Abstract
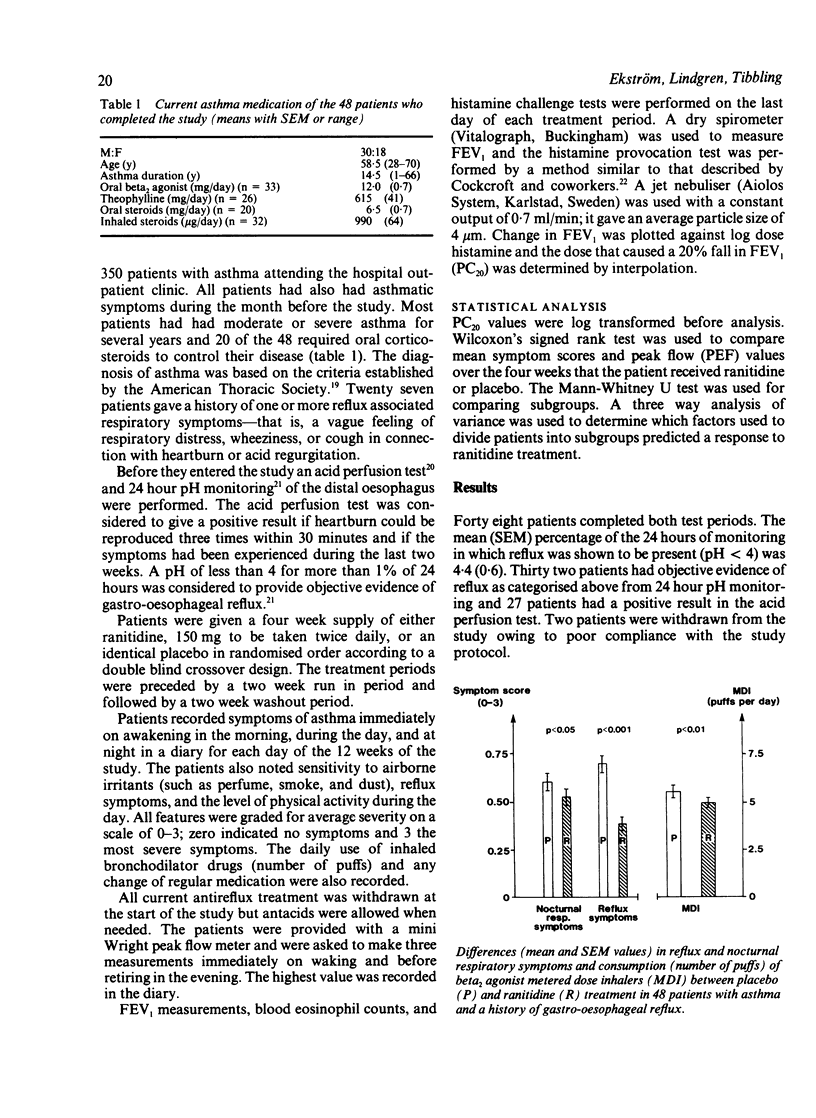
Forty eight patients with moderate to severe asthma were enrolled in a double blind crossover study designed to evaluate the effects of ranitidine treatment, 150 mg twice daily for four weeks, on gastro-oesophageal reflux, asthma control, and bronchial reactivity. All 48 had a history of reflux symptoms and 27 had in addition reflux associated respiratory symptoms. Thirty two patients had objective evidence of acid reflux on 24 hour pH monitoring (pH of less than 4 for more than 1% of the 24 hours) and 27 patients had a positive result in the acid perfusion test. Reflux symptoms were significantly improved after ranitidine treatment. Ranitidine treatment was associated with modest improvements in nocturnal asthma and daily use of inhaled bronchodilator drugs but there was no significant change in bronchial reactivity, lung function, peak flow, or the number of eosinophils in the blood. Comparisons between the effect of ranitidine treatment on asthma control were performed between patients with and without a history of reflux associated respiratory symptoms, with and without a positive result in the acid perfusion test, and with and without objective evidence of gastro-oesophageal reflux. A history of reflux associated respiratory symptoms was the only factor that predicted an improvement in asthma control after ranitidine treatment. These results indicate that antireflux treatment will produce only small improvements in asthma control in asthmatic patients with a history of gastro-oesophageal reflux.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERNSTEIN L. M., BAKER L. A. A clinical test for esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 1958 May;34(5):760–781. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengtsson U., Sandberg N., Bake B., Löwhagen O., Svedmyr N., Månsson I., Carlsson S. Gastro-oesophageal reflux and night-time asthma. Lancet. 1985 Jun 29;1(8444):1501–1502. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)92270-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berquist W. E., Rachelefsky G. S., Kadden M., Siegel S. C., Katz R. M., Fonkalsrud E. W., Ament M. E. Gastroesophageal reflux-associated recurrent pneumonia and chronic asthma in children. Pediatrics. 1981 Jul;68(1):29–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft D. W., Killian D. N., Mellon J. J., Hargreave F. E. Bronchial reactivity to inhaled histamine: a method and clinical survey. Clin Allergy. 1977 May;7(3):235–243. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1977.tb01448.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiser N. M., Mills J., Snashall P. D., Guz A. The role of histamine receptors in asthma. Clin Sci (Lond) 1981 Apr;60(4):363–370. doi: 10.1042/cs0600363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foglia R. P., Fonkalsrud E. W., Ament M. E., Byrne W. J., Berquist W., Siegel S. C., Katz R. M., Rachelefsky G. S. Gastroesophageal fundoplication for the management of chronic pulmonary disease in children. Am J Surg. 1980 Jul;140(1):72–79. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(80)90420-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greyson N. D., Reid R. H., Liu Y. C., Thomas P. Radionuclide assessment in nocturnal asthma. Clin Nucl Med. 1982 Jul;7(7):318–319. doi: 10.1097/00003072-198207000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper P. C., Bergner A., Kaye M. D. Antireflux treatment for asthma. Improvement in patients with associated gastroesophageal reflux. Arch Intern Med. 1987 Jan;147(1):56–60. doi: 10.1001/archinte.147.1.56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herve P., Denjean A., Jian R., Simonneau G., Duroux P. Intraesophageal perfusion of acid increases the bronchomotor response to methacholine and to isocapnic hyperventilation in asthmatic subjects. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 Nov;134(5):986–989. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1986.134.5.986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson K. E., Boeryd B., Fransson S. G., Tibbling L. Oesophageal reflux tests, manometry, endoscopy, biopsy, and radiology in healthy subjects. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1986 May;21(4):399–406. doi: 10.3109/00365528609015154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson K. E., Tibbling L. Gastric secretion and reflux pattern in reflux oesophagitis before and during ranitidine treatment. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1986 May;21(4):487–492. doi: 10.3109/00365528609015167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klotz S. D., Moeller R. K. Hiatal hernia and intractable bronchial asthma. Ann Allergy. 1971 Jun;29(6):325–328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansfield L. E., Stein M. R. Gastroesophageal reflux and asthma: a possible reflex mechanism. Ann Allergy. 1978 Oct;41(4):224–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin M. E., Grunstein M. M., Larsen G. L. The relationship of gastroesophageal reflux to nocturnal wheezing in children with asthma. Ann Allergy. 1982 Dec;49(6):318–322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mays E. E. Intrinsic asthma in adults. Association with gastroesophageal reflux. JAMA. 1976 Dec 6;236(23):2626–2628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan R. A., Segall N., Glover G. C., Schocket A. L. The effects of H1 and H2 antihistamines on histamine inhalation challenges in asthmatic patients. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979 Dec;120(6):1251–1258. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1979.120.6.1251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nogrady S. G., Bevan C. H2 receptor blockade and bronchial hyperreactivity to histamine in asthma. Thorax. 1981 Apr;36(4):268–271. doi: 10.1136/thx.36.4.268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrini C. A., DeMeester T. R., Johnson L. F., Skinner D. B. Gastroesophageal reflux and pulmonary aspiration: incidence, functional abnormality, and results of surgical therapy. Surgery. 1979 Jul;86(1):110–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramon P., Mallart-Voisin A., Wallaert B., Boudoux L., Marchandise X., Steinling M., Ballester L., Tonnel A. B. Association asthme et reflux gastro-oesophagien: stratégie des explorations paracliniques. Rev Mal Respir. 1985;2(5):289–294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro G. G., Christie D. L. Gastroesophageal reflux in steroid-dependent asthmatic youths. Pediatrics. 1979 Feb;63(2):207–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaulding H. S., Jr, Mansfield L. E., Stein M. R., Sellner J. C., Gremillion D. E. Further investigation of the association between gastroesophageal reflux and bronchoconstriction. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1982 Jun;69(6):516–521. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(82)90176-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson N. C., Kerr J. W. Effect of inhaled H1 and H2 receptor antagonist in normal and asthmatic subjects. Thorax. 1980 Jun;35(6):428–434. doi: 10.1136/thx.35.6.428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veyrac M., Bories P., Collet H., Parelon G., Fauroux P., Godard P., Michel H. Scintigraphie et pHmétrie oesophagienne chez des adultes asthmatiques suspects de reflux gastro-oesophagien. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 1986 May;10(5):400–404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson N. M., Charette L., Thomson A. H., Silverman M. Gastro-oesophageal reflux and childhood asthma: the acid test. Thorax. 1985 Aug;40(8):592–597. doi: 10.1136/thx.40.8.592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


