Abstract
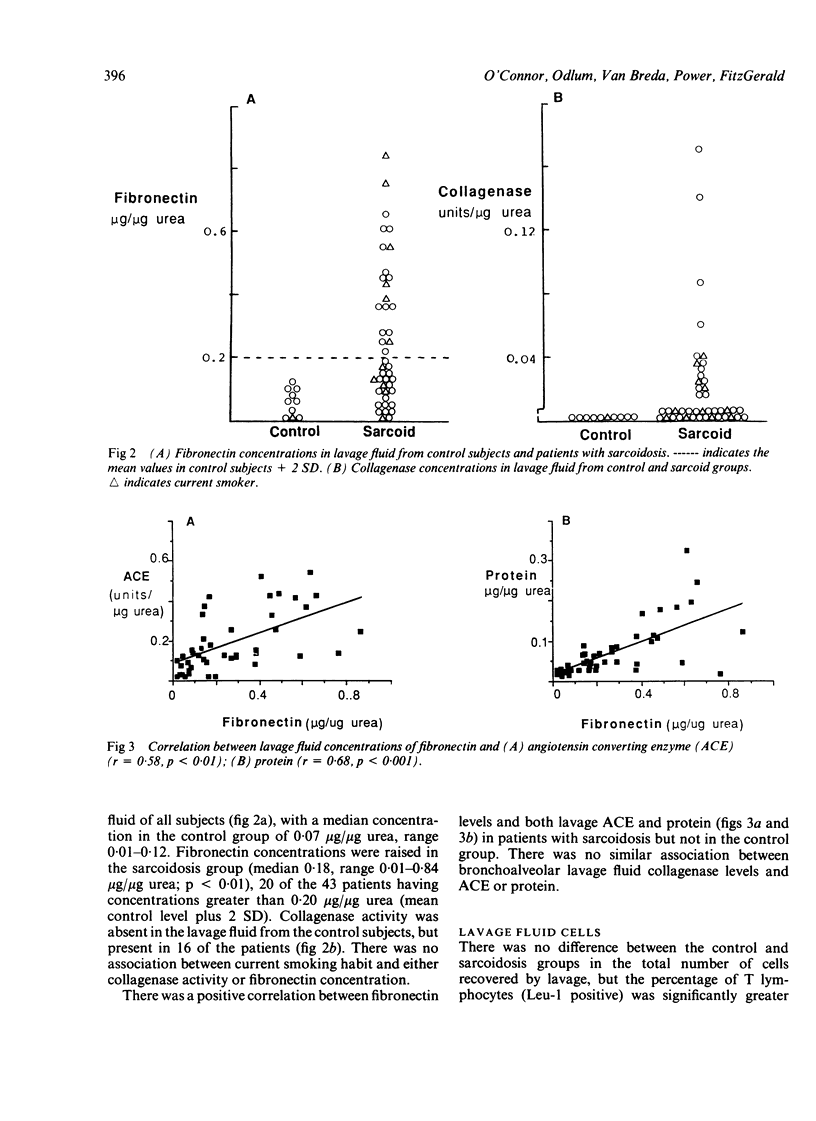
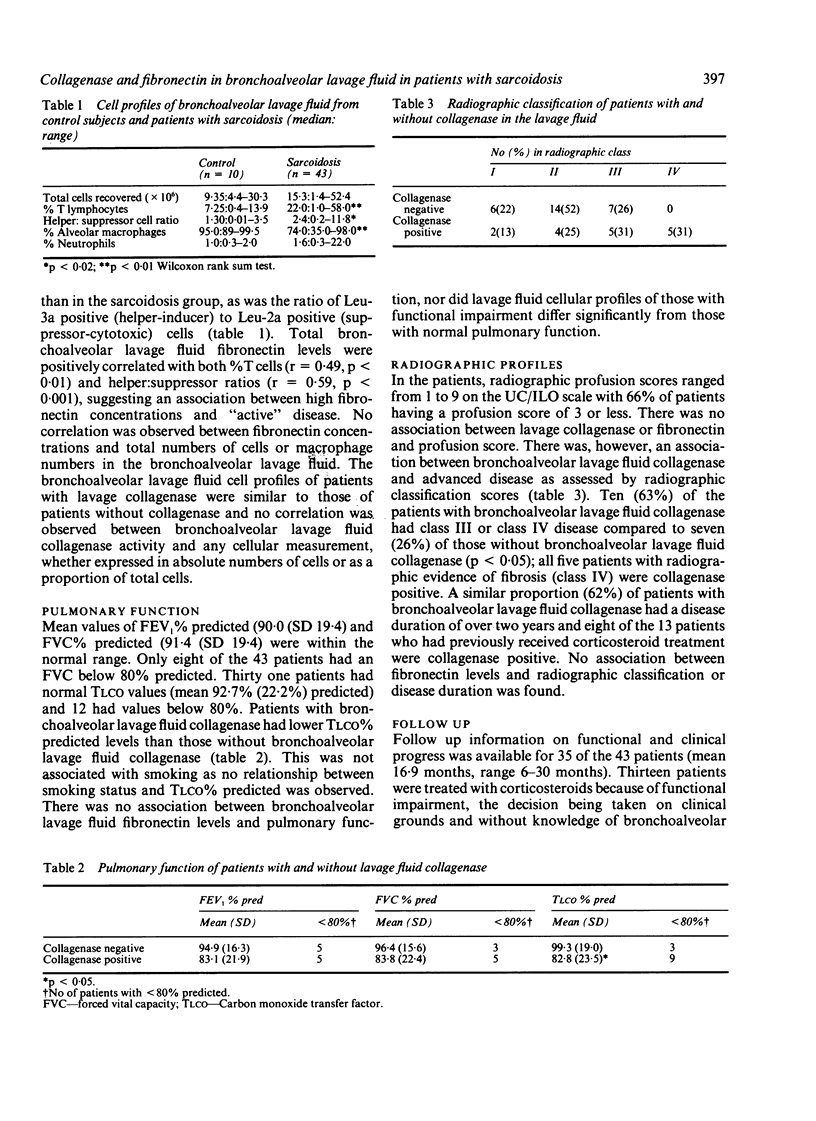
Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from 43 patients with biopsy proved sarcoidosis and 10 control subjects were assayed for fibronectin and collagenase activity. Fibronectin was significantly increased in the group with sarcoidosis and was found to be positively correlated with angiotensin converting enzyme activity, protein concentration, percentage of T cells and helper:suppressor ratios in the lavage fluid. Increased fibronectin in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid was not related to functional or radiographic indices of interstitial disease and did not identify patients subsequently requiring treatment. Latent collagenase was present in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from 16 patients with sarcoidosis but not in any control sample. There was no association between the collagenase activity and the cell profiles of the lavage fluid. Yet carbon monoxide transfer factor was decreased in patients with bronchoalveolar lavage fluid collagenase. Ten of 16 patients with bronchoalveolar lavage fluid collagenase had radiographic class III or IV disease and a disease duration of more than two years. On follow up 62% of patients with bronchoalveolar lavage fluid collagenase required subsequent treatment, compared with only 23% of patients without collagenase. These results indicate an association between bronchoalveolar lavage fluid collagenase and progressive, prolonged disease in sarcoidosis, whereas increased bronchoalveolar lavage fluid fibronectin is associated with indices of disease activity.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams D. O., Hamilton T. A. The cell biology of macrophage activation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1984;2:283–318. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.02.040184.001435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnoux A., Marsac J., Stanislas-Leguern G., Huchon G., Chretien J. Broncho-alveolar lavage in sarcoidosis. Correlation between alveolar lymphocytosis and clinical data. Pathol Res Pract. 1982 Oct;175(1):62–79. doi: 10.1016/S0344-0338(82)80043-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bitterman P. B., Adelberg S., Crystal R. G. Mechanisms of pulmonary fibrosis. Spontaneous release of the alveolar macrophage-derived growth factor in the interstitial lung disorders. J Clin Invest. 1983 Nov;72(5):1801–1813. doi: 10.1172/JCI111140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnett D., Reynolds J. J., Ward R. V., Afford S. C., Stockley R. A. Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases and collagenase inhibitory activity in lung secretions from patients with chronic obstructive bronchitis: effect of corticosteroid treatment. Thorax. 1986 Oct;41(10):740–745. doi: 10.1136/thx.41.10.740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell D. A., Poulter L. W., Du Bois R. M. Phenotypic analysis of alveolar macrophages in normal subjects and in patients with interstitial lung disease. Thorax. 1986 Jun;41(6):429–434. doi: 10.1136/thx.41.6.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cawston T. E., Murphy G., Mercer E., Galloway W. A., Hazleman B. L., Reynolds J. J. The interaction of purified rabbit bone collagenase with purified rabbit bone metalloproteinase inhibitor. Biochem J. 1983 May 1;211(2):313–318. doi: 10.1042/bj2110313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christner P., Fein A., Goldberg S., Lippmann M., Abrams W., Weinbaum G. Collagenase in the lower respiratory tract of patients with adult respiratory distress syndrome. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 May;131(5):690–695. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.131.5.690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crystal R. G., Bitterman P. B., Rennard S. I., Hance A. J., Keogh B. A. Interstitial lung diseases of unknown cause. Disorders characterized by chronic inflammation of the lower respiratory tract (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1984 Jan 19;310(3):154–166. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198401193100304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadek J. E., Kelman J. A., Fells G., Weinberger S. E., Horwitz A. L., Reynolds H. Y., Fulmer J. D., Crystal R. G. Collagenase in the lower respiratory tract of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 1979 Oct 4;301(14):737–742. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197910043011401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gisslow M. T., McBride B. C. A rapid sensitive collagenase assay. Anal Biochem. 1975 Sep;68(1):70–78. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90680-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg G. I., Wilhelm S. M., Kronberger A., Bauer E. A., Grant G. A., Eisen A. Z. Human fibroblast collagenase. Complete primary structure and homology to an oncogene transformation-induced rat protein. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 15;261(14):6600–6605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez-Lechon M. J., Castell J. V. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay to quantify fibronectin. Anal Biochem. 1985 Feb 15;145(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90318-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartree E. F. Determination of protein: a modification of the Lowry method that gives a linear photometric response. Anal Biochem. 1972 Aug;48(2):422–427. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90094-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasty K. A., Hibbs M. S., Kang A. H., Mainardi C. L. Secreted forms of human neutrophil collagenase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 25;261(12):5645–5650. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman J. Elevation of serum angiotensin-converting-enzyme (ACE) level in sarcoidosis. Am J Med. 1975 Sep;59(3):365–372. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(75)90395-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y. H., Haslam P. L., Turner-Warwick M. Chronic pulmonary sarcoidosis: relationship between lung lavage cell counts, chest radiograph, and results of standard lung function tests. Thorax. 1985 Jul;40(7):501–507. doi: 10.1136/thx.40.7.501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindblad W. J., Fuller G. C. An improved assay of mammalian collagenase activity, and its use to determine hepatic extracellular matrix susceptibility to degradation. Clin Chem. 1982 Oct;28(10):2134–2138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macartney H. W., Tschesche H. Characterisation of beta 1-anticollagenase from human plasma and its reaction with polymorphonuclear leukocyte collagenase by disulfide/thiol interchange. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jan 17;130(1):85–92. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07120.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLoud T. C., Epler G. R., Gaensler E. A., Burke G. W., Carrington C. B. A radiographic classification for sarcoidosis: physiologic correlation. Invest Radiol. 1982 Mar-Apr;17(2):129–138. doi: 10.1097/00004424-198203000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onal E., Lopata M., O'Connor T. Pathogenesis of apneas in hypersomnia-sleep apnea syndrome. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 Feb;125(2):167–174. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1982.125.2.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rennard S. I., Crystal R. G. Fibronectin in human bronchopulmonary lavage fluid. Elevation in patients with interstitial lung disease. J Clin Invest. 1982 Jan;69(1):113–122. doi: 10.1172/JCI110421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds H. Y. Bronchoalveolar lavage. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Jan;135(1):250–263. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1987.135.1.250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth C., Huchon G. J., Arnoux A., Stanislas-Leguern G., Marsac J. H., Chretien J. Bronchoalveolar cells in advanced pulmonary sarcoidosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1981 Jul;124(1):9–12. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1981.124.1.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spatafora M., Mirabella A., Rossi G. A., Bonanno A., Riccobono L., Carini C., Sacco O., Ravazzoni C. Lung inflammation in sarcoidosis: analysis of immunoglobulin levels in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid in active and inactive disease. Respiration. 1985;48(2):127–135. doi: 10.1159/000194812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welgus H. G., Campbell E. J., Bar-Shavit Z., Senior R. M., Teitelbaum S. L. Human alveolar macrophages produce a fibroblast-like collagenase and collagenase inhibitor. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jul;76(1):219–224. doi: 10.1172/JCI111949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welgus H. G., Connolly N. L., Senior R. M. 12-o-Tetradecanoyl-phorbol-13-acetate-differentiated U937 cells express a macrophage-like profile of neutral proteinases. High levels of secreted collagenase and collagenase inhibitor accompany low levels of intracellular elastase and cathepsin G. J Clin Invest. 1986 May;77(5):1675–1681. doi: 10.1172/JCI112485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]