Abstract
The rationale for neoadjuvant chemoradiation therapy (Neo-CRT) and the definition of borderline resectable pancreatic cancer (BRPC) are still controversial. In particular, surgical treatment of BRPC with isolated venous vascular involvement (IVVI) is debatable.
From January 2000 to December 2013, 84 patients diagnosed with BRPC according to NCCN guidelines were identified, and 70 patients were found to have BRPC with IVVI. We divided all 70 patients into 3 groups: surgery first without Neo-CRT (Group 1); pancreatectomy following Neo-CRT (Group 2); and no operation following Neo-CRT (Group 3). Patient characteristics including oncologic outcomes were analyzed for each of the 3 patients groups.
Thirty-seven patients were female and 33 were male, with a mean age of 61.7 ± 9.74 years. Among the 70 BRPC patients with IVVI, 28 patients (40%) belonged to Group 1, 30 patients (42.9%) belonged to Group 2, and 12 patients (17.1%) belonged to Group 3. Pathological tumor size (P < 0.001), pT stage (P = 0.001), pTNM stage (P = 0.002), combined vascular resection (P = 0.003), completeness of adjuvant therapy (P = 0.004) were found to be statistically significantly different between Groups 1 and 2. In addition, disease-free survival (P = 0.055) and disease-specific survival (DSS) (P = 0.006) were improved in Group 2. Interestingly, when comparing DSS, there was no statistically significant difference between Groups 1 and 3 (P = 0.991).
The clinical practice of pancreatectomy following Neo-CRT in BRPC with IVVI provided favorable oncologic outcomes. The effect of Neo-CRT in BRPC with IVVI may be multifactorial, providing proper patient selection, complete adjuvant chemotherapy, and potential therapeutic (downstaging) effect.
INTRODUCTION
Pancreatic cancer (PC) is a fatal malignant disease in gastrointestinal digestive systems and the fifth leading cause of cancer death in Korea.1 Until now, margin-negative pancreatectomy is the only known cure for the disease; however, PCs are often found to be already locally advanced or distantly metastasized. With such resection rate is only up to 10% to 20%.2,3 Even if the cancer is resectable, R0 resection rate is only 32% to 71%.4–7 It has also been reported that, when potentially curative resection is achieved, the 5-year survival rate is as low as 8% to 25%6,8 due to high loco-regional recurrence rate and distant metastasis to organs such as the liver.9,10 Therefore, treatment for pancreas cancer requires a multimodal approach to cure the systemic disease, for which surgery alone is not enough.
Many institutions have studied adjuvant therapy to prevent and treat high loco-regional recurrence and distant metastasis occurring after pancreas cancer operation. And their studies11–13 reported that adjuvant chemoradiation therapy after pancreas cancer operation increased patient survival. However, postoperative adjuvant therapy was not able to be performed to 24% ∼ 56% of patients.7,11,14,15 The most common causes of low adjuvant chemoradiation therapy were reported to be delayed recovery after major surgery, medical comorbidity, and disease progression.
For these reasons, recent researches have focused on preoperative neoadjuvant therapy rather than postoperative adjuvant therapy as treatment for PC in order to increase survival rates.14,16–22 In case of patients who underwent neoadjuvant chemoradiation therapy (Neo-CRT), it was reported that resection rate increased to 41% to 100%, and R0 resection rate increased to 84% to 96%, with an excellent median survival time of 21 to 40 months.16,21,23 In addition, over the past 20 years, advancement in surgical technique and perioperative management have brought improvements in surgical outcomes of patients with venous vascular involvement in PC. In past, operative mortality rate was greater than 15% to 21% when pancreatectomy with portal vein (PV) or superior mesenteric vein (SMV) resection was performed.24–26 Now, however, there is reportedly no difference in surgical mortality for pancreatectomy with or without PV or SMV resection.27 Kelly et al28 reported that vein involvement was not predictive of disease-free or overall survival, and the oncological outcome was not different between vein resection combined with pancreaticoduodenectomy (PD) and PD without combined vein resection. Therefore, while cases with venous vascular involvement were previously considered unresectable due to limitations of surgical technique, vascular combined resection has now become technically feasible and safe.29 Thus, many pancreatic surgeons may regard BRPC with isolated venous vascular involvement (IVVI) as resectable rather than borderline resectable. For this reason, there are conflicting opinions on treatment for BRPC, especially with IVVI.
In this study, we reviewed the clinical practice of treatment for PC with IVVI, verifying the effectiveness of Neo-CRT for patients of BRPC with IVVI.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Study Population
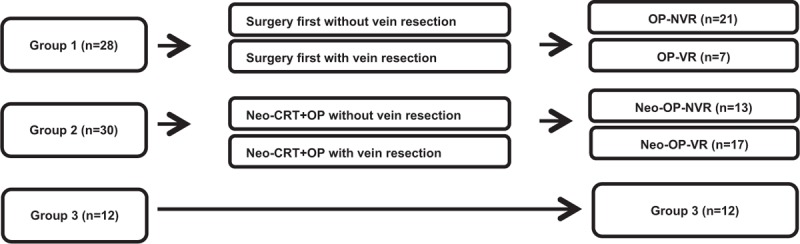
Medical records from January 2000 to December 2013 were reviewed, 84 patients with BRPC according to NCCN guidelines were selected30 and 70 patients were noted to have IVVI. We divided all 70 patients into 3 groups (Figure 1): surgery without neoadjuvant chemoradiation (Neo-CRT) (Group 1); PD following Neo-CRT (Group 2); and no operation following Neo-CRT (Group 3). And further we divided the Group 1 and the Group 2 into subgroups according to the vein resection (Figure 2): Group 1 (surgery first without vein resection, OP-NVR vs. surgery first with vein resection, OP-VR), Group 2 (Neo-CRT + OP without vein resection: Neo-OP-NVR vs. Neo-CRT + OP with vein resection, Neo-OP-VR). Patient characteristics including perioperative and long-term oncologic outcomes were analyzed and compared according to the sequence of Neo-CRT and surgery. This study has been approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of Severance Hospital.
FIGURE 1.
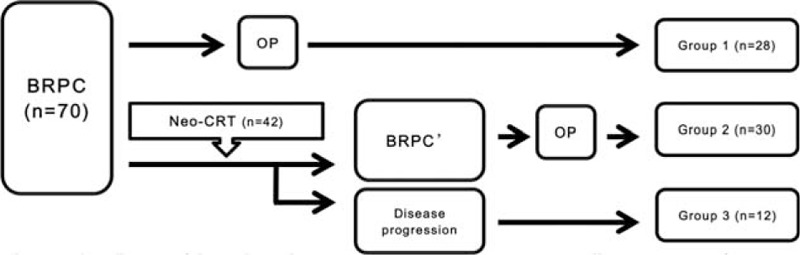
Flow diagram of the study: Patients were divided into 3 groups according to sequence of Neo-CRT and surgery in 70 patients.
FIGURE 2.
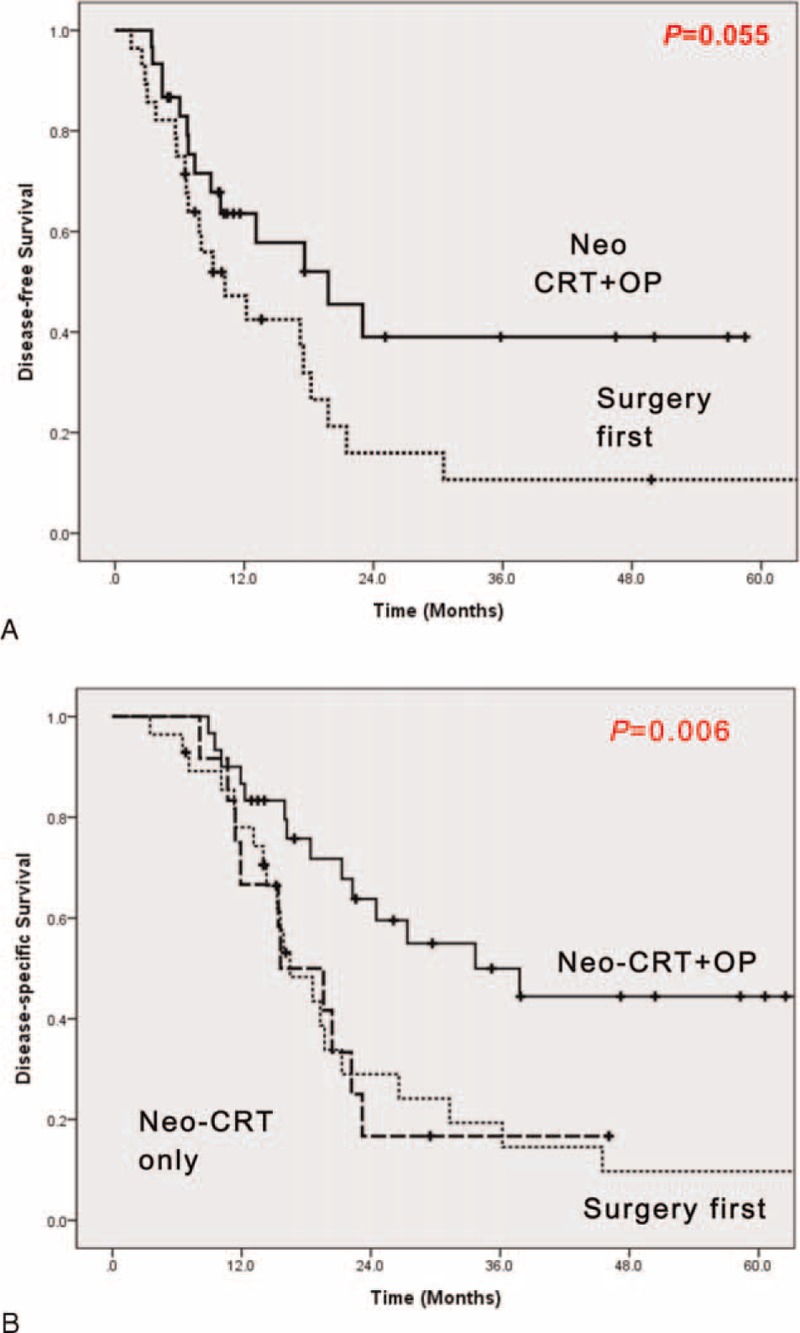
Oncologic outcomes according to sequence of Neo-CRT therapy and surgery. (A) Disease-free survival and (B) disease-specific survival. Survival differences according to sequence of Neo-CRT and surgery (DSS: P = 0.006; DFS: P = 0.055); Neo-CRT+OP group (bold linear line) versus surgery first group (thin linear line) versus Neo-CRT only group (bold dotted line). Subdivision of treatment groups.
Perioperative Assessment of Resectability and Staging
Preoperative contrast-enhanced computerized tomography (CT) imaging was performed on the 70 patients, and magnetic resonance and positron emission tomography (PET)-CT imaging were also performed according to additional necessity. Venous invasion was defined as tumor-to-vessel circumferential contiguity that either abutted (≤50% of the circumference) or encased (>50% of the circumference) the SMV, PV, or SMV/PV confluence. Perivascular halo (thin, low-attenuation lesion circumscribing the vessel) was not considered to be a sign of vascular invasion. There was fat which separates the tumor from the vessel, in this case we did not consider it as venous vascular invasion.31 We measured venous involvement length according to the coronal view of CT scan images with either tumor abutment or encasement. We also determined circumferential involvement by measuring the angle of maximum tumor abutment or encasement. Since the endoscopic ultrasound study (EUS) rate was 64.3% (45/70), we did not include the data of EUS finding in this study. Accordingly, we assessed resectability and staging of PC by preoperative contrast-enhanced CT image. Cancer staging was determined according to the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) Cancer Staging Manual, Seventh Edition.32
Neoadjuvant Chemoradiation Therapy
Forty-two patients (Groups 2 and 3) who underwent Neo-CRT received gemcitabine-based chemotherapy. Most of the patients were treated with gemcitabine (1000 mg/m2 on days 1, 8, 15, 29, and 36) with concurrent radiotherapy, while some patients were additionally treated with cisplatin (70 mg/m2 on days 1 and 29) or capecitabine (40 mg/m2 on days 1–14 and 21–35). Radiation therapy, 3-dimensional conformal radiotherapy, and tomotherapy were applied. Patients’ involved-field irradiation was decided in consideration of gross tumor volume and generous margin (2 cm) according to the standard protocol of concurrent chemoradiation therapy (CCRT). In cases when significant lymph nodes (LNs) were detected at preoperative examination, we conducted radiotherapy to include LNs as well. Generally, the 3-field technique, composed of opposed laterals and an anterior–posterior field, or the 4-field technique were applied to all patients. As total radiation dose, 45, 50.4, or 58.4 Gy was applied with daily fractions of 1.8 Gy, 5 days per week, using a 10 MV linear accelerator. Four weeks after completion of CCRT, chest X-rays and contrast-enhanced CT scans were conducted according to the World Health Organization (WHO) criteria. Treatment response was evaluated using the Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST).33 After treating patients in an adjuvant or neoadjuvant setting, we defined a case with both surgery and chemoradiation as complete treatment and a case with either surgery or chemoradiation as incomplete.34–36
Operation Method
Protocols for PD included en-bloc resection and no touch methods. At the time of surgery, when PC adherence to the SMV, PV, or SMV-PV confluence was encountered, the conductibility of vascular resection was decided according to adhesion degree between the pancreas and vasculature. If adhesion was serious and difficult to dissect, we conducted tangential or segmental vein resection to achieve R0 resection, regarding the adhesion as potential tumor invasion to venous vascular structure.
Statistical Analysis
All statistical analyses were performed using IBM SPSS for Windows, version 20.0 (SPSS, Inc., Chicago, IL). Disease-specific survival (DSS) was calculated from the time of diagnosis to death or last follow-up day, and disease-free survival (DFS) was calculated from the time of surgery to death or last follow-up day. Survival time was analyzed by the method of Kaplan and Meier. We compared differences in survival among the 3 groups with the log-rank test. Patient characteristics, perioperative outcomes, and oncologic outcomes among the 3 groups were analyzed with the independent t test for continuous variables and Chi-square test for categorical variables. And repeated measures data between the same subjects were analyzed with paired t test. P-values <0.05 were considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
Patient Characteristics
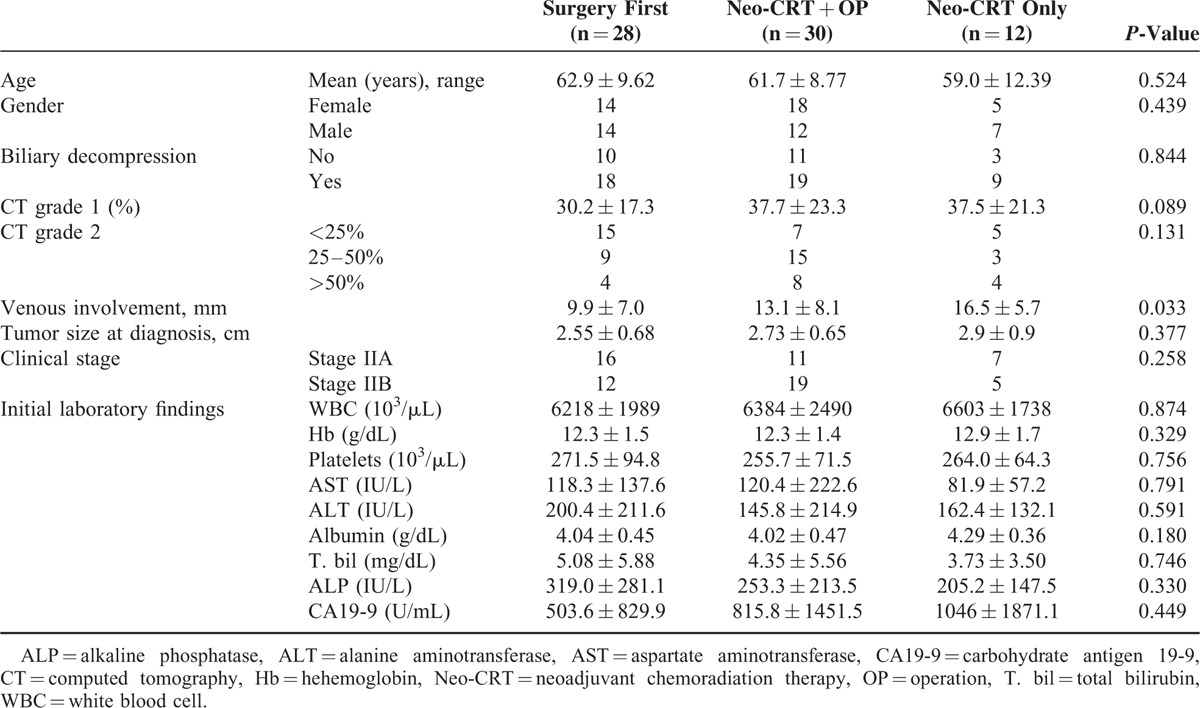
Thirty-seven patients were female, and 33 were male, with a mean age of 61.7 ± 9.7 years. Among the 70 patients, 28 patients (40%) belonged to Group 1, 30 patients (42.9%) to Group 2, and 12 patients (17.1%) to Group 3. Initial preoperative CT analysis showed tumors abutted to SMV or PV with 34.8 ± 20.8% of total vascular circumference. The mean length of venous involvement was 11.7 ± 7.8 mm. In comparative analysis, we found no statistically significant differences in terms of degree of initial isolated vascular circumference involvement, tumor size, clinical stage, or laboratory findings among the 3 groups. However, in terms of length of venous involvement, Group 1 was significantly shorter (P = 0.033, Table 1).
TABLE 1.
Patient Characteristics According to Sequence of Neo-CRT and Surgery
Perioperative Outcomes
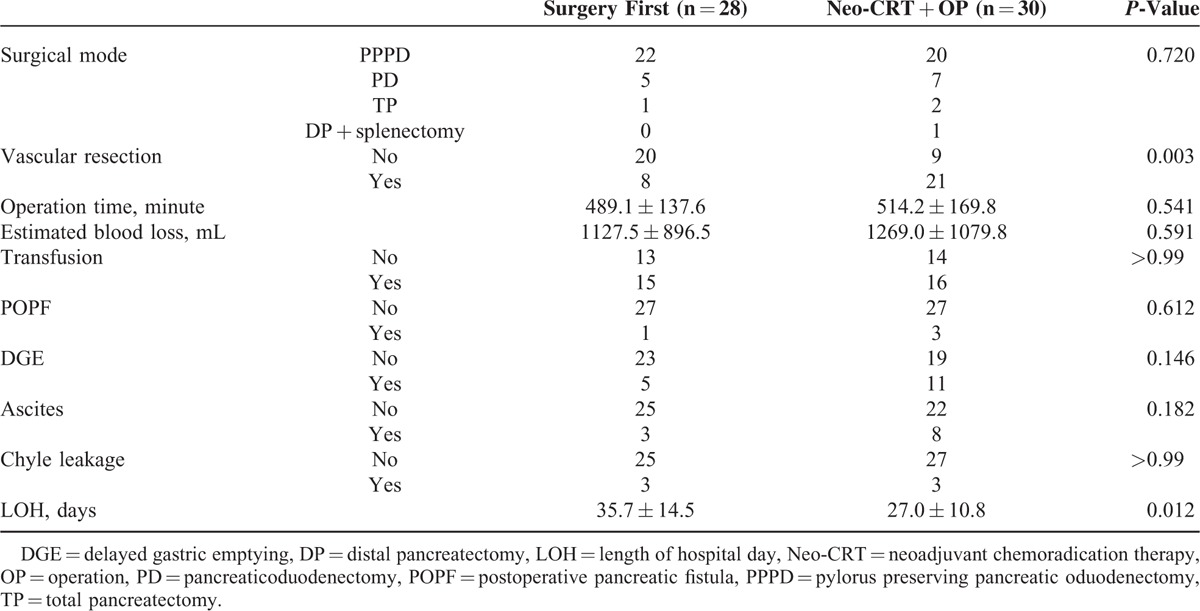
There were no significant perioperative differences between Groups 1 and 2 (Table 2). However, more frequent combined vascular resection (P = 0.003) was observed in Group 2. Twenty-nine patients underwent venous vascular resection (4 wedge resection, 25 segmental resection of SMV/PV). For segmental resection, end-to-end anastomosis was performed. There was no case of anastomosis using graft. Treatment completeness of systemic chemotherapy was also higher in Group 2 (P = 0.004) because all the patients in Group 2 safely received preoperative chemotherapy. Delayed gastric emptying (P = 0.146), chyle leakage (P = 1.000), POPF (P = 0.612), and ascites (P = 0.182) were not statistically difference between Group 1 and Group 2. However, length of hospital stay (35.7 ± 14.5 days vs. 27.0 ± 10.8 days, P = 0.012) was shorter in Group 2, suggesting that vascular resection and postoperative complications did not adversely influence postoperative course.
TABLE 2.
Operative and Postoperative Characteristics According to Sequence of Neo-CRT and Surgery
Short-Term and Long-Term Oncologic Outcomes
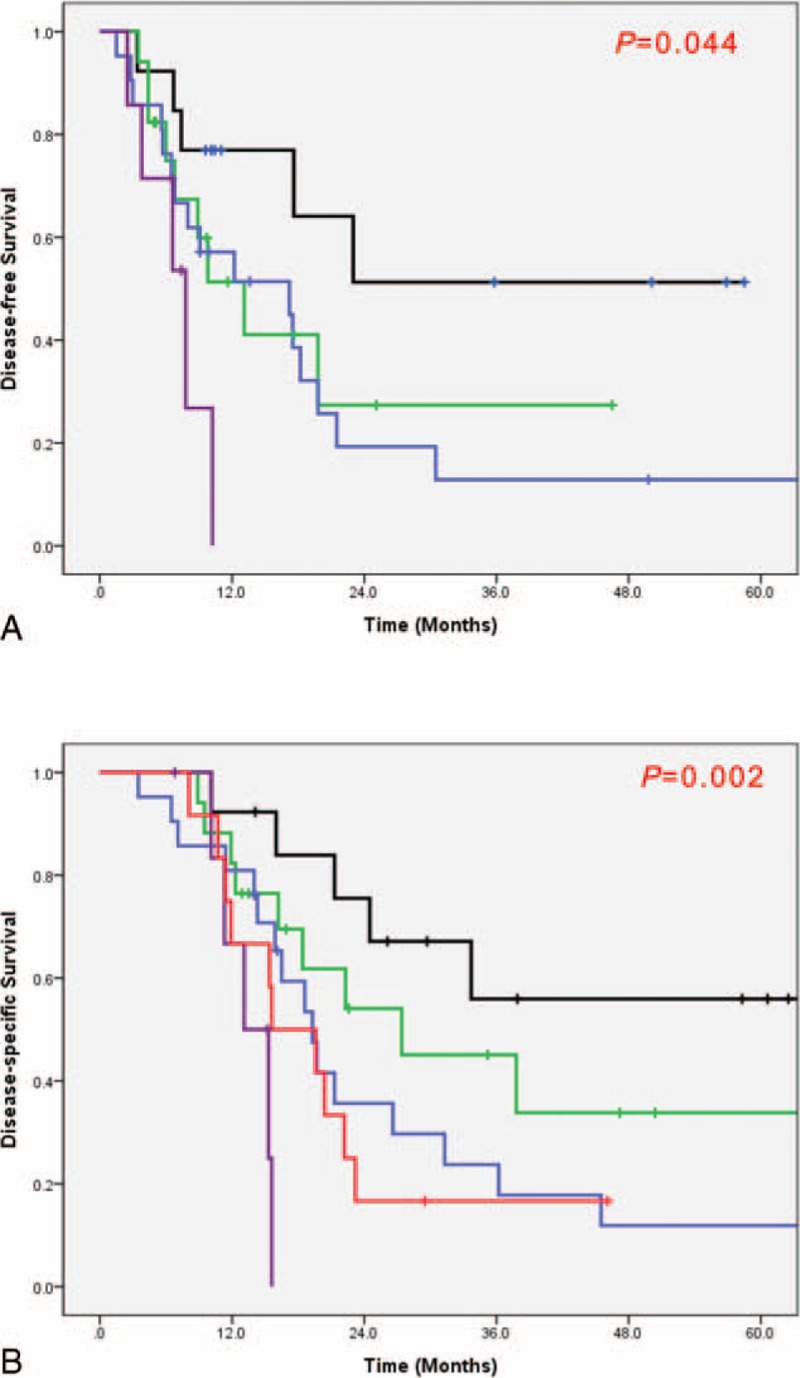
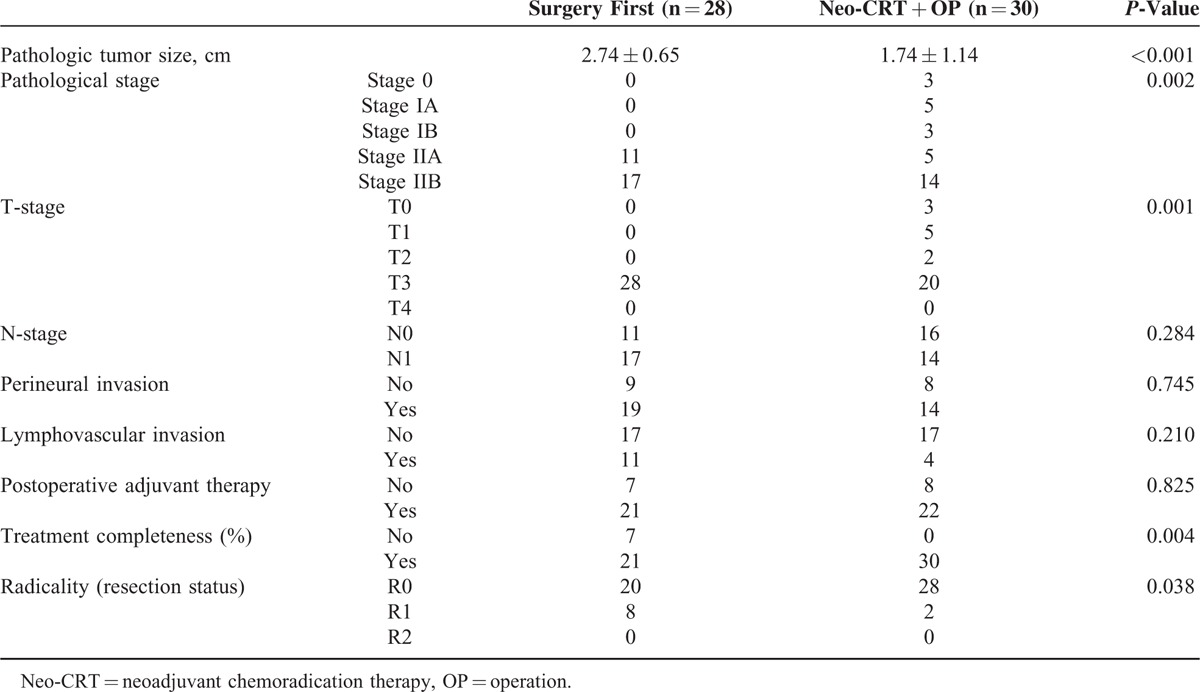
Overall R0 resection rate was reported to be 82.8% (48 out of 58 patients), and Group 2 was found to have higher R0 resection rate compared to those of Group 1 (71.4% (20/28) vs. 93.3% (28/30), P = 0.038). In addition, smaller pathological tumor size (P < 0.0001), lower pT stage (P = 0.001), and lower pTNM stage (P = 0.002) were observed in Group 2. Accordingly, Group 2 showed superior DFS compared to Group 1 (P = 0.055, Figure 3A). In addition, Group 2 experienced favorable long-term oncologic outcomes. Mean DSS was noted to be 30.9 ± 21.46 months in Group 2, followed by 21.3 ± 18.68 months in Group 1, and 19.5 ± 10.41 months in Group 3 (P = 0.006, Figure 3B). Notably, when comparing DSS between Group 1 and Group 3, there was no statistical significant difference. Only a few long-term survivors were identified in Group 1 (P = 0.991, Figure 3B). And Figure 4 shows the survival according to the vascular resections. Among the patients who underwent surgery, PD followed by Neo-CRT without vascular resection group shows the best DFS and DSS. And Surgery first with vascular resection group shows the worst DFS and DSS. Among the Group 1 patients, we analyzed survival rate according to adjuvant chemotherapy. But there showed no survival difference (DFS, P = 0.414; DSS, P = 0.394) between those who had received adjuvant chemotherapy and had not received.
FIGURE 3.
Subdivision of treatment groups. OP-NVR: surgery first without vein resection; OP-VR: surgery first with vein resection; Neo-OP-NVR: Neo-CRT+OP without vein resection; Neo-OP-VR: Neo-CRT+OP with vein resection.
FIGURE 4.
Oncologic outcomes according to sequence of Neo-CRT therapy and surgery with or without vein resection. (A) Disease-free survival and (B) disease-specific survival. Survival differences according to sequence of Neo-CRT and surgery with or without vein resection. Bold linear line: Neo-CRT+OP without veinresection (Neo-OPNVR); Thin linear line: Neo-CRT+OP with vein resection (Neo-OPVR); Bold dotted line: surgery first without vein resection (OP-NVR); Dashed dotted line: surgery first with vein resection (OP-VR); Dashed line: Neo-CRT only.
DISCUSSION
Surgical approaches for BRPC can be controversial because of 2 different definition systems: the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center (MDACC) criteria23,37 and the American Hepatopancreatobiliary Association (AHPBA)/Society of Surgical Oncology (SSO)/Society for Surgery of the Alimentary Tract (SSAT) criteria.38 In addition, PC with venous vascular involvement was once considered as unresectable clinical condition due to limited surgical techniques and high mortality rate. However, with advancement in surgical techniques and perioperative management, combined venous vascular resection is regarded as a safe and effective approach for R0 resection.39 Interestingly, PC with IVVI is generally regarded as potentially resectable PC according to MDACC criteria but only borderline resectable based on NCCD guidelines. Therefore, the surgical approach applied in these cases varies substantially. However, according to our surgical experiences of PC with IVVI, we would like to support the rationale of preoperative Neo-CRT followed by radical pancreatectomy with the following reasons.
Proper Selection
As shown in Figure 1, there were 12 patients who did not undergo pancreatectomy following Neo-CRT. This was because disease progressed during Neo-CRT, which acted as the window period for metastatic disease.37 Theses patients had high possibility of early recurrence and disease progression even after upfront surgery. As such, long-term favorable oncologic outcomes would not be expected for these patients. Therefore, Neo-CRT could play a role as one of the currently available tools for detecting patients who will be benefited from major pancreatectomy; such tools may be regarded as personalized surgical approaches to PC.40 The excellent survival outcomes in the present study indirectly support the potential benefit of proper patient selection by Neo-CRT. Interestingly, survival outcomes were similar in Group 1 and Group 3. Only a few long-term survival cases were found in Group 1, suggesting Neo-CRT without surgery also can provide acceptable oncologic outcome to most unresected patients with PC with IVVI.
Complete Treatment
Because PC is a systemic disease, it is difficult to expect improvement of oncologic outcome with surgery only.10 Adjuvant CRT created momentum for treating pancreas cancer. However, in the clinical setting of postoperative adjuvant treatment, problems often arose with ensuring appropriate timing for systemic treatment due to delayed postoperative recovery or medical comorbidity.11,14,15 That is, the possibility of preventing high loco-regional recurrence rates and distant metastasis was decreased because CRT could not be performed as needed after surgery. Therefore, Neo-CRT was proposed as a new method for systemic treatment for pancreas cancer, providing patients with conditions to receive adequate CRT and thereby enabling high completeness of treatment by combining systemic treatment with local treatment.16,22,23 Among patients who underwent operation after Neo-CRT, there were several cases where patients also received adjuvant treatment; the rate of postoperative adjuvant therapy showed no statistically significant difference between Groups 1 and 2 (P = 0.825, Table 3). However, considering patients in Group 2 received preoperative Neo-CRT as systemic treatment before surgery, this group underwent both systemic and local treatment. As such, Group 2 (100%) was superior to Group 1 (75%) in terms of completeness of treatment (P = 0.004, Table 3).37
TABLE 3.
Pathologic Characteristics According to Inclusion or Exclusion of Neo-CRT
Therapeutic Effect
Our study shows that there were several positive treatment effects for patients with BRPC with IVVI who underwent pancreatectomy after Neo-CRT. The positive treatment effects include downstaging.35,37,41,42
In Group 1, tumor size at diagnosis was 2.55 ± 0.68 cm, and postoperative pathologic tumor size was 2.73 ± 0.65 cm, which shows no significant difference before and after surgery on paired t test (P = 0.244). On the other hand, the tumor size in Group 2 was 2.70 ± 0.84 cm at diagnosis, however, at postoperative pathologic tumor size was 1.74 ± 1.14 cm, which is statistically significant (P = 0.003). These results suggest a tumor reducing effect of Neo-CRT. There were no statistically significant differences in terms of clinical T stage or clinical TNM stage between Groups 1 and 2. However, pathological examination showed downstaging effect37 in T stage (P = 0.001) and pTNM stage (P = 0.002) in Group 2 (Table 3). There was no significant difference in LN metastasis in our study; however, several studies have suggested that Neo-CRT is effective for reducing LN metastasis.14,22,23,41 Considering LN metastasis as a poor prognostic factor in PC,43 we can expect a potential treatment role for Neo-CRT for LN metastasis.41
The present study (Table 3) showed higher R0 resection rate in Group 2 (71.4% vs. 93.3%, P = 0.038). In Group 2 with pancreatectomy following Neo-CRT, combined vascular resection was frequent (P = 0.003). Our surgical policy indicates en-bloc resection method for suspicious cancerous lesions invading or severely abutting a major venous vascular structure. In the past, IVVI of the resection resulted in high operative mortality rate.24,26 However, combined venous vascular resection became feasible and safe without increasing the morbidity and mortality due to improvements in surgical experience, techniques, and perioperative management.39 In recent years, there has been no reported difference in oncologic outcomes in patients with or without combined venous vascular resection.28,29 In our study, although Group 2 received more vein resection, there was no statistically significant difference between Group 1 and Group 2 in terms of operation time (P = 0.541), estimated blood loss (P = 0.591), or transfusion (P = 1.000). In addition, Group 2 showed significantly shorter length of hospital day (LOH) (P = 0.012). Therefore, it seems that combined venous vascular resection does not adversely impact short-term or long-term oncologic outcome. For R0 resection, combined venous vascular resection should be actively considered.39,41,44,45
We analyzed survival rate among the patients underwent surgery according to the vein resections (Figure 2). The condition of vascular involvement was followed by the NCCN guidelines. And the vein resection was performed in case when adhesion was too serious to be dissected from pancreas to vessel. When we compare the pathologic characteristics according to vein resection, the perineural invasion was found more in patients with vein resection (P = 0.020) than without vein resection (Table 4). But the survival rate was not different between patient with vein resection and without vein resection (Figure 5). We divided the Group 1 and the Group 2 into subgroups according to the vein resection. The OP-VR group showed the worst DFS and DSS than those of Group 3 (Figure 4). However, Group 2, regardless of the vein resection, achieved better survival outcomes than Group 1. These results suggest the usefulness of Neo-CRT in borderline resectable pancreatic cancer (BRPC) linked to IVVI.
TABLE 4.
Pathologic Characteristics According to Vein Resection
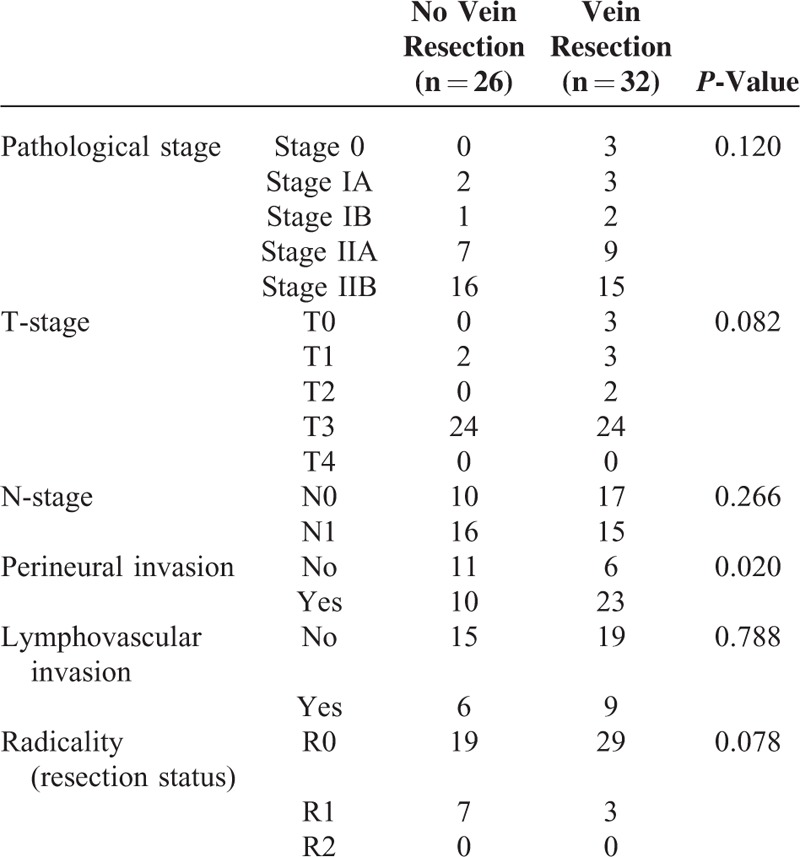
FIGURE 5.
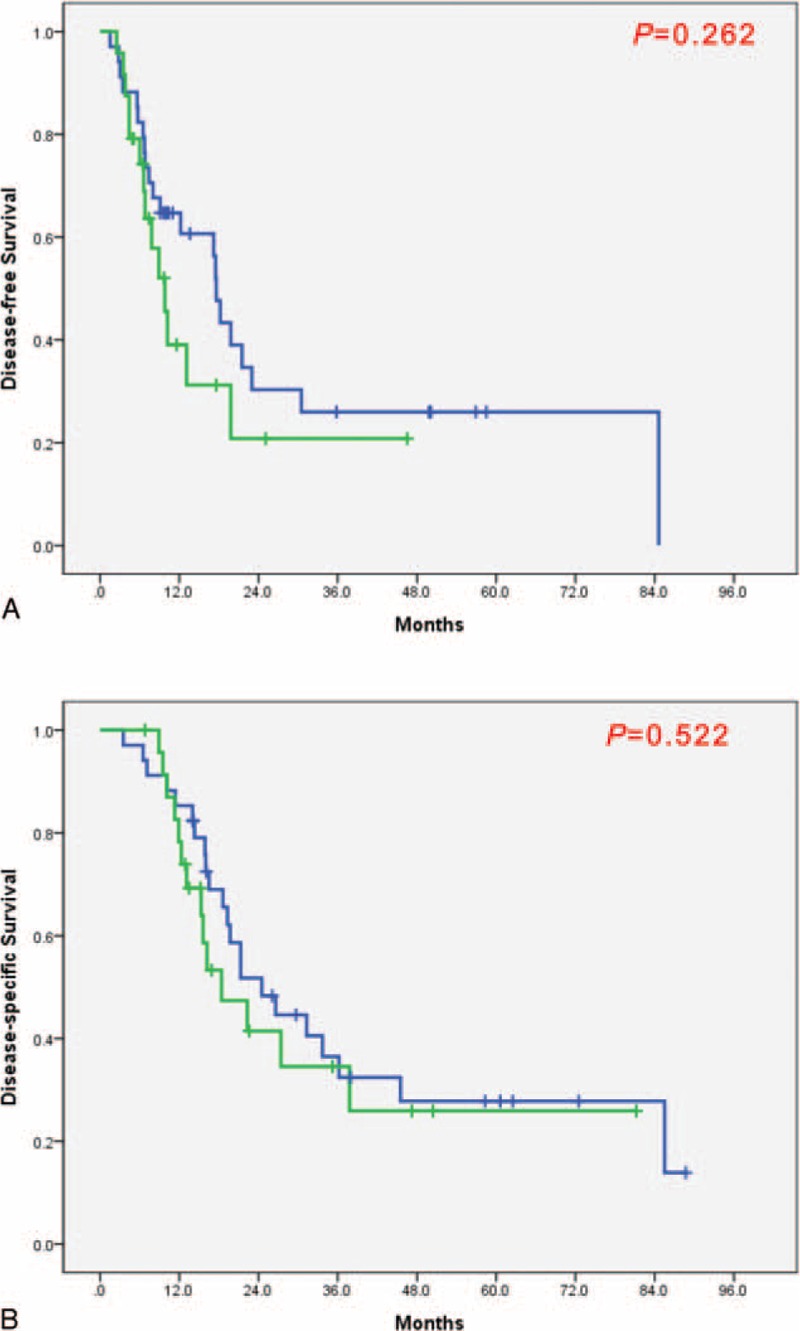
Survival rates of patients with surgical treatment according to vein resection. (A) Disease-free survival and (B) Disease-specific survival. Bold linear line: without vein resection; Thin linear line: with vein resection.
This study was conducted retrospectively by a single institution with a limited number of patients. To determine more proper approach to BRPC with IVVI patients, multiinstitutional study based on a standardized surgical protocol should be perform. In this context, Intergroup Trial led by the Alliance for Clinical Trials in Oncology, National Cancer Institute cooperative group is performing a pilot study to test the feasibility of induction therapy with FOLFIRINOX followed by 5-FU-based chemoradiation for patients with BRPC.46,47 This study will provide momentum for future clinical trials based on well-standardized consensus in terms of definition and perioperative surgical treatments of BRPC.46,47
In conclusion, upfront PD with combined venous vascular resection is technically feasible and safe for patients with PC with IVVI. However, our experiences indicate that PD with combined venous vascular resection following Neo-CRT provides excellent survival outcomes; in some cases, avoiding unnecessary major operations. These favorable oncologic benefits may result from multifactorial effects of preoperative Neo-CRT, such as proper patient selection, complete treatment, and therapeutic effect.
Footnotes
Abbreviations: BRPC = borderline resectable pancreatic cancer, CT = computerized tomography, DFS = disease-free survival, DSS = disease-specific survival, Gy = gray (a derived unit of ionizing radiation dose in the International System of Units), IVVI = isolated venous vascular involvement, LOH = length of hospital day, Neo-CRT = neoadjuvant chemoradiation therapy, NVR = without vein resection, OP = operation, PC = pancreatic cancer, PD = pancreaticoduodenectomy, PET = positron emission tomography, PV = portal vein, SMV = superior mesenteric vein, SV = splenic vein, VR = with vein resection.
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
REFERENCES
- 1.Office. KNS. Annual report on the cause of death statistics—2011. Available form: URL: http://kostat.go.kr (Korean). [Google Scholar]
- 2.Brennan MF, Moccia RD, Klimstra D. Management of adenocarcinoma of the body and tail of the pancreas. Ann Surg 1996; 223:506–511.discussion 502–511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Greer SE, Pipas JM, Sutton JE, et al. Effect of neoadjuvant therapy on local recurrence after resection of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. J Am Coll Surg 2008; 206:451–457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kuhlmann KF, de Castro SM, Wesseling JG, et al. Surgical treatment of pancreatic adenocarcinoma; actual survival and prognostic factors in 343 patients. Eur J Cancer 2004; 40:549–558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Millikan KW, Deziel DJ, Silverstein JC, et al. Prognostic factors associated with resectable adenocarcinoma of the head of the pancreas. Am Surg 1999; 65:618–623.discussion 614–623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Richter A, Niedergethmann M, Sturm JW, et al. Long-term results of partial pancreaticoduodenectomy for ductal adenocarcinoma of the pancreatic head: 25-year experience. World J Surg 2003; 27:324–329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Sohn TA, Yeo CJ, Cameron JL, et al. Resected adenocarcinoma of the pancreas-616 patients: results, outcomes, and prognostic indicators. J Gastrointest Surg 2000; 4:567–579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Dalton RR, Sarr MG, van Heerden JA, et al. Carcinoma of the body and tail of the pancreas: is curative resection justified? Surgery 1992; 111:489–494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Smeenk HG, van Eijck CH, Hop WC, et al. Long-term survival and metastatic pattern of pancreatic and periampullary cancer after adjuvant chemoradiation or observation: long-term results of EORTC trial 40891. Ann Surg 2007; 246:734–740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Tepper J, Nardi G, Sutt H. Carcinoma of the pancreas: review of MGH experience from 1963 to 1973. Analysis of surgical failure and implications for radiation therapy. Cancer 1976; 37:1519–1524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Yeo CJ, Abrams RA, Grochow LB, et al. Pancreaticoduodenectomy for pancreatic adenocarcinoma: postoperative adjuvant chemoradiation improves survival. A prospective, single-institution experience. Ann Surg 1997; 225:621–633.discussion 626–633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kalser MH, Ellenberg SS. Pancreatic cancer. Adjuvant combined radiation and chemotherapy following curative resection. Arch Surg 1985; 120:899–903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Corsini MM, Miller RC, Haddock MG, et al. Adjuvant radiotherapy and chemotherapy for pancreatic carcinoma: the Mayo Clinic experience (1975–2005). J Clin Oncol 2008; 26:3511–3516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Spitz FR, Abbruzzese JL, Lee JE, et al. Preoperative and postoperative chemoradiation strategies in patients treated with pancreaticoduodenectomy for adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. J Clin Oncol 1997; 15:928–937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Herman JM, Swartz MJ, Hsu CC, et al. Analysis of fluorouracil-based adjuvant chemotherapy and radiation after pancreaticoduodenectomy for ductal adenocarcinoma of the pancreas: results of a large, prospectively collected database at the Johns Hopkins Hospital. J Clin Oncol 2008; 26:3503–3510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Varadhachary GR, Wolff RA, Crane CH, et al. Preoperative gemcitabine and cisplatin followed by gemcitabine-based chemoradiation for resectable adenocarcinoma of the pancreatic head. J Clin Oncol 2008; 26:3487–3495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Talamonti MS, Small W, Jr, Mulcahy MF, et al. A multi-institutional phase II trial of preoperative full-dose gemcitabine and concurrent radiation for patients with potentially resectable pancreatic carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol 2006; 13:150–158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Pisters PW, Wolff RA, Janjan NA, et al. Preoperative paclitaxel and concurrent rapid-fractionation radiation for resectable pancreatic adenocarcinoma: toxicities, histologic response rates, and event-free outcome. J Clin Oncol 2002; 20:2537–2544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Pisters PW, Abbruzzese JL, Janjan NA, et al. Rapid-fractionation preoperative chemoradiation, pancreaticoduodenectomy, and intraoperative radiation therapy for resectable pancreatic adenocarcinoma. J Clin Oncol 1998; 16:3843–3850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Hoffman JP, Lipsitz S, Pisansky T, et al. Phase II trial of preoperative radiation therapy and chemotherapy for patients with localized, resectable adenocarcinoma of the pancreas: an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Study. J Clin Oncol 1998; 16:317–323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Evans DB, Varadhachary GR, Crane CH, et al. Preoperative gemcitabine-based chemoradiation for patients with resectable adenocarcinoma of the pancreatic head. J Clin Oncol 2008; 26:3496–3502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Evans DB, Rich TA, Byrd DR, et al. Preoperative chemoradiation and pancreaticoduodenectomy for adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. Arch Surg 1992; 127:1335–1339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Katz MH, Pisters PW, Evans DB, et al. Borderline resectable pancreatic cancer: the importance of this emerging stage of disease. J Am Coll Surg 2008; 206:833–846.discussion 838–846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Fortner JG. Regional pancreatectomy for cancer of the pancreas, ampulla, and other related sites. Tumor staging and results. Ann Surg 1984; 199:418–425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Fortner JG. Regional resection of cancer of the pancreas: a new surgical approach. Surgery 1973; 73:307–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Allema JH, Reinders ME, van Gulik TM, et al. Portal vein resection in patients undergoing pancreatoduodenectomy for carcinoma of the pancreatic head. Br J Surg 1994; 81:1642–1646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Harrison LE, Klimstra DS, Brennan MF. Isolated portal vein involvement in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. A contraindication for resection? Ann Surg 1996; 224:342–347.discussion 349–347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kelly KJ, Winslow E, Kooby D, et al. Vein involvement during pancreaticoduodenectomy: is there a need for redefinition of “borderline resectable disease”? J Gastrointest Surg 2013; 17:1209–1217.discussion 1217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Riediger H, Makowiec F, Fischer E, et al. Postoperative morbidity and long-term survival after pancreaticoduodenectomy with superior mesenterico-portal vein resection. J Gastrointest Surg 2006; 10:1106–1115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Tempero MA, Arnoletti JP, Behrman SW, et al. Pancreatic adenocarcinoma, version 2.2012: featured updates to the NCCN Guidelines. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 2012; 10:703–713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Kim EJ, Ben-Josef E, Herman JM, et al. A multi-institutional phase 2 study of neoadjuvant gemcitabine and oxaliplatin with radiation therapy in patients with pancreatic cancer. Cancer 2013; 119:2692–2700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Edge SB, Byrd DR, Compton CC, Fritz AG, Greene FL, Trotti A, et al. AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 7th ed.New York: Springer; 2010. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Therasse P, Arbuck SG, Eisenhauer EA, et al. New guidelines to evaluate the response to treatment in solid tumors. European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer, National Cancer Institute of the United States, National Cancer Institute of Canada. J Natl Cancer Inst 2000; 92:205–216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Koom WS, Seong J, Kim YB, et al. CA 19-9 as a predictor for response and survival in advanced pancreatic cancer patients treated with chemoradiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2009; 73:1148–1154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Kang CM, Chung YE, Park JY, et al. Potential contribution of preoperative neoadjuvant concurrent chemoradiation therapy on margin-negative resection in borderline resectable pancreatic cancer. J Gastrointest Surg 2012; 16:509–517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Hong SP, Park JY, Jeon TJ, et al. Weekly full-dose gemcitabine and single-dose cisplatin with concurrent radiotherapy in patients with locally advanced pancreatic cancer. Br J Cancer 2008; 98:881–887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Varadhachary GR, Tamm EP, Abbruzzese JL, et al. Borderline resectable pancreatic cancer: definitions, management, and role of preoperative therapy. Ann Surg Oncol 2006; 13:1035–1046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Vauthey JN, Dixon E. AHPBA/SSO/SSAT Consensus Conference on Resectable and Borderline Resectable Pancreatic Cancer: rationale and overview of the conference. Ann Surg Oncol 2009; 16:1725–1726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Nakao A, Takeda S, Inoue S, et al. Indications and techniques of extended resection for pancreatic cancer. World J Surg 2006; 30:976–982.discussion 974–983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Kang CM, Hwang HK, Choi SH, et al. Controversial issues of neoadjuvant treatment in borderline resectable pancreatic cancer. Surg Oncol 2013; 22:123–131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Sasson AR, Wetherington RW, Hoffman JP, et al. Neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy for adenocarcinoma of the pancreas: analysis of histopathology and outcome. Int J Gastrointest Cancer 2003; 34:121–128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Katz MH, Wang H, Fleming JB, et al. Long-term survival after multidisciplinary management of resected pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol 2009; 16:836–847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Raut CP, Tseng JF, Sun CC, et al. Impact of resection status on pattern of failure and survival after pancreaticoduodenectomy for pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Ann Surg 2007; 246:52–60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.White RR, Xie HB, Gottfried MR, et al. Significance of histological response to preoperative chemoradiotherapy for pancreatic cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 2005; 12:214–221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Ouaissi M, Hubert C, Verhelst R, et al. Vascular reconstruction during pancreatoduodenectomy for ductal adenocarcinoma of the pancreas improves resectability but does not achieve cure. World J Surg 2010; 34:2648–2661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Katz MH, Marsh R, Herman JM, et al. Borderline resectable pancreatic cancer: need for standardization and methods for optimal clinical trial design. Ann Surg Oncol 2013; 20:2787–2795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Katz MH, Ahmad S, Nelson H. Borderline resectable pancreatic cancer: pushing the technical limits of surgery. Bull Am Coll Surg 2013; 98:61–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


