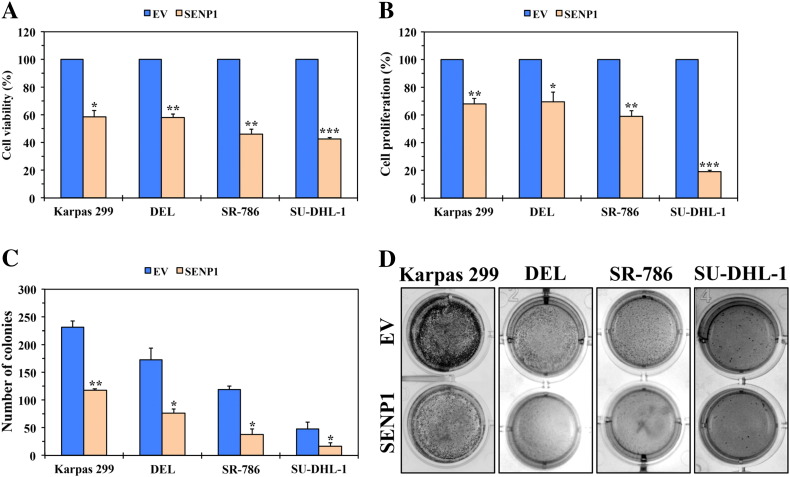
Figure 7.
De-SUMOylation of NPM-ALK by SENP1 decreases cell viability, proliferation, and anchorage-independent colony formation of NPM-ALK+ T-cell lymphoma. (A) Transfection of Karpas 299, DEL, SR-786, and SU-DHL-1 cells with the SENP1 protease expression plasmid resulted in a significant decrease in their viability after 48 hours (*P < .001, **P < .0001, ***P < .00001). (B) In addition, transfection of the lymphoma cells with SENP1 decreased their proliferation (*P < .05, **P < .001, ***P < .00001). (C) Transfection of SENP1 also decreased the anchorage-independent colony formation potential of the different lymphoma cells (*P < .05, **P < .01). (D) Representative examples of the colonies from each cell line are shown at 7 days after transfection with EV or SENP1. Results shown in panels A, B, and C represent the means ± SE of three independent experiments.