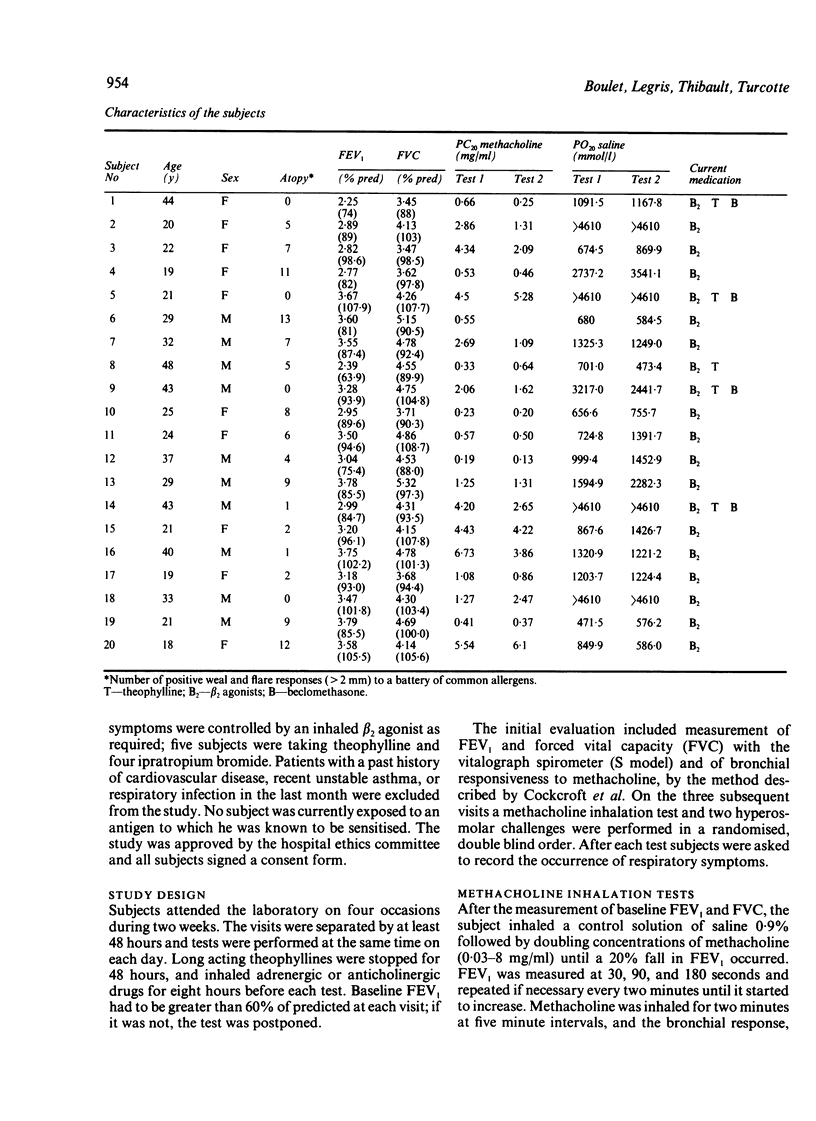
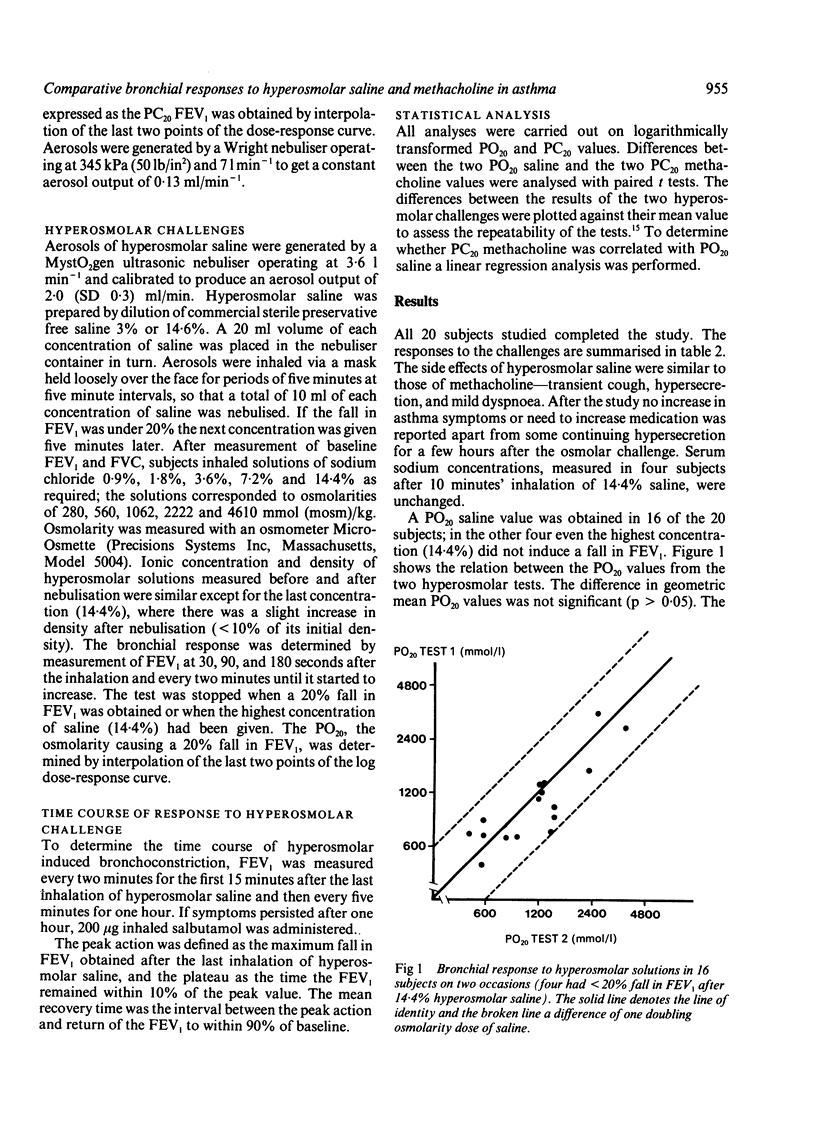
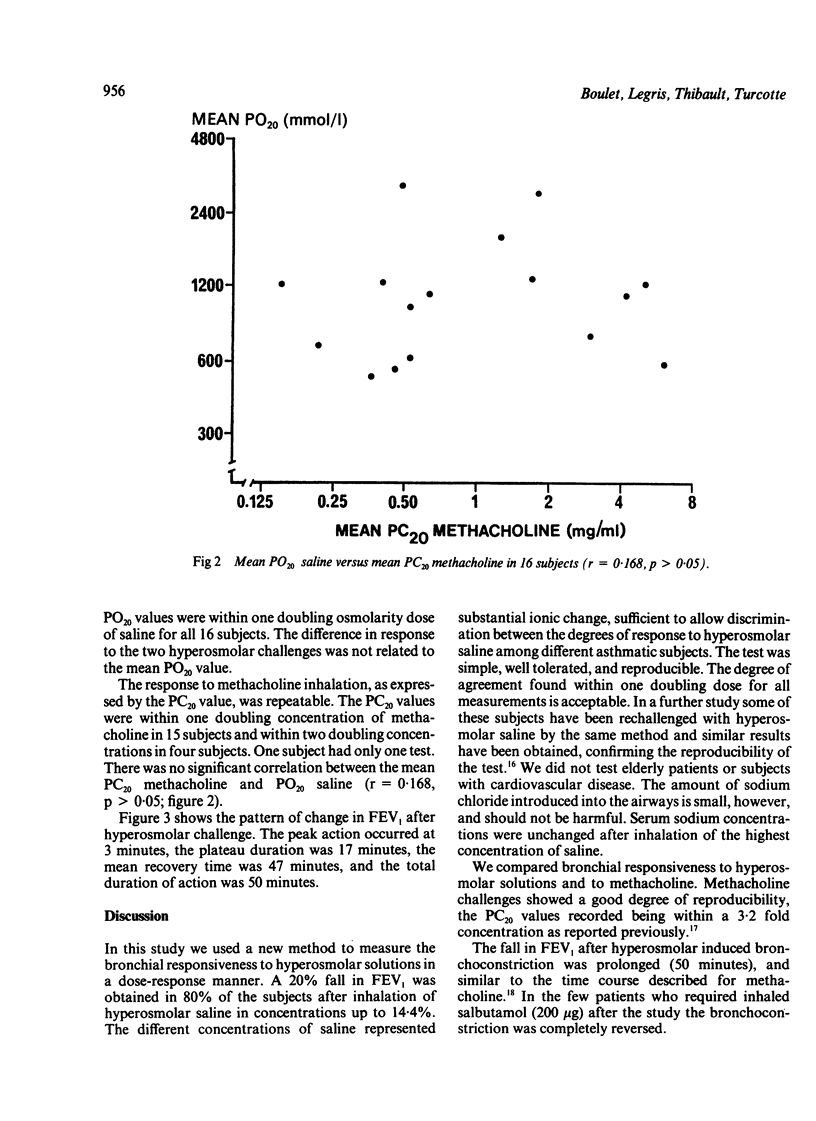
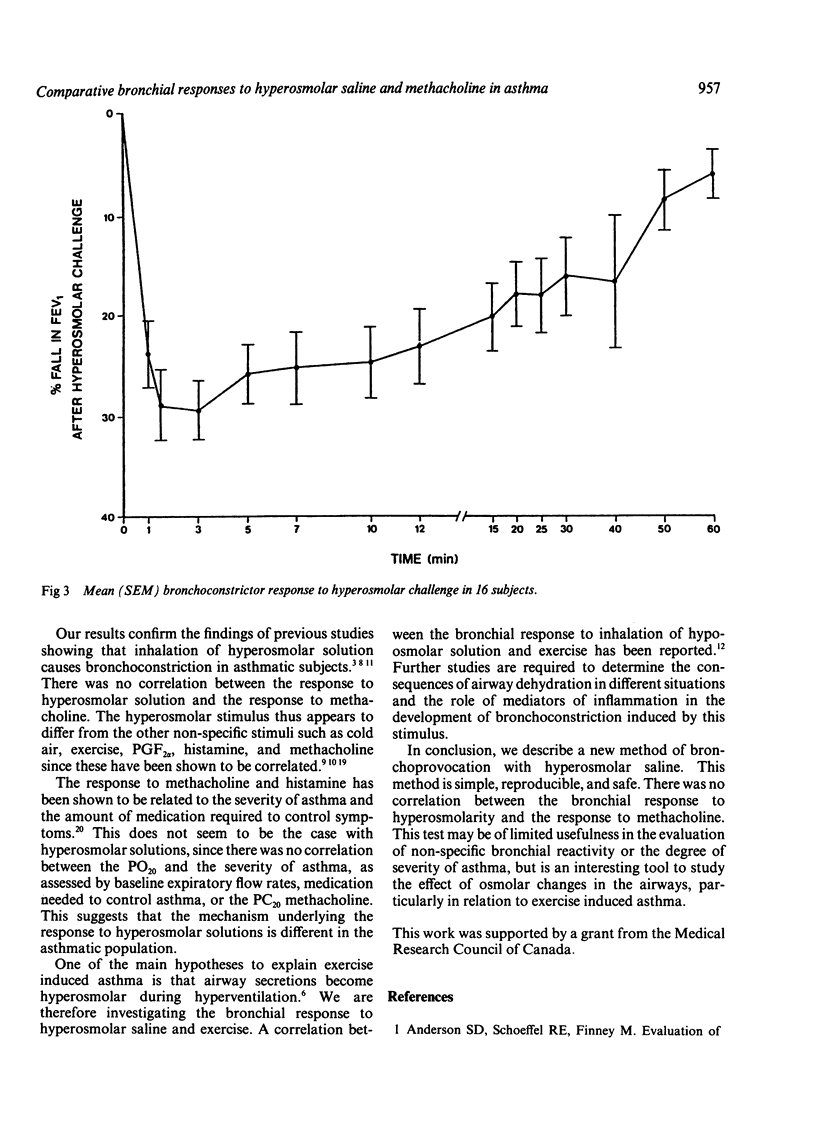
Abstract
Airway responsiveness to inhaled methacholine and to ultrasonically nebulised hyperosmolar saline was compared in 20 asthmatic subjects. Each subject had two hyperosmolar inhalation tests and a methacholine challenge in random order at least 48 hours apart over a period of two weeks. Hyperosmolar challenge, carried out with doubling concentrations of saline from 0.9% to 14.4% to obtain a dose-response curve, was well tolerated by all subjects. The response to hyperosmolar saline--expressed as the PO20, the osmolarity inducing a 20% fall in forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1) was obtained in 16 of the 20 subjects and in each was repeatable to within one doubling concentration of saline. The peak bronchoconstrictor effect of hyperosmolar saline inhalation occurred at 3 minutes and its mean total duration (FEV1 less than 90% of baseline) was 50 minutes. There was no significant correlation between the PO20 and the PC20 methacholine (the concentration inducing a 20% fall in FEV1). Thus by using a new method to obtain a quantitative airway response to inhaled hyperosmolar saline we found that the airway response to hyperosmolar inhalation differs from the airway response to methacholine.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson S. D. Is there a unifying hypothesis for exercise-induced asthma? J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1984 May;73(5 Pt 2):660–665. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(84)90301-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson S. D., Schoeffel R. E., Black J. L., Daviskas E. Airway cooling as the stimulus to exercise-induced asthma--a re-evaluation. Eur J Respir Dis. 1985 Jul;67(1):20–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson S. D., Schoeffel R. E., Finney M. Evaluation of ultrasonically nebulised solutions for provocation testing in patients with asthma. Thorax. 1983 Apr;38(4):284–291. doi: 10.1136/thx.38.4.284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderton R. C., Cuff M. T., Frith P. A., Cockcroft D. W., Morse J. L., Jones N. L., Hargreave F. E. Bronchial responsiveness to inhaled histamine and exercise. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1979 May;63(5):315–320. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(79)90125-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bascom R., Bleecker E. R. Bronchoconstriction induced by distilled water. Sensitivity in asthmatics and relationship to exercise-induced bronchospasm. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 Aug;134(2):248–253. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1986.134.2.248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bland J. M., Altman D. G. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet. 1986 Feb 8;1(8476):307–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartier A., Malo J. L., Bégin P., Sestier M., Martin R. R. Time course of the bronchoconstriction induced by inhaled histamine and methacholine. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1983 Mar;54(3):821–826. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1983.54.3.821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft D. W., Killian D. N., Mellon J. J., Hargreave F. E. Bronchial reactivity to inhaled histamine: a method and clinical survey. Clin Allergy. 1977 May;7(3):235–243. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1977.tb01448.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehaut P., Rachiele A., Martin R. R., Malo J. L. Histamine dose-response curves in asthma: reproducibility and sensitivity of different indices to assess response. Thorax. 1983 Jul;38(7):516–522. doi: 10.1136/thx.38.7.516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eschenbacher W. L., Boushey H. A., Sheppard D. Alteration in osmolarity of inhaled aerosols cause bronchoconstriction and cough, but absence of a permeant anion causes cough alone. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Feb;129(2):211–215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabbri L. M., Mapp C. E., Hendrick D. J. Comparison of ultrasonically nebulized distilled water and hyperventilation with cold air in asthma. Ann Allergy. 1984 Aug;53(2):172–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hargreave F. E., Ryan G., Thomson N. C., O'Byrne P. M., Latimer K., Juniper E. F., Dolovich J. Bronchial responsiveness to histamine or methacholine in asthma: measurement and clinical significance. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1981 Nov;68(5):347–355. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(81)90132-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magyar P., Dervaderics M., Tóth A. Bronchial challenge with hypertonic KCl solution in the diagnosis of bronchial asthma. A comparison with the challenge performed by inhalation of distilled water. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1984 Jun 23;114(25):910–913. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Byrne P. M., Ryan G., Morris M., McCormack D., Jones N. L., Morse J. L., Hargreave F. E. Asthma induced by cold air and its relation to nonspecific bronchial responsiveness to methacholine. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 Mar;125(3):281–285. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1982.125.3.281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoeffel R. E., Anderson S. D., Altounyan R. E. Bronchial hyperreactivity in response to inhalation of ultrasonically nebulised solutions of distilled water and saline. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1981 Nov 14;283(6302):1285–1287. doi: 10.1136/bmj.283.6302.1285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson N. C., Roberts R., Bandouvakis J., Newball H., Hargreave F. E. Comparison of bronchial responses to prostaglandin F2 alpha and methacholine. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1981 Nov;68(5):392–398. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(81)90138-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


