Abstract
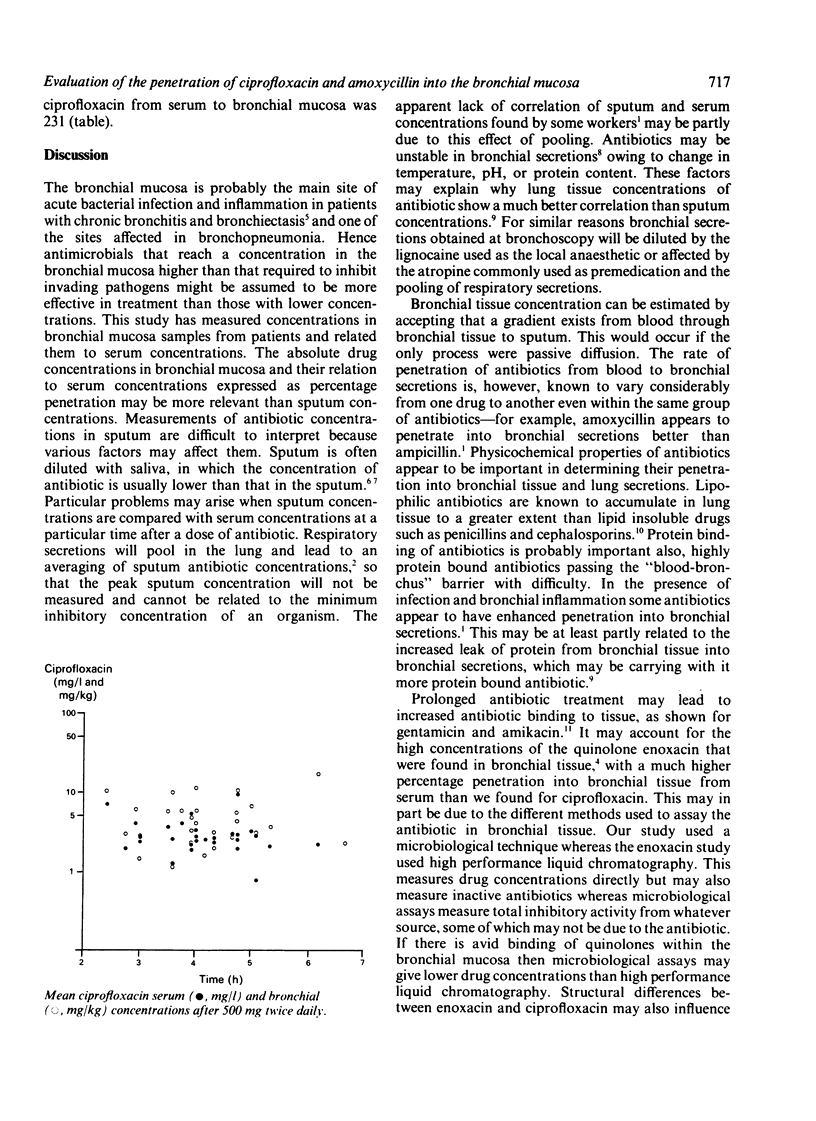
The concentrations of two antibiotics, amoxycillin and ciprofloxacin, were measured by microbiological assay in serum and in bronchial mucosa obtained at fibreoptic bronchoscopy in 38 patients undergoing diagnostic bronchoscopy for a range of respiratory symptoms. Patients had taken one of the two drugs orally for four days before bronchoscopy. The percentage penetration of antibiotic from serum to bronchial mucosa was calculated as the ratio of drug concentration in bronchial tissue to that in serum x 100. Of the nine patients who took amoxycillin 500 mg thrice daily the mean (SD) percentage penetration was 75. This was significantly lower than the mean percentage penetration of 147 in 29 patients who took ciprofloxacin 500 mg twice daily. Ten patients were given a single intravenous dose of ciprofloxacin 200 mg one hour before bronchoscopy and the mean percentage penetration was 231. This study has shown that the quinolone antibiotic ciprofloxacin is concentrated in the bronchial mucosa.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biagi G. L., Guerra M. C., Barbaro A. M., Gamba M. F. Influence of lipophilic character on the antibacterial activity of cephalosporins and penicillins. J Med Chem. 1970 May;13(3):511–516. doi: 10.1021/jm00297a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalhoff A., Weuta H. Penetration of ciprofloxacin into gynecologic tissues. Am J Med. 1987 Apr 27;82(4A):133–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fass R. J. Efficacy and safety of oral ciprofloxacin in the treatment of serious respiratory infections. Am J Med. 1987 Apr 27;82(4A):202–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfarb J., Stern R. C., Reed M. D., Yamashita T. S., Myers C. M., Blumer J. L. Ciprofloxacin monotherapy for acute pulmonary exacerbations of cystic fibrosis. Am J Med. 1987 Apr 27;82(4A):174–179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERS J. F., MULDER J. The mucosal epithelium of the respiratory tract in muco-purulent bronchitis caused by Haemophilus influenzae. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1953 Jul;66(1):103–108. doi: 10.1002/path.1700660114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King A., Phillips I. The comparative in-vitro activity of eight newer quinolones and nalidixic acid. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Nov;18 (Suppl 500):1–20. doi: 10.1093/jac/18.supplement_d.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornguth M. L., Kunin C. M. Distribution of gentamicin and amikacin in rabbit tissues. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Jun;11(6):974–977. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.6.974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marlin G. E., Braude P. D., Whelan A. J., Somogyi A. A. Penetration of enoxacin into human bronchial mucosa. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 Dec;134(6):1209–1212. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1986.134.5.1209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marlin G. E., Nicholls A. J., Funnell G. R., Bradbury R. Penetration of cefaclor into bronchial mucosa. Thorax. 1984 Nov;39(11):813–817. doi: 10.1136/thx.39.11.813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon C., Gatzemeier U. Serum and sputum levels of cefaclor. Postgrad Med J. 1979;55 (Suppl 4):30–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart S. M., Fisher M., Young J. E., Lutz W. Ampicillin levels in sputum, serum, and saliva. Thorax. 1970 May;25(3):304–311. doi: 10.1136/thx.25.3.304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R., Andrews J. M., Edwards L. J. In vitro activity of Bay 09867, a new quinoline derivative, compared with those of other antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Apr;23(4):559–564. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.4.559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollschlager C. M., Raoof S., Khan F. A., Guarneri J. J., LaBombardi V., Afzal Q. Controlled, comparative study of ciprofloxacin versus ampicillin in treatment of bacterial respiratory tract infections. Am J Med. 1987 Apr 27;82(4A):164–168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


