Abstract
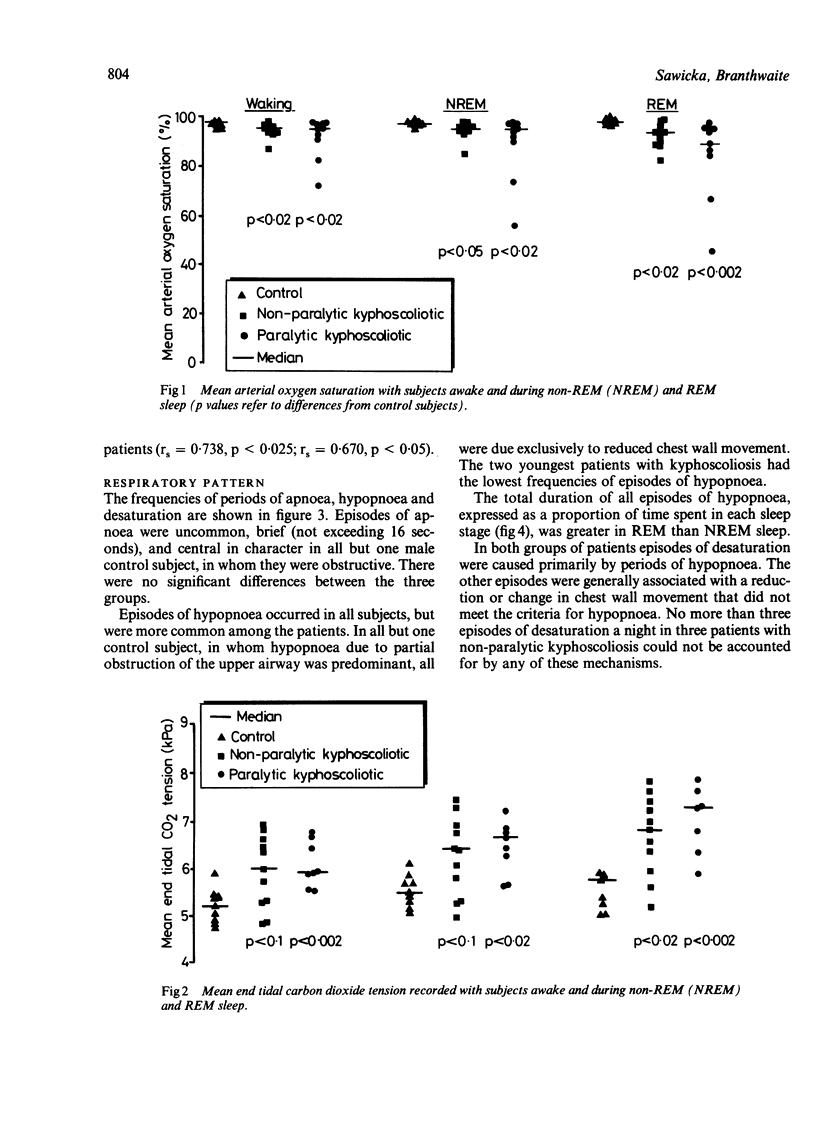
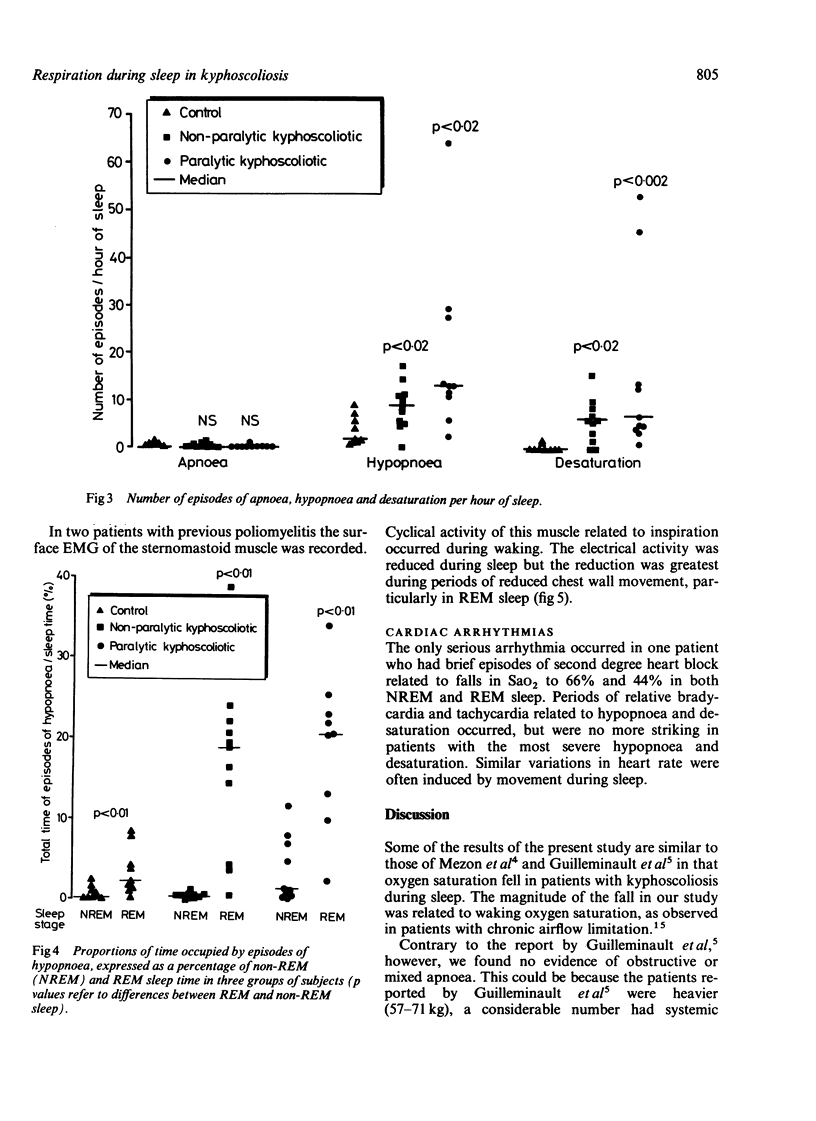
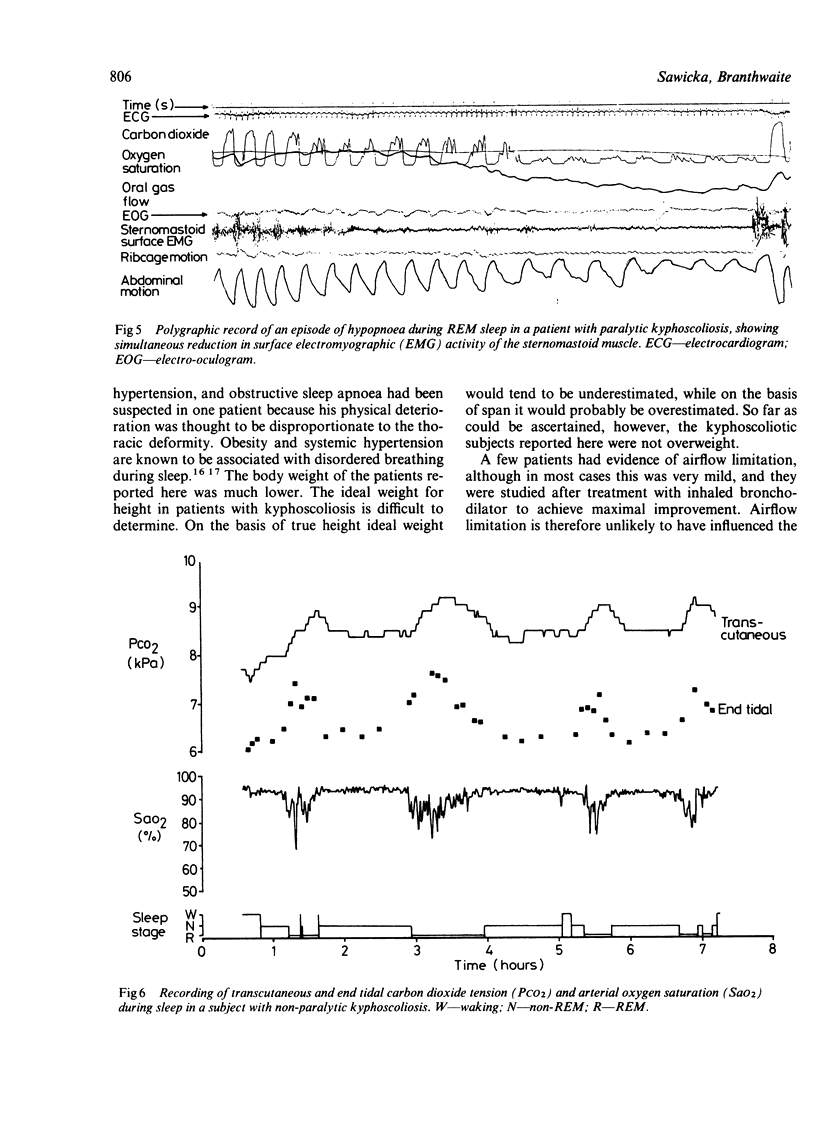
Eleven subjects with non-paralytic and 10 with paralytic kyphoscoliosis and nine normal control subjects were studied during sleep. The Cobb angle of those with kyphoscoliosis varied from 60 degrees to 140 degrees (median 100 degrees) and the vital capacity varied from 17% to 56% (median 28%) of the value predicted on the basis of span. Recordings made during sleep included expired carbon dioxide tension at the nose, gas flow at the mouth, arterial oxygen saturation, chest wall movement, and the electroencephalogram, electro-oculogram, and electrocardiogram. In three subjects transcutaneous carbon dioxide tension was measured simultaneously. Patients with kyphoscoliosis hypoventilated during sleep, particularly in rapid eye movement sleep, resulting in a rise in end tidal and transcutaneous carbon dioxide tension, and a reduction in oxygen saturation to a degree not observed in normal subjects. Reduced chest wall movement was the major cause of these episodes, which were more frequent and occupied a greater proportion of sleep time in those with kyphoscoliosis than in normal subjects. Serious cardiac arrhythmias were rarely associated. It is concluded that disturbances of respiration during sleep occur in patients with kyphoscoliosis and that these may be important in the pathogenesis of cardiorespiratory failure.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERGOFSKY E. H., TURINO G. M., FISHMAN A. P. Cardiorespiratory failure in kyphoscoliosis. Medicine (Baltimore) 1959 Sep;38:263–317. doi: 10.1097/00005792-195909000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bass C., Gardner W. N. Respiratory and psychiatric abnormalities in chronic symptomatic hyperventilation. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1985 May 11;290(6479):1387–1390. doi: 10.1136/bmj.290.6479.1387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergofsky E. H. Respiratory failure in disorders of the thoracic cage. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979 Apr;119(4):643–669. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1979.119.4.643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boysen P. G., Block A. J., Wynne J. W., Hunt L. A., Flick M. R. Nocturnal pulmonary hypertension in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Chest. 1979 Nov;76(5):536–542. doi: 10.1378/chest.76.5.536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray G. A. Obesity in America. An overview of the Second Fogarty International Center Conference on Obesity. Int J Obes. 1979;3(4):363–375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilleminault C., Kurland G., Winkle R., Miles L. E. Severe kyphoscoliosis, breathing, and sleep: the "Quasimodo" syndrome during sleep. Chest. 1981 Jun;79(6):626–630. doi: 10.1378/chest.79.6.626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilleminault C., Tilkian A., Dement W. C. The sleep apnea syndromes. Annu Rev Med. 1976;27:465–484. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.27.020176.002341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jardim J., Farkas G., Prefaut C., Thomas D., Macklem P. T., Roussos C. The failing inspiratory muscles under normoxic and hypoxic conditions. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1981 Sep;124(3):274–279. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1981.124.3.274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson M. W., Remmers J. E. Accessory muscle activity during sleep in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1984 Oct;57(4):1011–1017. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1984.57.4.1011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juan G., Calverley P., Talamo C., Schnader J., Roussos C. Effect of carbon dioxide on diaphragmatic function in human beings. N Engl J Med. 1984 Apr 5;310(14):874–879. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198404053101402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mead J., Peterson N., Grimby G., Mead J. Pulmonary ventilation measured from body surface movements. Science. 1967 Jun 9;156(3780):1383–1384. doi: 10.1126/science.156.3780.1383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mezon B. L., West P., Israels J., Kryger M. Sleep breathing abnormalities in kyphoscoliosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980 Oct;122(4):617–621. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.122.4.617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remmers J. E. Effects of sleep on control of breathing. Int Rev Physiol. 1981;23:111–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shneerson J. M. Pulmonary artery pressure in thoracic scoliosis during and after exercise while breathing air and pure oxygen. Thorax. 1978 Dec;33(6):747–754. doi: 10.1136/thx.33.6.747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stradling J. R., Lane D. J. Nocturnal hypoxaemia in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Clin Sci (Lond) 1983 Feb;64(2):213–222. doi: 10.1042/cs0640213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



