Abstract
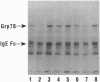
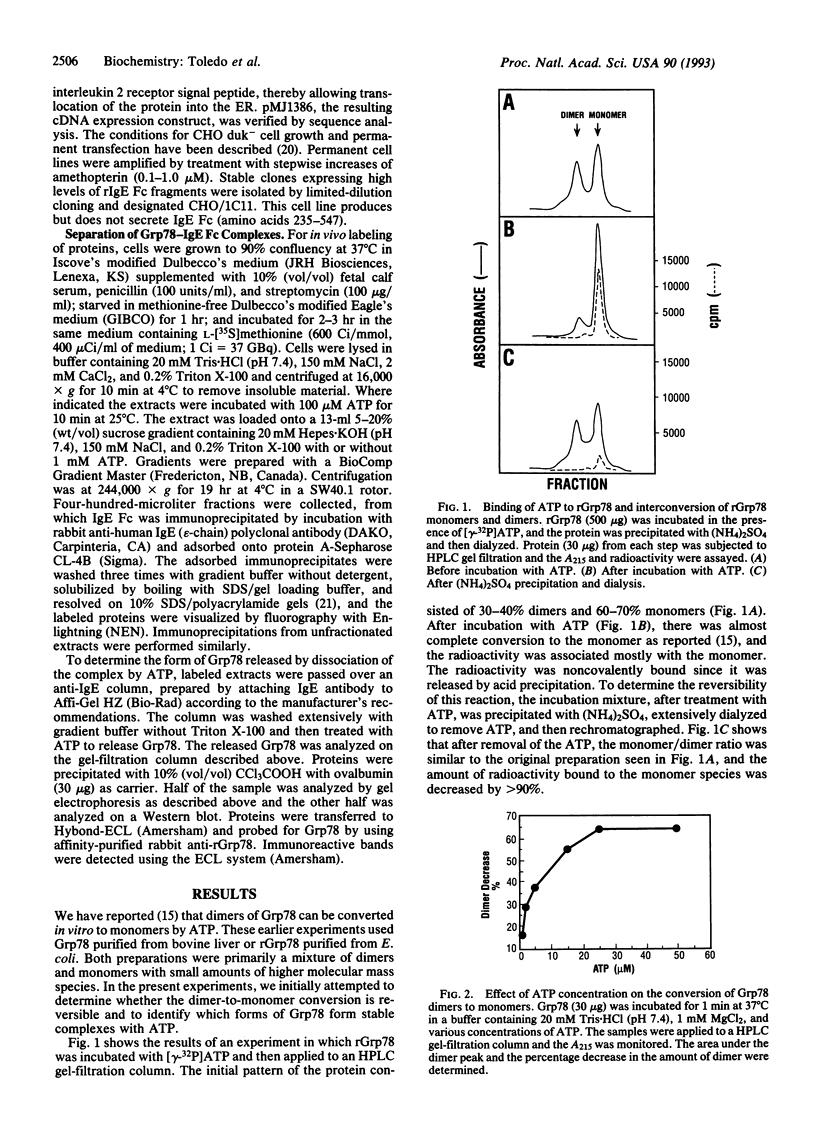
Recent studies have shown that ATP can dissociate dimers of the glucose-regulated protein Grp78 to monomers. In the present study, we have used purified recombinant Grp78 from Escherichia coli to investigate this reaction in more detail. During the course of the Grp78 dimer-monomer conversion, a stable Grp78 monomer-ATP complex is formed. Upon removal of the ATP, the Grp78 dimer is reformed. ADP, nonhydrolyzable ATP analogues, and GTP do not effect the dissociation of Grp78 dimers. A cell line that overproduces IgE Fc has been used to examine the nature of the Grp78-IgE Fc complexes present and the effect of ATP on them. Grp78-IgE Fc complexes ranging from 100 kDa to 300 kDa were observed by sucrose gradient analysis, suggesting that aggregate forms of Grp78 may be present in some of these complexes. Treatment of the extracts with ATP resulted in release of a Grp78 monomer from the complex. These results suggest that the dissociation of Grp78 oligomers by ATP may be involved in the function of Grp78 in protein translocation through the endoplasmic reticulum.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bole D. G., Hendershot L. M., Kearney J. F. Posttranslational association of immunoglobulin heavy chain binding protein with nascent heavy chains in nonsecreting and secreting hybridomas. J Cell Biol. 1986 May;102(5):1558–1566. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.5.1558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlino A., Toledo H., Skaleris D., DeLisio R., Weissbach H., Brot N. Interactions of liver Grp78 and Escherichia coli recombinant Grp78 with ATP: multiple species and disaggregation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2081–2085. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R. Use of eukaryotic expression technology in the functional analysis of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:684–704. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52074-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorner A. J., Bole D. G., Kaufman R. J. The relationship of N-linked glycosylation and heavy chain-binding protein association with the secretion of glycoproteins. J Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;105(6 Pt 1):2665–2674. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.6.2665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flynn G. C., Chappell T. G., Rothman J. E. Peptide binding and release by proteins implicated as catalysts of protein assembly. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):385–390. doi: 10.1126/science.2756425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freiden P. J., Gaut J. R., Hendershot L. M. Interconversion of three differentially modified and assembled forms of BiP. EMBO J. 1992 Jan;11(1):63–70. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05028.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gething M. J., Sambrook J. Protein folding in the cell. Nature. 1992 Jan 2;355(6355):33–45. doi: 10.1038/355033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas I. G., Wabl M. Immunoglobulin heavy chain binding protein. Nature. 1983 Nov 24;306(5941):387–389. doi: 10.1038/306387a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendershot L., Bole D., Köhler G., Kearney J. F. Assembly and secretion of heavy chains that do not associate posttranslationally with immunoglobulin heavy chain-binding protein. J Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;104(3):761–767. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.3.761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassenbrock C. K., Garcia P. D., Walter P., Kelly R. B. Heavy-chain binding protein recognizes aberrant polypeptides translocated in vitro. Nature. 1988 May 5;333(6168):90–93. doi: 10.1038/333090a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassenbrock C. K., Kelly R. B. Interaction of heavy chain binding protein (BiP/GRP78) with adenine nucleotides. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1461–1467. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03529.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knittler M. R., Haas I. G. Interaction of BiP with newly synthesized immunoglobulin light chain molecules: cycles of sequential binding and release. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1573–1581. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05202.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozutsumi Y., Segal M., Normington K., Gething M. J., Sambrook J. The presence of malfolded proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum signals the induction of glucose-regulated proteins. Nature. 1988 Mar 31;332(6163):462–464. doi: 10.1038/332462a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leustek T., Toledo H., Brot N., Weissbach H. Calcium-dependent autophosphorylation of the glucose-regulated protein, Grp78. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1991 Sep;289(2):256–261. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(91)90469-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melnick J., Aviel S., Argon Y. The endoplasmic reticulum stress protein GRP94, in addition to BiP, associates with unassembled immunoglobulin chains. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 25;267(30):21303–21306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris-Vasios C., Kochan J. P., Skalka A. M. Avian sarcoma-leukosis virus pol-endo proteins expressed independently in mammalian cells accumulate in the nucleus but can be directed to other cellular compartments. J Virol. 1988 Jan;62(1):349–353. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.1.349-353.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro S., Pelham H. R. An Hsp70-like protein in the ER: identity with the 78 kd glucose-regulated protein and immunoglobulin heavy chain binding protein. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):291–300. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90746-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng D. T., Watowich S. S., Lamb R. A. Analysis in vivo of GRP78-BiP/substrate interactions and their role in induction of the GRP78-BiP gene. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Feb;3(2):143–155. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.2.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olden K., Pratt R. M., Jaworski C., Yamada K. M. Evidence for role of glycoprotein carbohydrates in membrane transport: specific inhibition by tunicamycin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):791–795. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pouysségur J., Shiu R. P., Pastan I. Induction of two transformation-sensitive membrane polypeptides in normal fibroblasts by a block in glycoprotein synthesis or glucose deprivation. Cell. 1977 Aug;11(4):941–947. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90305-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiu R. P., Pastan I. H. Properties and purification of a glucose-regulated protein from chick embryo fibroblasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jan 25;576(1):141–150. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(79)90493-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch W. J., Feramisco J. R. Rapid purification of mammalian 70,000-dalton stress proteins: affinity of the proteins for nucleotides. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1229–1237. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]