Abstract
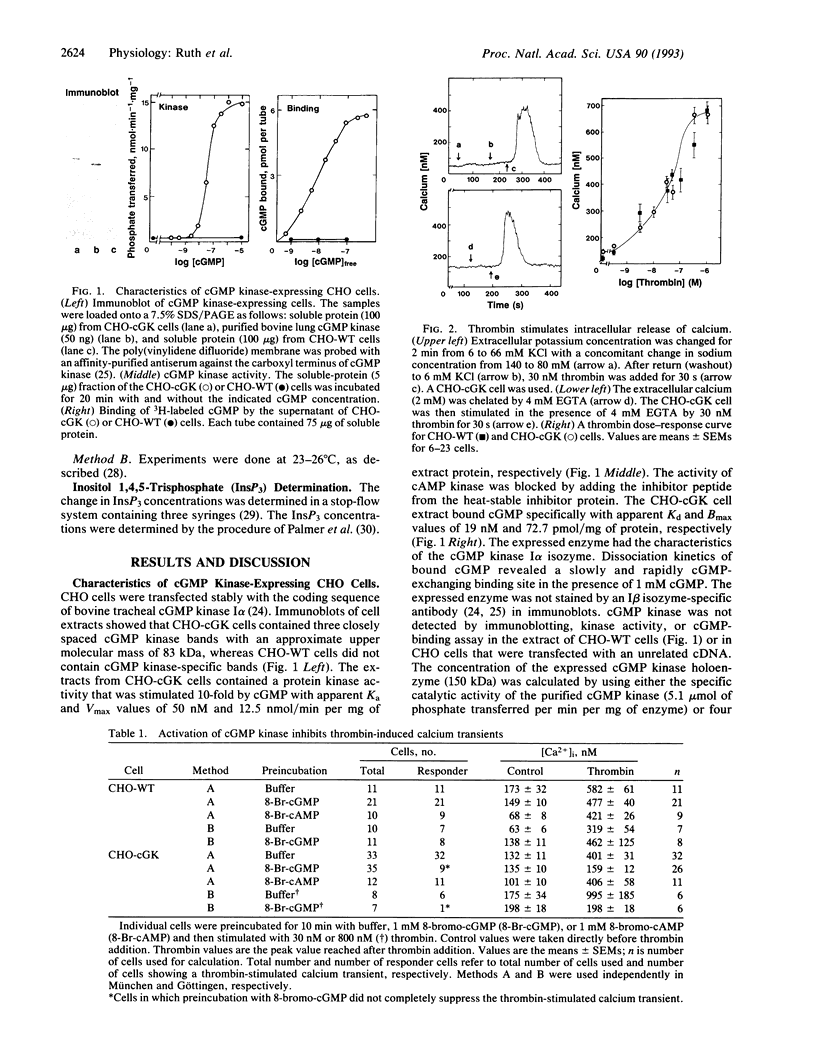
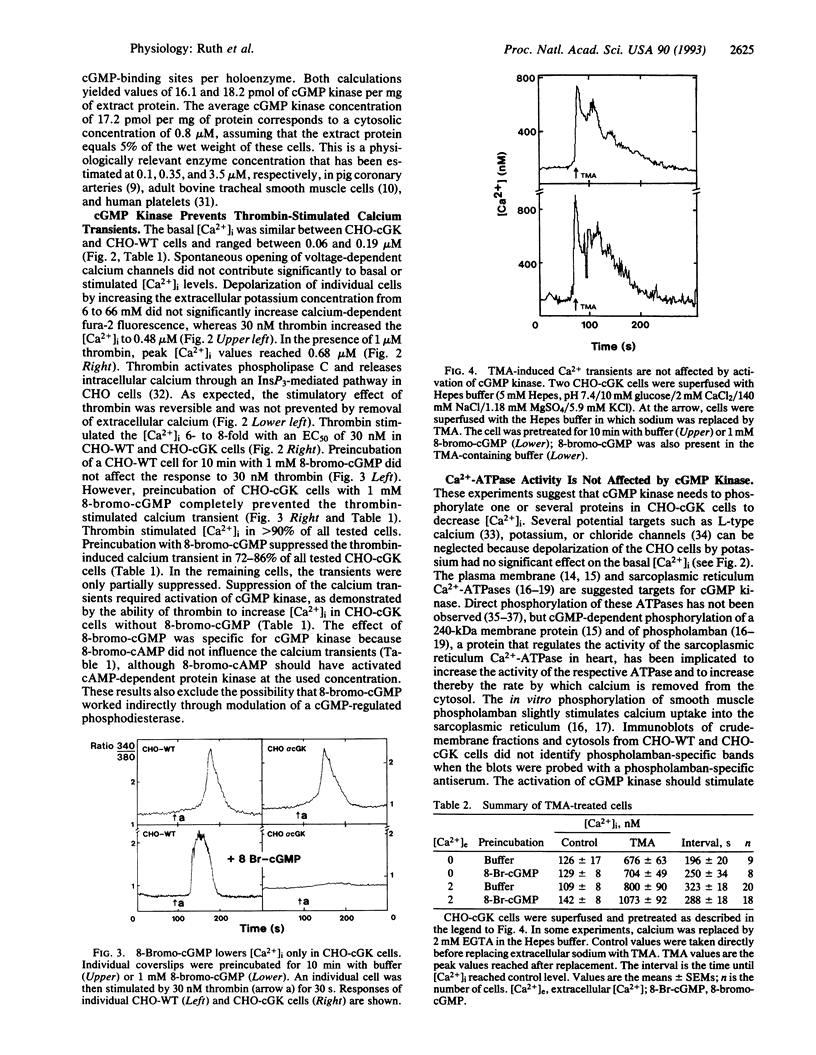
cGMP is a key regulatory molecule in visual transduction, integration of neuronal response to excitatory neurotransmitters, relaxation of smooth muscle, intestinal secretion of water and salt, and reabsorption of sodium and water in the distal tubules of the nephron. Some of these cellular functions are associated with the activation of cGMP kinase and a decrease in cytosolic calcium levels ([Ca2+]i). The mechanism by which cGMP kinase lowers [Ca2+]i is controversial. We have used CHO cells stably transfected with cGMP kinase to test several of the proposed [Ca2+]i-lowering mechanisms. Thrombin induces a calcium transient in wild-type and cGMP kinase-expressing CHO cells by releasing calcium from intracellular stores. Preincubation of wild-type cells with 8-bromo-cGMP had no effect on the calcium transient, whereas 8-bromo-cGMP prevented the thrombin-stimulated calcium transient in cGMP kinase-expressing CHO cells. In both cell types 8-bromo-cGMP had no effect on [Ca2+]i transients induced by replacing extracellular sodium by tetramethylammonium, ruling out an effect of cGMP kinase on Ca(2+)-ATPases. However, cGMP kinase activation effectively suppressed thrombin-induced stimulation of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate production. These results show that cGMP kinase lowers [Ca2+]i by interfering with the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate synthesis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashkenazi A., Peralta E. G., Winslow J. W., Ramachandran J., Capon D. J. Functionally distinct G proteins selectively couple different receptors to PI hydrolysis in the same cell. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):487–493. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90251-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltensperger K., Chiesi M., Carafoli E. Substrates of cGMP kinase in vascular smooth muscle and their role in the relaxation process. Biochemistry. 1990 Oct 16;29(41):9753–9760. doi: 10.1021/bi00493a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertolino M., Llinás R. R. The central role of voltage-activated and receptor-operated calcium channels in neuronal cells. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1992;32:399–421. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.32.040192.002151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boekhoff I., Tareilus E., Strotmann J., Breer H. Rapid activation of alternative second messenger pathways in olfactory cilia from rats by different odorants. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2453–2458. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07422.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredt D. S., Glatt C. E., Hwang P. M., Fotuhi M., Dawson T. M., Snyder S. H. Nitric oxide synthase protein and mRNA are discretely localized in neuronal populations of the mammalian CNS together with NADPH diaphorase. Neuron. 1991 Oct;7(4):615–624. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90374-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredt D. S., Snyder S. H. Nitric oxide, a novel neuronal messenger. Neuron. 1992 Jan;8(1):3–11. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90104-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornwell T. L., Lincoln T. M. Regulation of intracellular Ca2+ levels in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. Reduction of Ca2+ by atriopeptin and 8-bromo-cyclic GMP is mediated by cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):1146–1155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornwell T. L., Pryzwansky K. B., Wyatt T. A., Lincoln T. M. Regulation of sarcoplasmic reticulum protein phosphorylation by localized cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase in vascular smooth muscle cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Dec;40(6):923–931. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felbel J., Trockur B., Ecker T., Landgraf W., Hofmann F. Regulation of cytosolic calcium by cAMP and cGMP in freshly isolated smooth muscle cells from bovine trachea. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):16764–16771. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis S. H., Noblett B. D., Todd B. W., Wells J. N., Corbin J. D. Relaxation of vascular and tracheal smooth muscle by cyclic nucleotide analogs that preferentially activate purified cGMP-dependent protein kinase. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 Oct;34(4):506–517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiger J., Nolte C., Butt E., Sage S. O., Walter U. Role of cGMP and cGMP-dependent protein kinase in nitrovasodilator inhibition of agonist-evoked calcium elevation in human platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 1;89(3):1031–1035. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.3.1031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haley J. E., Wilcox G. L., Chapman P. F. The role of nitric oxide in hippocampal long-term potentiation. Neuron. 1992 Feb;8(2):211–216. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90288-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata M., Kohse K. P., Chang C. H., Ikebe T., Murad F. Mechanism of cyclic GMP inhibition of inositol phosphate formation in rat aorta segments and cultured bovine aortic smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 25;265(3):1268–1273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann F., Dostmann W., Keilbach A., Landgraf W., Ruth P. Structure and physiological role of cGMP-dependent protein kinase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Apr 30;1135(1):51–60. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(92)90165-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamm K. E., Stull J. T. Regulation of smooth muscle contractile elements by second messengers. Annu Rev Physiol. 1989;51:299–313. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.51.030189.001503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keilbach A., Ruth P., Hofmann F. Detection of cGMP dependent protein kinase isozymes by specific antibodies. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Sep 1;208(2):467–473. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17209.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landgraf W., Hofmann F. The amino terminus regulates binding to and activation of cGMP-dependent protein kinase. Eur J Biochem. 1989 May 15;181(3):643–650. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14771.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang D., Lewis M. J. Endothelium-derived relaxing factor inhibits the formation of inositol trisphosphate by rabbit aorta. J Physiol. 1989 Apr;411:45–52. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang D., Lewis M. J. Inhibition of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate formation by cyclic GMP in cultured aortic endothelial cells of the pig. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Jan;102(1):277–281. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12166.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Light D. B., Corbin J. D., Stanton B. A. Dual ion-channel regulation by cyclic GMP and cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase. Nature. 1990 Mar 22;344(6264):336–339. doi: 10.1038/344336a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lincoln T. M., Cornwell T. L., Taylor A. E. cGMP-dependent protein kinase mediates the reduction of Ca2+ by cAMP in vascular smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol. 1990 Mar;258(3 Pt 1):C399–C407. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.258.3.C399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T. Cell signaling by second messenger waves. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):675–678. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90496-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Palmer R. M., Higgs E. A. Nitric oxide: physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacol Rev. 1991 Jun;43(2):109–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Méry P. F., Lohmann S. M., Walter U., Fischmeister R. Ca2+ current is regulated by cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase in mammalian cardiac myocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1197–1201. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer S., Hughes K. T., Lee D. Y., Wakelam M. J. Development of a novel, Ins(1,4,5)P3-specific binding assay. Its use to determine the intracellular concentration of Ins(1,4,5)P3 in unstimulated and vasopressin-stimulated rat hepatocytes. Cell Signal. 1989;1(2):147–156. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(89)90004-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penner R., Neher E., Takeshima H., Nishimura S., Numa S. Functional expression of the calcium release channel from skeletal muscle ryanodine receptor cDNA. FEBS Lett. 1989 Dec 18;259(1):217–221. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81532-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raeymaekers L., Hofmann F., Casteels R. Cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase phosphorylates phospholamban in isolated sarcoplasmic reticulum from cardiac and smooth muscle. Biochem J. 1988 May 15;252(1):269–273. doi: 10.1042/bj2520269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapoport R. M. Cyclic guanosine monophosphate inhibition of contraction may be mediated through inhibition of phosphatidylinositol hydrolysis in rat aorta. Circ Res. 1986 Mar;58(3):407–410. doi: 10.1161/01.res.58.3.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rashatwar S. S., Cornwell T. L., Lincoln T. M. Effects of 8-bromo-cGMP on Ca2+ levels in vascular smooth muscle cells: possible regulation of Ca2+-ATPase by cGMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5685–5689. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruth P., Landgraf W., Keilbach A., May B., Egleme C., Hofmann F. The activation of expressed cGMP-dependent protein kinase isozymes I alpha and I beta is determined by the different amino-termini. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Dec 18;202(3):1339–1344. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16509.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarcevic B., Brookes V., Martin T. J., Kemp B. E., Robinson P. J. Atrial natriuretic peptide-dependent phosphorylation of smooth muscle cell particulate fraction proteins is mediated by cGMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 5;264(34):20648–20654. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarcevic B., Robinson P. J., Pearson R. B., Kemp B. E. The smooth muscle 132 kDa cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase substrate is not myosin light chain kinase or caldesmon. Biochem J. 1990 Oct 15;271(2):493–499. doi: 10.1042/bj2710493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takuwa Y., Takuwa N., Rasmussen H. The effects of isoproterenol on intracellular calcium concentration. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 15;263(2):762–768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tare M., Parkington H. C., Coleman H. A., Neild T. O., Dusting G. J. Hyperpolarization and relaxation of arterial smooth muscle caused by nitric oxide derived from the endothelium. Nature. 1990 Jul 5;346(6279):69–71. doi: 10.1038/346069a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twort C. H., van Breemen C. Cyclic guanosine monophosphate-enhanced sequestration of Ca2+ by sarcoplasmic reticulum in vascular smooth muscle. Circ Res. 1988 May;62(5):961–964. doi: 10.1161/01.res.62.5.961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vrolix M., Raeymaekers L., Wuytack F., Hofmann F., Casteels R. Cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase stimulates the plasmalemmal Ca2+ pump of smooth muscle via phosphorylation of phosphatidylinositol. Biochem J. 1988 Nov 1;255(3):855–863. doi: 10.1042/bj2550855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldmann R., Bauer S., Göbel C., Hofmann F., Jakobs K. H., Walter U. Demonstration of cGMP-dependent protein kinase and cGMP-dependent phosphorylation in cell-free extracts of platelets. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Jul 1;158(1):203–210. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09739.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wernet W., Flockerzi V., Hofmann F. The cDNA of the two isoforms of bovine cGMP-dependent protein kinase. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jul 17;251(1-2):191–196. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81453-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida Y., Sun H. T., Cai J. Q., Imai S. Cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase stimulates the plasma membrane Ca2+ pump ATPase of vascular smooth muscle via phosphorylation of a 240-kDa protein. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 15;266(29):19819–19825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



