Abstract
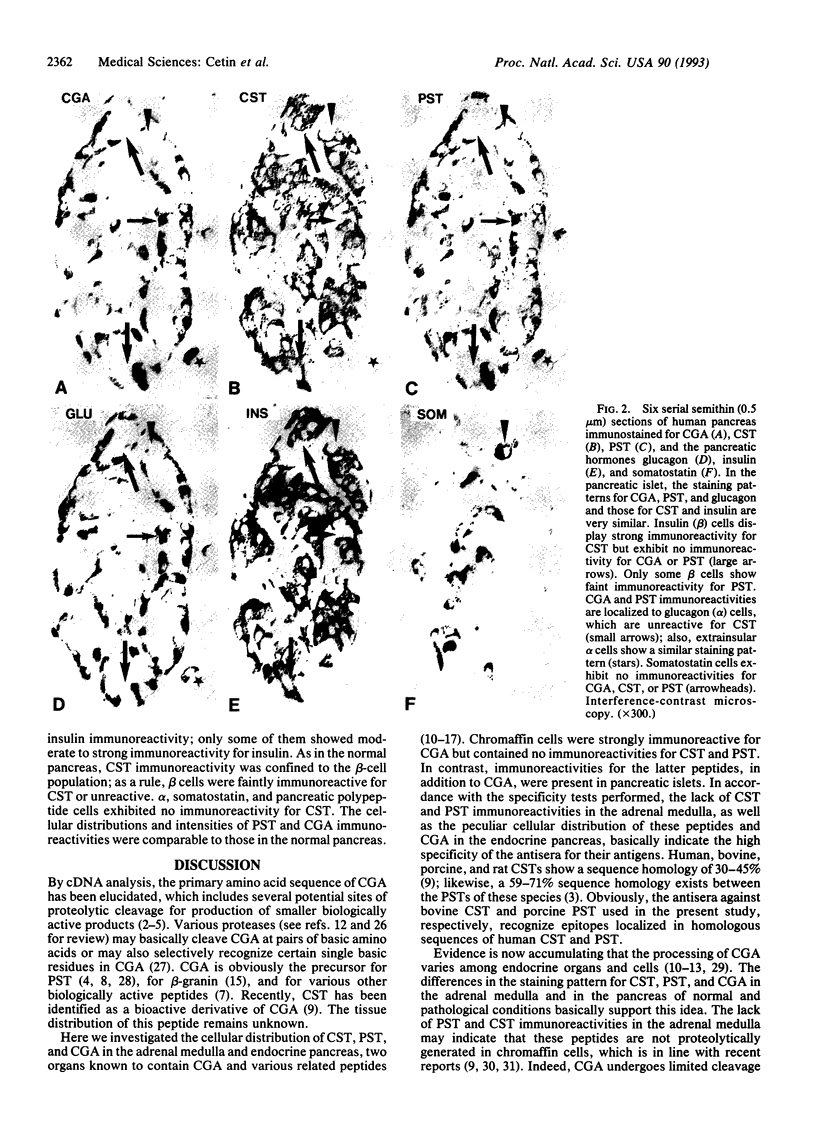
Chromogranin A (CGA) is a secretory protein present in the adrenal medulla and in a variety of endocrine organs. This protein may serve as precursor for pancreastatin (PST) and for other biologically active peptides. Recently, chromostatin (CST), a CGA derivative, has been identified that possesses high biological activity. The cellular distribution of CST in various endocrine organs is completely unknown. Using immunohistochemistry on plastic sections, we investigated the occurrence and cellular distribution of CST, PST, and CGA in human endocrine pancreas of healthy and diseased states and in the adrenal medulla. In the normal and diabetic pancreas, CST immunoreactivity was localized exclusively in beta cells, which were mostly unreactive for PST and CGA. Both latter peptides were confined mainly to glucagon (alpha) cells. Insulinoma cells displayed strong insulin, PST, and CGA immunoreactivities, but they were faintly immunoreactive for CST or unreactive. Adrenal chromaffin cells exhibited strong immunoreactivity for CGA but lacked CST and PST immunoreactivities. Based on the peculiar distributive pattern of CST, PST, and CGA, we suggest that CGA is differentially processed in chromaffin and islet tissues and in insulinoma cells. The unique cellular localization of CST in the endocrine pancreas of normal and pathological conditions may indicate that CST is involved in beta-cell function.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbosa J. A., Gill B. M., Takiyyuddin M. A., O'Connor D. T. Chromogranin A: posttranslational modifications in secretory granules. Endocrinology. 1991 Jan;128(1):174–190. doi: 10.1210/endo-128-1-174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cetin Y., Bargsten G., Grube D. Mutual relationships between chromogranins A and B and gastrin in individual gastrin cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2912–2916. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curry W. J., Johnston C. F., Hutton J. C., Arden S. D., Rutherford N. G., Shaw C., Buchanan K. D. The tissue distribution of rat chromogranin A-derived peptides: evidence for differential tissue processing from sequence specific antisera. Histochemistry. 1991;96(6):531–538. doi: 10.1007/BF00267079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson H. W., Peshavaria M., Hutton J. C. Proteolytic conversion of proinsulin into insulin. Identification of a Ca2+-dependent acidic endopeptidase in isolated insulin-secretory granules. Biochem J. 1987 Sep 1;246(2):279–286. doi: 10.1042/bj2460279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Docherty K., Steiner D. F. Post-translational proteolysis in polypeptide hormone biosynthesis. Annu Rev Physiol. 1982;44:625–638. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.44.030182.003205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrhart M., Grube D., Bader M. F., Aunis D., Gratzl M. Chromogranin A in the pancreatic islet: cellular and subcellular distribution. J Histochem Cytochem. 1986 Dec;34(12):1673–1682. doi: 10.1177/34.12.2878021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiden L. E. Is chromogranin a prohormone? Nature. 1987 Jan 22;325(6102):301–301. doi: 10.1038/325301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkensammer G., Fischer-Colbrie R., Richter K., Winkler H. Cell-free and cellular synthesis of chromogranin A and B of bovine adrenal medulla. Neuroscience. 1985 Feb;14(2):735–746. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(85)90323-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer-Colbrie R., Hagn C., Schober M. Chromogranins A, B, and C: widespread constituents of secretory vesicles. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1987;493:120–134. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1987.tb27189.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funakoshi S., Tamamura H., Ohta M., Yoshizawa K., Funakoshi A., Miyasaka K., Tateishi K., Tatemoto K., Nakano I., Yajima H. Isolation and characterization of a tumor-derived human pancreastatin-related protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Oct 16;164(1):141–148. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91694-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galindo E., Mendez M., Calvo S., Gonzalez-Garcia C., Ceña V., Hubert P., Bader M. F., Aunis D. Chromostatin receptors control calcium channel activity in adrenal chromaffin cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 5;267(1):407–412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galindo E., Rill A., Bader M. F., Aunis D. Chromostatin, a 20-amino acid peptide derived from chromogranin A, inhibits chromaffin cell secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1426–1430. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galindo E., Zwiller J., Bader M. F., Aunis D. Chromostatin inhibits catecholamine secretion in adrenal chromaffin cells by activating a protein phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7398–7402. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grube D., Aunis D., Bader F., Cetin Y., Jörns A., Yoshie S. Chromogranin A (CGA) in the gastro-entero-pancreatic (GEP) endocrine system. I. CGA in the mammalian endocrine pancreas. Histochemistry. 1986;85(6):441–452. doi: 10.1007/BF00508425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutton J. C., Davidson H. W., Grimaldi K. A., Peshavaria M. Biosynthesis of betagranin in pancreatic beta-cells. Identification of a chromogranin A-like precursor and its parallel processing with proinsulin. Biochem J. 1987 Jun 1;244(2):449–456. doi: 10.1042/bj2440449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutton J. C., Davidson H. W., Peshavaria M. Proteolytic processing of chromogranin A in purified insulin granules. Formation of a 20 kDa N-terminal fragment (betagranin) by the concerted action of a Ca2+-dependent endopeptidase and carboxypeptidase H (EC 3.4.17.10). Biochem J. 1987 Jun 1;244(2):457–464. doi: 10.1042/bj2440457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutton J. C., Nielsen E., Kastern W. The molecular cloning of the chromogranin A-like precursor of beta-granin and pancreastatin from the endocrine pancreas. FEBS Lett. 1988 Aug 29;236(2):269–274. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80036-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutton J. C., Peshavaria M., Johnston C. F., Ravazzola M., Orci L. Immunolocalization of betagranin: a chromogranin A-related protein of the pancreatic B-cell. Endocrinology. 1988 Mar;122(3):1014–1020. doi: 10.1210/endo-122-3-1014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutton J. C. Secretory granules. Experientia. 1984 Oct 15;40(10):1091–1098. doi: 10.1007/BF01971456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iacangelo A. L., Fischer-Colbrie R., Koller K. J., Brownstein M. J., Eiden L. E. The sequence of porcine chromogranin A messenger RNA demonstrates chromogranin A can serve as the precursor for the biologically active hormone, pancreastatin. Endocrinology. 1988 May;122(5):2339–2341. doi: 10.1210/endo-122-5-2339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iacangelo A. L., Grimes M., Eiden L. E. The bovine chromogranin A gene: structural basis for hormone regulation and generation of biologically active peptides. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Nov;5(11):1651–1660. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-11-1651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iacangelo A., Affolter H. U., Eiden L. E., Herbert E., Grimes M. Bovine chromogranin A sequence and distribution of its messenger RNA in endocrine tissues. Nature. 1986 Sep 4;323(6083):82–86. doi: 10.1038/323082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konecki D. S., Benedum U. M., Gerdes H. H., Huttner W. B. The primary structure of human chromogranin A and pancreastatin. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 15;262(35):17026–17030. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leduc R., Hendy G. N., Seidah N. G., Chrétien M., Lazure C. Fragmentation of bovine chromogranin A by plasma kallikrein. Life Sci. 1990;46(20):1427–1433. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(90)90458-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porte D., Jr Banting lecture 1990. Beta-cells in type II diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1991 Feb;40(2):166–180. doi: 10.2337/diab.40.2.166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravazzola M., Orci L. Glucagon and glicentin immunoreactivity are topologically segregated in the alpha granule of the human pancreatic A cell. Nature. 1980 Mar 6;284(5751):66–67. doi: 10.1038/284066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rehfeld J. F., Bardram L., Cantor P., Hilsted L., Schwartz T. W. Cell-specific processing of pro-cholecystokinin and pro-gastrin. Biochimie. 1988 Jan;70(1):25–31. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(88)90155-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt W. E., Creutzfeldt W. Pancreastatin--a novel regulatory peptide? Acta Oncol. 1991;30(4):441–449. doi: 10.3109/02841869109092399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt W. E., Siegel E. G., Lamberts R., Gallwitz B., Creutzfeldt W. Pancreastatin: molecular and immunocytochemical characterization of a novel peptide in porcine and human tissues. Endocrinology. 1988 Sep;123(3):1395–1404. doi: 10.1210/endo-123-3-1395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz T. W. The processing of peptide precursors. 'Proline-directed arginyl cleavage' and other monobasic processing mechanisms. FEBS Lett. 1986 May 5;200(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80500-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon J. P., Aunis D. Biochemistry of the chromogranin A protein family. Biochem J. 1989 Aug 15;262(1):1–13. doi: 10.1042/bj2620001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon J. P., Bader M. F., Aunis D. Proteolytic processing of chromogranin A in cultured chromaffin cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Feb 19;1051(2):123–130. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(90)90183-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon J. P., Bader M. F., Aunis D. Secretion from chromaffin cells is controlled by chromogranin A-derived peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1712–1716. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeekens S. P., Steiner D. F. Identification of a human insulinoma cDNA encoding a novel mammalian protein structurally related to the yeast dibasic processing protease Kex2. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):2997–3000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner D. F., Quinn P. S., Chan S. J., Marsh J., Tager H. S. Processing mechanisms in the biosynthesis of proteins. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1980;343:1–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb47238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatemoto K., Efendić S., Mutt V., Makk G., Feistner G. J., Barchas J. D. Pancreastatin, a novel pancreatic peptide that inhibits insulin secretion. Nature. 1986 Dec 4;324(6096):476–478. doi: 10.1038/324476a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkinson A., Jönsson A. C., Davison M., Young J., Lee C. M., Moore S., Dockray G. J. Heterogeneity of chromogranin A-derived peptides in bovine gut, pancreas and adrenal medulla. Biochem J. 1991 Jun 1;276(Pt 2):471–479. doi: 10.1042/bj2760471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiler R., Fischer-Colbrie R., Schmid K. W., Feichtinger H., Bussolati G., Grimelius L., Krisch K., Kerl H., O'Connor D., Winkler H. Immunological studies on the occurrence and properties of chromogranin A and B and secretogranin II in endocrine tumors. Am J Surg Pathol. 1988 Nov;12(11):877–884. doi: 10.1097/00000478-198811000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedenmann B., Huttner W. B. Synaptophysin and chromogranins/secretogranins--widespread constituents of distinct types of neuroendocrine vesicles and new tools in tumor diagnosis. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1989;58(2):95–121. doi: 10.1007/BF02890062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wohlfarter T., Fischer-Colbrie R., Hogue-Angeletti R., Eiden L. E., Winkler H. Processing of chromogranin A within chromaffin granules starts at C- and N-terminal cleavage sites. FEBS Lett. 1988 Apr 11;231(1):67–70. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80704-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. J., Rozansky D. J., Parmer R. J., Gill B. M., O'Connor D. T. Structure and function of the chromogranin A gene. Clues to evolution and tissue-specific expression. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 15;266(20):13130–13134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]