Abstract
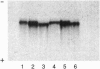
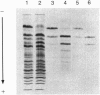
The rhesus monkey, Macaca mulatta, exhibits a geographically restricted polymorphism of serum albumins Mac A and Mac B that is recognized by electrophoresis and is associated with a difference in bilirubin-binding parameters. To identify the basis of the polymorphism, the cDNA and protein sequences of serum albumin from M. mulatta were determined. Screening of a lambda gt11 rhesus liver cDNA library yielded a 1988-bp cDNA sequence that encodes the complete amino acid sequence of mature albumin, the entire propeptide, and part of the prepropeptide. Isoelectric focusing and amino-terminal protein sequencing of CNBr fragments of albumin from A/A and B/B homozygotes were performed, and the structural difference was localized to a CNBr fragment (MCB3) spanning residues 124-264. Sequence analysis of lysyl endopeptidase peptides of MCB3 established that Mac A albumin has a glutamine residue at position 188 while the Mac B albumin has a glutamic residue at the same position. PCR amplification, subcloning, and DNA sequence analysis of clones from A/A and B/B homozygotes confirmed the protein sequence data and the codon difference of CAA versus GAA, respectively. Comparison of macaque and human serum albumin shows a 93.5% identity at the amino acid level. In human serum albumin, Glu188 is located close to the IIA binding pocket for ligands, probably including bilirubin. Derivatives of coumarin compete more efficiently with bilirubin for binding sites on the Mac A albumin than on the Mac B albumin. In regions where coumarin-containing plants are important food resources, Mac B albumin may confer a selective advantage because bilirubin is less readily displaced from it.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arai K., Huss K., Madison J., Putnam F. W., Salzano F. M., Franco M. H., Santos S. E., Freitas M. J. Amino acid substitutions in albumin variants found in Brazil. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):1821–1825. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.1821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arai K., Madison J., Shimizu A., Putnam F. W. Point substitutions in albumin genetic variants from Asia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):497–501. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRAMBEL C. E., HUNTER R. E. Effect of dicoumarol on the nursing infant. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1950 May;59(5):1153–1159. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(16)39185-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson J., Sakamoto Y., Laurell C. B., Madison J., Watkins S., Putnam F. W. Alloalbuminemia in Sweden: structural study and phenotypic distribution of nine albumin variants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 1;89(17):8225–8229. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.17.8225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He X. M., Carter D. C. Atomic structure and chemistry of human serum albumin. Nature. 1992 Jul 16;358(6383):209–215. doi: 10.1038/358209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kragh-Hansen U. Molecular aspects of ligand binding to serum albumin. Pharmacol Rev. 1981 Mar;33(1):17–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorey F. W., Ahlfors C. E., Smith D. G., Neel J. V. Bilirubin binding by variant albumins in Yanomama Indians. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Sep;36(5):1112–1120. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorey F. W., Smith D. G., Ahlfors C. E. Bilirubin binding by the fractionated alternate allelic components of heterozygous monkey albumin. Am J Phys Anthropol. 1985 Oct;68(2):169–171. doi: 10.1002/ajpa.1330680204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madison J., Arai K., Sakamoto Y., Feld R. D., Kyle R. A., Watkins S., Davis E., Matsuda Y., Amaki I., Putnam F. W. Genetic variants of serum albumin in Americans and Japanese. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9853–9857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minghetti P. P., Ruffner D. E., Kuang W. J., Dennison O. E., Hawkins J. W., Beattie W. G., Dugaiczyk A. Molecular structure of the human albumin gene is revealed by nucleotide sequence within q11-22 of chromosome 4. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 25;261(15):6747–6757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters T., Jr Serum albumin. Adv Protein Chem. 1985;37:161–245. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60065-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakamoto Y., Davis E., Madison J., Watkins S., McLaughlin H., Leahy D. T., Putnam F. W. Purification and structural study of two albumin variants in an Irish population. Clin Chim Acta. 1991 Dec 31;204(1-3):179–187. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(91)90229-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. G. Paternity exclusion in six captive groups of Rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta). Am J Phys Anthropol. 1980 Aug;53(2):243–249. doi: 10.1002/ajpa.1330530208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi N., Takahashi Y., Isobe T., Putnam F. W., Fujita M., Satoh C., Neel J. V. Amino acid substitutions in inherited albumin variants from Amerindian and Japanese populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):8001–8005. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.8001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins S., Madison J., Davis E., Sakamoto Y., Galliano M., Minchiotti L., Putnam F. W. A donor splice mutation and a single-base deletion produce two carboxyl-terminal variants of human serum albumin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):5959–5963. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.5959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wet J. R., Fukushima H., Dewji N. N., Wilcox E., O'Brien J. S., Helinski D. R. Chromogenic immunodetection of human serum albumin and alpha-L-fucosidase clones in a human hepatoma cDNA expression library. DNA. 1984 Dec;3(6):437–447. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1984.3.437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]