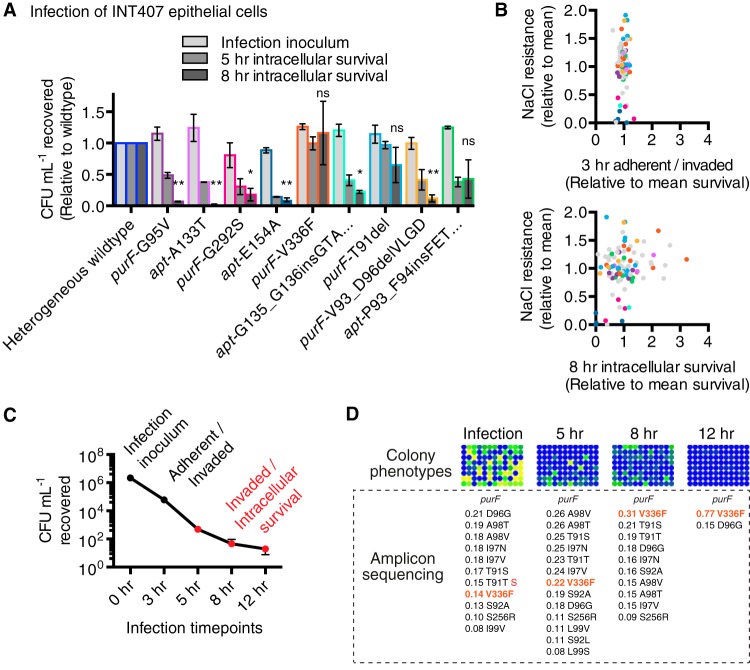
FIG 6 .
Fitness selection and effects of purF and apt mutations in invasion and intracellular survival in infection of INT407 epithelial cells. (A) Invasiveness and intracellular survival of representative-allele-bearing strains in semiconfluent epithelial cells assessed by gentamicin protection assay. The numbers of wild-type CFU recovered following host cell lysis were normalized to 1.0 for each assay time point (0 h, infection inoculum; 5 h and 8 h, intracellular bacteria). Counts of CFU of representative-allele-bearing strains recovered are compared to those of heterogeneous wild type at each relevant time point. Mean results with SEM from three independent experiments are shown, and statistics are shown for 8-h time point: *, P ≤ 0.05; **, P ≤ 0.01; ns, not significant. (B) Adherent/intracellular bacteria (3 h, top), and intracellular survival (8 h, bottom) of 96 purF- and apt-genotyped single-colony isolates in INT407 epithelial cells. Each dot represents an isolate (out of 96); the average CFU count recovered from host cells for an individual isolate relative to the average CFU count recovered for the entire population is shown on the x axis, and growth on NaCl relative to the population average is on the y axis (data are from the experiment whose results are shown in Fig. 4). CFU data are from three independent experiments. CFU recovered at 3 h include bacteria adherent to host cells and intracellular bacteria; CFU recovered at 8 h from gentamicin-treated host cells are from intracellular bacteria only. Dots (B) and bars (A) are color coded to represent the families of representative alleles shown in Fig. 4, and grey dots are used for all other variants (B). (C) CFU recovered from typical INT407 infection with heterogeneous wild-type C. jejuni 81-176 at infection (0 h), adherent and intracellular (3 h), and intracellular survival (5, 8, and 12 h) time points. The infection inoculum is the total number of bacteria used to infect host cells (MOI of 100). (D) Strain selection for allele fitness as shown by intracellular survival and examination of NaCl resistance/sensitivity phenotypes in 96 colonies after liberation from host cells. Amplicon-sequencing analysis of variants was performed on genomic DNA from pooled colonies recovered on MH plates at each intracellular time point. Each pool was the equivalent of three independent experiments with 24 technical replicates (total of 72 infections at each intracellular time point to maximize CFU/allele recovery).