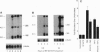Abstract
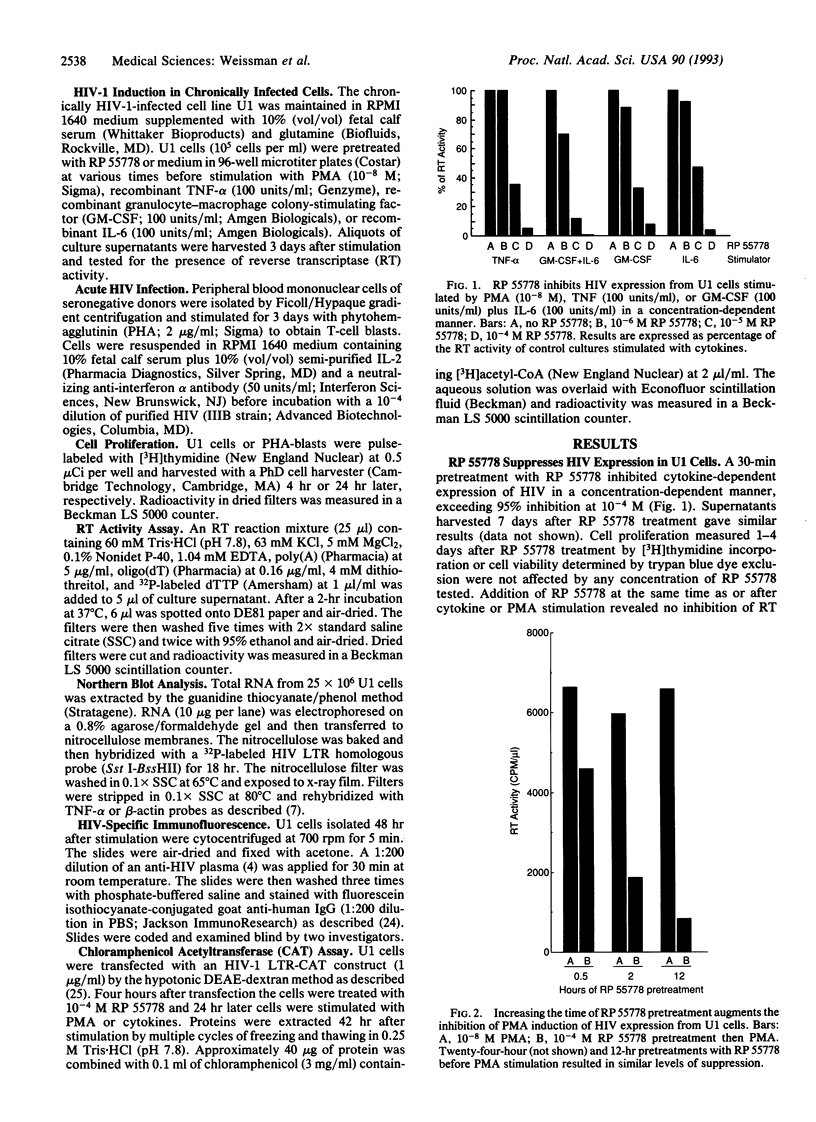
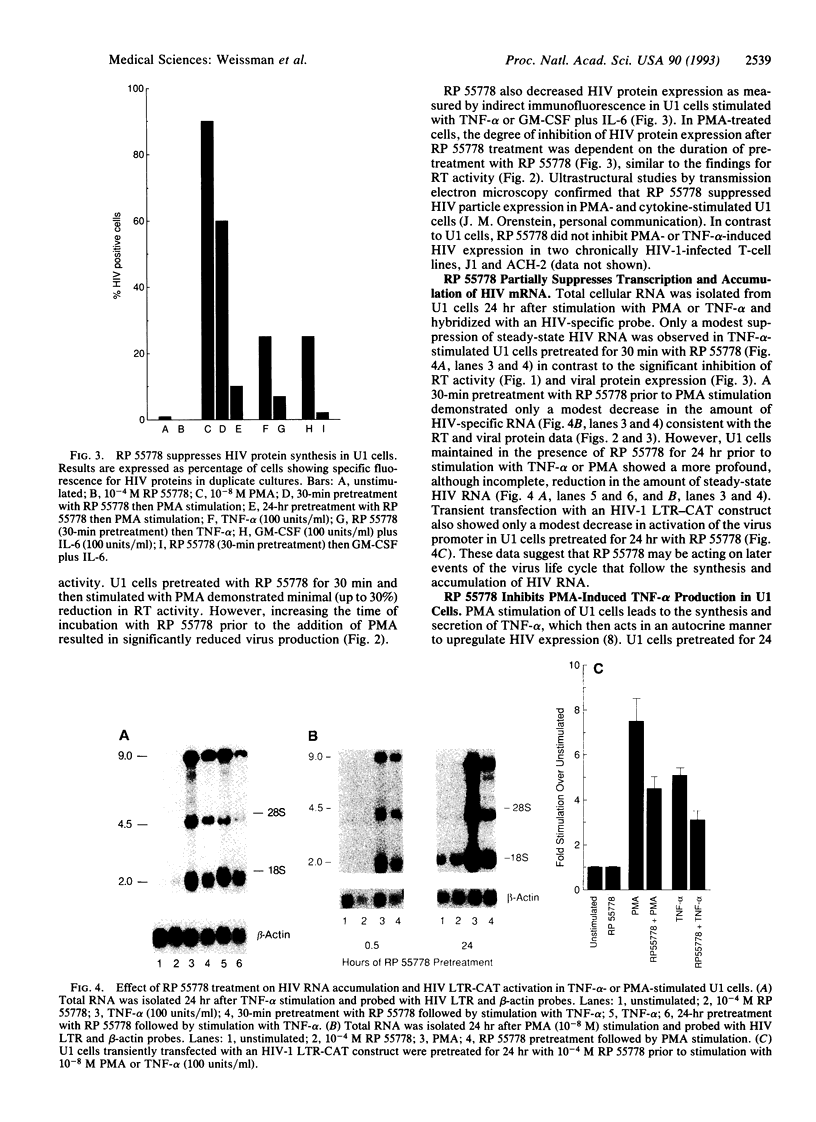
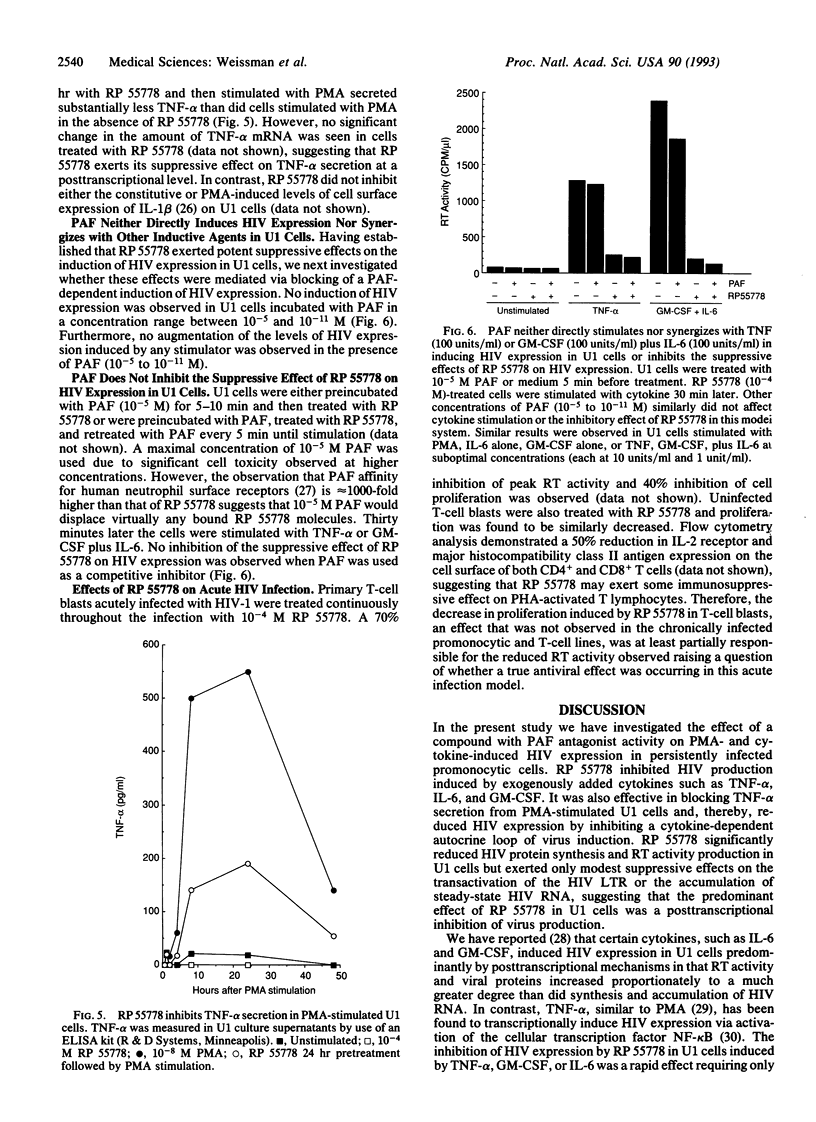
A platelet-activating factor antagonist, RP 55778, potently suppressed the induction of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) expression in chronically infected promonocytic U1 cells. RP 55778 inhibited the production of reverse transcriptase activity in U1 cells stimulated with the transcriptionally active inducers of virus production, tumor necrosis factor alpha and phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate. This effect was correlated only in part with a reduction in the levels of HIV RNA, suggesting that this agent was also affecting posttranscriptional levels of virus production. In this regard, RP 55778 effectively blocked the induction of HIV expression in U1 cells stimulated with interleukin 6 and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, which act predominantly as posttranscriptional activators of HIV expression. Finally, RP 55778 inhibited the production of endogenous tumor necrosis factor alpha in phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate-stimulated cells, thereby interfering with an autocrine pathway of virus expression. The suppressive effects of RP 55778 on HIV expression appeared to be independent of the platelet-activating factor cell surface receptor on U1 cells. RP 55778 inhibited acute HIV replication in primary T-cell blasts and the proliferative capacity of these cells. This study suggests that RP 55778 may represent potentially useful compounds in the treatment of HIV infection.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Breen E. C., Rezai A. R., Nakajima K., Beall G. N., Mitsuyasu R. T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T., Martinez-Maza O. Infection with HIV is associated with elevated IL-6 levels and production. J Immunol. 1990 Jan 15;144(2):480–484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bressler P., Pantaleo G., Demaria A., Fauci A. S. Anti-CD2 receptor antibodies activate the HIV long terminal repeat in T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1991 Oct 1;147(7):2290–2294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coombs R. W., Collier A. C., Allain J. P., Nikora B., Leuther M., Gjerset G. F., Corey L. Plasma viremia in human immunodeficiency virus infection. N Engl J Med. 1989 Dec 14;321(24):1626–1631. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198912143212402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois C., Bissonnette E., Rola-Pleszczynski M. Platelet-activating factor (PAF) enhances tumor necrosis factor production by alveolar macrophages. Prevention by PAF receptor antagonists and lipoxygenase inhibitors. J Immunol. 1989 Aug 1;143(3):964–970. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duh E. J., Maury W. J., Folks T. M., Fauci A. S., Rabson A. B. Tumor necrosis factor alpha activates human immunodeficiency virus type 1 through induction of nuclear factor binding to the NF-kappa B sites in the long terminal repeat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5974–5978. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauci A. S., Schnittman S. M., Poli G., Koenig S., Pantaleo G. NIH conference. Immunopathogenic mechanisms in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. Ann Intern Med. 1991 Apr 15;114(8):678–693. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-114-8-678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleisher L. N., Ferrell J. B., Smith M. G., McGahan M. C. Lipid mediators of tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced uveitis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1991 Jul;32(8):2393–2399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floch A., Bousseau A., Hetier E., Floc'h F., Bost P. E., Cavero I. RP 55778, a PAF receptor antagonist, prevents and reverses LPS-induced hemoconcentration and TNF release. J Lipid Mediat. 1989 Nov-Dec;1(6):349–360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folks T. M., Justement J., Kinter A., Dinarello C. A., Fauci A. S. Cytokine-induced expression of HIV-1 in a chronically infected promonocyte cell line. Science. 1987 Nov 6;238(4828):800–802. doi: 10.1126/science.3313729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folks T. M., Justement J., Kinter A., Schnittman S., Orenstein J., Poli G., Fauci A. S. Characterization of a promonocyte clone chronically infected with HIV and inducible by 13-phorbol-12-myristate acetate. J Immunol. 1988 Feb 15;140(4):1117–1122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo P., Frei K., Rordorf C., Lazdins J., Tavolato B., Fontana A. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) infection of the central nervous system: an evaluation of cytokines in cerebrospinal fluid. J Neuroimmunol. 1989 Jul;23(2):109–116. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(89)90029-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. J. Platelet activating factor: a biologically active phosphoglyceride. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:483–509. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.002411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuer H. Effect of a new and specific PAF-antagonist, WEB 2086, on PAF and endotoxin/tumor necrosis factor induced changes in mortality and intestinal transit velocity. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1989;308:919–924. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho D. D., Moudgil T., Alam M. Quantitation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in the blood of infected persons. N Engl J Med. 1989 Dec 14;321(24):1621–1625. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198912143212401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hocking D. C., Phillips P. G., Ferro T. J., Johnson A. Mechanisms of pulmonary edema induced by tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Circ Res. 1990 Jul;67(1):68–77. doi: 10.1161/01.res.67.1.68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau A. S., Livesey J. F. Endotoxin induction of tumor necrosis factor is enhanced by acid-labile interferon-alpha in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1989 Sep;84(3):738–743. doi: 10.1172/JCI114231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lähdevirta J., Maury C. P., Teppo A. M., Repo H. Elevated levels of circulating cachectin/tumor necrosis factor in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Am J Med. 1988 Sep;85(3):289–291. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(88)90576-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcheselli V. L., Rossowska M. J., Domingo M. T., Braquet P., Bazan N. G. Distinct platelet-activating factor binding sites in synaptic endings and in intracellular membranes of rat cerebral cortex. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 5;265(16):9140–9145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuya H., Yarchoan R., Broder S. Molecular targets for AIDS therapy. Science. 1990 Sep 28;249(4976):1533–1544. doi: 10.1126/science.1699273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabel G., Baltimore D. An inducible transcription factor activates expression of human immunodeficiency virus in T cells. Nature. 1987 Apr 16;326(6114):711–713. doi: 10.1038/326711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poli G., Bressler P., Kinter A., Duh E., Timmer W. C., Rabson A., Justement J. S., Stanley S., Fauci A. S. Interleukin 6 induces human immunodeficiency virus expression in infected monocytic cells alone and in synergy with tumor necrosis factor alpha by transcriptional and post-transcriptional mechanisms. J Exp Med. 1990 Jul 1;172(1):151–158. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.1.151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poli G., Fauci A. S. The effect of cytokines and pharmacologic agents on chronic HIV infection. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1992 Feb;8(2):191–197. doi: 10.1089/aid.1992.8.191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poli G., Kinter A., Justement J. S., Kehrl J. H., Bressler P., Stanley S., Fauci A. S. Tumor necrosis factor alpha functions in an autocrine manner in the induction of human immunodeficiency virus expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):782–785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riches D. W., Young S. K., Seccombe J. F., Henson J. E., Clay K. L., Henson P. M. The subcellular distribution of platelet-activating factor in stimulated human neutrophils. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 1;145(9):3062–3070. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rieckmann P., Poli G., Kehrl J. H., Fauci A. S. Activated B lymphocytes from human immunodeficiency virus-infected individuals induce virus expression in infected T cells and a promonocytic cell line, U1. J Exp Med. 1991 Jan 1;173(1):1–5. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders R. N., Handley D. A. Platelet-activating factor antagonists. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1987;27:237–255. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.27.040187.001321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnittman S. M., Psallidopoulos M. C., Lane H. C., Thompson L., Baseler M., Massari F., Fox C. H., Salzman N. P., Fauci A. S. The reservoir for HIV-1 in human peripheral blood is a T cell that maintains expression of CD4. Science. 1989 Jul 21;245(4915):305–308. doi: 10.1126/science.2665081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherry B., Cerami A. Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor exerts endocrine, paracrine, and autocrine control of inflammatory responses. J Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;107(4):1269–1277. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.4.1269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squinto S. P., Braquet P., Block A. L., Bazan N. G. Platelet-activating factor activates HIV promoter in transfected SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells and MOLT-4 T lymphocytes. J Mol Neurosci. 1990;2(2):79–84. doi: 10.1007/BF02876914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun X. M., Hsueh W. Platelet-activating factor produces shock, in vivo complement activation, and tissue injury in mice. J Immunol. 1991 Jul 15;147(2):509–514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun X. M., Hsueh W., Torre-Amione G. Effects of in vivo 'priming' on endotoxin-induced hypotension and tissue injury. The role of PAF and tumor necrosis factor. Am J Pathol. 1990 Apr;136(4):949–956. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valone F. H., Goetzl E. J. Specific binding by human polymorphonuclear leucocytes of the immunological mediator 1-O-hexadecyl/octadecyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphorylcholine. Immunology. 1983 Jan;48(1):141–149. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vyakarnam A., McKeating J., Meager A., Beverley P. C. Tumour necrosis factors (alpha, beta) induced by HIV-1 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells potentiate virus replication. AIDS. 1990 Jan;4(1):21–27. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199001000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]