Abstract
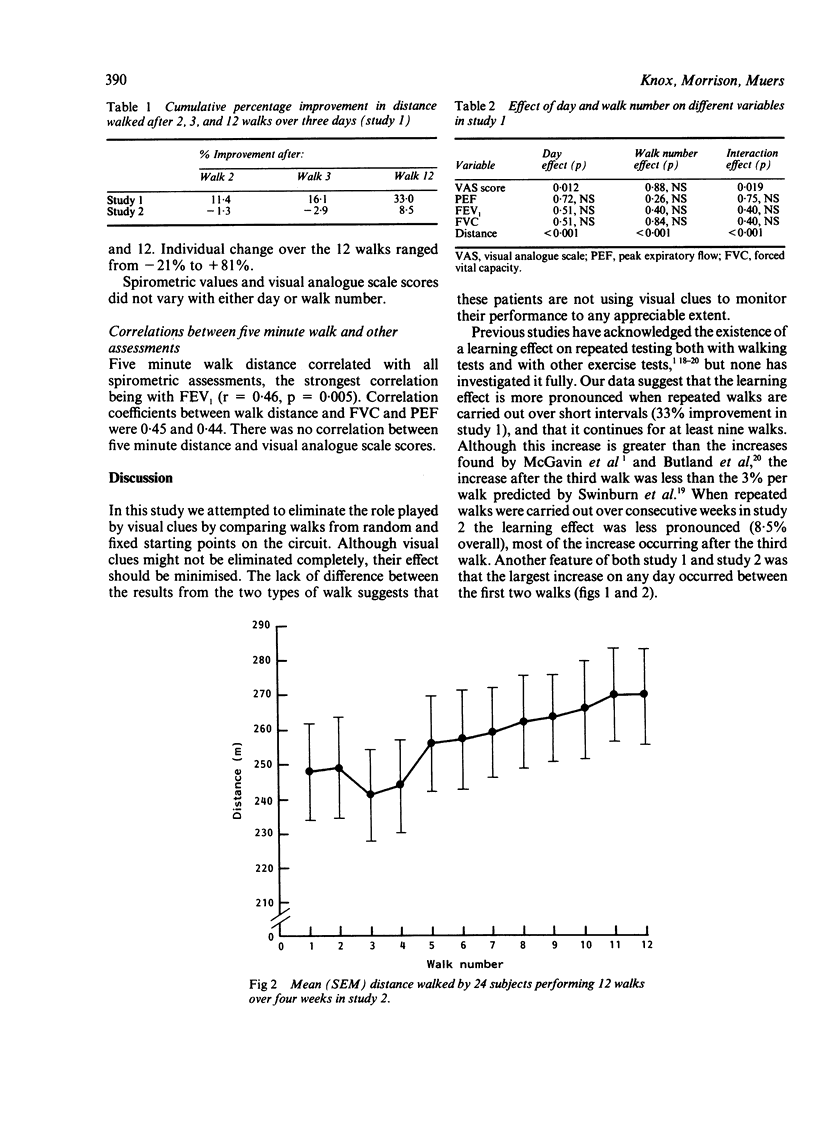
Thirty six patients with chronic airflow obstruction were studied to examine (1) the reproducibility and order effect of repeated walking tests when performed over consecutive days or consecutive weeks; (2) the correlation between walking distance and spirometric measurements; and (3) the effect of static visual clues on performance. In study 1, where 12 patients performed 12 walks over three consecutive days, five minute walking distance increased by 33% between walks 1 and 12, half of the increase occurring after the first three walks. In study 2, where 24 patients performed 12 walks over four consecutive weeks, five minute walking distance increased by 8.5% between walks 1 and 12. A learning effect was seen over the first nine walks. Static visual clues to performance did not affect the distance walked. Spirometric measurements showed no order effect in either study. Although walking distance correlated significantly with FEV1, forced vital capacity, and peak expiratory flow, these measurements were poor predictors of exercise performance. The learning effects seen on repeated performance of walking tests over short intervals should be considered when an individual's response to treatment is being interpreted. When walking tests are used in clinical trials a placebo group or randomised crossover design is essential.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belman M. J., Mittman C. Ventilatory muscle training improves exercise capacity in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980 Feb;121(2):273–280. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.121.2.273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. E., Nagendran R. C., McHugh J. W., Stansbury D. W., Fischer C. E., Light R. W. Effects of a large carbohydrate load on walking performance in chronic air-flow obstruction. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Nov;132(5):960–962. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.132.5.960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butland R. J., Pang J., Gross E. R., Woodcock A. A., Geddes D. M. Two-, six-, and 12-minute walking tests in respiratory disease. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1982 May 29;284(6329):1607–1608. doi: 10.1136/bmj.284.6329.1607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connellan S. J., Gough S. E. The effects of nebulized salbutamol on lung function and exercise tolerance in patients with severe airflow obstruction. Br J Dis Chest. 1982 Apr;76(2):135–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly C. K., Chan N. S. Salbutamol and ipratropium in partially reversible airway obstruction. Br J Dis Chest. 1987 Jan;81(1):55–61. doi: 10.1016/0007-0971(87)90108-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans W. V. Plasma theophylline concentrations, six minute walking distances, and breathlessness in patients with chronic airflow obstruction. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1984 Dec 15;289(6459):1649–1651. doi: 10.1136/bmj.289.6459.1649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyatt G. H., Pugsley S. O., Sullivan M. J., Thompson P. J., Berman L., Jones N. L., Fallen E. L., Taylor D. W. Effect of encouragement on walking test performance. Thorax. 1984 Nov;39(11):818–822. doi: 10.1136/thx.39.11.818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leggett R. J., Flenley D. C. Portable oxygen and exercise tolerance in patients with chronic hypoxic cor pulmonale. Br Med J. 1977 Jul 9;2(6079):84–86. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6079.84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leitch A. G., Hopkin J. M., Ellis D. A., Merchant S., McHardy G. J. The effect of aerosol ipratropium bromide and salbutamol on exercise tolerance in chronic bronchitis. Thorax. 1978 Dec;33(6):711–713. doi: 10.1136/thx.33.6.711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipkin D. P., Scriven A. J., Crake T., Poole-Wilson P. A. Six minute walking test for assessing exercise capacity in chronic heart failure. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1986 Mar 8;292(6521):653–655. doi: 10.1136/bmj.292.6521.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGavin C. R., Gupta S. P., Lloyd E. L., McHardy G. J. Physical rehabilitation for the chronic bronchitic: results of a controlled trial of exercises in the home. Thorax. 1977 Jun;32(3):307–311. doi: 10.1136/thx.32.3.307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGavin C. R., Gupta S. P., McHardy G. J. Twelve-minute walking test for assessing disability in chronic bronchitis. Br Med J. 1976 Apr 3;1(6013):822–823. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6013.822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan A. D., Peck D. F., Buchanan D. R., McHardy G. J. Effect of attitudes and beliefs on exercise tolerance in chronic bronchitis. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1983 Jan 15;286(6360):171–173. doi: 10.1136/bmj.286.6360.171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mungall I. P., Hainsworth R. Assessment of respiratory function in patients with chronic obstructive airways disease. Thorax. 1979 Apr;34(2):254–258. doi: 10.1136/thx.34.2.254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Reilly J. F., Shaylor J. M., Fromings K. M., Harrison B. D. The use of the 12 minute walking test in assessing the effect of oral steroid therapy in patients with chronic airways obstruction. Br J Dis Chest. 1982 Oct;76(4):374–382. doi: 10.1016/0007-0971(82)90073-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair D. J., Ingram C. G. Controlled trial of supervised exercise training in chronic bronchitis. Br Med J. 1980 Feb 23;280(6213):519–521. doi: 10.1136/bmj.280.6213.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swinburn C. R., Wakefield J. M., Jones P. W. Performance, ventilation, and oxygen consumption in three different types of exercise test in patients with chronic obstructive lung disease. Thorax. 1985 Aug;40(8):581–586. doi: 10.1136/thx.40.8.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams I. P., Smith C. M., McGavin C. R. Diaphragmatic breathing training and walking performance in chronic airways obstruction. Br J Dis Chest. 1982 Apr;76(2):164–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


