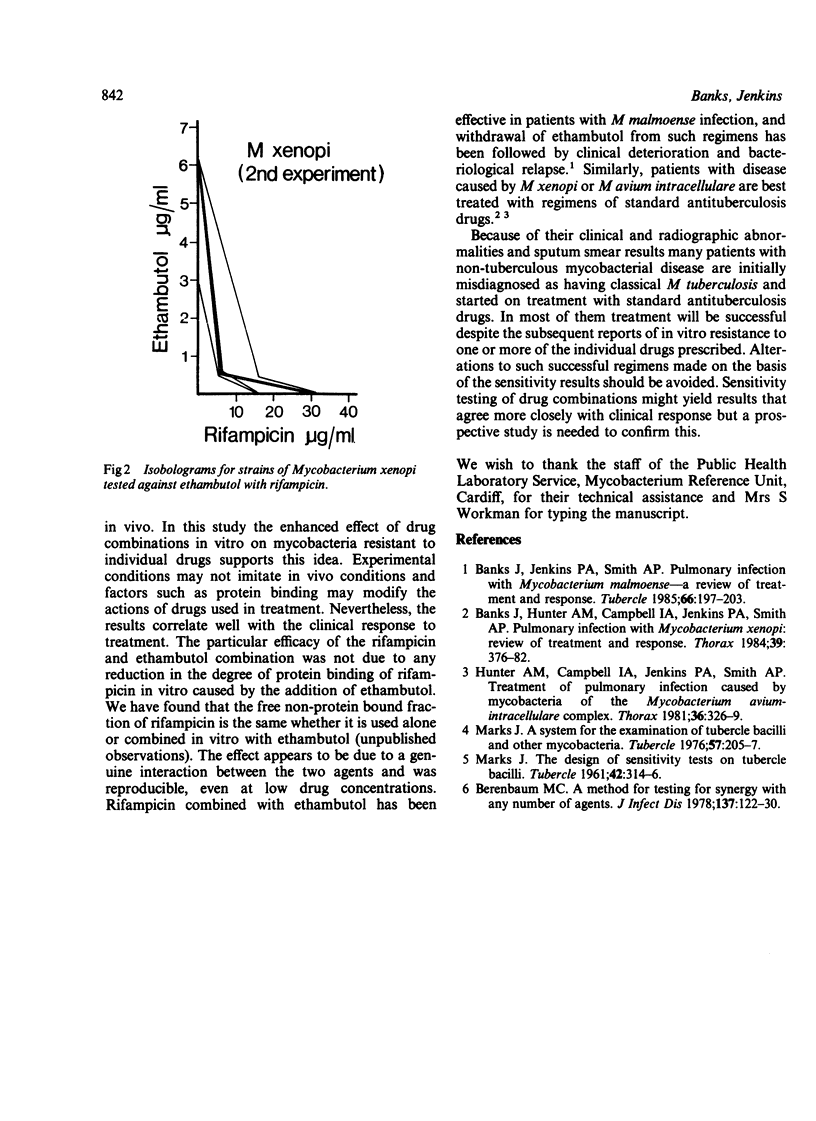
Abstract
Drug sensitivity tests were performed for ethambutol, rifampicin, streptomycin, and isoniazid both alone and in paired combinations, on 16 strains of Mycobacterium avium intracellulare, seven strains of Mycobacterium xenopi, and eight strains of Mycobacterium malmoense. Most strains were resistant to the individual drugs, but all strains of M malmoense, 86% of M xenopi, and 31% of M avium intracellulare were completely suppressed by the lowest concentrations of ethambutol and rifampicin when the two drugs were combined in vitro. Streptomycin combined with ethambutol or with rifampicin in the lowest combined concentrations suppressed 50% and 62% respectively of strains of M malmoense. All strains of M xenopi were suppressed by the lowest combined concentrations of streptomycin with rifampicin. Combinations with isoniazid were less effective. It is postulated that similar effects in vivo might account for the satisfactory clinical response seen in patients with disease caused by these mycobacteria who have received treatment with combinations of standard antituberculosis drugs despite in vitro resistance to the individual agents.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banks J., Hunter A. M., Campbell I. A., Jenkins P. A., Smith A. P. Pulmonary infection with mycobacterium xenopi: review of treatment and response. Thorax. 1984 May;39(5):376–382. doi: 10.1136/thx.39.5.376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banks J., Jenkins P. A., Smith A. P. Pulmonary infection with Mycobacterium malmoense--a review of treatment and response. Tubercle. 1985 Sep;66(3):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0041-3879(85)90037-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berenbaum M. C. A method for testing for synergy with any number of agents. J Infect Dis. 1978 Feb;137(2):122–130. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.2.122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARKS J. The design of sensitivity tests on tubercle bacilli. Tubercle. 1961 Sep;42:314–316. doi: 10.1016/s0041-3879(61)80114-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



