this study
| Specifity | Genetic marker | Sequences of primer (5’- 3’) | Annealing temperature (°C) | Amplicon size (bp) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anaplasmataceae | 16S | EHR16SD: GGT ACC YAC AGA AGA AGT CC | 54 | 345 | [9] |
| EHR16SR: TAG CAC TCA TCG TTT ACA GC | |||||
| Candidatus Neoehrlichia | groEL | NeoeGroELFw: CAG GTG AAG CAC TAG ATA AGT CCA | 54 | 806 | This study |
| NeoeGroELRv: ACA GCA GCA ACA TGC AAT CCA | |||||
| Candidatus Neoehrlichia | 16S | 16SCNM_for: GTG GCA GAC GGG TGA GTA AT | 60 | 1,053 | This study |
| 16SCNM_rev: TGC AGC ACC TGT GTA AGG TC |
A phylogenetic tree was constructed with the combined 16S [KT833357] and groEL [KT833358] sequences of the sample FU98 and Candidatus Neoehrlichia sequences published at the NCBI data base (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov). 16S and groEL sequences originating from the same hosts were published only for nine samples of CNM and one of CNL, respectively. For outgroup comparison, 16S and groEL sequences were extracted from the complete genome of Ehrlichia chaffensis [CP007479]. The two sequence sections were aligned separately with MAFFT v.7.215 [10], resulting in alignments of 884 bp and 686 bp for 16S and groEL, respectively. The two alignments were concatenated and a model test was performed with JModeltest v.2.1.5 [11]. A Maximum Likelihood (ML) bootstrap tree (1000 replicates) was calculated with MEGA6 v.6.06 [12] with the suggested substitution model GTR + G + I and Subtree-Pruning-Regrafting as heuristic method.
Phylogenetic networks were calculated with the 16S and groEL sequences of the newly found Candidatus Neoehrlichia sp. (FU98) and published data. BLAST searches for Candidatus Neoehrlichia were performed at the NCBI data base with the 16S and groEL sequences. The sequences of both data sets were aligned with MAFFT v.7.215 [10] and Median-Joining networks were calculated with Network v.4.6.0.0 (fluxus-engineering.com) applying the default settings. Genetic distances were calculated with MEGA6 v.6.06 [12] based on the 16S and groEL alignments used for the phylogenetic networks. Mean p-distances were calculated between CNM and CNL and maximum p-distances were calculated within those taxa.
The ML bootstrap tree calculated with the concatenated alignments of 16S and groEL (1,570 bp) (Fig. 1a) shows two highly supported clades, the first with samples classified as CNM, the second containing the only CNL sample published yet, RAC413 [2], as well as the new Candidatus Neoehrlichia sp. (FU98) originated from a fox in the present study. The Median-Joining networks (Fig. 1b and c) both show well separated clades containing exclusively sequences of CNM and CNL. The maximum p-distances within CNL (= between FU98 and RAC413) are 0.5 % (16S) and 4.2 % (groEL), whereas the maximum p-distances within CNM are slightly higher with 1.2 % (16S) and 5.7 % (groEL). The mean genetic p-distances between CNM and CNL are 1.3 % (16S) and 8.9 % (groEL), and thus higher than the maximum intraspecific distances measured within the two taxa.
Fig. 1.
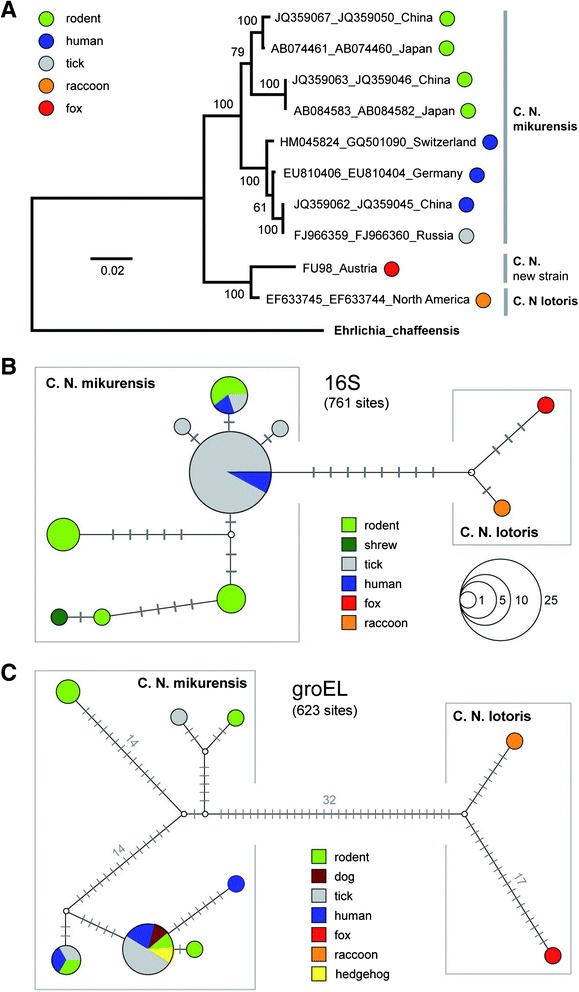
a Maximum Likelihood bootstrap tree with 16S and groEL sequences of CNM and CNL. ML bootstrap values are indicated at the nodes. The tree is drawn to scale, with branch lengths measured in the number of substitutions per site. b Median-Joining network with 16S sequences of Candidatus Neoehrlichia. The sizes of the nodes correspond to the number of haplotypes (right lower corner). Grey bars indicate the number of substitutions between haplotypes. c Median-Joining network with groEL sequences of Candidatus Neoehrlichia
Conclusions
This study reports the presence of Candidatus Neoehrlichia sp. in a red fox for the first time worldwide. The obtained sequences are considered as CNL in the present study because of the similarity with the strain RAC413, which was isolated from raccoons in the south-eastern USA. In the phylogenetic tree calculated with sections of the 16S and groEL genes, the strains FU98 and RAC413 from well supported clade, clearly distinct from CNM. Genetic distances between FU98 and RAC413 are only slightly lower than those within CNM. However, the current data is not sufficient to explicitly state whether the new FU98 sequences belong to CNL or rather represents a new species of Candidatus Neoehrlichia. According to the national surveillance for the occurrence of raccoons and raccoon dogs, there is an oral report of a sighting in 2010 in this particular area and a proven evidence of raccoons ~15 km north of the investigation area in 2011 (Duscher T., person. comm.), although their abundance is sporadic. Nevertheless spill over from these raccoons cannot be excluded. However, investigations of free ranging Austrian raccoons are needed to trace the infection ways. Moreover, a continuing screening of wild carnivores, especially foxes, and ticks for this potential pathogen is required to see the actual occurrence and distribution of these bacteria. Further research is needed to elucidate the relationships of Neoehrlichia, as well as their reservoir and impact on wildlife, pets and humans.
Ethical statement
All foxes were shot during routine hunting events under the restrictions of the game laws of Austria.
Acknowledgements
The work was done under the frame of EurNegVec COST Action TD1303. We thank Barbara Eigner from the Institute of Parasitology, University of Veterinary Medicine Vienna for technical support.
Footnotes
Competing interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Authors’ contributions
HPF, GGD, AH: conceived and designed the study; GGD, AH, JH: wrote the manuscript; AH, RC: performed laboratory investigations; HPF, JH: performed sequence analyses; JH: performed phylogenetic analyses; WG: collected the samples. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Contributor Information
Adnan Hodžić, Email: adnan.hodzic@vetmeduni.ac.at.
Rita Cézanne, Email: rita.cezanne@gmx.at.
Georg Gerhard Duscher, Email: georg.duscher@vetmeduni.ac.at.
Josef Harl, Email: harl_josef@hotmail.com.
Walter Glawischnig, Email: walter.glawischnig@ages.at.
Hans-Peter Fuehrer, Phone: +43 1 25077-2211, Email: hans-peter.fuehrer@vetmeduni.ac.at.
References
- 1.Silaghi C, Beck R, Oteo JA, Pfeffer M, Sprong H. Neoehrlichiosis: An emerging tick-borne zoonosis caused by Candidatus Neoehrlichia mikurensis. Exp Appl Acarol. 2015 doi: 10.1007/s10493-015-9935-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Yabsley MJ, Murphy SM, Luttrell MP, Wilcox BR, Howerth EW, Munderloh UG. Characterization of “Candidatus Neoehrlichia lotoris” (family Anaplasmataceae) from raccoons (Procyon lotor) Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2008;58(Pt 12):2794–8. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.65836-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Grankvist A, Sandelin LL, Andersson J, Fryland L, Wilhelmsson P, Lindgren PE, Forsberg P, Wennerås C. Infections with Candidatus Neoehrlichia mikurensis and cytokine responses in 2 persons bitten by ticks. Sweden Emerg Infect Dis. 2015;21:1462–5. doi: 10.3201/eid2108.150060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Földvári G, Jahfari S, Rigó K, Jablonszky M, Szekeres S, Majoros G, Tóth M, Molnár V, Coipan EC, Sprong H. Candidatus Neoehrlichia mikurensis and Anaplasma phagocytophilum in urban hedgehogs. Emerg Infect Dis. 2014;20:496–8. doi: 10.3201/eid2003.130935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Diniz PPVP, Schulz BS, Hartmann K, Breitschwerdt EB. “Candidatus Neoehrlichia mikurensis” infection in a dog from Germany. J Clin Microbiol. 2011;49:2059–62. doi: 10.1128/JCM.02327-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Szekeres S, Claudia Coipan E, Rigó K, Majoros G, Jahfari S, Sprong H, Földvári G. Candidatus Neoehrlichia mikurensis and Anaplasma phagocytophilum in natural rodent and tick communities in Southern Hungary. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2015;6:111–6. doi: 10.1016/j.ttbdis.2014.10.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Yabsley MJ, Murphy SM, Luttrell MP, Wilcox BR, Ruckdeschel C. Raccoons (Procyon lotor), but not rodents, are natural and experimental hosts for an ehrlichial organism related to “Candidatus Neoehrlichia mikurensis”. Vet Microbiol. 2008;131:301–8. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2008.04.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Andersson M, Zaghdoudi-Allan N, Tamba P, Stefanache M, Chitimia L. Co-infection with “Candidatus Neoehrlichia mikurensis” and Borrelia afzelii in an Ixodes ricinus tick that has bitten a human in Romania. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2014;5:706–8. doi: 10.1016/j.ttbdis.2014.05.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Brown GK, Martin AR, Roberts TK, Aitken RJ. Detection of Ehrlichia platys in dogs in Australia. Aust Vet J. 2001;79:554–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.2001.tb10747.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Katoh K, Standley DM. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: improvements in performance and usability. Mol Biol Evol. 2013;30:772–80. doi: 10.1093/molbev/mst010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Darriba D, Taboada GL, Doallo R, Posada D. jModelTest 2: more models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nat Methods. 2012;9:772. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S. MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol. 2013;30:2725–9. doi: 10.1093/molbev/mst197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


