Abstract
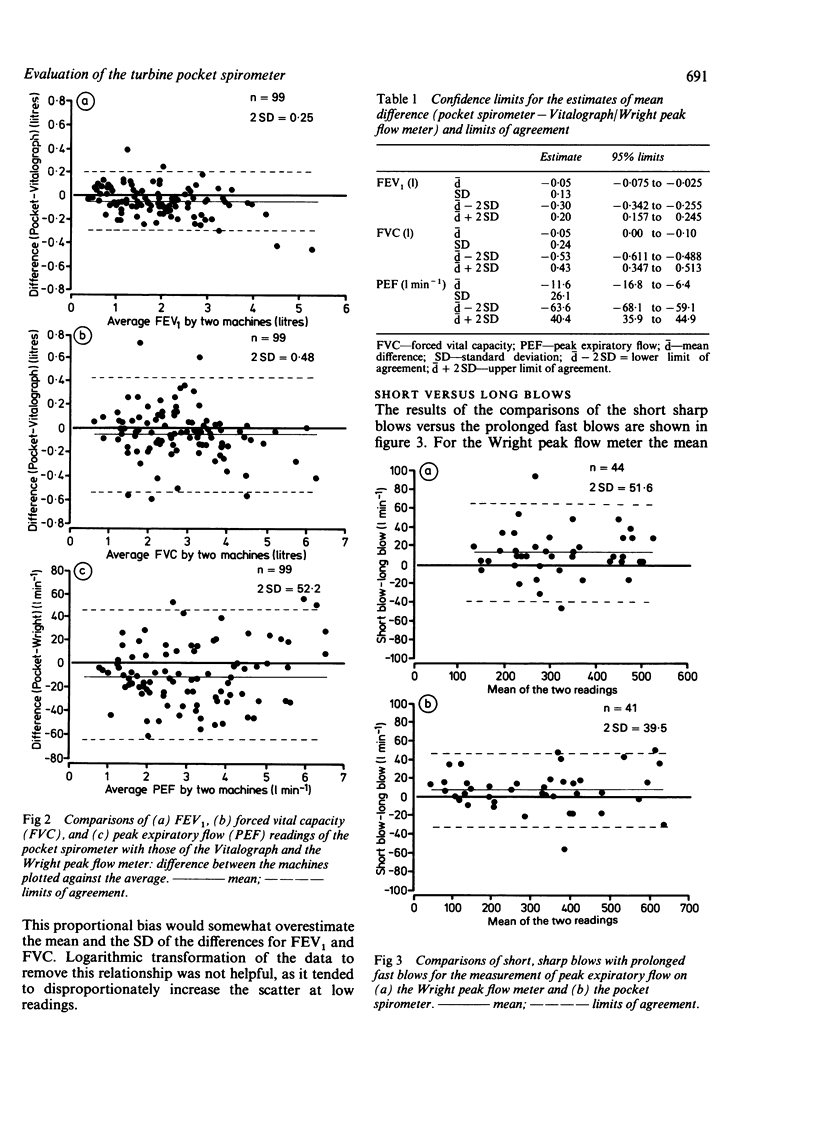
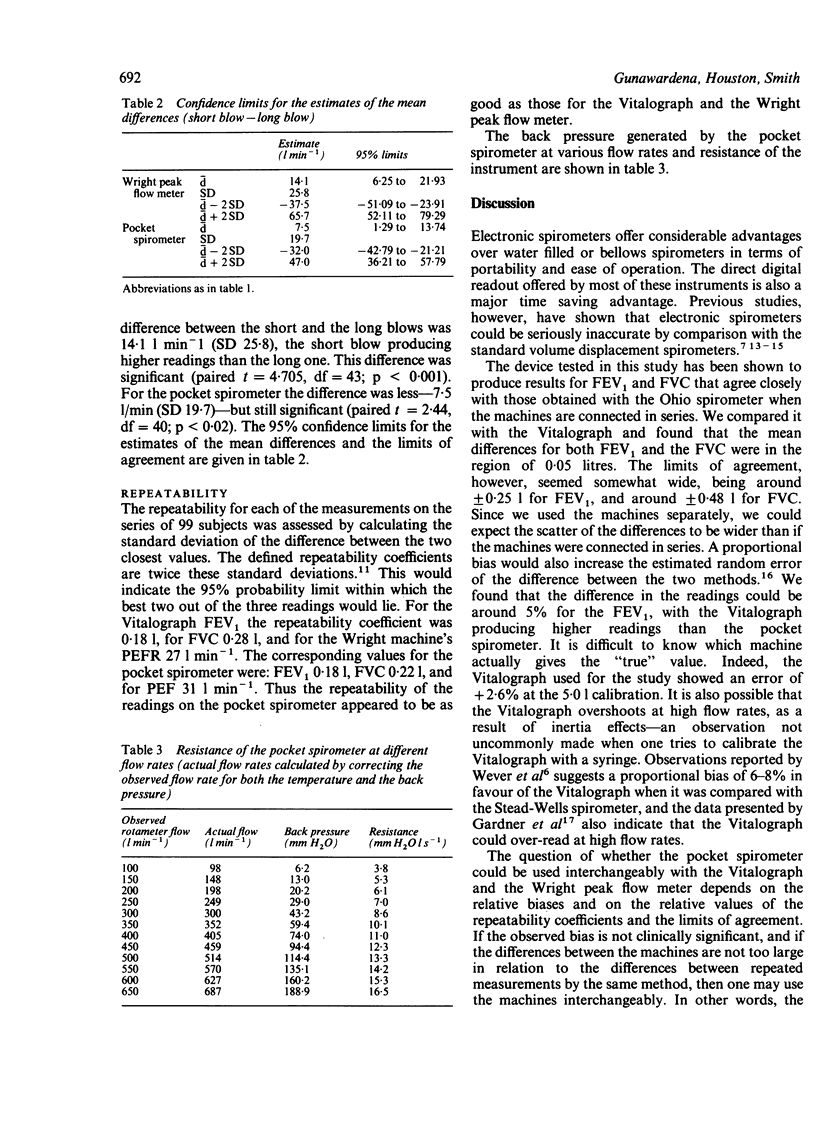
A compact electronic spirometer, the turbine pocket spirometer, which measures the FEV1, forced vital capacity (FVC), and peak expiratory flow (PEF) in a single expiration, was compared with the Vitalograph and the Wright peak flow meter in 99 subjects (FEV1 range 0.40-5.50 litres; FVC 0.58-6.48 l; PEF 40-650 l min-1). The mean differences between the machines were small--0.05 l for FEV1, 0.05 l for FVC, and 11.6 l min-1 for PEF, with the limits of agreement at +/- 0.25 l, +/- 0.48 l, and +/- 52.2 l min-1 respectively. The wide limits of agreement for the PEF comparison were probably because of the difference in the technique of blowing: a fast, long blow was used for the pocket spirometer and a short, sharp one for the Wright peak flow meter. The FEV1 and FVC showed a proportional bias of around 4-5% in favour of the Vitalograph. The repeatability coefficient for the pocket spirometer FEV1 was 0.18 l, for FVC 0.22 l, and for PEF 31 l min-1. These compared well with the repeatability coefficients of the Vitalograph and the Wright peak flow meter, which gave values of 0.18 l, 0.28 l, and 27 l min-1 respectively. At flow rates of over 600 l min-1 the resistance of the pocket spirometer marginally exceeded the American Thoracic Society recommendations. The machine is easy to operate and portable, and less expensive than the Vitalograph and Wright peak flow meter combined. It can be recommended for general use.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bland J. M., Altman D. G. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet. 1986 Feb 8;1(8476):307–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chowienczyk P. J., Lawson C. P. Pocket-sized device for measuring forced expiratory volume in one second and forced vital capacity. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1982 Jul 3;285(6334):15–17. doi: 10.1136/bmj.285.6334.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew C. D., Hughes D. T. Characteristics of the Vitalograph spirometer. Thorax. 1969 Nov;24(6):703–706. doi: 10.1136/thx.24.6.703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FitzGerald M. X., Smith A. A., Gaensler E. A. Evaluation of "electronic" spirometers. N Engl J Med. 1973 Dec 13;289(24):1283–1288. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197312132892406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner R. M., Hankinson J. L., West B. J. Evaluating commercially available spirometers. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980 Jan;121(1):73–82. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.121.1.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOCKHART W., SMITH D. H., MAIR A., WILSON W. A. Practical experience with the peak flow meter. Br Med J. 1960 Jan 2;1(5165):37–38. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5165.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perks W. H., Cole M., Steventon R. D., Tams I. P., Prowse K. An evaluation of the vitalograph pulmonary monitor. Br J Dis Chest. 1981 Apr;75(2):161–164. doi: 10.1016/0007-0971(81)90048-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHEPHARD R. J. Some observations on peak expiratory flow. Thorax. 1962 Mar;17:39–48. doi: 10.1136/thx.17.1.39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanks D. E., Morris J. F. Clinical comparison of two electronic spirometers with a water-sealed spirometer. Chest. 1976 Apr;69(4):461–466. doi: 10.1378/chest.69.4.461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WRIGHT B. M., McKERROW C. B. Maximum forced expiratory flow rate as a measure of ventilatory capacity: with a description of a new portable instrument for measuring it. Br Med J. 1959 Nov 21;2(5159):1041–1046. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5159.1041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westgard J. O., Hunt M. R. Use and interpretation of common statistical tests in method-comparison studies. Clin Chem. 1973 Jan;19(1):49–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wever A. M., Britton M. G., Hughes D. D. Evaluation of two spirometers: a comparative study of the Stead-Wells and the vitalograph spirometers. Chest. 1976 Aug;70(2):244–250. doi: 10.1378/chest.70.2.244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright B. M. A miniature Wright peak-flow meter. Br Med J. 1978 Dec 9;2(6152):1627–1628. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6152.1627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




