Abstract
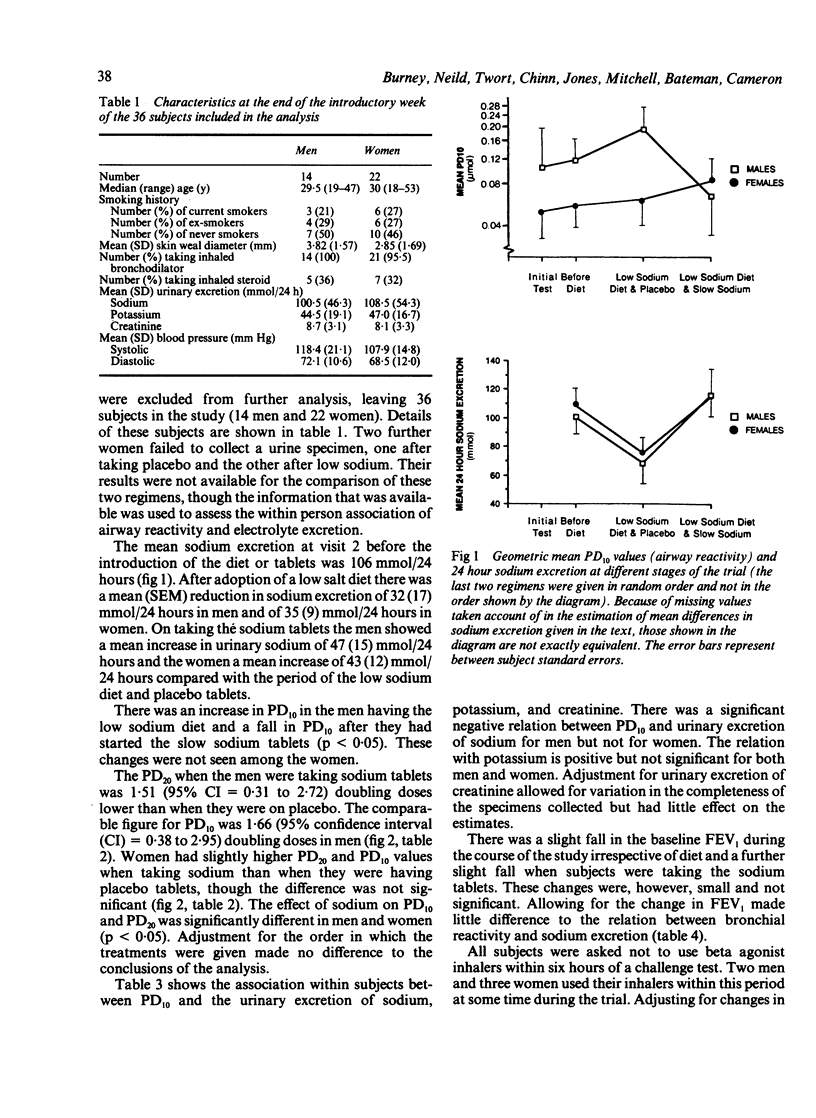
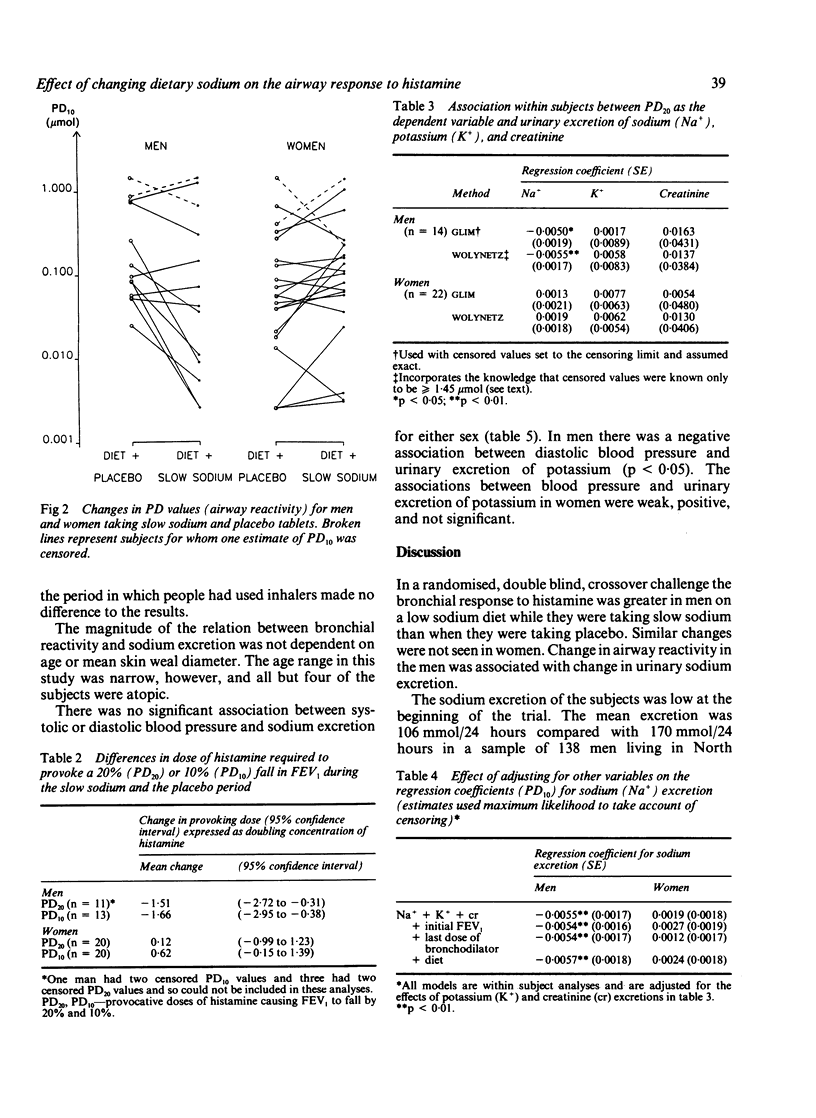
The airway response to histamine has been shown to be related to the 24 hour urinary excretion of sodium. To assess whether this relation is likely to represent a direct causal association a randomised double blind crossover trial of slow sodium (80 mmol/day) was compared with placebo in 36 subjects having a low sodium diet. The dose of histamine causing a 20% fall in FEV1 (PD20) was 1.51 doubling doses lower when the men were taking sodium than when they were taking placebo (p less than 0.05). On the basis of PD10 values, the difference in men was 1.66 doubling doses of histamine (p less than 0.05). There was no corresponding effect in women. Regressing PD10 against urinary excretion of electrolytes with data from the two occasions during the trial and the measurements made before the trial showed a significant association with sodium excretion after allowance had been made for any effect associated with potassium or creatinine excretion, the latter being a marker of the completeness of the urine collection. Again there was no corresponding effect among women. These findings are compatible with the differences in regional mortality data for England and Wales, which show a relation between asthma mortality and regional per person purchases of table salt for men but not for women.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson H. R. Respiratory abnormalities in Papua New Guinea children: the effects of locality and domestic wood smoke pollution. Int J Epidemiol. 1978 Mar;7(1):63–72. doi: 10.1093/ije/7.1.63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beynon H. L., Garbett N. D., Barnes P. J. Severe premenstrual exacerbations of asthma: effect of intramuscular progesterone. Lancet. 1988 Aug 13;2(8607):370–372. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)92837-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulpitt C. J., Broughton P. M., Markowe H. L., Marmot M. G., Rose G., Semmence A., Shipley M. J. The relationship between both sodium and potassium intake and blood pressure in London Civil Servants. A report from the Whitehall Department of Environment Study. J Chronic Dis. 1986;39(3):211–219. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(86)90026-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burney P. G., Britton J. R., Chinn S., Tattersfield A. E., Platt H. S., Papacosta A. O., Kelson M. C. Response to inhaled histamine and 24 hour sodium excretion. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1986 Jun 7;292(6534):1483–1486. doi: 10.1136/bmj.292.6534.1483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinn S., Britton J. R., Burney P. G., Tattersfield A. E., Papacosta A. O. Estimation and repeatability of the response to inhaled histamine in a community survey. Thorax. 1987 Jan;42(1):45–52. doi: 10.1136/thx.42.1.45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliasson O., Scherzer H. H., DeGraff A. C., Jr Morbidity in asthma in relation to the menstrual cycle. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1986 Jan;77(1 Pt 1):87–94. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(86)90328-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs C. J., Coutts I. I., Lock R., Finnegan O. C., White R. J. Premenstrual exacerbation of asthma. Thorax. 1984 Nov;39(11):833–836. doi: 10.1136/thx.39.11.833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey R. C. Asthma and IgE levels in rural and urban communities of The Gambia. Clin Allergy. 1975 Jun;5(2):201–207. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1975.tb01853.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Javaid A., Cushley M. J., Bone M. F. Effect of dietary salt on bronchial reactivity to histamine in asthma. BMJ. 1988 Aug 13;297(6646):454–454. doi: 10.1136/bmj.297.6646.454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juniper E. F., Kline P. A., Roberts R. S., Hargreave F. E., Daniel E. E. Airway responsiveness to methacholine during the natural menstrual cycle and the effect of oral contraceptives. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 May;135(5):1039–1042. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1987.135.5.1039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor G. A., Markandu N. D., Best F. E., Elder D. M., Cam J. M., Sagnella G. A., Squires M. Double-blind randomised crossover trial of moderate sodium restriction in essential hypertension. Lancet. 1982 Feb 13;1(8268):351–355. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)91389-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith W. C., Crombie I. K., Tavendale R. T., Gulland S. K., Tunstall-Pedoe H. D. Urinary electrolyte excretion, alcohol consumption, and blood pressure in the Scottish heart health study. BMJ. 1988 Jul 30;297(6644):329–330. doi: 10.1136/bmj.297.6644.329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staessen J., Bulpitt C. J., Fagard R., Joossens J. V., Lijnen P., Amery A. Contraceptive pill use, urinary sodium and blood pressure. A population study in two Belgian towns. Acta Cardiol. 1984;39(1):55–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Niekerk C. H., Weinberg E. G., Shore S. C., Heese H. V., Van Schalkwyk J. Prevalence of asthma: a comparative study of urban and rural Xhosa children. Clin Allergy. 1979 Jul;9(4):319–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1979.tb02489.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waite D. A., Eyles E. F., Tonkin S. L., O'Donnell T. V. Asthma prevalence in Tokelauan children in two environments. Clin Allergy. 1980 Jan;10(1):71–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1980.tb02082.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan K., Salome C., Woolcock A. J. Rapid method for measurement of bronchial responsiveness. Thorax. 1983 Oct;38(10):760–765. doi: 10.1136/thx.38.10.760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


