Abstract
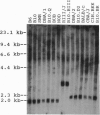
Four genes, closely linked to major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II genes, have been identified in humans, mice, and rats and are thought to be involved in the generation and transport of endogenous immunogenic peptides for the MHC class I antigen-processing pathway. The Tap-1 and Tap-2 genes presumably encode a heterodimeric protein complex responsible for transporting endogenous immunogenic peptides to the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum. The Lmp-2 and Lmp-7 gene products are two subunits of the large cytosolic proteasome complex possibly involved in generation of endogenous peptides. To study the genetic polymorphism of the Lmp-2 gene, we used a published cDNA sequence as a consensus sequence and PCR-amplified, cloned, and sequenced the Lmp-2 gene from 12 inbred mouse strains. We found three amino acid variants, LMP-2d, LMP-2b, and LMP-2q, which partially correlated with restriction fragment length polymorphism variants identified with Southern blots. Allelic polymorphism of the Lmp-2 gene may be involved in peptide selection, leading to autoimmune disease susceptibility.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Attaya M., Jameson S., Martinez C. K., Hermel E., Aldrich C., Forman J., Lindahl K. F., Bevan M. J., Monaco J. J. Ham-2 corrects the class I antigen-processing defect in RMA-S cells. Nature. 1992 Feb 13;355(6361):647–649. doi: 10.1038/355647a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodsky F. M., Guagliardi L. E. The cell biology of antigen processing and presentation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:707–744. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.09.040191.003423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. G., Driscoll J., Monaco J. J. Structural and serological similarity of MHC-linked LMP and proteasome (multicatalytic proteinase) complexes. Nature. 1991 Sep 26;353(6342):355–357. doi: 10.1038/353355a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. Z., Evans G. A. A simple screening method for transgenic mice using the polymerase chain reaction. Biotechniques. 1990 Jan;8(1):32–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colonna M., Bresnahan M., Bahram S., Strominger J. L., Spies T. Allelic variants of the human putative peptide transporter involved in antigen processing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 1;89(9):3932–3936. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.9.3932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faustman D., Li X. P., Lin H. Y., Fu Y. E., Eisenbarth G., Avruch J., Guo J. Linkage of faulty major histocompatibility complex class I to autoimmune diabetes. Science. 1991 Dec 20;254(5039):1756–1761. doi: 10.1126/science.1763324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynne R., Powis S. H., Beck S., Kelly A., Kerr L. A., Trowsdale J. A proteasome-related gene between the two ABC transporter loci in the class II region of the human MHC. Nature. 1991 Sep 26;353(6342):357–360. doi: 10.1038/353357a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori M., Buse J. B., Jackson R. A., Glimcher L., Dorf M. E., Minami M., Makino S., Moriwaki K., Kuzuya H., Imura H. The NOD mouse: recessive diabetogenic gene in the major histocompatibility complex. Science. 1986 Feb 14;231(4739):733–735. doi: 10.1126/science.3003909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly A., Powis S. H., Glynne R., Radley E., Beck S., Trowsdale J. Second proteasome-related gene in the human MHC class II region. Nature. 1991 Oct 17;353(6345):667–668. doi: 10.1038/353667a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingstone A. M., Powis S. J., Diamond A. G., Butcher G. W., Howard J. C. A trans-acting major histocompatibility complex-linked gene whose alleles determine gain and loss changes in the antigenic structure of a classical class I molecule. J Exp Med. 1989 Sep 1;170(3):777–795. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.3.777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez C. K., Monaco J. J. Homology of proteasome subunits to a major histocompatibility complex-linked LMP gene. Nature. 1991 Oct 17;353(6345):664–667. doi: 10.1038/353664a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaco J. J., Cho S., Attaya M. Transport protein genes in the murine MHC: possible implications for antigen processing. Science. 1990 Dec 21;250(4988):1723–1726. doi: 10.1126/science.2270487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaco J. J., McDevitt H. O. H-2-linked low-molecular weight polypeptide antigens assemble into an unusual macromolecular complex. 1984 Jun 28-Jul 4Nature. 309(5971):797–799. doi: 10.1038/309797a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaco J. J., McDevitt H. O. The LMP antigens: a stable MHC-controlled multisubunit protein complex. Hum Immunol. 1986 Apr;15(4):416–426. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(86)90019-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neefjes J. J., Stollorz V., Peters P. J., Geuze H. J., Ploegh H. L. The biosynthetic pathway of MHC class II but not class I molecules intersects the endocytic route. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):171–183. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90224-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nepom G. T., Erlich H. MHC class-II molecules and autoimmunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:493–525. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.09.040191.002425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz-Navarrete V., Seelig A., Gernold M., Frentzel S., Kloetzel P. M., Hämmerling G. J. Subunit of the '20S' proteasome (multicatalytic proteinase) encoded by the major histocompatibility complex. Nature. 1991 Oct 17;353(6345):662–664. doi: 10.1038/353662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powis S. H., Mockridge I., Kelly A., Kerr L. A., Glynne R., Gileadi U., Beck S., Trowsdale J. Polymorphism in a second ABC transporter gene located within the class II region of the human major histocompatibility complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 15;89(4):1463–1467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.4.1463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powis S. J., Deverson E. V., Coadwell W. J., Ciruela A., Huskisson N. S., Smith H., Butcher G. W., Howard J. C. Effect of polymorphism of an MHC-linked transporter on the peptides assembled in a class I molecule. Nature. 1992 May 21;357(6375):211–215. doi: 10.1038/357211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spies T., Bresnahan M., Bahram S., Arnold D., Blanck G., Mellins E., Pious D., DeMars R. A gene in the human major histocompatibility complex class II region controlling the class I antigen presentation pathway. Nature. 1990 Dec 20;348(6303):744–747. doi: 10.1038/348744a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. Selective inactivation of the exonuclease activity of bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase by in vitro mutagenesis. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 15;264(11):6447–6458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trowsdale J., Hanson I., Mockridge I., Beck S., Townsend A., Kelly A. Sequences encoded in the class II region of the MHC related to the 'ABC' superfamily of transporters. Nature. 1990 Dec 20;348(6303):741–744. doi: 10.1038/348741a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uematsu Y., Fischer Lindahl K., Steinmetz M. The same MHC recombinational hot spots are active in crossing-over between wild/wild and wild/inbred mouse chromosomes. Immunogenetics. 1988;27(2):96–101. doi: 10.1007/BF00351082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. M., Doyle M. V., Mark D. F. Quantitation of mRNA by the polymerase chain reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9717–9721. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wooley P. H., Chapedelaine J. M. Immunogenetics of collagen-induced arthritis. Crit Rev Immunol. 1987;8(1):1–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]